Neuro Part 3/Cases PD I
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
lethargic
drowsy but arousable
obtunded
open eyes, but slow and confused
stuporous
require painful stimuli to arouse
comatose
unarousable
cheyne-stokes
cycles of alternating deep and shallow breathing, followed by a period of no breathing
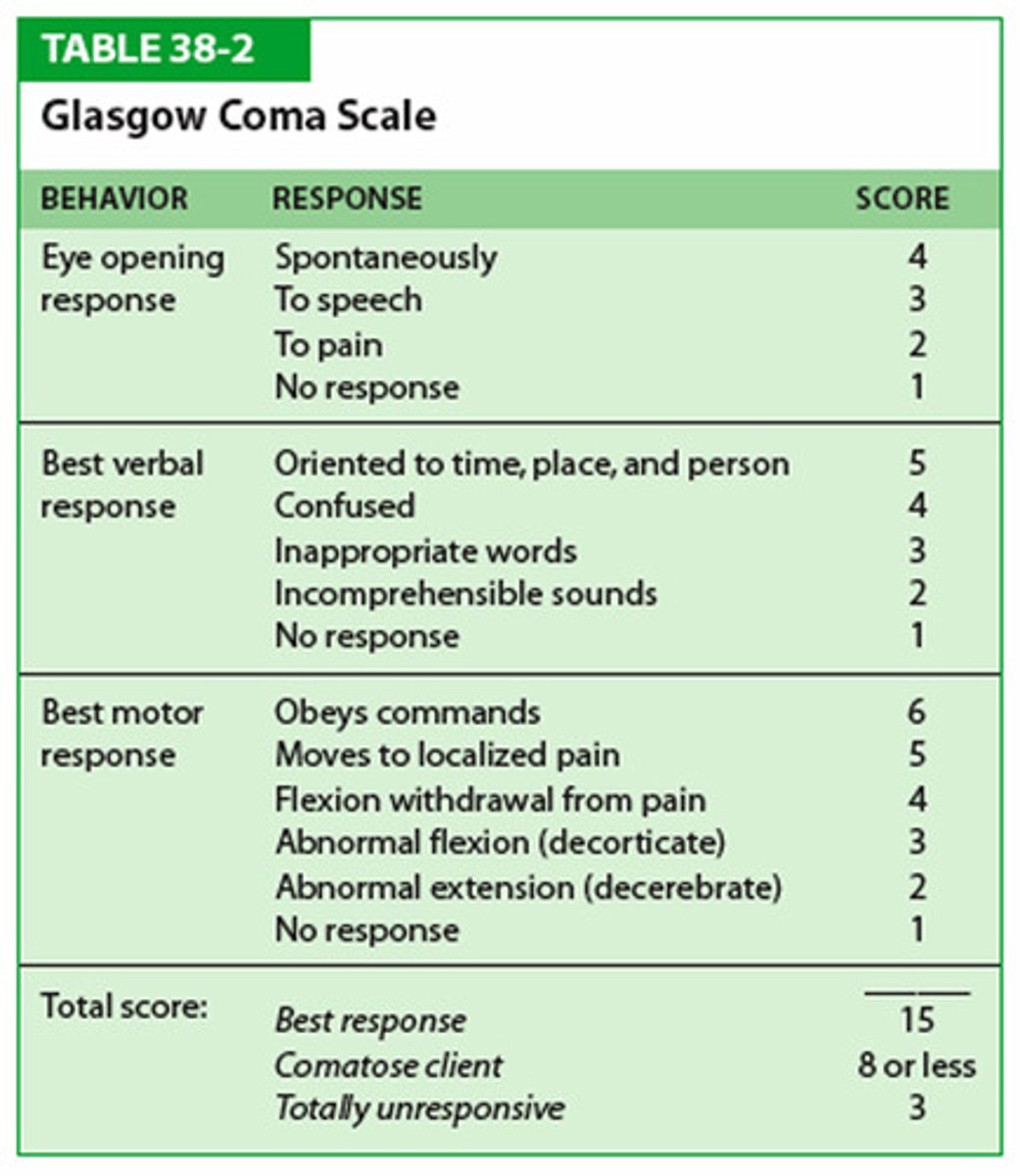
regarding the glasgow coma score, what score is considered comatose?
8 or less
Stereotypic
painful stimulus evokes a postural response
decorticate
flexor response
decerebrate
extensor response
flaccid
no response, no tone
what cranial nerves for pupillary light reflex?
CN II, III
what cranial nerves for ocular position and movement?
CN III, IV, VI
what cranial nerves for oculocephalic reflex?
CN III, VI, VIII
what cranial nerves for oculovestibular reflex with caloric stimulation?
CN III, IV, VI, VIII
what cranial nerves for corneal reflex?
CN V, VII
what cranial nerves for facial asymmetry and grimace to painful stim?
CN VII
what cranial nerves for gag reflex?
CN IX, X
you are doing a pupillary exam on a comatose patient. if their pupils are asymmetric or have no response to light what would you suspect the cause of the coma?
structural
you are doing a pupillary exam on a comatose patient. if their pupils have a positive response to light what would you suspect the cause of the coma?
metabolic
you are performing the oculocephalic reflex on your patient with suspected brainstem dysfunction. what result would you expect if the patients brainstem is intact? what about if there was a brainstem lesion?
intact – eyes turn to keep looking at the same spot
lesion – eyes move with head
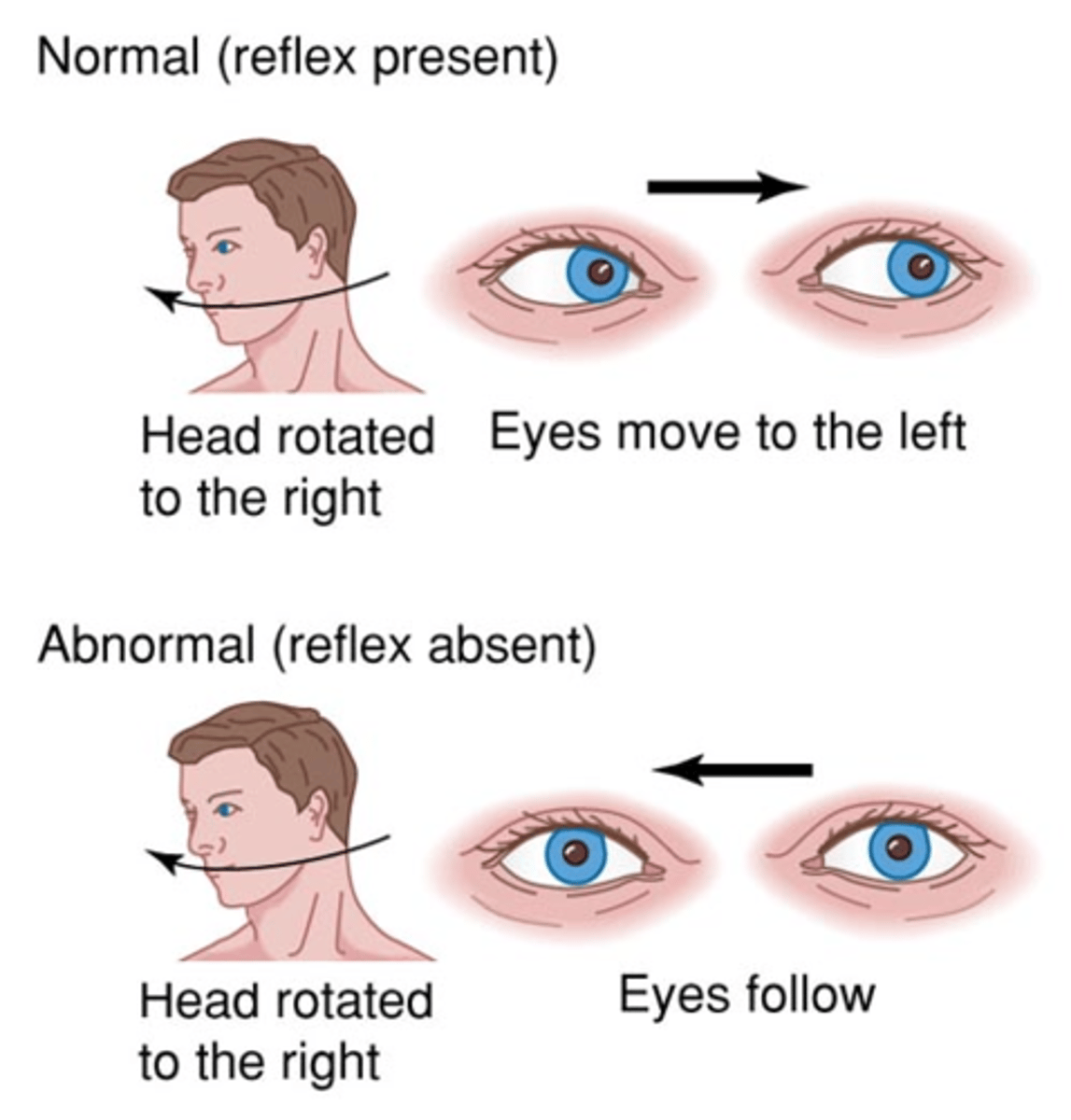
how is the oculovestibular reflex with caloric stimulation performed and what would be the result if the brainstem is intact?
Cold water into EAC; Eyes deviate toward water
cerebral lesions
contralateral body
cerebellar hemispheric lesions
ipsilateral body
brainstem lesions
4 Ds with crossed findings- Diplopia, dysarthria, dysphagia, dizziness
Patient presents with difficulty speaking. They also have mild weakness in the right arm and hand. Where do you think the lesion is?
left cerebral hemisphere
Patient presents with difficulty speaking. They also have mild weakness in the right arm and hand. What other s/s do you think the patient would also have?
May have right arm numbness, have right sided hyper-reflexia and Babinski sign; increased muscle tone (except may not in acute stage)
Patient presents with right sided weakness in the arm and leg. They also admit to diplopia and have left ptosis on exam with the left eye being laterally deviated and inferior.
Where do you think the lesion is?
Left midbrain; This is known as "weber syndrome" when it is from a stroke
Ipsilateral CN3 (oculomotor nerve) palsy and Contralateral arm and leg weakness (hemiparesis)
Patient presents with neck pain and left arm paresthesia that goes into the middle finger. They have ipsilateral absent triceps reflex. The biceps and brachioradialis reflexes are intact. Where do you think the lesion is? What other s/s may the patient have?
Neck pain and ipsilateral Shooting pain down arm, paresthesias, numbness in c7 dermatome- middle finger May have Ipsilateral weakness in c7 myotome- elbow extension (triceps) and wrist flexion
C-7 cervical radiculopathy
Patient presents with LBP and pain that radiates down the right leg. It goes from the lateral thigh, crosses at the knee to medial lower leg, to the medial foot. There is numbness and paresthesia in these areas. There is absent right patellar reflex, with an intact achilles reflex.
Where do you think the lesion is? What other s/s may the patient have?
Ipsilateral Weakness in L4 myotome- foot dorsiflexion (tibialis anterior) L 4 Lumbar radiculopathy