Diagnostic Imaging Final Exam Study Terms & Definitions
1/304
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
305 Terms
The range of frequency that the transducer creates depends on the thickness of the _______________
crystals
Stationary anodes in portable x-ray machines are known for causing damage known as ______________ due to excess heat
Pitting
What transducers have piezoelectric crystals aligned linearly that are activated in sequence?
Phased array transducers
Frequency is measured in
Hertz (Hz)
Isoechoic
areas where returning echoes are the same as surrounding tissues
What kind of ultrasound is used primarily for evaluating blood flow?
Doppler ultrasound
What has to happen before an ultrasound is performed?
The hair must be clipped, the skin has to be cleaned, and a acoustic gel should be used as an interface between the skin and the probe
A endoscope is composed of three parts:
the insertion tube, hand piece, and the umbilical chord
The ________________ __________ of the endoscope is responsible for light transmission
umbilical chord
Which type of endoscope is usually used for structures that are not tubular?
Rigid endoscope! Usually for evaluation of the body cavity, joint spaces, and in ear canals
Taller sound waves are _______________ sound waves
louder sound waves
M-mode creates a:
B-Mode image in motion
What form of ultrasound is used primarily for evaluating blood flow?
Doppler
What are the primary uses for the A-mode setting?
Ophthalmology evaluations and in the measurement of subq fat in production animals (usually pigs)
What should you do to a used probe head before placing it back in the probe holder?
Clean it- wipe off any residual gel & wipe again using alcohol to disenfect
A sector array transducer produces a ____________ shaped image
wedge
What kind of ultrasound transducer is most common?
Linear array transducers
Areas that do not generate an echo are described as
anechoic
Hypochoic areas have little returning echo and appear what color?
Darker gray
Ultrasound imaging is used for _________________ imaging in large animals
Reproductive
Flexible endoscopes are commonly used for
upper and lower GI procedures
What characteristics are essential for endoscopy?
Insufflation and irrigation
Evaluation of the caudal area of the lower GI tract is referred to as:
colonoscopy
A ultrasound field that appears very dark w/ very few returning echoes is described as
Anechoic
Which of the following statements about ultrasound transducers is true?
Higher frequency probes have increased image resolution and decreased penetrating ability relative to lower frequency probes
Time-gain compensation is used to adjust the __________________ of a ultrasound image
brightness
Which type of technique is frequently used in emergency medicine assessing for abdominal trauma?
aFAST
The overall Gain control is used for
strengthening the returning echoes and increasing the overall brightness of the image
What advantage does endoscopy have over exploratory surgery?
Endoscopy is less invasive bc it doesn't require incising the patient
MRI machines use ___________________ energy to obtain images
Magnetic
CT imaging is superior to standard radiographs when imaging:
Soft tissues. Think brain, organs, & muscles.
Which imaging technique is useful in equine medicine?
Nuclear scintigraphy. Most facilities don't have a CT/MRI machine big enough for a horse
Do you have to wear PPE & a dosimetry badge when performing fluoroscopy on a patient?
Yes! Fluoroscopy is a real time imaging technique that utilizes radiation.
Reverberation
This artifact is caused by repeated back and forth reflection of sound waves between two highly reflective surfaces or by the transducer and a strong reflector. Also occurs if not enough acoustic gel is used
Mirror image
This artifact happens in highly reflective areas like the lungs/diaphragm interface when a sound wave reflects off of the liver
Acoustic shadowing
This artifact happens when sound is reflected before it can penetrate into deeper tissues. Usually caused by interaction with tissues like bone, gallstones, and fat. This artifact is minimized with a lower frequency transducer.
Comet tail
This artifact is caused by sound waves interacting with metal objects. Usually involves foreign bodies, biopsy needles, etc.
Nuclear scintigraphy
Involved injecting a patient with radioactive isotopes to determine the location of an injury of disease. The energy given off from the isotope is detected by a special camera
Patients who have undergone a nuclear scintigraphy study remain in the testing facility for at least _______ hours
24 hours (most go home within 48-72 hours following the study)
Digital infrared thermography creates a visual picture of what?
Superficial skin temperature changes that result from increased/decreased blood flow
Patients should be positioned with the area of interest:
as close as possible to the x-ray table
What do you do when there are significant differences in measurement of the cranial and caudal abdomen of a patient?
Take two separate images of each region
When the area of interest is a long bone what other areas are included in the final image?
the joint above and below the bone
Decubitus
refers to a lateral projection that is exposed using a horizontal beam technique
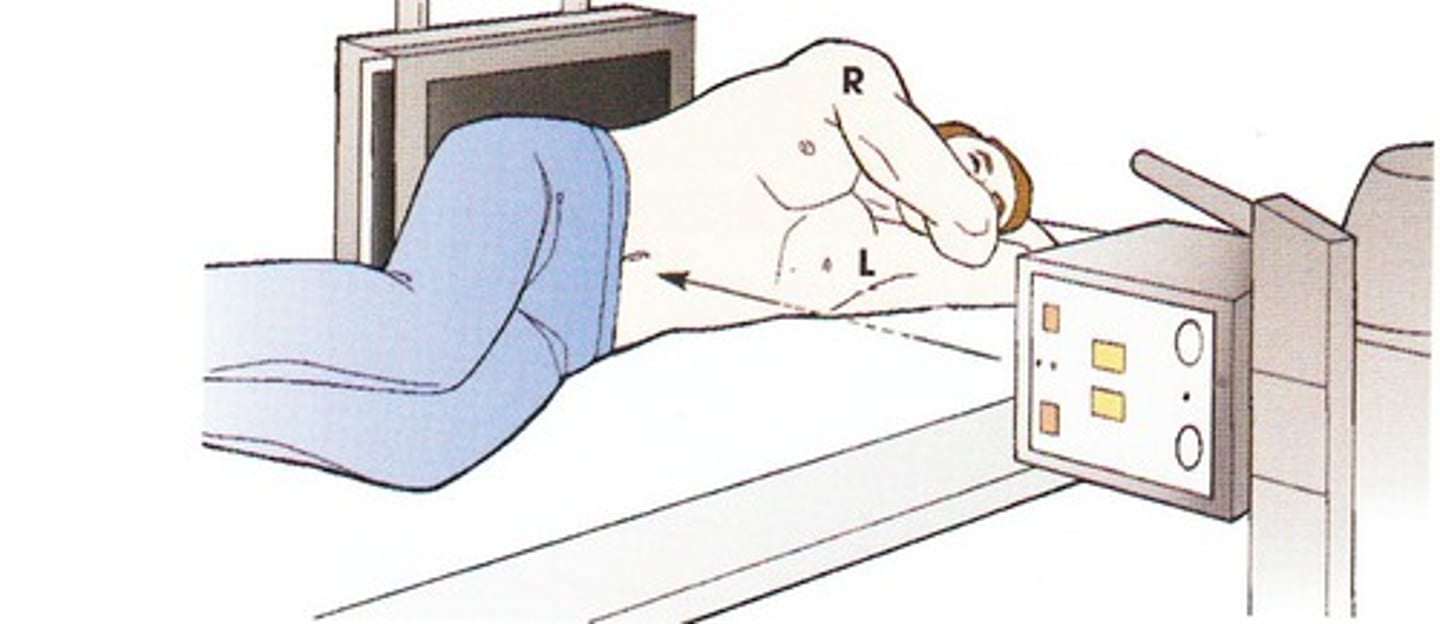
In most cases, two x-ray exposures are made at _____________ angles to each other
right
V-troughs
Positions patients into dorsal recumbency. When obtaining a caliper measurement you should include the depth of the trough
Split plate
Cassette that uses a lead blocker to block half of the film while the other half is exposed. Split plates can take two views on a single cassette & are used for distal limb views and small animals
Caudal (Cd)
Structures or areas situated toward the tail
Caudocranial (CdCr)
From the back of the limb to the front of the limb. Primarily used for views proximal to the carpus/tarsus joint
Dorsopalmar (DPa)
Enters dorsal surface of forelimb (from carpus distally) and exits palmar surface
Dorsoplantar (DPI)
Enters dorsal surface of forelimb (from carpus distally) and exits plantar surface
Oblique (O)
The x-ray beam enters at an angle (other than 90 degrees) to a structure. Commonly used for dental images
Patients must be __________ and _________ before radiographs are exposed
clean & dry
What organization determines the directional terminology used in veterinary radiology?
American College of Veterinary Radiology (ACVR)
For most imaging studies (excluding dental and oblique images) the patient is placed with the area of interest _________________ to the x-ray tube to minimize image distortion
Perpendicular
Abdominal images should be taken during the ___________________ _______________
Respiratory pause
Lateral decubitus
Lying down on the side (with x-ray beam horizontally positioned). Used when free fluid/gas is suspected or when a regular VD would compromise the pt
Modified Lateral Abdominal View
Used when evaluation of the entire length of the urinary tract is needed & limbs would've obscured the final image in standard lateral

Which bones make up the thoracic girdle?
scapula and clavicles
Dorsoventral (DV) positioning is primarily used in thoracic views when imaging the:
Heart
Ventrodorsal (VD) positioning provides better visualization of the _____________
Lungs
Thoracic images are exposed at peak _______________ unless pneumothorax is suspected
inspiration. Pneumothorax images should be taken during the expiratory pause
How can you tell a VD/DV thoracic view is properly positioned?
The sternum will be superimposed over the thoracic vertebrae
What organization provides services for dogs to certify they don't have hip dysplasia or elbow dysplasia
Orthopedic Foundation for Animals (OFA)
Which technique is used to evaluate the quality of the hip joint and the degree of laxity?
the PennHIP technique
How are hindlimb images taken for cats and dogs?
With the x-ray cassette on the tabletop
Techniques for imaging the thorax are similar to techniques for imaging the _______________
abdomen
When should the measurement be done when setting up for radiographs?
When the patient is in position
Where should the central beam be positioned when taking abdominal images?
Below the last rib
How can you tell the patient is in proper position for a lateral abdominal view?
The rib heads will be superimposed over the coxofemoral joints and the intervertebral foramina will be the same size in the final image
The ventral border of collimation on an abdominal view should be the:
sternum
For thoracic views the central beam is centered:
at the caudal border of the scapula
Thoracic views usually measure at the:
caudal border of the scapula/5th intercostal space
The cranial border for thoracic films is the:
thoracic inlet
How are forelimbs positioned in VD thoracic films?
Forelimbs are extended cranially
Where should markers be placed on lateral thoracic films?
Near the axilla (armpit area)
How are stifles positioned in VD hip films for OFA evaluation?
stifles are rotated medially so they are parallel to each other and the patella has to be centered over the trochlear groove
How do you know you've positioned a patient correctly for a lateral pelvic film?
The beam should be centered on the greatest trochanter of the femur. In the final image either the hip joints and legs are superimposed over each other or the limbs are in a scissor position
Where is the affected limb positioned during a craniocaudal image of the humerus?
extended cranially
When positioning for a flexed mediolateral image of the elbow, the elbow is flexed:
dorsally
The collimation borders for a radius/ulna projection are
above the elbow and below the carpus
Positioning technique for DV skull views
Place a strip of tape across the cervical region to maintain the position. Center the beam between the canthi of the eyes
VD cervical spine views are collimated
from the base of the skull to the shoulder joint
What should you do if there is a significant difference in the measurement between the cranial and caudal areas of the cervical spine?
Take two views: measure and center on the C2-C3 space for the cranial view and measure and center on the C5-C6 space for the caudal view
What collimation window is used when taking a lateral lumbar spinal radiograph?
from the last rib to the acetabulum (hip joint)
For a lateral coccygeal spine projection the measurement is taken:
at the thickest part of the tail
Due to the divergence of the X-ray beam, intervertebral disc spaces will appear _____________ towards the center of the film and ________________ towards the end of the film
wider, narrower
What are the components of a x-ray cassette in order from front to back?
Front, padding, intensifying screen, film, intensifying screen, padding, back
Precise positioning is important in skull radiographs to obtain images that represent
the symmetry of the skull
When placing craniocaudal radiographs of the stifle joint on a viewer to evaluate, how should you orient the film?
The lateral side of the right limb should be on the viewers left & the lateral side of the left limb should be on the viewers right
Standard Lateral Projection
Also used when the presence of air or fluid within the thorax is suspected or when the animal would be compromised using the standard positioning. Mitchell marker should be used to show direction of gravity
Where should you measure for a ventrodorsal cervical spine projection?
at the C4-C5 intervertebral space
A boxing glove shape of air on the abdominal film of a dog is indicative of:
Gastric dilation and volvus
If an animal is in respiratory distress, many times will the veterinarian request they be positioned lying on their belly for chest films. What position is this called?
Dorsoventral
If lung sounds aren't present during auscultation you should place the patient onto the table with the _________________ side down
unaffected
What landmark is used as the cranial border for thoracic films?
the thoracic inlet
Where should you center the x-ray beam when taking abdominal films?
slightly caudal to the last rib
Where do you measure when taking a mediolateral image of the carpus?
Directly over the carpal joint
For an oblique view which markers are required?
Mark both sides
If the dog being submitted for OFA hip film evaluation is an AKC registered dog, where is this information recorded?
On the film