DCAP Ch 2
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

71 Terms
Acid
Compound that releases hydrogen ions (H+) in solution; proton donors
Activation Energy
Amount of energy greater than the energy contained in the reactants, which must be overcome for a reaction to proceed
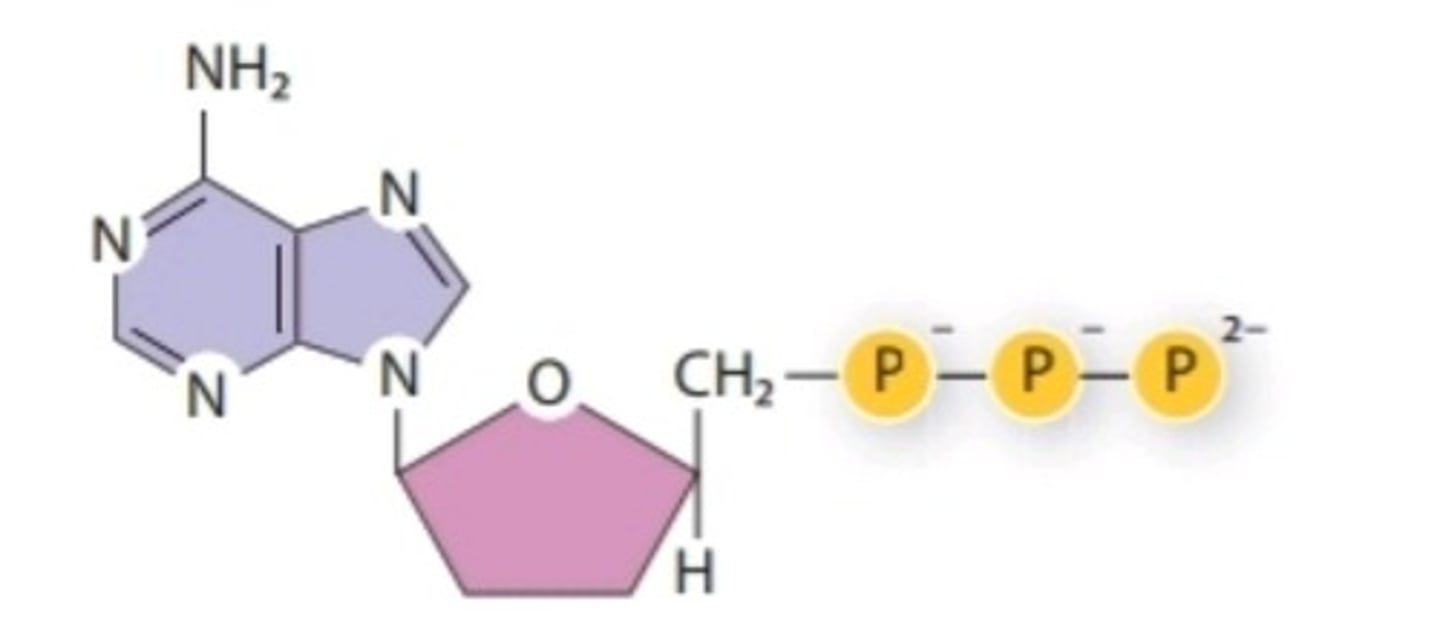
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Nucleotide containing ribose and an adenine base that is essential in energy transfer
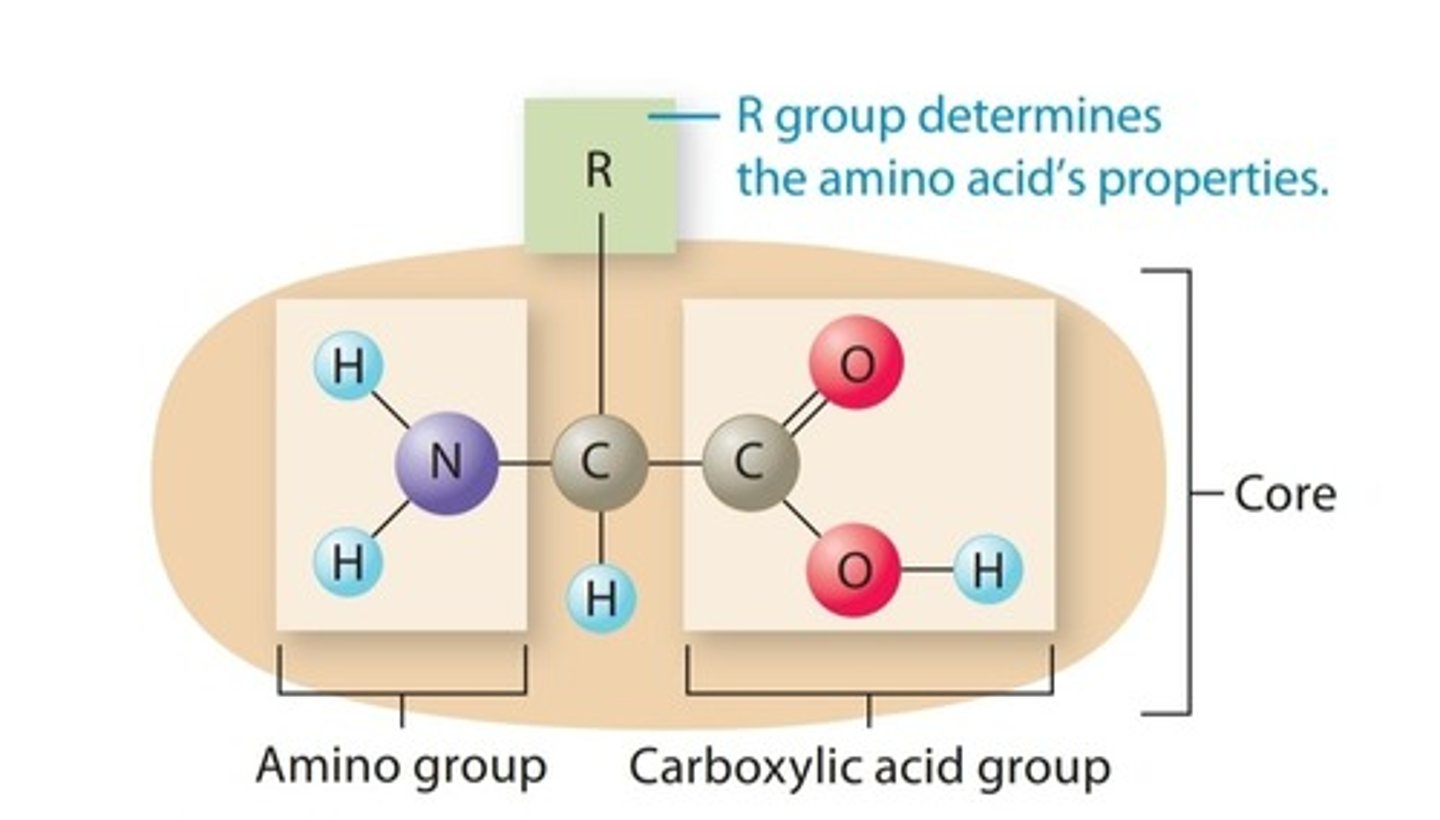
Amino Acid
Building block of proteins
Anion
Atom with a negative charge
Amphipathic molecule
A molecule that has both hydrophilic (polar) and hydrophobic (nonpolar) properties, enabling it to interact with both water and lipid environments
Anabolic
endergonic reactions that build molecules
Atom
Smallest unit of an element that retains the unique properties of that element
Atomic Number
Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Base
Substance that produces hydroxide ions (OH-) and accepts hydrogen ions (H+) proton acceptor
Buffer
Solution containing a weak acid or a weak base that opposes wide fluctuations in the pH of body fluids; ex: buffers in blood work to keep it between 7.35-7.45
Carbohydrate
Class of organic compounds built from sugars, molecules containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1-2-1 ratio
Catabolic
exergonic reaction that break down molecules
Catalyst
Substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself being changed in the process
Cation
Atom with a positive charge
Cellulose
A complex carbohydrate that is a source of indigestible fiber for humans
Compound
Substance composed of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
Concentration
Number of particles within a given space
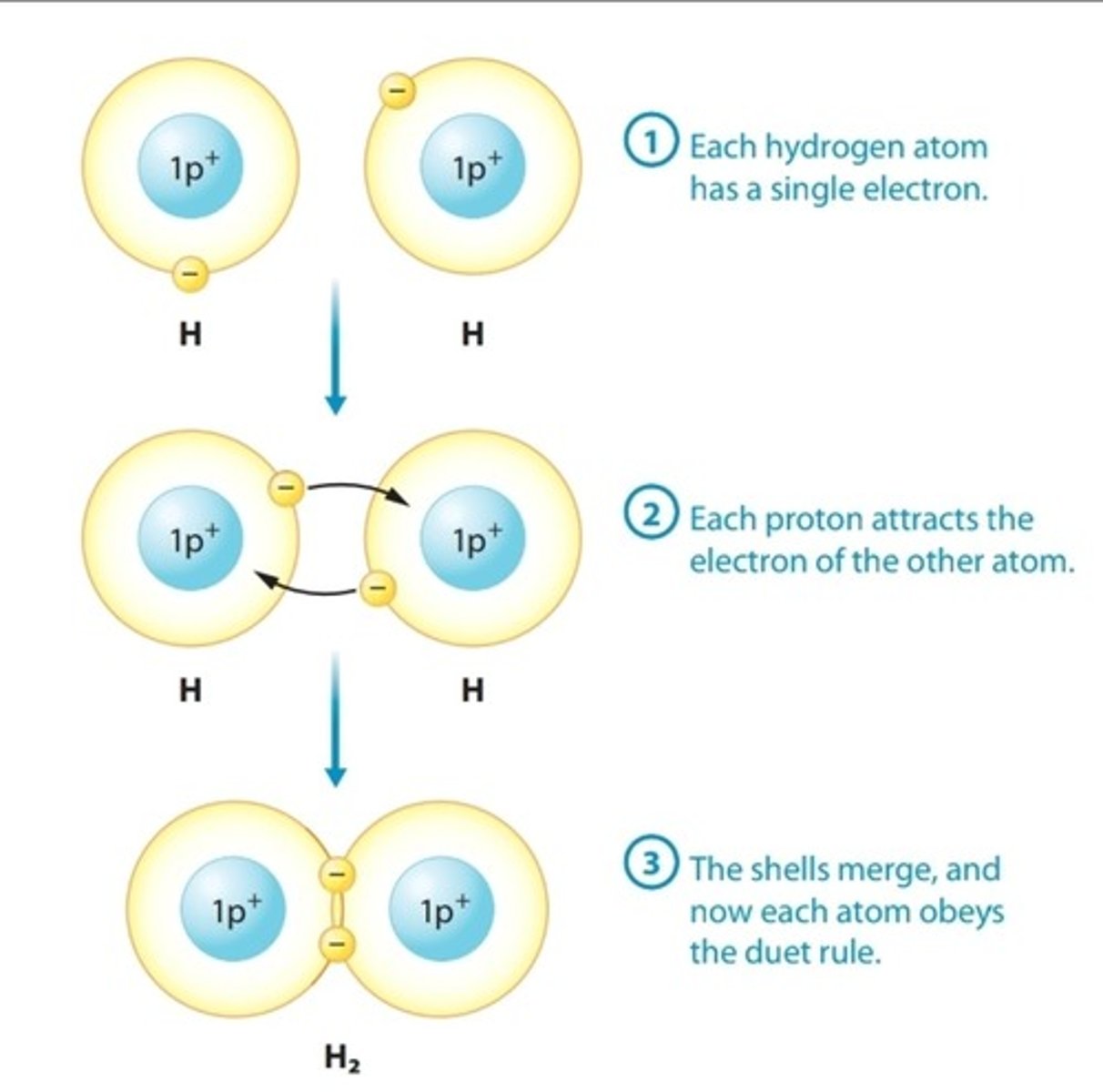
Covalent Bond
Chemical bond in which two atoms share electrons, thereby completing their valence shells
Decomposition Reaction
Type of catabolic reaction in which one or more bonds within a larger molecule are broken, resulting in the release of smaller molecules or atoms; AB—> A+B
Denaturation
Change in the structure of a molecule through physical or chemical means
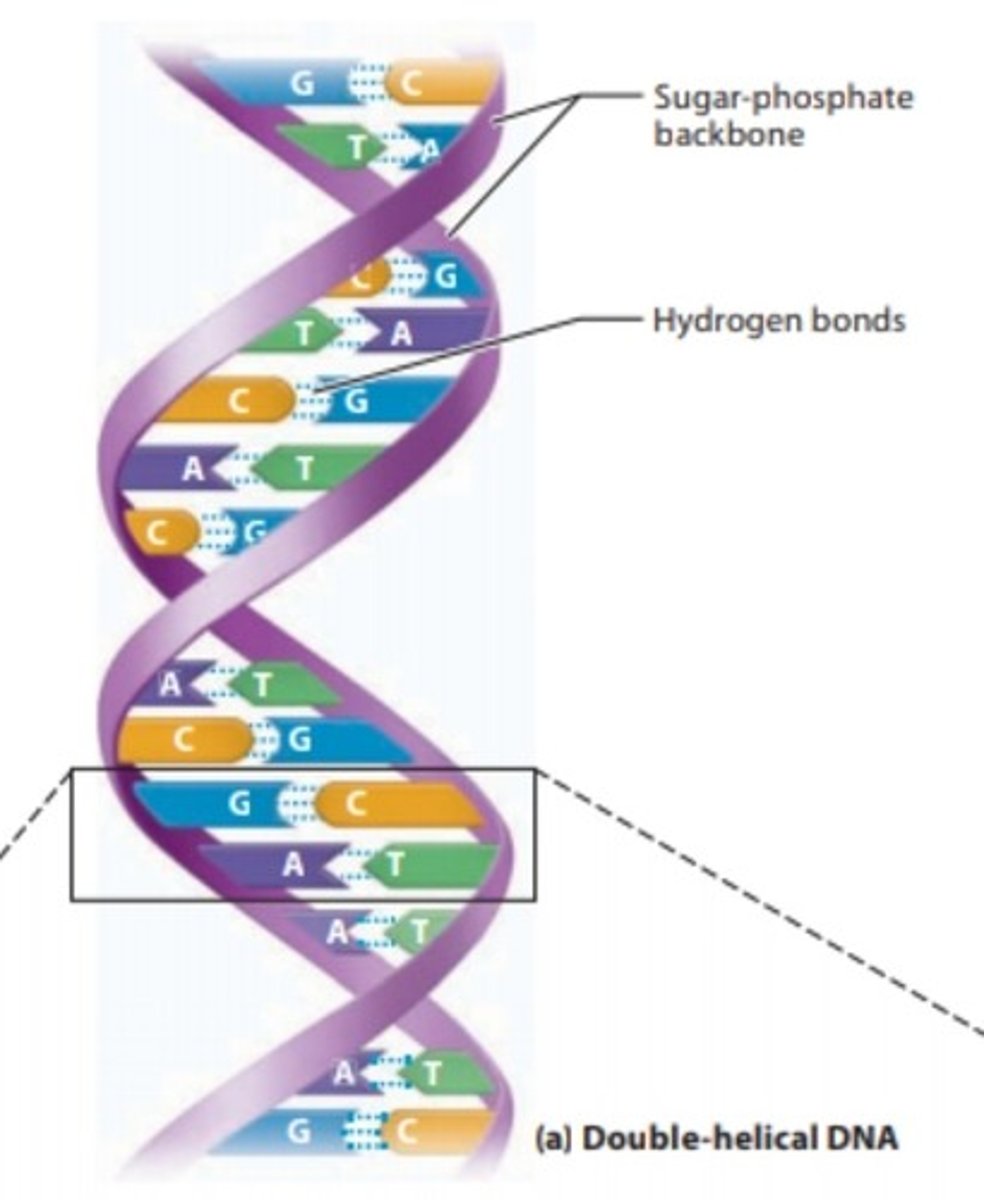
DNA
double-stranded nucleic acid that stores genetic information
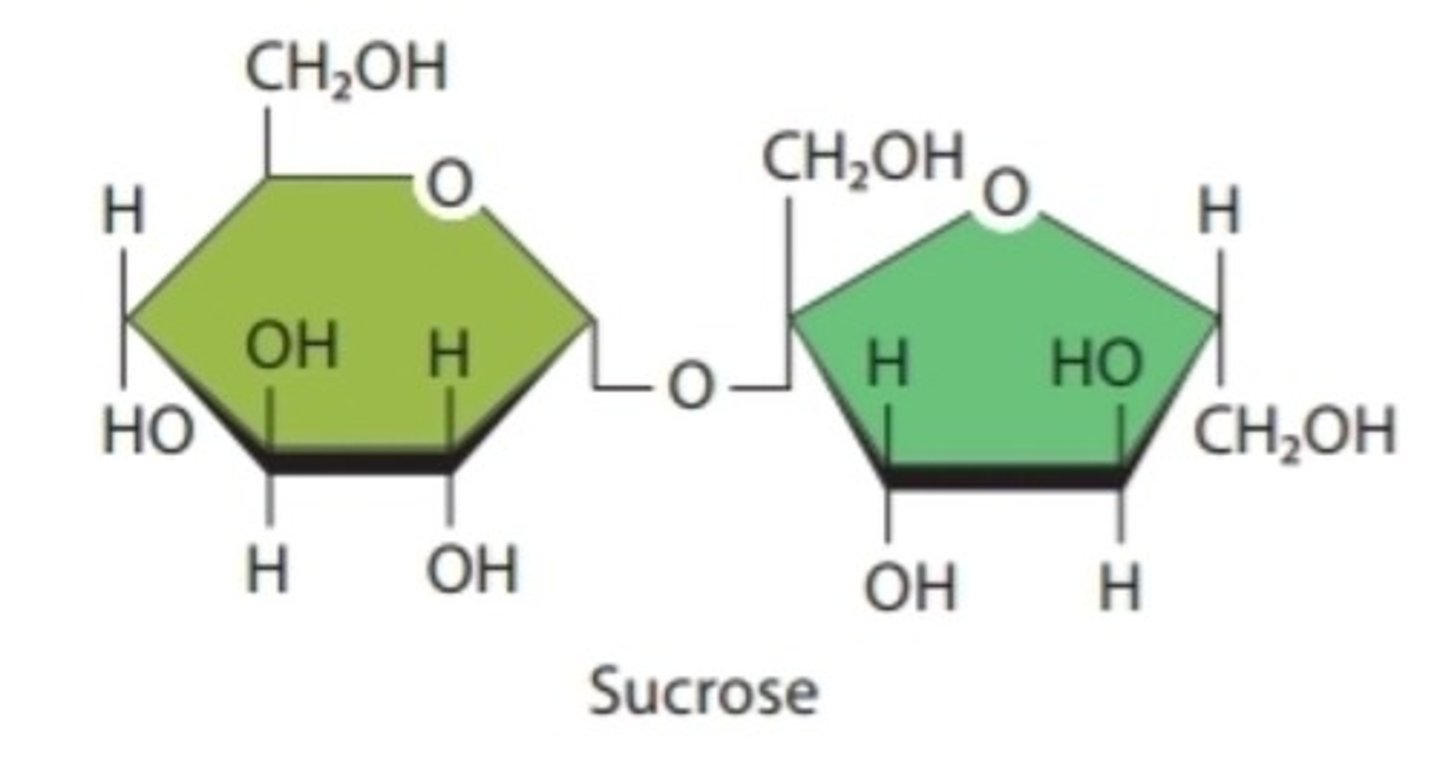
Disaccharide
Pair of carbohydrate monomers; ex: sucrose, lactose
Electron
Subatomic particle having a negative charge and nearly no mass; found orbiting the atom's nucleus
Electron Shell
Area of space a given distance from an atom's nucleus in which electrons are grouped
Element
Substance that cannot be created or broken down by ordinary chemical means
Endergonic reactions
reactions that absorb more energy than they release and require energy input to proceed (endothermic)
Enzyme
Protein or RNA that catalyzes chemical reactions
Exchange Reaction
Type of chemical reaction in which bonds are both formed and broken, resulting in the transfer of components; AB + CD —> AC + BD
Exergonic reaction
reactions that release more energy than they absorb (exothermic)
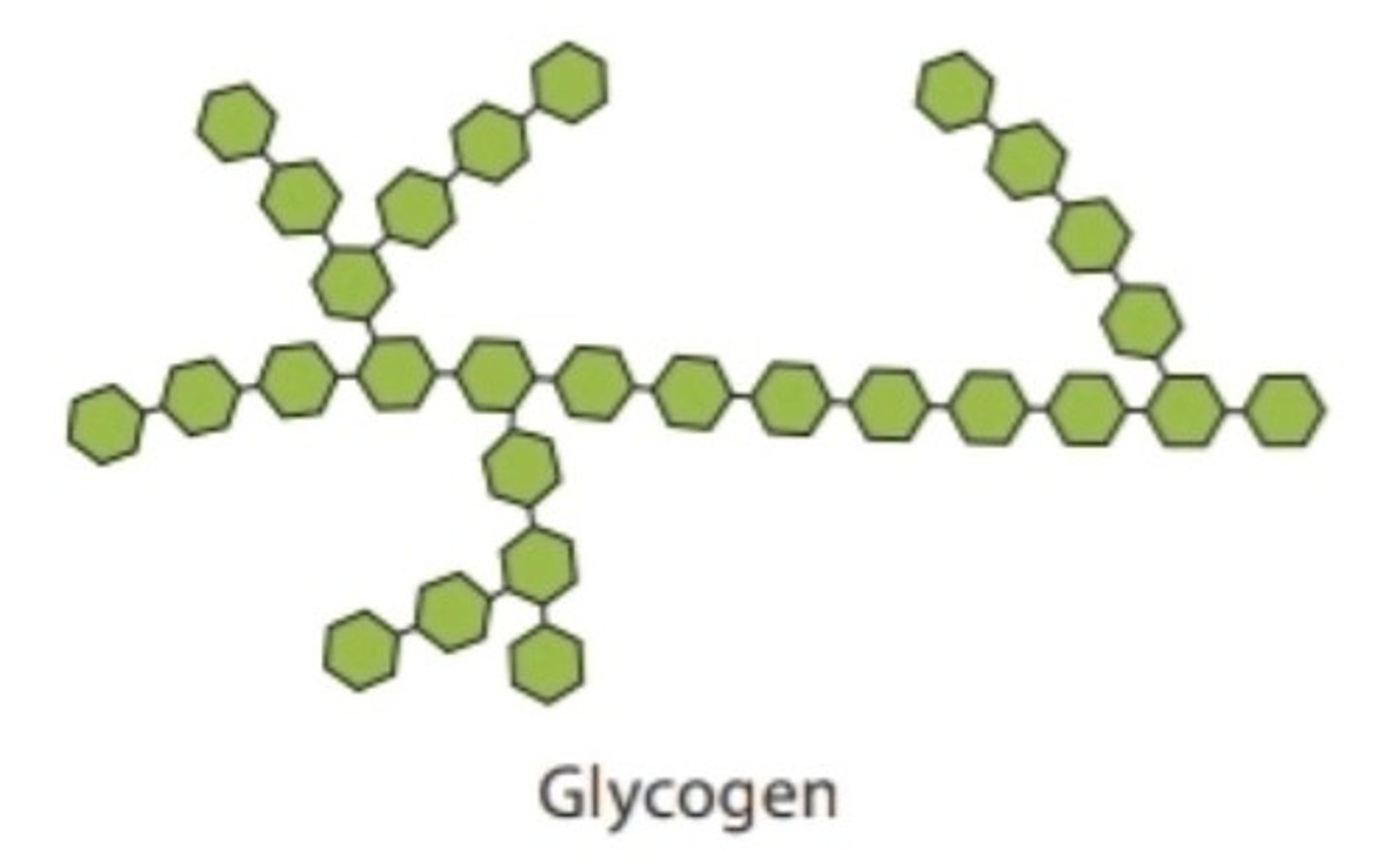
Glycogen
common carbohydrate in animals; glucose storage in the liver and skeletal muscles
Hydrophilic
Substances that are attracted to water and can dissolve in it, often polar or charged molecules
Hydrophobic
Substances that repel water and do not dissolve in it, typically nonpolar molecules
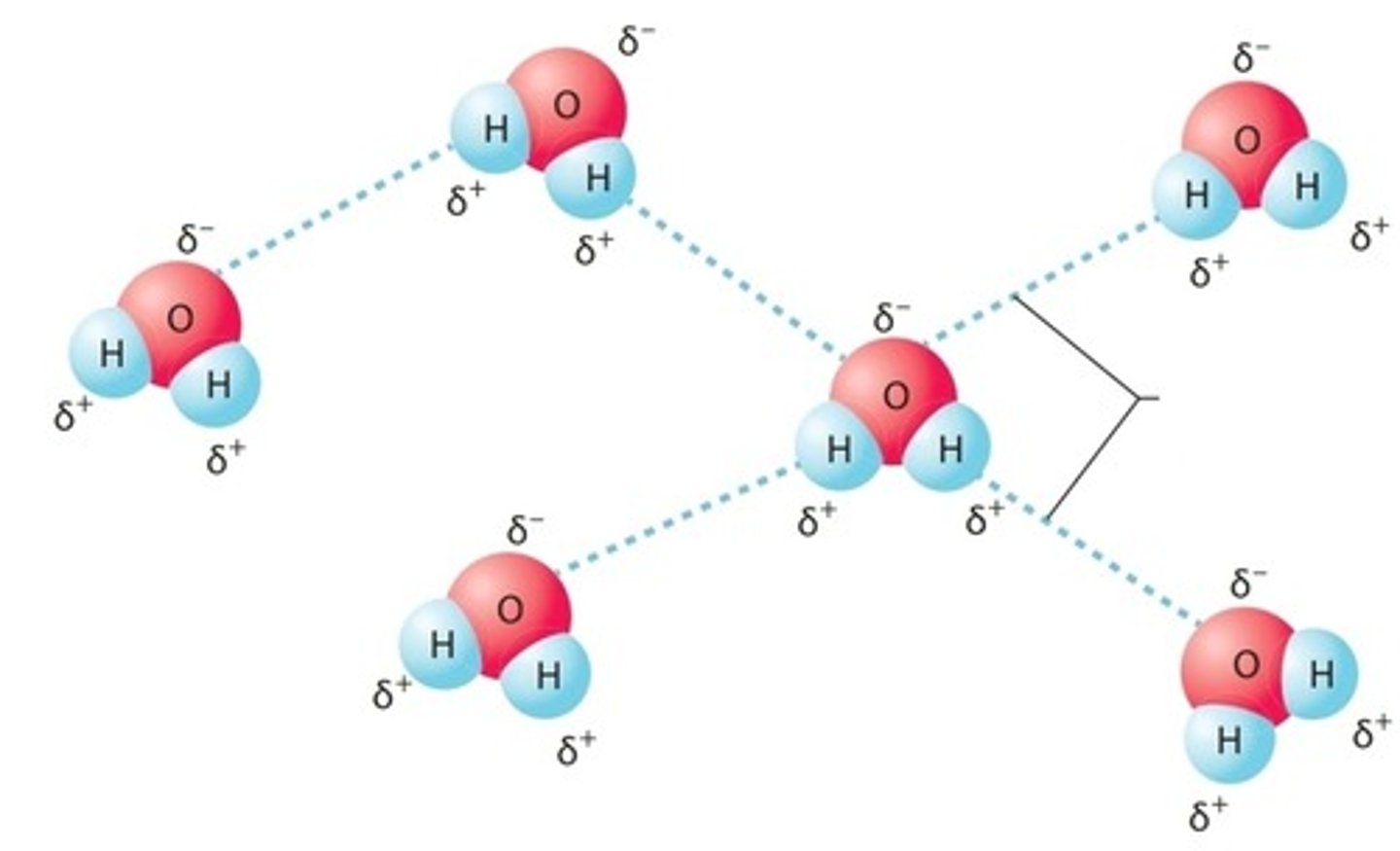
Hydrogen Bond
Type of bond in which a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom is weakly attracted to a second electronegative atom
Inorganic Compound
Substance that does not contain both carbon and hydrogen
Ion
an atom that has lost or gained one or more electrons and as a result has a non-neutral charge
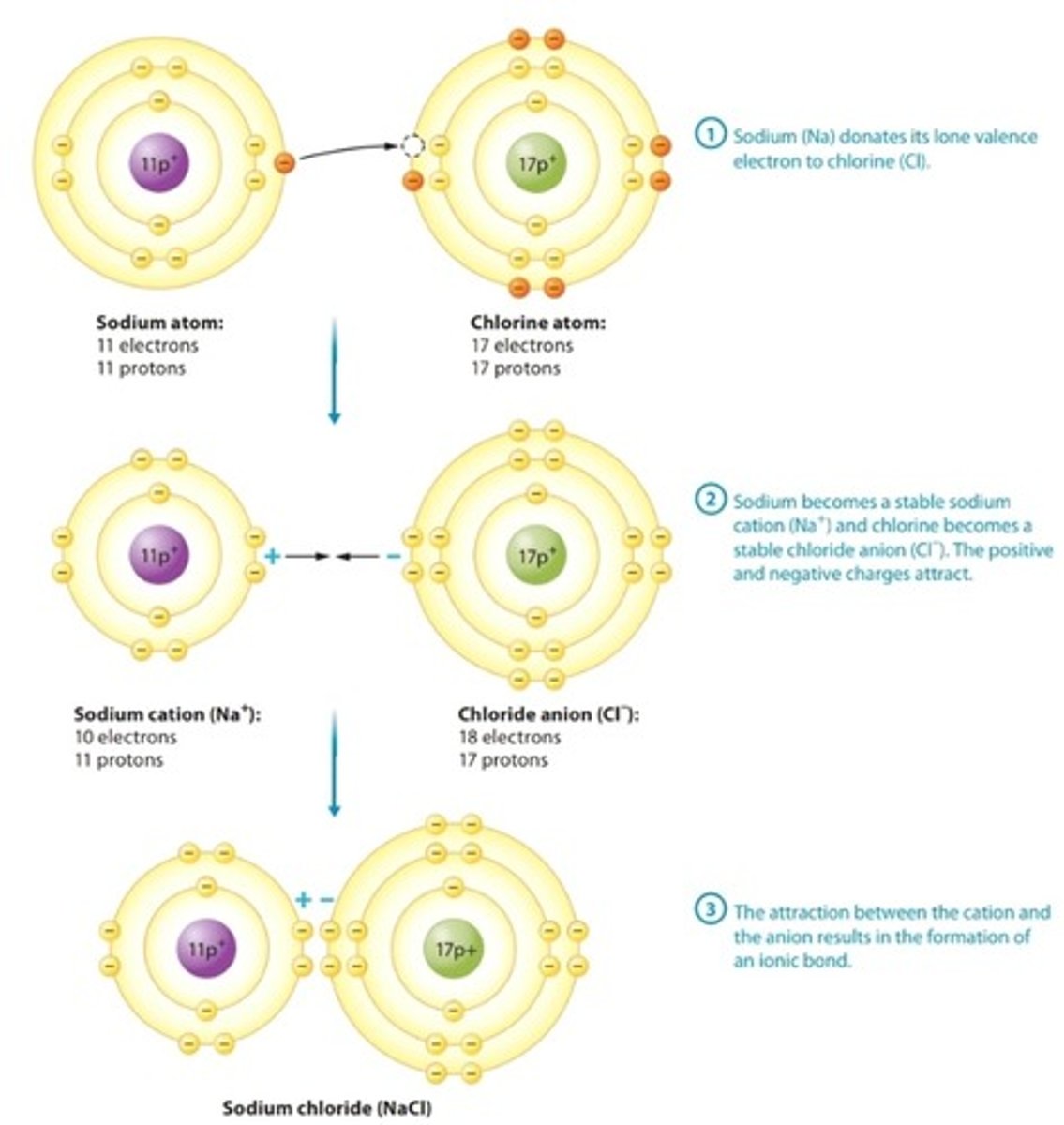
Ionic Bond
Attraction between an anion and a cation
Isotope
One of the variations of an element in which the number of neutrons differ from each other
Lipid
Class of mostly nonpolar organic compounds built from hydrocarbons and distinguished by the fact that they are not soluble in water
Macromolecule
Large molecule formed by covalent bonding
Mass Number
Sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
Matter
Physical substance; that which occupies space and has mass
Monomer
Building block of a macromolecule, capable of joining to form polymers
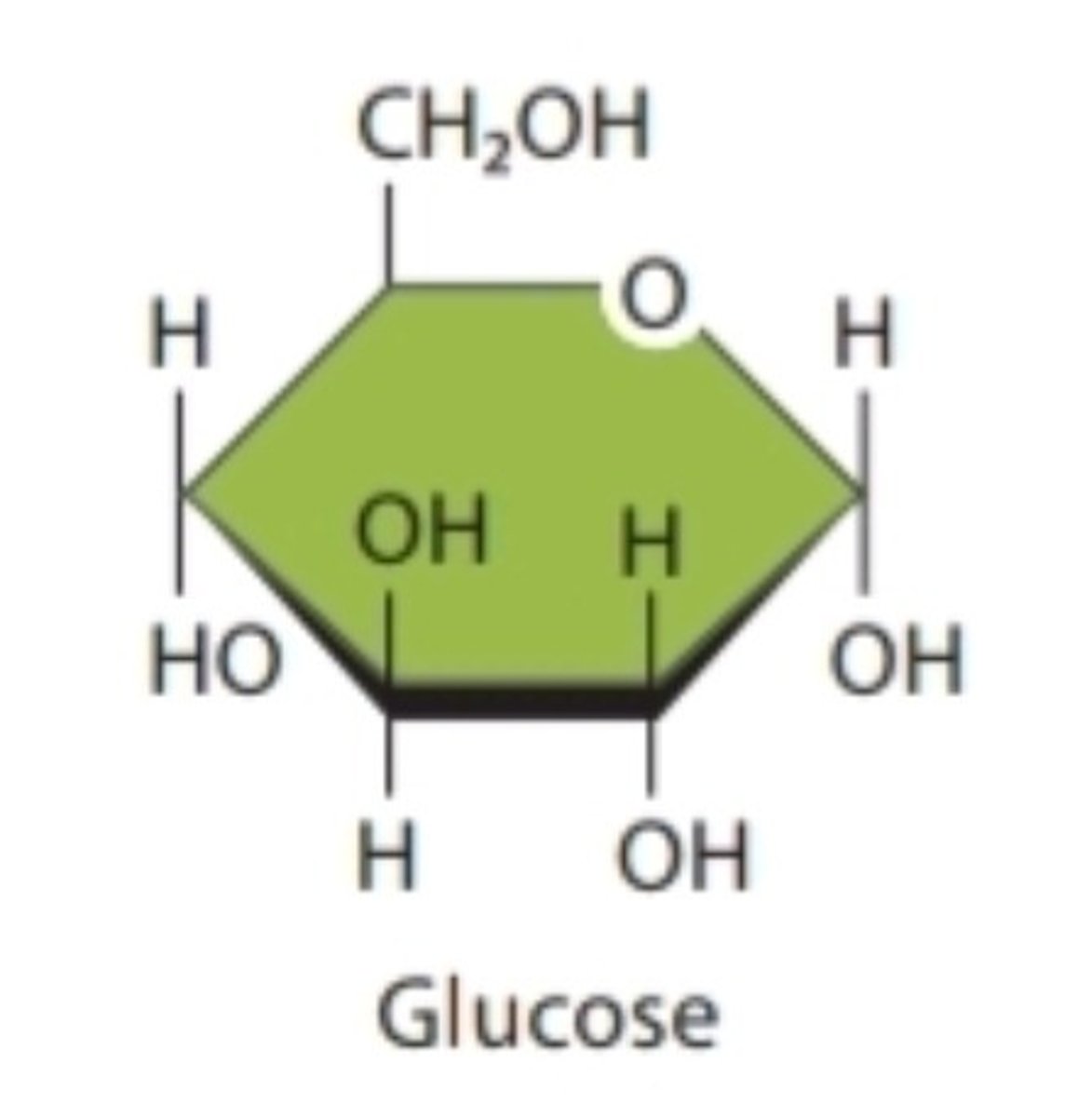
Monosaccharide
Monomer of carbohydrate; primary nutrient that provides energy to cells (glucose)
Neutron
Heavy subatomic particle having no electrical charge and found in the atom's nucleus
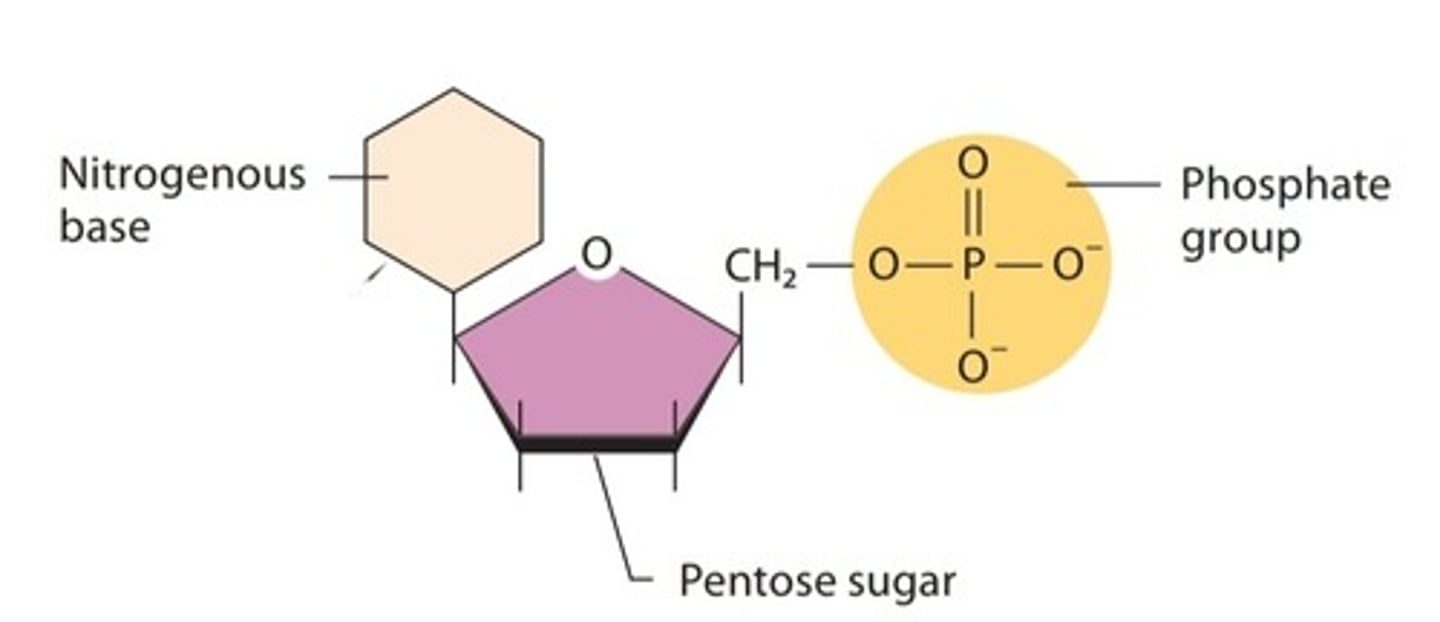
Nucleotide
monomers of nucleic acid composed of one or more phosphate groups, a pentose sugar, and a base
Organic Compound
Substance that contains both carbon and hydrogen
pH
Measurement of the hydrogen ion (H+) concentration of a solution; expressed as a number between 0-14
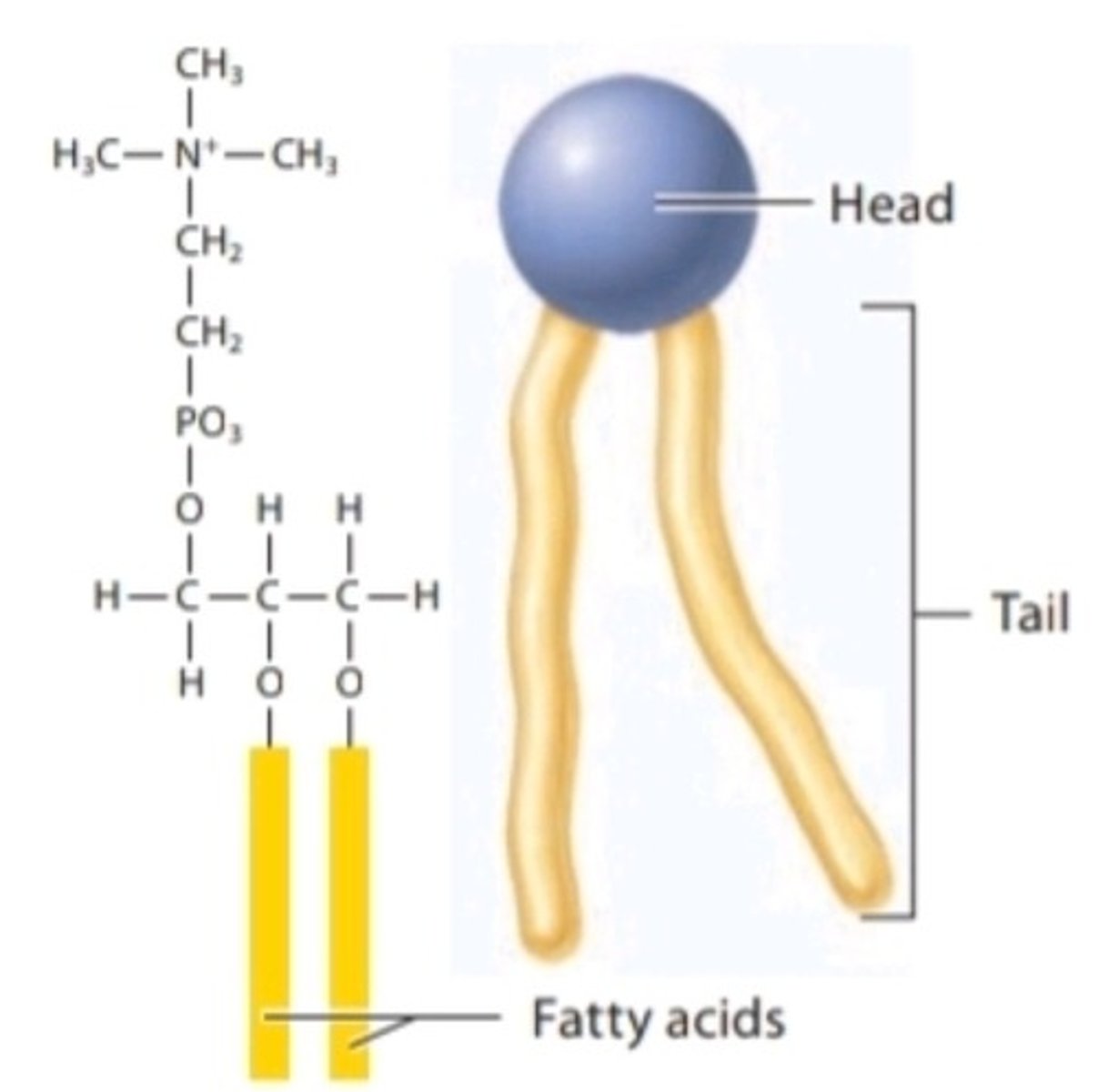
Phospholipid
The main component of a cell membrane; composed of a hydrophilic phosphate head and two fatty acid hydrophobic tails
Polymer
A large molecule composed of repeating structural units called monomers
Polysaccharide
Compound consisting of more than two carbohydrate monomers; function to store energy and provide structural support in cells
Product
One or more substances produced by a chemical reaction
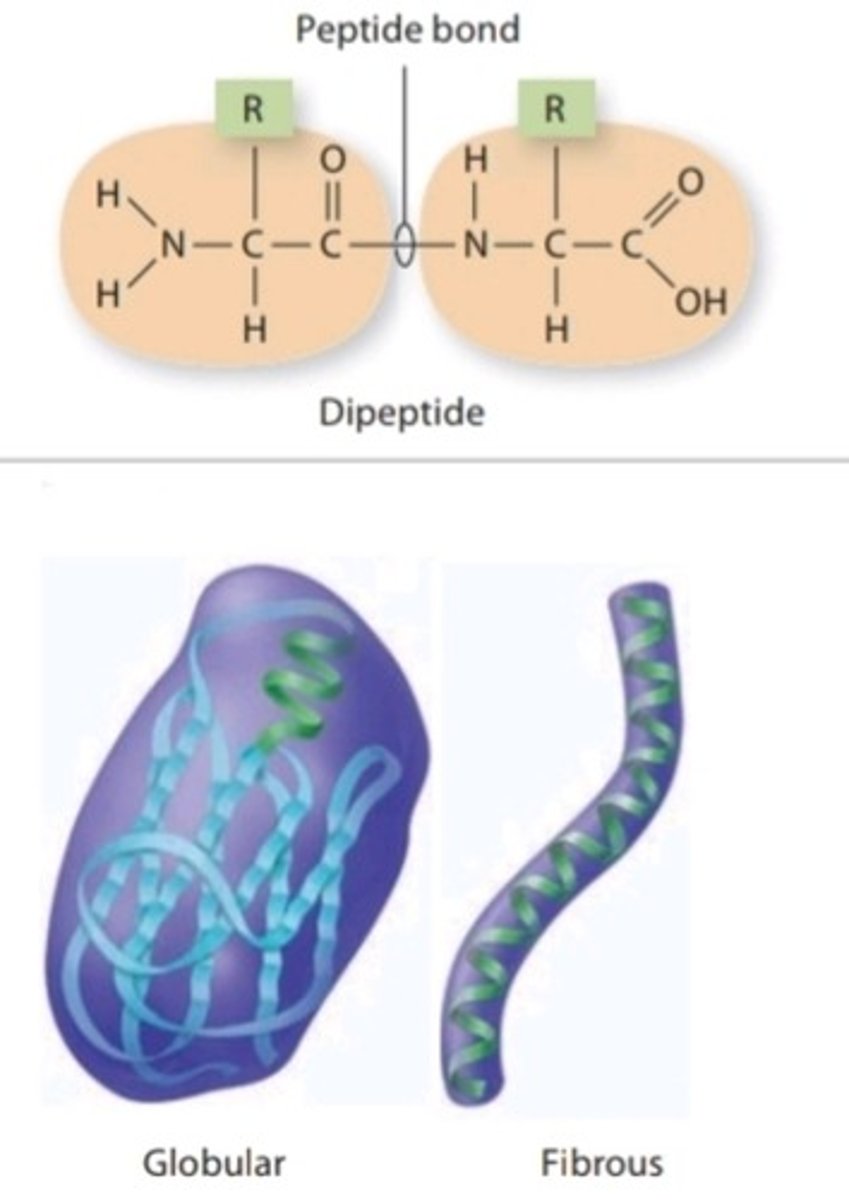
Protein
Class of organic compounds that are composed of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds
Proton
Heavy subatomic particle having a positive charge and found in the atom's nucleus
Reactant
One or more substances that enter into the reaction
RNA
Single stranded nucleic acid that functions to transmit genetic material
Solution
Homogeneous liquid mixture in which a solute is dissolved into molecules within a solvent
Starch
Complex plant carbohydrate that serves as a major source of glucose for humans
Steroid
Lipid compound composed of four hydrocarbon rings bonded to a variety of other atoms and molecules
Substrate
Reactant in an enzymatic reaction
Suspension
Liquid mixture in which particles distributed in the liquid settle out over time
Synthesis Reaction
Type of anabolic reaction in which two or more atoms or molecules bond, resulting in the formation of a larger molecule; A+B —> C
Triglyceride
lipid compound that contains three fatty acid chains; functions as a long-term energy storage molecule in the body
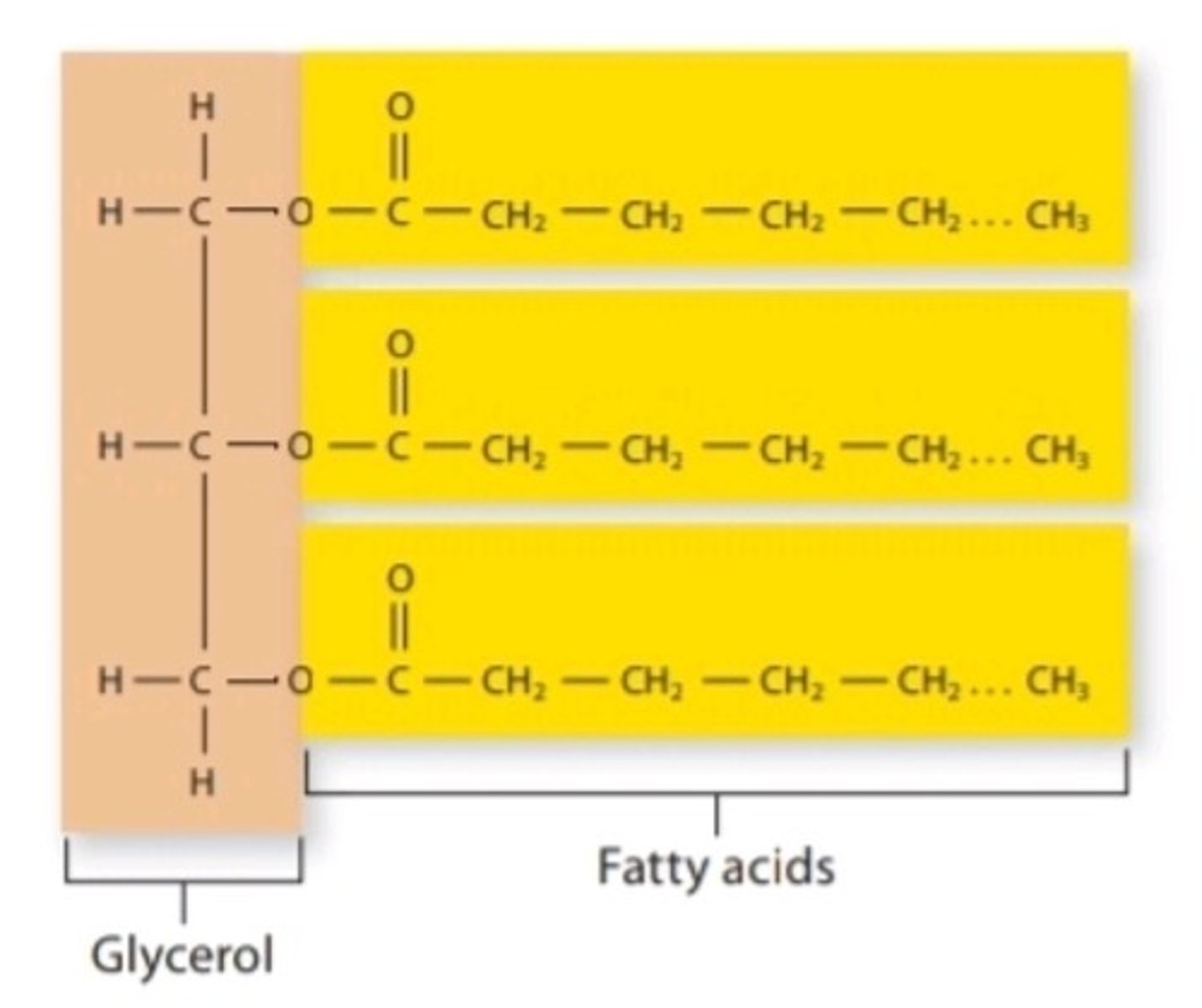
Valence Shell
Outermost electron shell of an atom
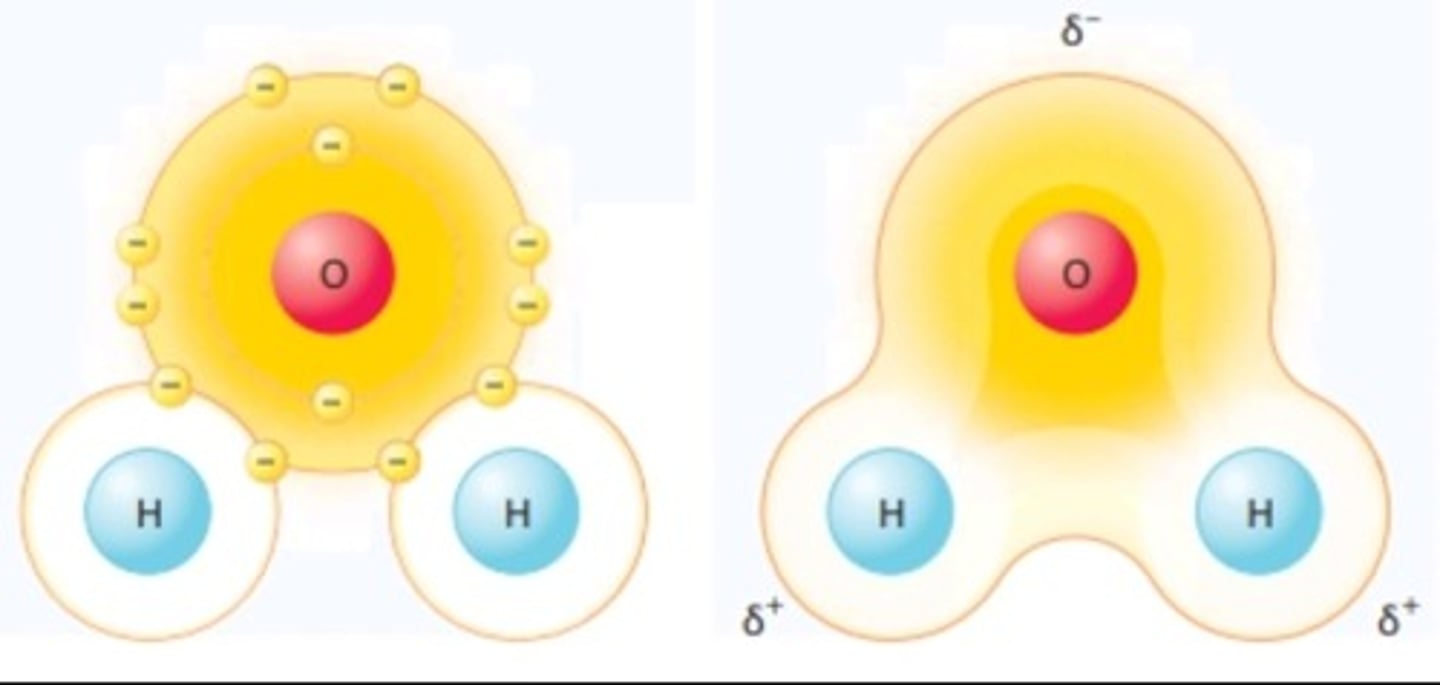
Polar covalent bond
A covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally
e.g. H2O
CHONPS
Main elements in living organisms: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur
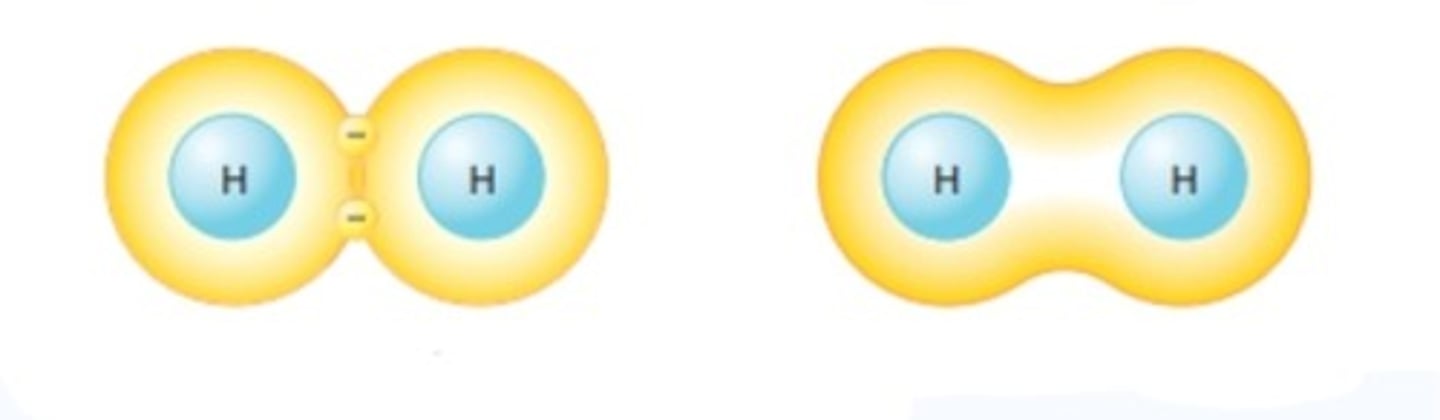
Nonpolar covalent bond
Covalently bonded molecules that are electrically balanced
e.g fats, lipids, and oils

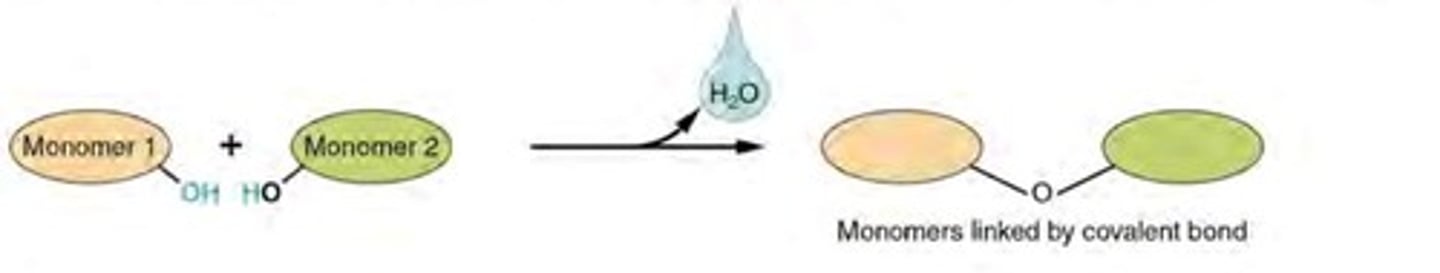
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule.
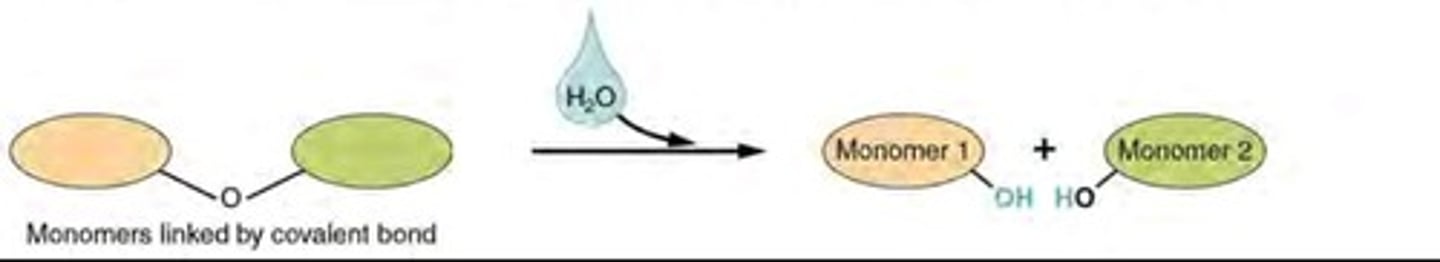
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
Factors that slow down reaction rate
More bonds
Less reactants
Decreased temperature
Decreased concentration and pressure
Factors that speed up reaction rate
Less bonds
More reactants
Increased temperature
Increased concentration and pressure