Chapter 6: Corporate governance
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What is corporate governance? Who is it important for?

What major corporate scandal in the US highlighted the need for improved corporate governance?
The Enron scandal
What was the primary reason for Enron’s collapse?
Unsustainable growth funded by borrowing and hidden through off-balance-sheet subsidiaries.
What was the purpose of Enron creating multiple legal subsidiaries?
To hide excessive borrowing and maintain the appearance of creditworthiness.
What happened to Enron in late 2001?
It filed for bankruptcy protection.
What was revealed during the investigation of Enron's financial statements?
They were propped up by systematic, creatively planned accounting fraud.
What was the impact on Enron’s share price after the fraud was exposed?
It fell from over $90 to just a few cents.
What happened to Arthur Andersen as a result of the Enron scandal?
They were accused of obstruction of justice, stopped auditing public companies, and ceased trading.
What are two common forms of abuse of investor trust by management in public companies?
Extracting excessive personal benefits and manipulating share prices through misrepresented profitability.
What US legislation was passed in response to Enron’s collapse?
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (2002).
What is the main goal of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act?
To protect investors by improving corporate disclosure and reporting accuracy.
What board was established by the Sarbanes-Oxley Act to oversee auditors?
The Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB).
What does the Sarbanes-Oxley Act prohibit auditors from doing?
Providing certain non-audit services to audit clients.
In the UK, what scandals revealed failures in director oversight?
The Guinness scandal and the Robert Maxwell case.
What major reports in the 1990s shaped UK corporate governance?
The Cadbury and Greenbury reports, leading to the Combined Code.
What replaced the Combined Code in the UK?
The UK Corporate Governance Code, first drafted in 1998.
What is the EU’s approach to corporate governance post-2003?
No single code, but a unified approach through Directives on key governance issues.
What are some focus areas of EU corporate governance Directives?
Independent non-executive directors, director remuneration transparency, and financial disclosure.
What UK scandal raised concerns about principle-based corporate governance?
The BHS pension scandal.
How might Brexit impact corporate governance?
It may affect the alignment between UK and EU governance practices.
Explain the two different approaches to corporate governance.
The decision as to which approach to use for a country can be governed by many factors, list some of them.

What is ‘comply or explain’?

What are the 7 key SOX points?
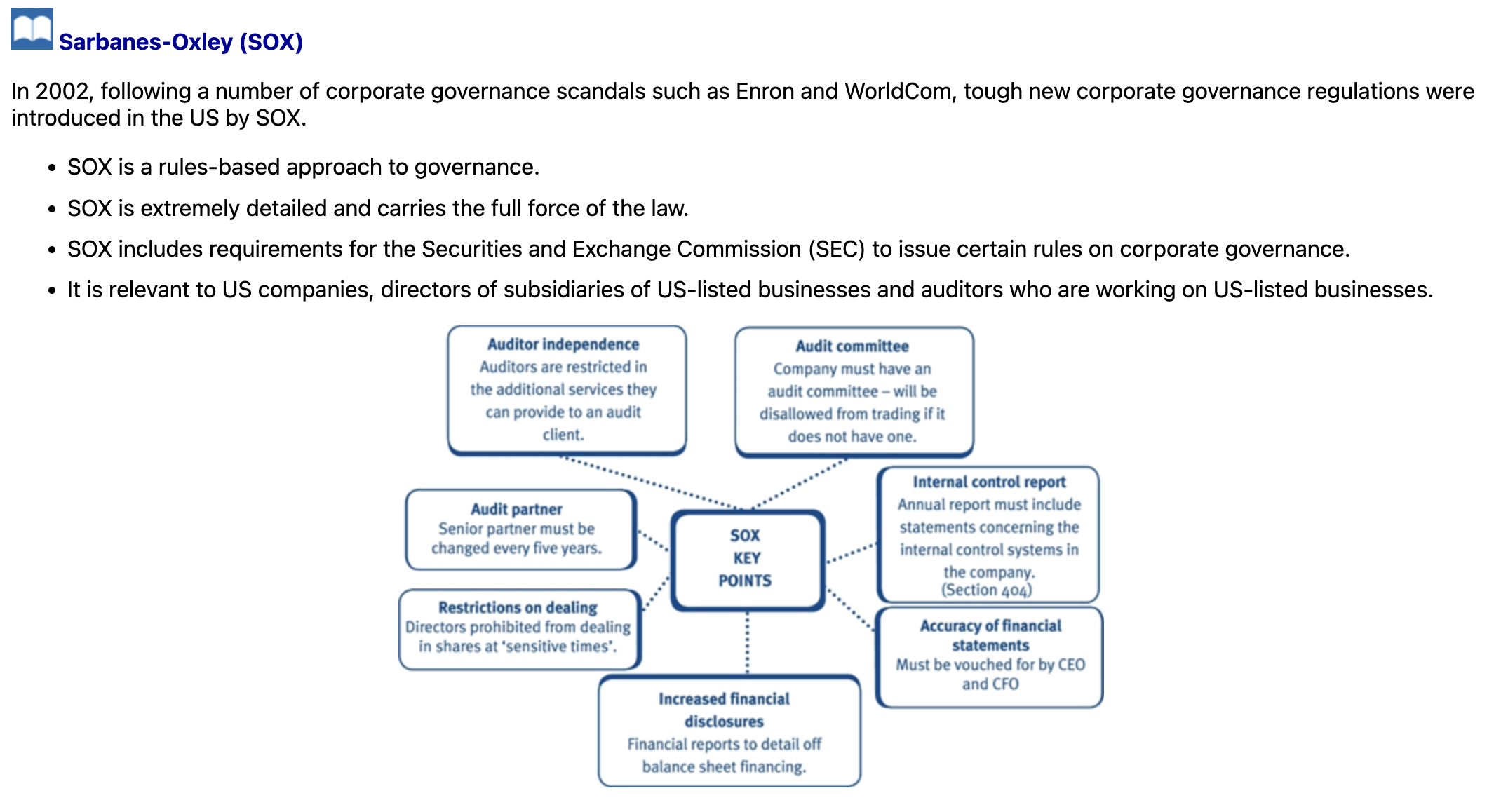
What are some arguments in favour of a rules-based approach (and against a principles-based approach)

What are some arguments against a rules-based approach (and in favour of a principles-based approach)

What regulatory body's listing rules must UK stock exchange-listed entities comply with?
The Financial Services Authority (FSA) listing rules.
What two statements must UK listed entities include in their annual reports regarding corporate governance?
A statement of how the entity has applied the main principles set out in the Code.
A statement as to whether the entity has complied with all relevant provisions of the Code.
What are the five main provisions of the UK Corporate Governance Code?
Board Leadership and Company Purpose
Division of Responsibilities
Composition, Succession and Evaluation
Audit, Risk and Internal Control
Remuneration
What organization developed the 'Principles of Corporate Governance' in 1999?
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
What are the two main aims of the OECD Principles of Corporate Governance?
To help governments evaluate and improve their legal and regulatory corporate governance frameworks.
To offer guidance to stock exchanges, investors, corporations, and others in developing good governance.
Who can benefit from applying the OECD Principles, besides publicly traded entities?
Non-traded entities, to the extent the principles are applicable.
When were the OECD Principles of Corporate Governance first published?
In 1999.
What is the primary focus of the OECD Principles of Corporate Governance?
Publicly traded entities.
Explain the 6 principles

What do the OECD Principles of Corporate Governance represent for OECD member countries?
A common basis considered essential for the development of good governance practice.
What are the OECD Principles of Corporate Governance intended to be?
Concise, understandable, and accessible to the international community.
Are the OECD Principles meant to replace detailed national or private sector governance initiatives?
No, they are not a substitute for more detailed government or private sector 'best practice' initiatives.
UK Corporate Governance Code – Role of the Board
What should the board assess to ensure long-term success?
The basis on which the company generates and preserves value over the long term.
What aspect of the company should the board monitor alongside performance?
Company culture.
What should the chair do beyond formal meetings to engage shareholders?
Seek regular engagement with major shareholders.
What is required if 20% or more of votes are cast against a board recommendation?
The company must explain the actions it intends to take to consult shareholders and understand the reasons behind the result.
How should the board address stakeholder interests in its annual report?
By describing how key stakeholder interests have been considered in board discussions and decision-making
What mechanism should the board establish for the workforce?
A way to raise concerns in confidence and anonymously, if desired.
What must the board do regarding conflicts of interest?
Identify and manage conflicts, and ensure independent judgement is not overridden by third-party influence.
What should happen if directors have unresolved concerns?
Their concerns should be recorded in the board minutes.
Why should the board include a balance of executive and non-executive directors?
To avoid an unfavourable concentration of power in executives' hands.
Who do NEDs primarily owe a fiduciary duty to?
The shareholders of the company.
Why might prior industry involvement of a NED be problematic?
It can reduce their independence and objectivity.
Why is it sometimes easier to demonstrate NED independence when recruited from outside the industry?
Because they are less likely to be influenced by pre-existing views or relationships.
What makes a non-executive board effective in practice?
A mix of talents and areas of expertise among NEDs.
List three reasons why NED independence is important.
To provide objective views on decisions
To offer shareholder representation
To enhance confidence in corporate governance
Why should the roles of Chairman and CEO be held by different people?
To prevent excessive concentration of power in a single individual.
What is the purpose of board committees?
To act as control mechanisms for areas like audit, remuneration, risk, and nominations.
What is the role of the internal audit function in a company?
To review internal controls, assess performance, and recommend improvements to reduce fraud and error.
Who does the internal audit team report to, and who gives their instructions?
They are employees of the entity and work under the direction of the board or directors.