Lecture 4 - Lipids and Nutrition
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Digestion
Breaking down large food molecules into water-soluble ones to be absorbed
Ways to Digest
Acid
High temperature (not for humans)
Enzymatic (protein biocatalysts)
Why don’t high temperatures work for humans?
The body functions at a specific temperature, or humans would die
Proteins as Enzymes
Biocatalysts that speed up reaction; named with ‘ase’
Mechanism of Enzymes
Binding to active site on substrate to form enzyme-substrate complex, release broken-down products
Enzyme Specificity
Enzymes often only react with 1 molecule
Different active site shapes
Factors that affect Enzymes
Temperature
pH
Path of food through GI Tract
Stomach
Small Intestine
Large Intestine
Rectum
Accessory organs of GI system
Pancreas
Liver
Gallbladder
Sphincters
Stomach Function
Production of HCl, acidic digestion of foods
Small Intestine Function
Absorption of nutrients
Large Intestine Function
Absorption of water
Rectum Function
Excretion of food wastes
Sphincter Functions
Muscles that open/close between GI passages
Autonomic control except for anal sphincter (controlled by us)
Liver Function
Production of bile
Gallbladder Function
Storage of bile
Pancreas Function
Secretion of digestive enzymes
Enzymes in Digestive Tract
Lingual lipase in saliva breaks down food first
Gastric lipase in the stomach hydrolyzes lipids
Both digest short and medium fatty acids
pH of Small Intestine
Want to be stabilized at neutral 7
Hormone secretin stimulates bicarbonate secretion from pancreas to neutralize HCl from stomach
Cholecystokinin (CCK) Function
Secreted by small intestine cells
Stimulate bile release by gallbladder
Stimulate pancreas to secrete pancreatic juice containing lipase
Pancreatic Juice
Juice secreted by pancreas containing all digestive enzymes; catalyzing cleavage of molecules
Cholesterol Esterase
Secreted by the pancreas
Breaks down esters, tri/monoglycerides, phospholipids, Vitamin A and D
“Phospholipases”
Bile Secretion
By CCK in liver, containing polar and nonpolar sides
Bile Function
Attach to fat globules for emulsification, forming micelles
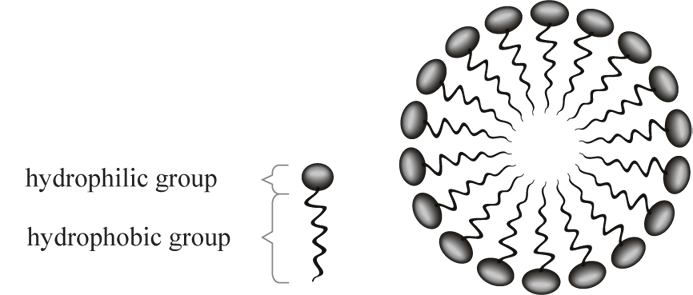
Concentration Gradient
Digestion products flow from high to low concentration due to rapid re-esterification inside cells
Chylomicron Location
Small Intestine
Chylomicron Structure
Phospholipid outer layer, triglyceride inner layer containing embedded lipoproteins
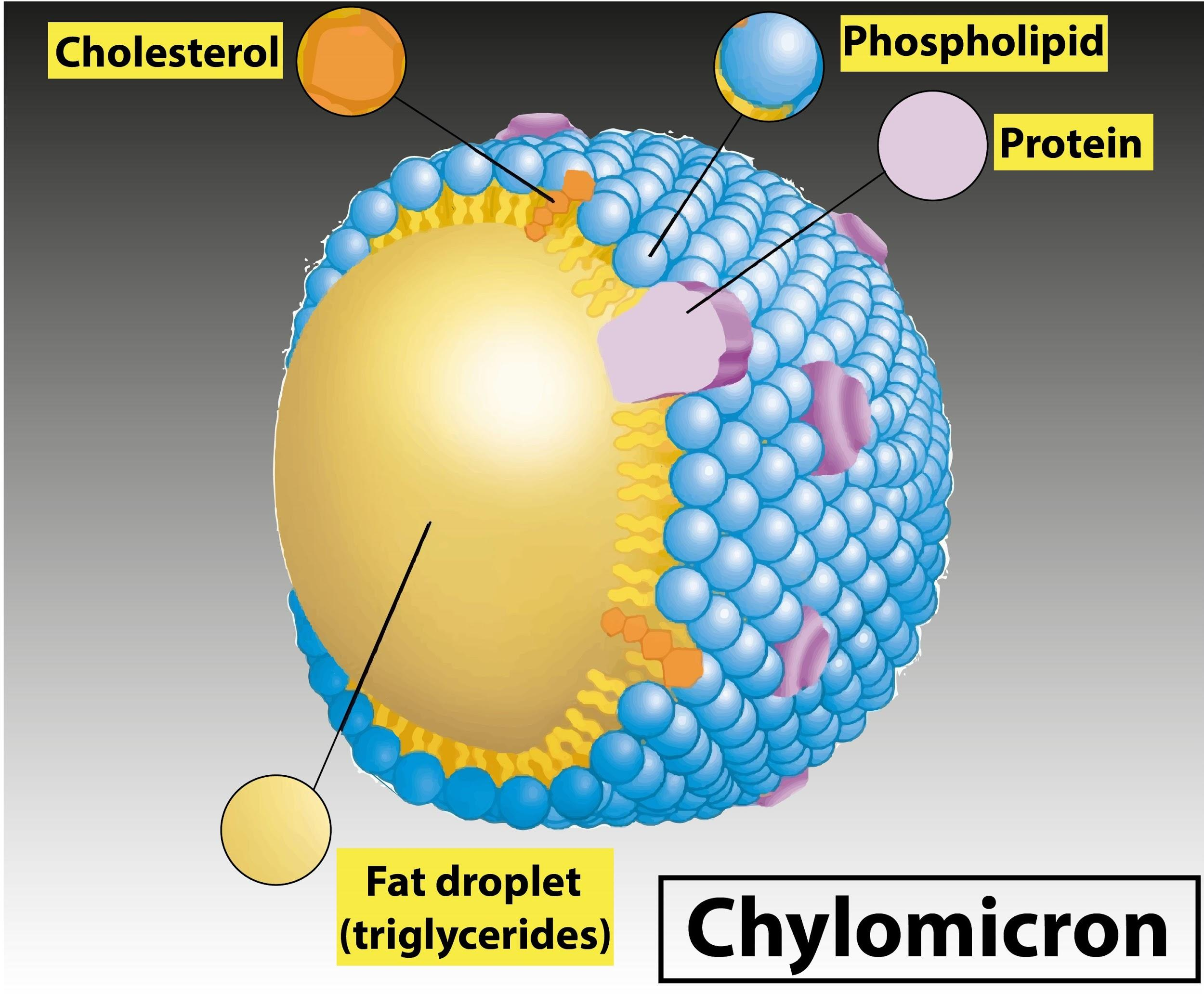
Lipoprotein Lipase Function
Digest triglycerides to allow into blood
Essential Nutrients
Nutrients we need but can’t make
Is cholesterol an essential nutrient?
No, it is made in the liver.
HDL (High Density Lipoprotein) Cholesterol
“Good” cholesterol because it regulates LDL and promoted its excretion
Made mostly of lipoproteins (high density)
LDL and VLDL Cholesterol (Low-density)
Stored in the blood and made mostly of triglycerides
Essential Fatty Acids
Linoleic and Linolenic (Omega 3 and 6); enzymes can’t place double bonds in positions 3 and 6
Where do we get Omega 3 and 6 from?
Oils/seafood oil
Are EPA and DHA essential?
No, we make them and also consume them in seafood
Omega-3 Benefits
Reduce triglycerides
Raise HDL
Lower BP, prevent clots, prevent plaque
Prevent blindness
Promote brain health and prevent mental disorders
Schizophrenia, BPD, etc.
Fight Alzheimers
Help with diabetes, obesity, and autoimmune disorder
Prevent cancer by promoting apoptosis
Boost calcium to strength bones
Fight inflammation
DHA Location
Retinal cell membranes
Normal Functions of DHA
Development and function of eyes; recycled when low
Function of DHA during pregnancy
More intelligent, better communication, less behavior issues
Decrease developmental issues, ADHD, autism, cerebral palsy
Lipid Functions
Provide and store energy (1 g = 9 kcal)
Insulation
Transport fat-soluble vitamins in chylomicrons
Cell membranes
Saturated Fatty acids do this to cholesterol:
Decrease HDL, increase LDL
Polyunsaturated fatty acids do this to cholesterol:
Decrease HDL and LDL
Monounsaturated fatty acids do this to cholesterol:
Decrease LDL, increase HDL
Diabetes and Lipids
Insulin increases cholesterol synthesis in liver; indication of CVD
Non-modifiable factors for atherosclerosis:
Genes
Age
Vessels narrow and stiffen automatically
Gender
Women lower risk due to high estrogen, reducing plaque
Modifiable Factors of atherosclerosis
Smoking
Stress (cytokines inflame vessels)
Diet (increase LDL)
Exercise
Obesity and diabetes
Plant Stanols/Sterols
Reduce cholesterol absorption in small intestine
Phytosterols
Abundant in seeds and nuts
Stanols = wood pulp
Sterols = soybeans