Honors Bio Unit 1
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I did all of this for you. You're welcome.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
All life is made of
Carbon
The 4 main organic molecules
Carbs, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids
Monomer
“ONE” building block or single unit
Polymer
“MANY” blocks or units make up a larger molecule
Carbs Formula
C6 H12 O6 (1:2:1 ratio)
Carbs Structure
Ring shape (Penta/Hexagons)
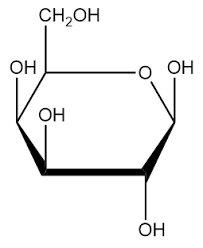
Carbs Function
Quick energy
Carbs Monomer
Monosaccharide
Carbs Polymer
Polysaccharide
Lipids Formula
C H O (no set ratio)
Lipids Polymer
Lipid Triglyceride
Lipids Function
Long term energy, insulation, storage, protect organs
Lipids Structure
Long chains
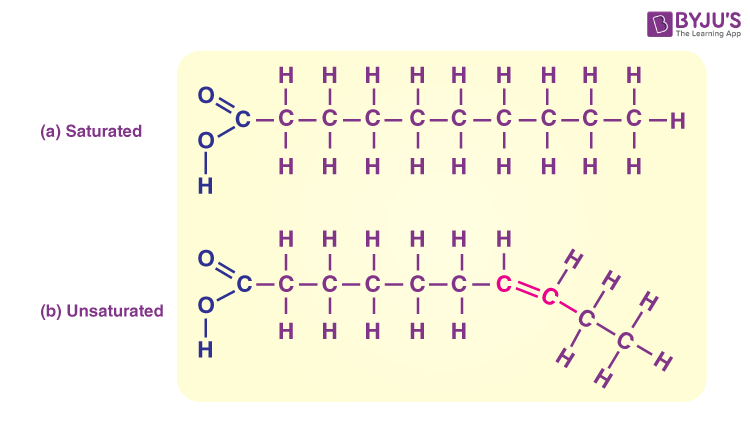
Which chain of lipids is bent: saturated or unsaturated
Unsaturated
Lipids Monomer
Glycerol + Fatty acid chains
Protein Formula
C H O N
Protein Structure
Central Branches
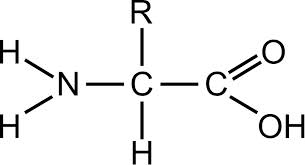
Protein Function
Muscle & Bones, Build/repair cells; speed up reactions
Protein Monomer
Amino Acids
Protein Polymer
Polypeptides
Nucleic Acids Formula
C H O N P
Nucleic Acids Structure
Rings that fuse into spiral (helix)
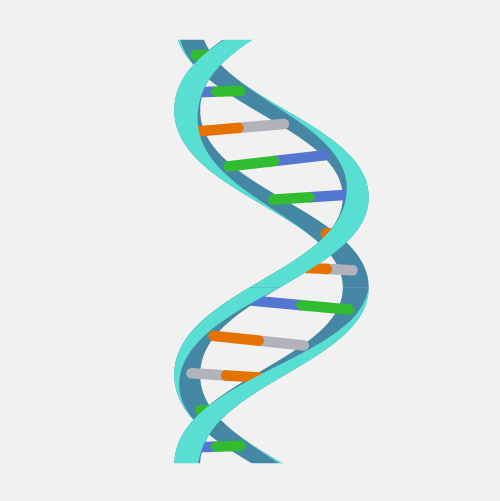

Nucleic Acids Function
Store genetic information (DNA and RNA)
Nucleic Acids Monomer
Nucleotide
Nucleic Acids Polymer
Nucleic Acid
Bar graph is best used when you have ____ as your independent variable
Categories
Line graph is best used when you are dealing with ____ as your independent variable
Time
______ variable is changed in experiment
Independent
_____ variable responds; affected by the change
Dependent
Dehydration Synthesis
Turns monomers into polymers. Removes water (H2O). NEEDS energy.
Hydrolysis
Breaks down polymers into monomers. Adds water (H2O). Releases energy.
Cell Theory
Cells are the basic unit of life, all organisms are made of 1 or more cells, and all cells come from pre-existing cells
The 2 types of cells
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Prokaryote
Bacteria, has no nucleus, small and simple, unicellular ONLY, DNA floats in cytoplasm, and has NO membrane bound organelles
Eukaryote
Has a nucleus, larger and complex, uni OR multicellular, DNA in the nucleus, and has membrane bound organelles
2 types of Eukayrotes
Plant and Animal
Endosymbiotic theory
Eukaryotes evolved from ancient prokaryotes and one prokaryote engulfed another prokaryote and became a eukaryote.
Endomembrane System
Group of membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package and transport lipids and proteins
Nucleus Function
Brain of the cell, controls activities from day to day
Chloroplast Function
Found only in plants, green, and makes food using sun’s energy
Smooth ER Function
Synthesizes lipids (hormones) and carbs
Rough ER Function
Synthesizes and folds proteins
Ribosome Function
Makes proteins, in the cytoplasm or attached to the ER’s wall
Cell Membrane Function
Controls what goes in and out of the cell
Lysosome Function
Contains many enzymes, can digest an injured cell, and can break down large/small molecules
Golgi Apparatus Function
Packages and tags molecules ready for transport
Vesicle Function
Vehicle transporting molecules all around and out of the cell
Characteristics of ALL living things
Can respire/breathe, can make their own energy (ATP), can move, has a natural lifespan, can metabolize, can reproduce independently, and can maintain homeostasis
Viruses are ____
Abiotic (Non-living)
Cells are ____
Living
Building blocks of life
Cells