Lipids/Fats Introduction (L13)
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Nutrition Unit 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
There is ___ as much energy in lipids than in carbs and proteins.
Twice
Why are lipids a better source of energy than glucose?
Lipids are made up of fatty acids. Fatty acids have more hydrogen per carbon. The more hydrogen, the more ATP you can generate.
________ has the maximum number of hydrogens, no double bonds, and are typically solid at room temperature.
_________ has at least one double bond, and are typically liquid at room temperature.
Saturated, unsaturated
_____ chain fatty acids are 2-6 carbons.
Short
______ chain fatty acids have 8-12 carbons.
Medium
_____ chain fatty acids have 14-24 carbons.
long
As fatty acid chain length increases, melting point ______
increases
Fatty acids synthesized by plants and animals have an ____ number of carbons. (odd/even)
even
What are the characteristics of a fatty acid
Even number of carbon atoms, arranged in an unbranched line, hava a carboxyl group at one end and a methyl group at the other end
In terms of firmness, animal oils are typically _____ and vegetable oils are typically _____. (solid/liquid)
solid, liquid
Fatty acid melting point is dependent on _____ and _____.
Chain length, degree of saturation.
Melting point ______ with chain length and _____ with number of double bonds.
Increases, decreases
If you could from the carboxyl group, it is _____. If you count from the methyl group it is _____.
Delta, omega
For omega naming, you count the first double bond from the ______ end.
Methyl
For delta naming, you count from the ______ end.
Carboxyl
In the _____ naming system, you take note over every double bond. In ______, you only take note of the first double bond.
delta (Δ), omega (ω)
Linoleic acid has ___ double bonds, linolenic has ___.
2, 3
(T or F) Proteins have over twice the amount of energy as fats
False
(T or F)The more hydrogens in a molecule, the more energy it provides.
True
The less reduced a fat is, the more energy it provides.
False
(T or F) The more double bonds a fatty acid has, the lower its boiling temperature
True
(T or F) The longer a fatty acid chain is, the lower its boiling temperature.
False
__________ is the process of forcing hydrogen atoms into an unsaturated fatty acid and making it into a saturated fatty acid. This is often used in food products.
Hydrogenation
The fatty acid all cis-Δ9,12-octadecadienoic acid is an omega _______________ fatty acid. The common name for this fatty acid is _________________ acid.
omega 6, linoleic
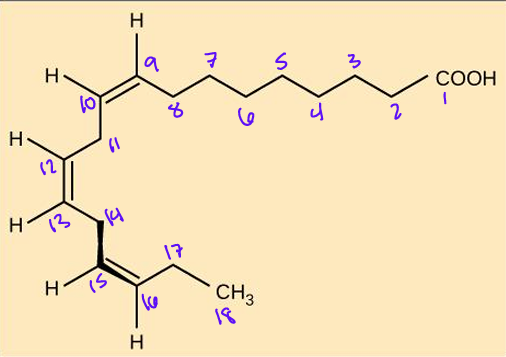
What is the omega nomenclature?
Delta Nomenclature?
Name of fatty acid?
18:3 w-3
18:3Δ9,12,15
Linolenic acid
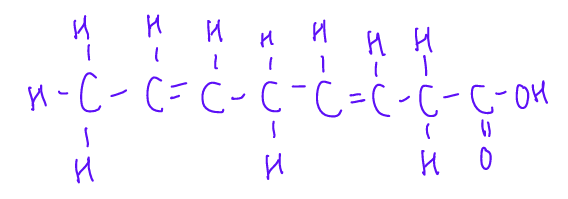
This is a _______ fatty acid.
non-conjugated
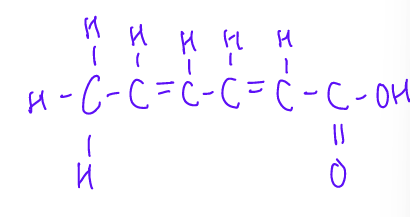
This is a ______ fatty acid
Conjugated
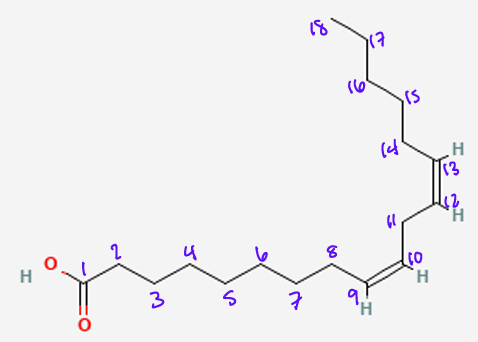
What is the omega nomenclature?
Delta Nomenclature?
Name of fatty acid?
18:2 w-6
18:2 Δ9,12
Linoleic acid