WEEK 2:Cytology- The cytoplasm:
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is cytoplasm and what 4 things does it consist?
Cytoplasm is everything within the cell
cytosol viscous liquid mainly made of water has sugars, proteins and salts
cytoskeleton ‘cell skeleton’ protein strands determining the cell shape and it can move
membrane bound organelles: individual structures that carry out specific functions.
inclusions: substances found in some cells not others eg. melanin, lipids (energy storage
Functions of the cytoskeleton:
gives shape to the cell
mediates cytoplasmic movements of organelles
crucial in cell division
responsible for cell movement
provides a framework to organise enzymatic reactions
What 3 protein filaments are in the cytoskeleton?
Actin filaments
Intermediate filaments
Microtubules
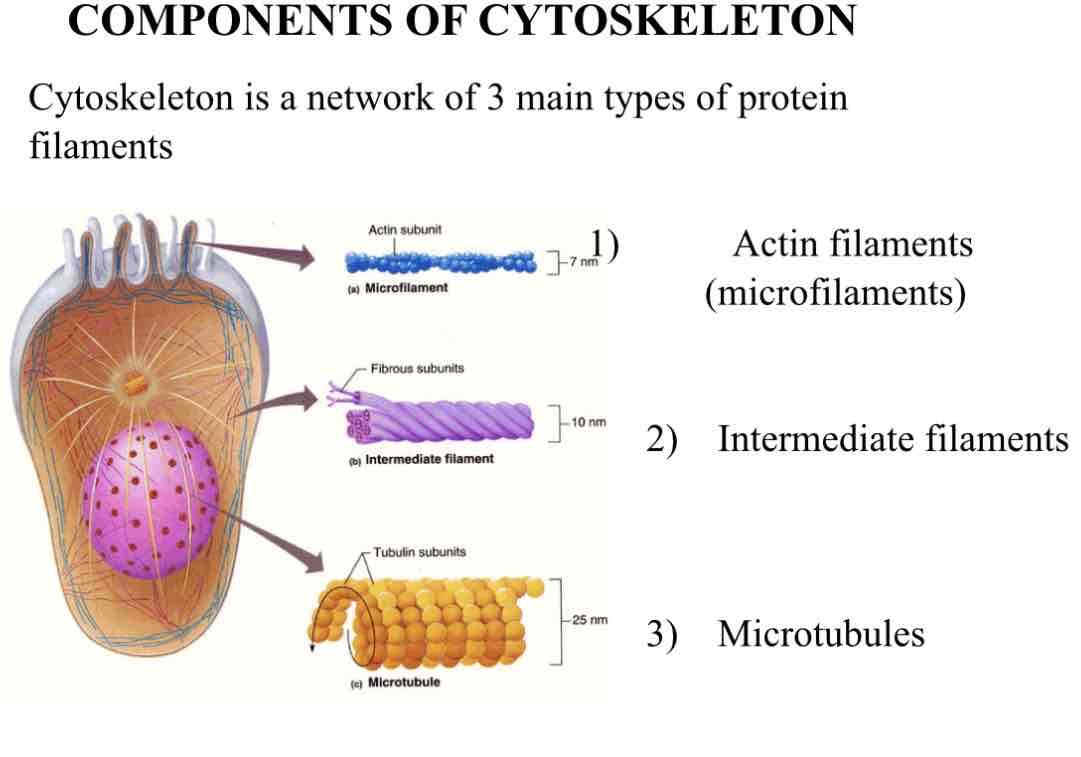
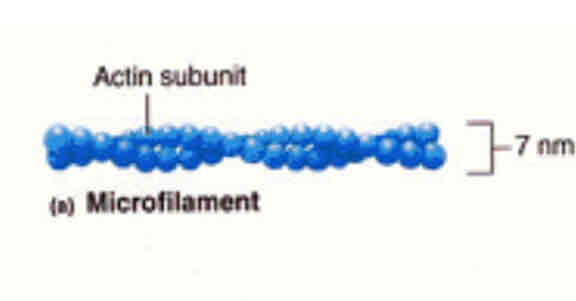
What are actin filaments (microfilaments) and what are there structures.
Thin strands of actin-7-8nm diameter.
10-30% of total cell volume
Clustered around the inner surface of the phospholipid membrane.
Contains two globular actin monomers, packed into a tight helix
SUPPORTS CELL BUT IS INVOLVED IN MOVEMENT TOO
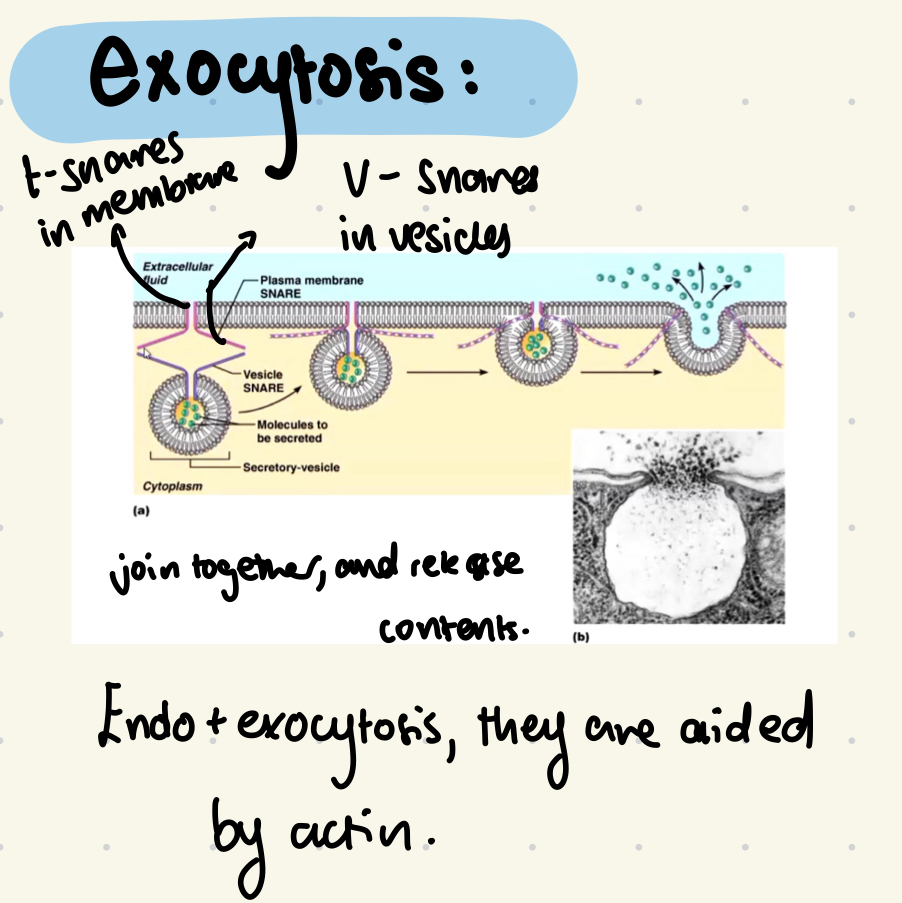
What are actin filaments involved in?
They’re involved in exocytois and endocytosis of cell.
More on actin and endo/exo cytosis
Are microtubules the largest cytoskeletal
Yes, each microtubule is 25nm in diameter
They are made of alpha and beta
An adaptation of microtubules are ..
They determine cell shape but aren’t static, they form a hollow hinge and are able to rapidly form and disassociate.
Whats the centrosome?
Centrosomes are small organising centres. They contain a pair of centrioles at right angles to each other.
Actin filaments (microfilaments)
Thin strands of actin 8nm in diameter.
They are in a lot of cells (10-30%) of volume.
Structure of actin filaments
Actin filaments consist of two globular actin monomers packed into a tight helix.
involved in move,ents of the cell.
And endo and exocytosis.
Microtubules and their structure and function
Largest diameter of cytoskeleton, 25 nanometres in diameter.
Mainly made of alpha and beta tubulin arranged in long hollow tubes.
They are major determinants of cell shape, not static but are able to assemble and disassemble very quickly.
Do microtubules have a centrosome
Yes microtubules have an organising centre called centrosome.
This is where centrioles are at 90 degrees to each other.
They are 0.2 micrometers wide and 0.4 micrometers long.
Centrioles structure:
9 groups of microtubules triplets form onto the wall of each centriole, anchored onto by microtubules.
What are cilia?
Cilia are tiny hair like appendages (2-10 micrometers long) on the surface of many cells.
Primary function move fluid and its contents over the surface of the cell.
How do microtubules form the structural core of cilia?
A cilium consists of 9 microtubule doublets and 2 central microtubules.
Long cilia are known as flagella (eg in sperm)
Photoreceptors too evolved from cells w cilia.
Intermediate filaments:
They are in between actin filaments and microtubules where they are 10 to 12 micrometers.
Very tough and durable more stable than others..
Organised as rope-like polymers and particularly prominent where cells subjected to mechanical stress (e.g. epithelia – desmosomes)
These intermediate filaments form a basket around the nucleus and extend outwards in curving arrays to cell periphery.
Do different cell types have different types of intermediate filaments?
Yes.
What do epithelial and epidermal cells contain
Keratin as their intermediate filaments.
What do fibroblasts and white blood cells contain
Vimentin
What do striated and smooth muscle comtain
Desmin.
What do astrocytes and Schwann cells contain.
They contain glial fibrillary acidic protein.