Chapter 15: Nonrenewable Energy
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Oil and Natural Gas
Two most widely used natural resources in the U.S.
Oil Consumption is Increasing
-new extractions from oil shale cause envi harm
-burning oil and natural gas will continue adding greenhouse gases to the atmosphere
Net energy yield
Total amount of useful energy available from a resource minus the energy needed to make the energy available to consumers
*energy resources vary greatly in their net energy yields
Energy return on investment
Energy obtained per unit energy used to obtain it
First Law of Thermodynamics
It takes high-quality energy to get high-quality energy
pumping oil from ground, refining it, and transporting it
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Some high-quality energy is wasted at every step
Some energy resources need help to compete in the marketplace
Many alternatives cannot compete in open markets with alternatives that have higher net energy yields [need subsidies from tax payers]
Nuclear power [uranium fuel cycle is costly]
Advantages of Oil
Conventional crude oil is abundant and has a medium net energy yield
Disadvantages of Oil
Using it causes air and water pollution and releases greenhouse gases to the atmosphere
Unconventional heavy oil from oil shale rock and tar sands exists in potentially large supplies but has a low net energy yield and a higher envi impact than conventional oil
Crude Oil (petroleum)
•A naturally occurring, yellow-to black liquid found in geological formations beneath the Earth's surface, which is commonly refined into various
types of fuels
-it consists of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other organic compounds
•A fossil fuel, petroleum is formed when large quantities
of dead organisms, usually zooplankton and algae, are buried underneath sedimentary rock and subjected to both intense heat and pressure
*primary focus of our energy
*cannot be used as it comes out of the ground [must be refined, petrochemicals]
Plankton
Made up of 3 types of atoms:
-carbon
-hydrogen
-oxygen
From plankton to petroleum...
Forms when partially decayed plankton gets "cooked" and "smushed" under layers of mud, sand, and rock
-the high temps and pressures cause the chemical rearrangement of the atoms and oxygen is released
Availability of Crude Oil Determined By:
-demand
-technology
-rate at which we remove the oil
-cost of making oil available
-market price
Unconventional heavy oil
-higher envi cost; production cost
-oil industries and governments across the globe are investing in unconventional oil sources due to the increasing scarcity of conventional oil reserves
Unconventional oil
Petroleum produced or extracted using techniques other than the conventional oil well method
-oil sands
-tight oil
-oil shale
Oil Sands
Generally consist of extra heavy crude oil or crude bitumen trapped in unconsolidated sandstone
Tight Oil
Crude oil contained in petroleum-bearing formations of low permeability, often shale or tight sandstone
Oil Shale
An organic-rich fine-grained sedimentary rock containing significant amounts of kerogen (a solid mix of organic chemical compounds) from which technology can extract liquid hydrocarbons (shale oil) and combustible oil shale gas
-sub for conventional crude oil
-more costly to extract
-deposits all over world
-72% of world's reserve is in arid areas of western US [locked up in rock, lack of water needed for extraction, low net energy yield]
Coal and gas conversion
Using synthetic fuel processes, the conversion of coal and natural gas has the potential to yield great
quantities of unconventional oil and/or refined products, albeit at much lower net energy output than the historic average for conventional oil extraction
Thermal depolymerization
Recover energy from existing sources of waste such as petroleum coke as well as pre-existing waste deposits
Are We Running Out of Conventional Oil?: Three major options
1) Live w/ much higher oil prices
2) Extend oil supplies - use alternative sources of oil [unconventional]
3) Use other energy sources
Environmental Cost of Conventional Oil Use
-Land disruption, greenhouse gas emission, air pollution, water pollution, and loss of biodiversity
-Burning oil accounts for 43% of global CO2 emissions
Conventional Oil Advantages
-ample supply for several decades
-net energy yield is medium but decreasing
-low land disruption
-efficient distribution system
Conventional Oil Disadvantages
-water pollution
-envi costs not included in market price
-releases CO2 and other air pollutants when burned
-vulnerable to international supply interruptions
Oil Production and Consumption in the United States
The U.S.:
-produces 9% of the world's oil and uses 23% of world's oil
-has about 2% of world's proven oil reserves
-imports 52% of its oil
Kerogen
A solid mixture of organic chemical compounds
Heavy Oil from Tar Sands
-contains bitumen
-extensive deposits in Canada and Venezuela
-extraction: serious envi impact before strip-mining; low net energy yield
Heavy Oils from Tar Sands and Oil Shale: Advantages
-large potential supplies
-easily transported within and b/t countries
-efficient distribution system in place
Heavy Oils from Tar Sands and Oil Shale: Disadvantages
-low net energy yield
-severe land distribution and high water use
-releases CO2 and other air pollutants when produced and burned
Natural Gas
A fossil fuel that exist in a gaseous state and is composed mainly of methane (CH4) a small percentage of other hydrocarbons (e.g. ethane)
-50-90% methane CH4
Conventional Natural Gas
-more plentiful than oil
-has a medium net energy yield and a fairly low production cost
-is a clean-burning fuel
-2 forms:
~liquefied petroleum gas
~liquefied natural gas
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG)
Stored in tanks
Liquefied natural gas (LNG)
-low net energy yield
-makes U.S. dependent upon unstable countries like Russia and Iran
Conventional Natural Gas Advantages
-ample supplies
-versatile fuel
-medium net energy yield
-emits less CO2 and other air pollutants than other fossil fuels when burned
Conventional Natural Gas Disadvantages
-low net energy yield for LNG
-production and delivery may emit more CO2 and CH4 per unit of energy produced than coal
-fracking uses and pollutes large volumes of water
-potential groundwater pollution from fracking
Fracking
Drilling wells; using huge amounts of water, sand, and chemicals; dealing with toxic wastewater; transporting the natural gas
Impacts of Fracking
-drinking water contaminated with natural gas can catch fire
-fracking has several harmful environmental effects
Coal Bed Methane Gas
-in coal beds near the earth's surface; in shale beds
-high envi impacts of extraction
Methane Hydrate
-trapped in icy water; in permafrost envis; on ocean floor
-costs of extraction is currently too high
Unconventional Natural Gas
-Coal bed methane gas
-Methane hydrate
Coal starts as...
peat
Coal formation
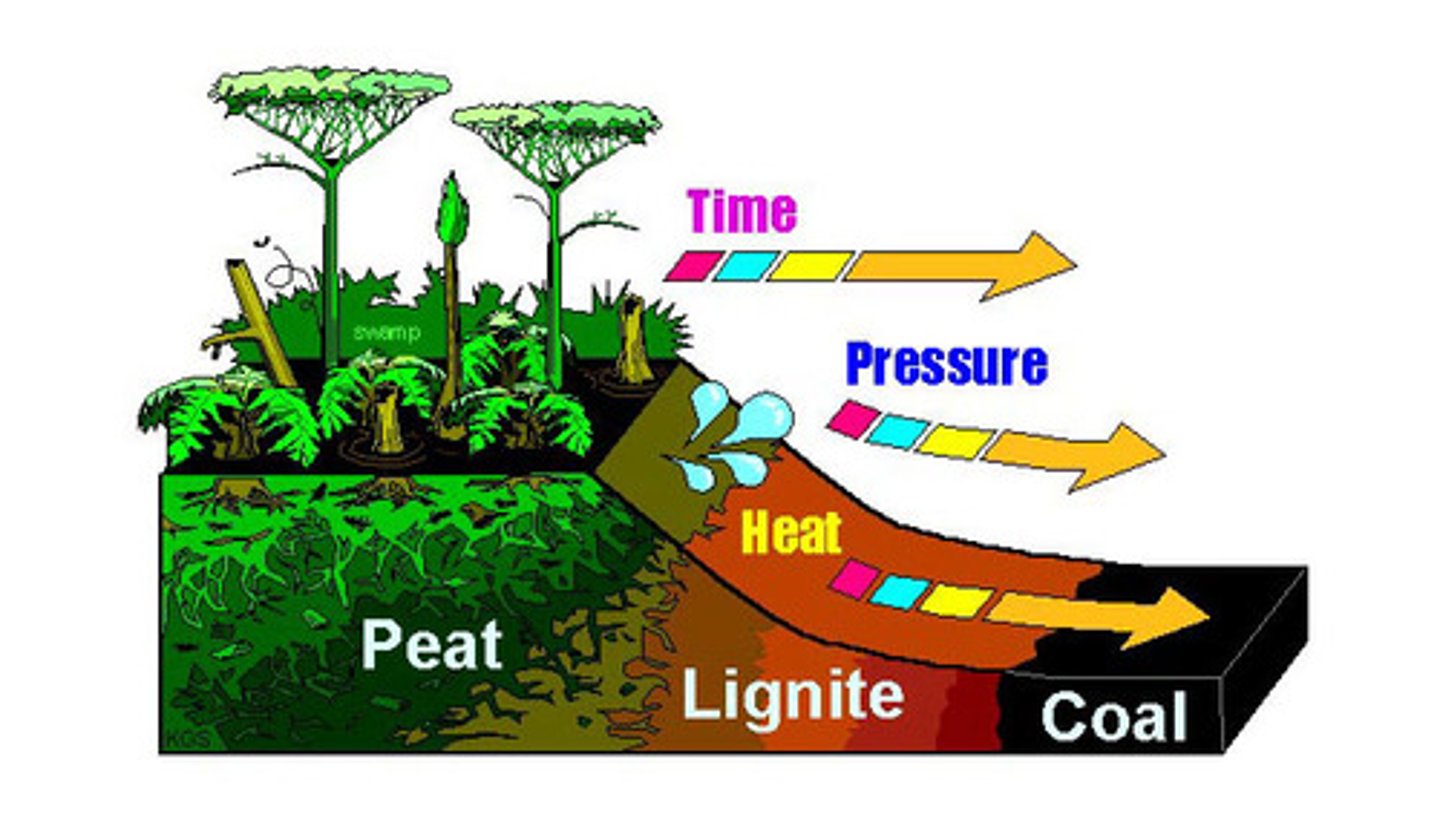
Stages of coal formation
1) Peat [more moisture]
2) Lignite
3) Bituminous Coal
4) Anthracite Coal [increasing heat and carbon content]
Coal is plentiful but dirty fuel
-Coal [solid fossil fuel]
-Burned in power plants [generates 42% of the world's electricity]
World's largest coal reserves
-United States
-Russia
-China
Environmental Costs of Burning Coal
Severe air pollution
-sulfur released as SO2
-large amount of soot
-CO2
-trace amounts of mercury and radioactive materials
Clean Coal Campaign
Coal companies and energy companies has fought:
-classifying carbon dioxide as a pollutant
-classifying coal ash as hazardous waste
-air pollution standards for emissions
The 2008 Clean Coal Campaign
-Note: there is no such thing as clean coal
Coal Advantages
-ample supplies in many countries
-medium to high net energy yield
-low cost when environmental costs are not included
Coal Disadvantages
-severe land disturbance and water pollution
-fine particle and toxic mercury emissions threaten human health
-emits large amounts of CO2 and other air pollutants when produced and burned
Conversion of solid coal to:
-synthetic natural gas (SNG) by coal gasification
-methanol or synthetic gasoline by coal liquefaction
-synfuels
Synthetic Fuels Advantages
-vehicle fuel
-lower air pollution than goal
-large potential supply in many countries
Synthetic Fuels Disadvantages
-low to medium net energy yield
-higher CO2 emissions than coal
-requires mining 50% more coal w/ increased land disturbance, water pollution and water use
Nuclear power has a low environmental impact and a very low accident risk, but its use has been limited by:
-a low net energy yield, high costs, fear of accidents, and long-lived radioactive wastes
-its role in spreading nuclear weapons technology
Nuclear Fission Reactor
-Controlled nuclear fission reaction in a reactor
~light-water reactors
~very inefficient
-Fueled by uranium ore and packed as pellets in fuel rods and fuel assemblies
-Control rods absorb neutrons
-Water is usual coolant
-Containment shell around the core for protection
-Water-filled pools or dry casks for storage of radioactive spent fuel rod assemblies
What is the Nuclear Fuel Cycle?
1) Mine the uranium
2) Process the uranium to make the fuel
3) Use it in the reactor
4) Safely store the radioactive waste
5) Decommission the reactor
Conventional Nuclear Fuel Cycle Advantages
-low environmental impact (w/o accidents)
-emits 1/6 as much CO2 as coal
-low risk of accidents in modern plants
Conventional Nuclear Fuel Cycle Disadvantages
-low net energy yield
-high overall cost
-produces long-lived, harmful radioactive wastes
-promotes spread of nuclear weapons
Storing Radioactive Spent-Fuel Rods Present Risks
-rods must be replaced every three or four years
-cooled in water-filled pools
-placed in dry casks
-must be stored for thousands of yrs
-vulnerable to terrorist attack
High level radioactive wastes must be stored
For 10,000-240,000 yrs
Where can it be stored
-deep burial
-shooting into space [too dangerous]
Problems with the Yucca Mountain desert region
-cost of $96 billion
-rock fractures
-earthquake zone
-decrease national security
Dealing with old nuclear power plants:
-decommission or retire the power plant
-dismantle the plant and safely store the radioactive materials
-enclose the plant behind a physical barrier with full-time security until a storage facility has been built
-enclose the plant behind a physical barrier with full-time security until a storage facility has been built
-enclose the plant in a tomb [monitor for thousands of years]
Nuclear power plants vs Nuclear fuel cycle
Nuclear power plants
-no CO2 emission
Nuclear fuel cycle
-emits CO2
Proponents of Nuclear Power
-fund more research and development
-pilot-plant testing of potentially cheaper and safer reactors
-test breeder fission and nuclear fusion
Opponents of nuclear power
fund rapid development of energy efficient and renewable energy resources
New Technologies (Future Nuclear Power)
-Advanced light water reactors
->safer
-Thorium based reactors
->less costly and safer
Thorium based nuclear power is...
-Nuclear reactor-based electrical power generation fueled primarily by the nuclear fission of the isotope uranium-233 produced from the fertile element thorium
-According to proponents, a thorium fuel cycle offers several potential advantages over a uranium fuel cycle—including much greater abundance on Earth, superior physical and nuclear fuel properties, and reduced nuclear waste production
The 2011 Nuclear Power Plant Accident in Japan
-triggered by a major offshore earthquake and resulting tsunami
-4 key human related factors:
1) no worst case scenarios
2) Seawalls too short
3) design flaws
4) relationship between plant owners and government
Fusion
-two isotopes fused together to form a heavier nucleus
-releases energy
-very difficult to develop
-Wendelstein 7-X stellarator
Wendelstein 7-X stellarator
-A stellarator fusion reactor
-Different to a tokamak fusion reactor [based on uniform toroid shape]
-Twists in a figure 8 which gets around the problems tokamaks dace when magnetic coils confining the plasma are necessarily less dense on the outside of the toroidal ring
Three Big Ideas #1
Conventional oil, natural gas, and coal:
-plentiful and have moderate to high net energy yields
-use of these fossil fuels, especially coal, has a high envi impact
Three Big Ideas #2
The nuclear power fuel cycle has a low environmental impact and a very low accident risk, but limited use because of:
-high costs
-a low net energy yield
-long-lived radioactive wastes
-its role in spreading nuclear weapons tech
Tying It All Together: A New U.S. Oil and Natural Gas Era and Sustainability
-Conventional fossil fuels have high net energy yields
-We cannot recycle energy
~>recycling materials can help reduce energy needs
-Relying on a diversity of energy resources
~>will reduce environmental impacts