SVSU PHYS 106C Keen Chp 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:17 PM on 9/29/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
1
New cards
Focus
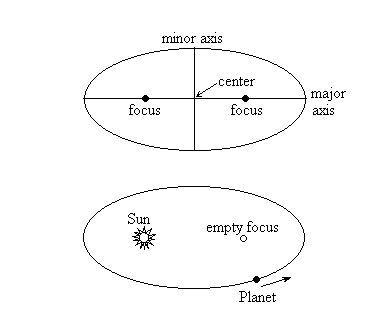
either of the two points interior to an ellipse that defines its shape. The sun is always at one focus of a planet's elliptical orbit
2
New cards
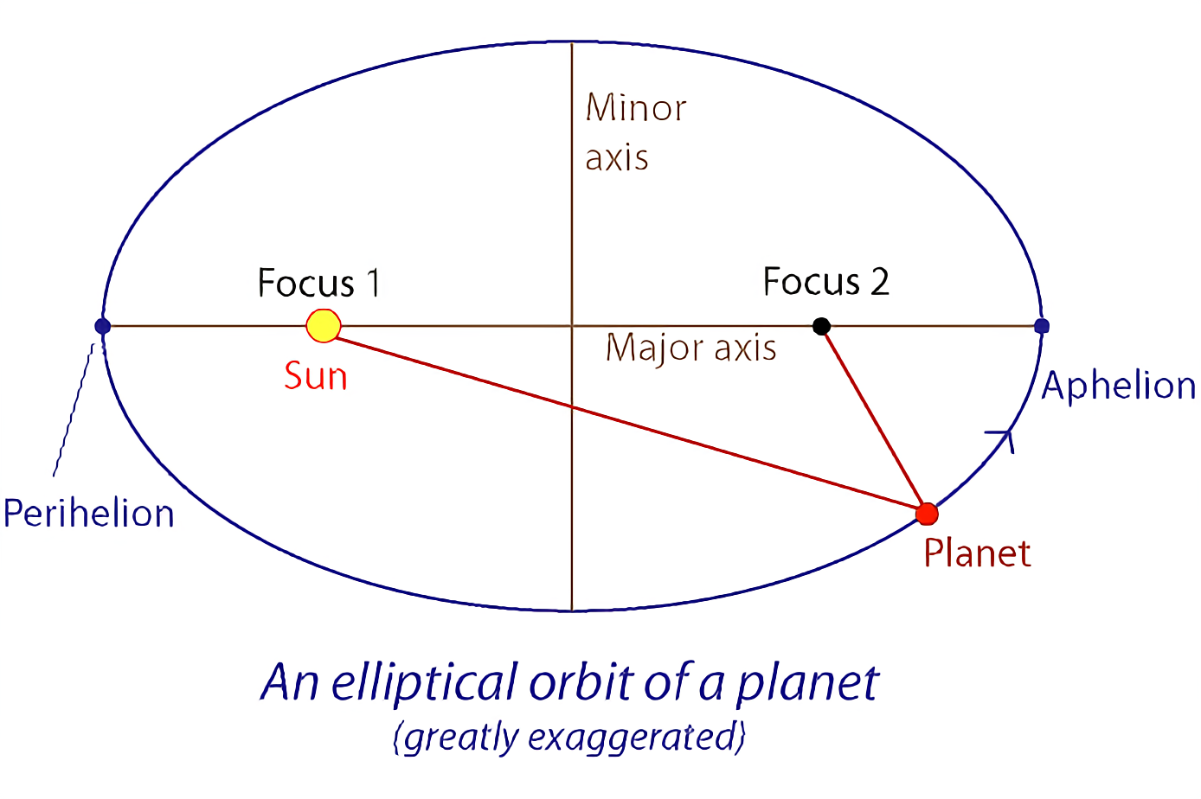
first law of planetary motion (kepler)
the principle stating that planets more on elliptical orbits with the sun at one focus
3
New cards
semimajor axis
half of the long axis of an ellipse
4
New cards
semiminor axis
half of the short axis of an ellipse
5
New cards
eccentricity
a measure of the roundness of an ellipse, calculated as a ration: the distance from the ellipse's center to its foci, divided by the length of the semimajor axis

6
New cards
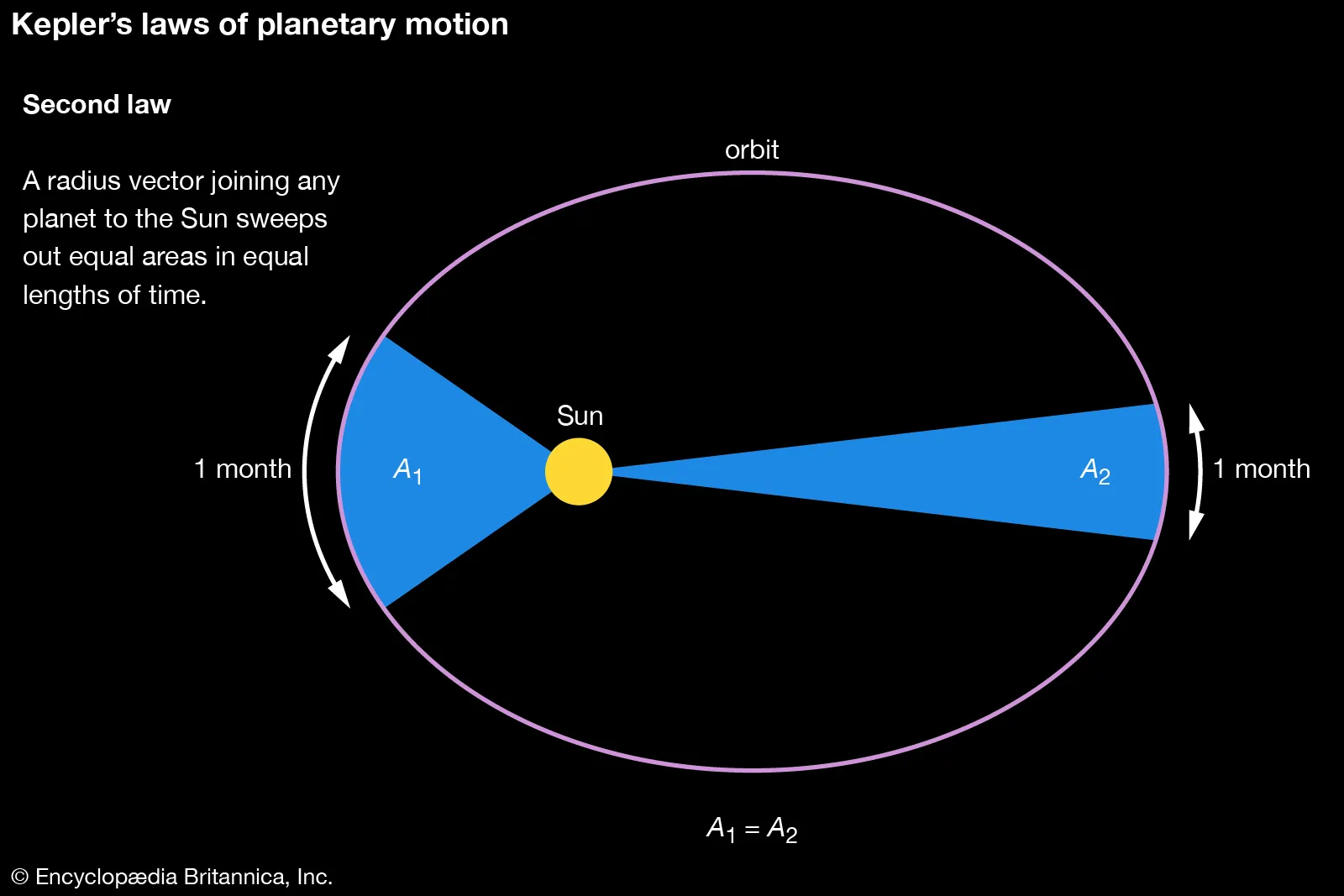
second law of planetary motion (kepler)
The principle stating that the line connecting a planet to the sun will sweep out equal areas of its orbit in equal times
7
New cards
conservation of angular momentum
the principle whereby the rotational speed of an object that spins or orbits a central point increase as the distance from the center decreases and vice versa
8
New cards
orbital period
the time an object takes to complete on revolution of an orbit
9
New cards
third law of planetary motion (kepler)
the principle stating that the square of a planet's orbital period (in years) equals its average orbital radius (in AU) cubed (p^2=r3)
10
New cards
Galilean moons
the 4 largest moons of Jupiter: io, Ganymede, Callisto, and Europa
11
New cards
Nebulosity
clouds in space
12
New cards
Force
an interaction between two bodies that, if unbalanced, can change their speed and/or direction of motion
13
New cards
Velocity
rate of change in position per unit of time
14
New cards
speed
an object's change in position per unit of time
15
New cards
acceleration
an object's change of velocity per unit of time
16
New cards
mass
a quantity of matter that is related to an object's resistance to changes in velocity, measured in kg,
17
New cards
inertia
an object's resistance to change in velocity
18
New cards
inertial law (issac newton 1st)
the principle stating that objects in motion and constant velocity along a straight line continue that way unless acted on by a net force
19
New cards
force law ( 2nd newton)
the principle stating that the change in an object's velocity due to an applied net force is in the same direction as, and directly proportional to, the force but inversely proportional to the object's mass
20
New cards
reaction law (3rd newton)
the principle stating that for every applied force, there is an equal and opposite force
21
New cards
net force
the sum of all forces acting on an object
22
New cards
momentum
the mass of an object multiplied by its velocity. Only the application of a force can change an object's momentum
23
New cards
gravity
an attractive force between any two massive bodies that depends on the product of the bodies' masses and the inverse square of the distance between them
24
New cards
universal law of gravity
the dependence of the force of gravity between two objects as the product of their masses multiplied by newton's constant divided by their distance of separation squared
25
New cards
constant of nature
a term that does not change from one situation or time to another. The value of a constant of nature must be measured to be determined
26
New cards
inverse square law
a relationship whereby a quantity (ex. gravity) decreases in proportion to the square of a variable (ex. distance) as the variable increases
27
New cards
weight
the downward force that gravity produces on an object
28
New cards
centripetal acceleration
acceleration involving a force that keeps an object moving on a circular path. The acceleration is directed toward the path's center of curvature
29
New cards
centrifugal force
the illusion of outward force when an object is moving on a curved path
30
New cards
orbital velocity
the velocity required to keep a body in orbit around another body
31
New cards
escape velocity
the velocity required to escape the pull of a massive body's gravity