Chapter 13 Body Planes - Lecture Specific
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
What is Anatomy the study of?
The study, classification, and description of structures and organs of the body
What is Physiology the study of?
Explains the processes and functions of the various structures and how they interrelate
What is ‘A’?
Cranial or towards the head
What is ‘B’?
Anterior or towards the front of the body
What is ‘C’?
Caudal or towards the feet
What is ‘D’?
Posterior or towards the back
What is ‘A’?
Proximal or nearest to the origin of the structure
Nearest to the trunk
What is ‘B’?
Distal or farthest from the origin of the structure
Farthest from the trunk
What is ‘C’?
Medial or towards the midline of the body
What is ‘D’?
Lateral or towards the side
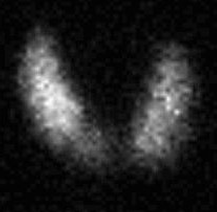
What type of scan is this?
Thyroid scan
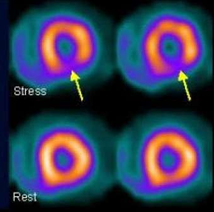
What type of study is this?
Cardiac study
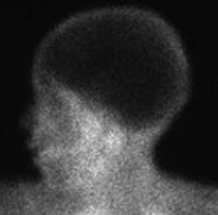
What type of study is this?
Brain study
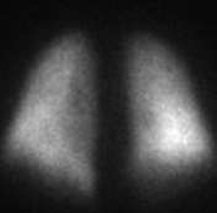
What type of study is this?
Lung study

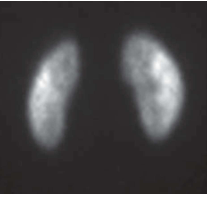
What type of scan is this?
What organ system is it imaging?
Liver or HIDA or Hepatobiliary scan
Scan for the Hepatobiliary system containing the Liver and the Gallbladder
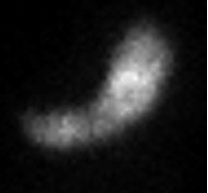
What type of scan is this?
What organ system is it imaging?
Kidney scan
Genitourinary system
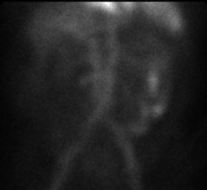
What organ is scanned here?
What organ system is this apart of?
Stomach scan
Scan for the Gastrointestinal system
What organ is being scanned here?
What organ system is it apart of?
Small bowel scan
Scan for the Gastrointestinal system
Define ‘superficial’
Nearer to the surface
Define ‘deep’
Farther away from the surface of the body
What are the 2 main cavities that separate the main cavities of the body?
Dorsal body cavity
Ventral body cavity
What are the two cavities within the dorsal body cavity?
Cranial cavity
Spinal cavity
What does the cranial cavity contain?
The brain
What does the spinal cavity contain?
The spinal cord
What are the three cavities within the ventral body cavity?
Thoracic cavity
Abdominal cavity
Pelvic cavity
What does the thoracic cavity consist of? (3 things)
Trachea, heart, and lungs
What does the abdominal cavity consist of? (7 things)
Liver, gallbladder, stomach, spleen, pancreas, small intestine, parts of the large intestine
What does the pelvic cavity consist of? (4 things)
Lower (sigmoid colon), rectum, urinary bladder, reproductive organs
What is ‘A’?
The dorsal cavity
What is ‘B’?
The cranial cavity
What is ‘C’?
The spinal cavity
What is ‘D’?
The thoracic cavity
What is ‘E’?
The abdominal cavity
What is ‘F’?
The pelvic cavity
What is ‘G’?
The abdominopelvic cavity
What is ‘H’?
The ventral cavity
What is ‘A’?
Sagittal body plane
What is ‘B’?
Transverse body plane
What is ‘C’?
Frontal body plane
What is ‘A’?
Medial view
What is ‘B’?
Lateral view
What is quadrant ‘A’?
Right Upper Quadrant
What is quadrant ‘B’?
Left Upper Quadrant
What is quadrant ‘C’?
Right Lower Quadrant
What is quadrant ‘D’?
Left Lower Quadrant
What is ‘A’?
The skull
What is ‘B’?
The thorax
What is ‘C’?
The vertebral column
What is ‘A’?
Shoulders
What is ‘B’?
Upper extremities
What is ‘C’?
Hips
What is ‘D’?
Lower extremities
What are the 4 levels of organization in the body?
Cells
Tissue
Organ
Organ system
Explain what cells in the organization of the body are
Considered the smallest living unit of structure and function in the body
Explain what tissue in the organization of the body are
Organization of many similar cells that act together to perform a function
Explain what organs in the organization of the body are
Group of several different kinds of tissues arranged to perform a special function
Explain what organ systems in the organization of the body are
Most complex units
Organization of varying numbers and kinds of organs arranged to perform complex functions of the body
What are the 3 main cell anatomy that they want us to know from the lecture?
Plasma membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
What is active transport?
A transport process that requires cellular energy to move substances from a low concentration to a high concentration
What is passive transport?
A transport process in which solid particles in a fluid move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, resulting in an even distribution of the particles
What are the 3 main functions of epithelial tissues?
Protection
Absorption
Secretion
What is the protection function of epithelial tissues?
Covering the body and organs, serving as a protective barrier against invasion of organisms
What is the absorption function of epithelial tissue?
Can absorb material in the body – like the lining of the small intestine
What is the secretion function of epithelial tissue?
Mucus secretion in areas such as the respiratory and digestive tracts
What is the main function of connective tissue?
‘Connects’ or joins tissues or structures of the body
Supports and protects the structures of the body
What are the 3 types of muscle tissues?
Skeletal muscle
Cardiac muscle
Smooth muscle
Of the 3 types of muscle tissue, which are voluntary, and which are involuntary?
Skeletal muscle is voluntary
Cardiac and Smooth muscle is involuntary
Describe skeletal muscle tissue
Skeletal muscle cells are striated in appearance and attach to bones to produce voluntary movement
Describe cardiac muscle tissue
Cardiac muscle cells are striated, and the regular contractions of the cardiac muscle produce the heartbeat
Describe smooth muscle tissue
Smooth muscle cells are non-striated and appear in the viscera – internal organs – like the stomach and intestines as well as in the walls of blood vessels and the uterus
What is the function of nervous tissue?
Nervous tissue allows rapid communication between the brain or spinal cord and the other structures of the body
Allows control of body functions
What are the 3 main components of a neuron that we should know from lecture?
Dendrites
Cell body
Axon
What is the function of dendrites?
Carry impulse toward the cell body
What is the function of axons?
Carry impulses away from the cell body
What is the integumentary system composed of? (4 things)
Skin
Hair and sweat glands
Nails
Oil glands
What is the skeletal system composed of? (2 things)
Bones
Joints
The muscular system is made up of muscles that do voluntary and involuntary functions, what are the 4 main functions of the muscles?
Movement
Posture
Joint stability
Heat production
What does the nervous system contain? What is its main function?
Contains the body’s control center
Responsible for all the coordination of the body’s activities
The endocrine system consists of many glands, name 7 of the glands/organs found in the system
Pineal gland
Hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
Thyroid gland
Parathyroid gland
Adrenal glands
Pancreas
What is the main function of the heart and blood vessels of the cardiovascular system?
Transportation of nutrients, water, oxygen, and wastes
What are the 5 organs and vessels that make up the lymphatic system?
Lymph nodes
Lymphatic vessels
Thymus
Spleen
Tonsils
What are the 6 organs that make up the respiratory system?
Nose
Pharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchi
Lungs
The digestive system is divided into primary and accessory organs, what are the 8 main primary organs?
Mouth
Pharynx
Esophagus
Stomach
Small intestine
Large intestine
Rectum
Anal canal
The digestive system is divided into primary and accessory organs, what are the 7 main accessory organs?
Teeth
Salivary glands
Tongue
Liver
Gallbladder
Pancreas
Appendix
What are the 4 main organs in the urinary system?
Kidneys
Ureters
Urinary bladder
Urethra
What is the main function of the reproductive system?
Survival of species
What is a healthcare record?
A legal record that’s used to meet the many demands of the health, accreditation, medical insurance, and legal systems
What is charting (recording or documenting)?
Process of adding information to the chart
Only document when things have already taken place
What is the electronic health record?
The electronic version of a patient’s chart
Patient data can be exchanged within the facility and also to another outside facility when permitted
What is the electronic medical record?
Another electronic version of a patient’s chart
Normally set up to exchange patient data to an outside facility
What is the main purpose of patient records?
Current regulations require chart audits by officially appointed auditors
What is the purpose of an audit in healthcare?
Specific procedures to provide for quality assurance, assessment, and improvement
Evaluates services provided and the results achieved compared with accepted standards
What are the 5 components that make up the purpose of patient records?
Documented communication
Permanent record for accountability
Legal record of care
Teaching
Research and data collection
What is record keeping?
Professionally executed charting is legal proof of care given
Communicates the patient’s status and progress and that interventions were implemented to meet their needs
What is the importance of taking a history of the patient? (4 points specific to the radiographer)
Provides clinical context for accurate image interpretation
Aids in choosing the correct imaging modality and protocol
Identifies contraindications – allergies, medications, diet…
Ensures patient safety and minimizes unnecessary exposure to radiation
What is the best type of question you should begin with when obtaining a history?
Begin with open-ended questions
What type of questions should you use to obtain clarification details?
Use closed-ended questions
What are double-barreled questions?
Questions that are asked all at once and should be avoided
Better to ask one question at a time
What are the 5 special considerations that may be obtained in a patient’s history?
Allergies
Renal function
Pregnancy
Implants and /or devices
Claustrophobia or anxiety
What type of information should you be asking when obtaining a patient history?
Clarifying the chief complaint
Duration and progression of condition
Prior imaging done
Identification of any procedures or surgeries