Lattice enthalpy, entropy, free energy
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What is lattice enthalpy?
formation of 1 mol of ionic lattice from gaseous ions
(Eg Na+1(g) + Cl-1(g) → NaCl(s) )
What is the symbol for lattice enthalpy?
∆LEH
What is enthalpy of formation?
1 mole of a substance formed from its constiutent elements in stndard state (Eg Na(s) +1/2 Cl2(g) → NaCl(s)
What is ionisation energy?
Energy to remove 1 mole of electrons from gaseous atoms to form 1 mole of gaseous +1 ions (Eg Na(g) → Na+1(g) +e- )
What is enthalpy of atomisation?
1 mole of gaseous atoms formed from elements in their standard state (Eg Na(s) → Na(g) )
What is the symbol for enthalpy of atomisation?
ΔHat
What is electron affinity?
1 mole of gaseous -1 ions formed from its gaseous atoms (Eg Cl(g) + e- → Cl-1(g)
What is a constant feature of lattice enthalpy?
Always exothermic (always negative)
What does the more exothermic lattice enthalpy mean?
Stronger ionic bonds forming (higher thermal stability)
What determines how strong ionic bonds formed are?
Smaller ions can get closer together so stronger ionic bonds & larger charge creates greater attraction so stronger ionic bonds
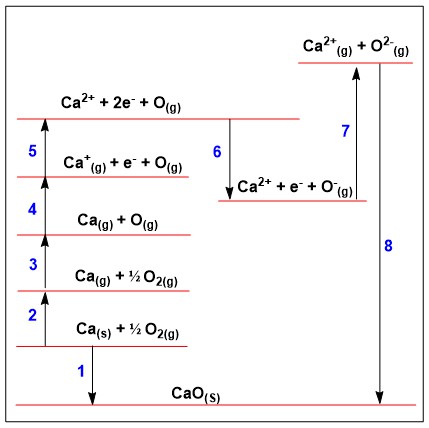
Name the processes for each stage within this born haber cycle:
1 = enthalpy of formation, 2 = enthalpy of atomisation for METAL, 3 = enthalpy of atomisation for NON-METAL, 4 = 1st Ionisation energy, 5 = 2nd Ionisation energy, 6 = 1st Electron affinity, 7 = 2nd Electron affinity, 8 = lattice enthalpy
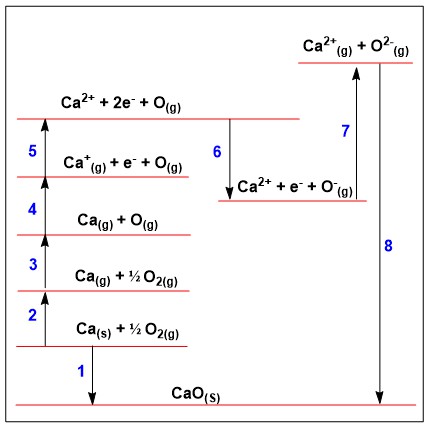
Within this born haber cycle how would you calculate enthalpy of formation if given the other data?
ΔHfꝋ = ΔHatꝋ + ΔHatꝋ + IE + EA + ΔHlattꝋ
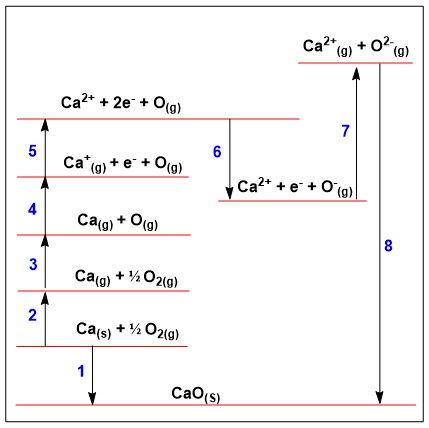
Within this born haber cycle how would you calculate lattice enthalpy?
ΔHlattꝋ = ΔHfꝋ - (everything else added together)
What is enthalpy of hydration (ΔHhyd)?
1 mole of GASEOUS ions dissolve in water to become aqueous (g → aq)
What is enthalpy of solution ΔHsol
1 mole of SOLID solute dssolved in water to form aqueous ions (s → aq)
What are the best conditions for dissolving?
higher charge as greater attraction to water & smaller ion so easier to surround the water molecules
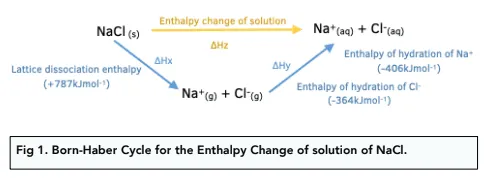
What does this show?
Hess cycle for enthalpy of solution, enthalpy of hydration, and negative lattice enthalpy
Is exothermic or endothermic more insoluble?
Endothermic is slightly insoluble so more difficult to dissolve in water
What is entropy?
measure of the dispersal of energy in a system which is greater, the more disordered a system
What is the symbol for change in entropy?
ΔS
How does entropy change from a solid to gas?
entropy increases as there is more disorder due to the gas particles moving in random movement (the most stable form as entropy can’t further increase)
What are the ways an increase in entropy can be seen from an equation?
If the products have more moles of gases, more products formed compared to reactants, presence of a gas in products
What is the equation for entropy change?
Entropy of products - Entropy of reactants
What is free energy?
measure used to predict if a reaction is feasible (if it can happen)
Symbol for free energy:
ΔG
What does a reaction being feasible mean?
Once started the reaction can complete without any energy being supplied
What is the equation for free energy & units?
ΔG (Jmol-1) = ΔH (Jmol-1)- TΔS (T = K, S = Jmol-1K-1)
What does the Gibbs equation mean?
If a negative or equal to 0 free energy result is produced, the reaction is feasible at that temperature
If the reaction is not feasible at the temp in question how do you calculate temp needed in order for the reaction to be feasible?
T = ΔH / ΔS
If the enthalpy change is negative, entropy is postive, and free energy is negative, will the reaction be feasible?
Yes but will be spontaneous
If the enthalpy change is negative, entropy change is negative, free energy is negative, will the reaction be feasible?
yes but only at LOW TEMP
If the enthalpy change is positive, entropy is positive, free energy is negative, will the reaction be feasible?
Yes but only at HIGH temp
If the enthalpy change is positive, entropy is negative, free energy is positive, will the reaction be feasible?
NEVER FEASIBLE
What does feasibility depend on?
Entropy change, temp in system, enthalpy change of the system, rate of reaction, activation energy