Cells and Transport PPQs #1
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
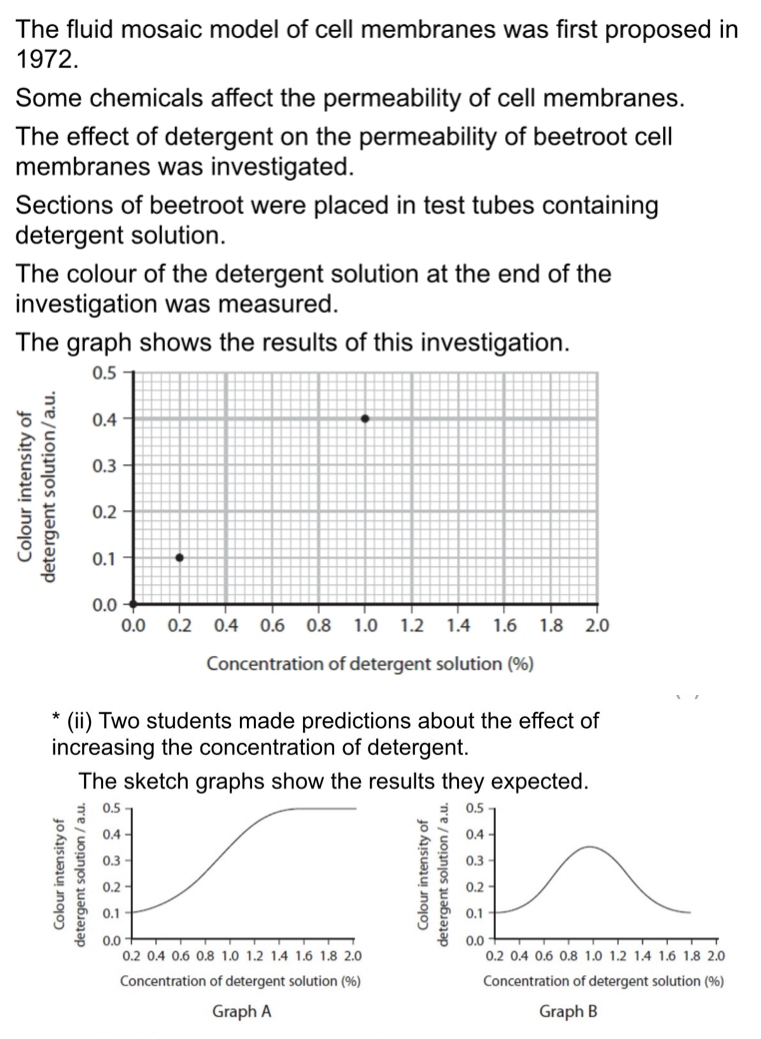
Explain how to carry out an investigation to test these predictions
Use cork bearer to get beetroot cores of similar ages and cut to same size
Use water bath to control temperature
Remove excess pigment
Use blue green colour filter in calorimeter to measure absorbance
Repeat with at least 5 different concentrations
Use smaller intervals between 0.8 and 1 to see which peak correct from the graphs
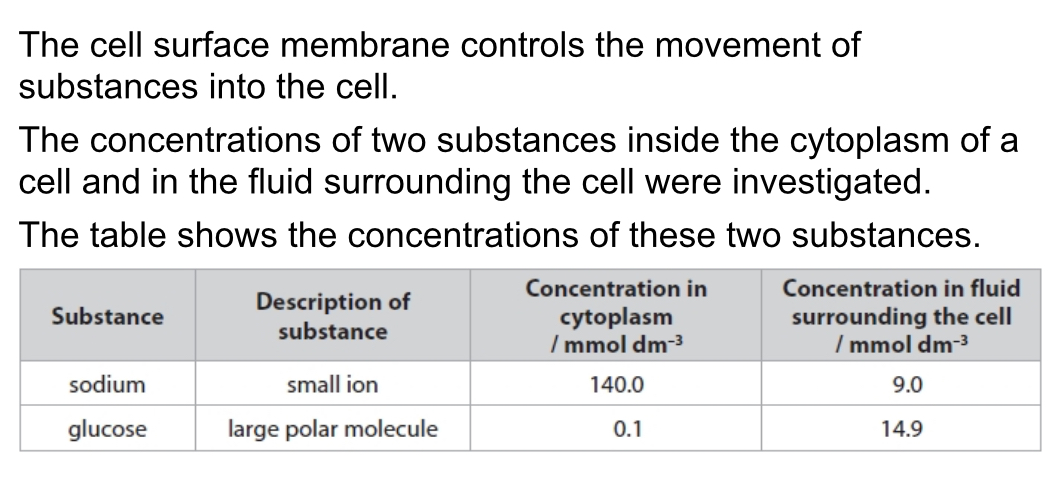
Explain why ATP is required for the movement of sodium ions into the cell
Sodium ions are being moved against concentration gradient using active transport
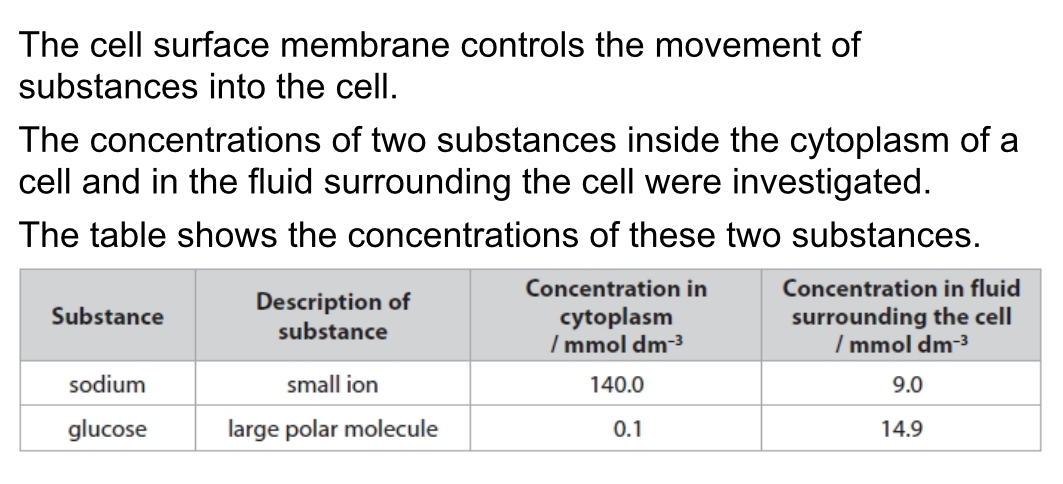
Describe how glucose molecules move into the cell
By facilitated diffusion through carrier proteins
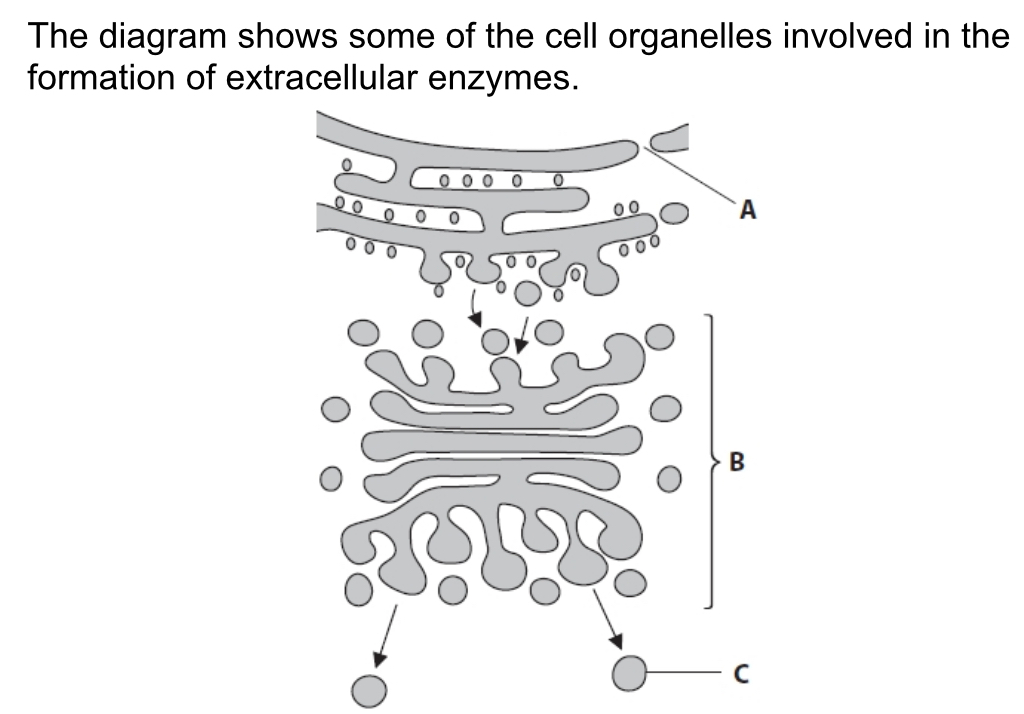
Describe the roles of parts B and C in the formation and transport of extracellular enzymes
Vesicle fuses with Golgi
Modifies protein
Packages into secretory vesicle
Vesicle fuses with cell surface membrane
Glycoproteins and phospholipids are molecules found in the cell surface membrane. Give one function of the glycoproteins found in the cell surface membrane.
Involved in cell recognition
A cell surface membrane is partially permeable. The phospholipid bilayer is important in controlling the movement of molecules through the membrane. Explain how the structure of a phospholipid molecule contributes to the partially permeability of a cell surface membrane.
Phospholipid has hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
Allows non-polar molecules to pass through membrane
Polar molecules can’t pass through
Describe how scientists could have determined that P.falciparum is a eukaryotic organism and not a prokaryotic organism
Eukaryotic have membrane bound organelles
Prokaryotes have 70s ribosomes, Eukaryotic have 80s
Eukaryotic have linear DNA
Prokaryotic have plasmids
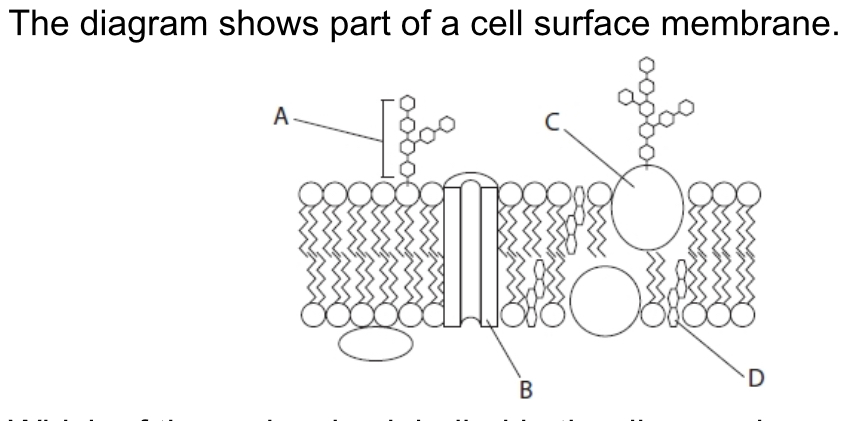
Which one is a glycoprotein?
C
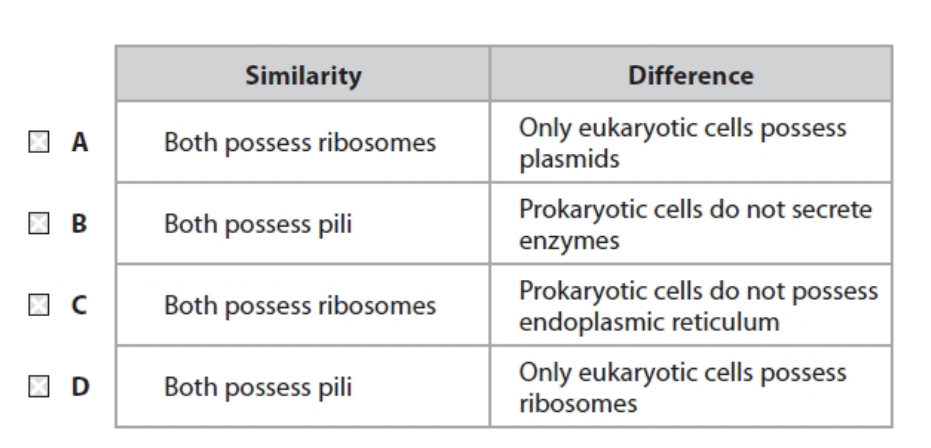
Which is true for both eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells
C
Give one difference between a tissue and an organ
Tissue is made of one type of cell but organ is made of different tissues
In bacteria, where is the capsule located?
D

What do plant and animal cells both contain?
D

Cytoplasmic connections are between a plant cell and what?
B

What do prokaryotic cells and plant cells both contain?
D

What is the evidence that Woese suggested that the three domains are based on?
B

What are the two domains that contain prokaryotic cells?
B