Web Systems FINALS (W1-W4)
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Typography
Overall design and practice of organizing text to communicate and engage with the reader.
Make written language legible, readable, visually appealing
Typeface
The design of a set of letters, numbers, and symbols that share common design features.
It encompasses the style, shape, and visual characteristics of the characters.
Font
The specific instance of a typeface.
It includes variations such as size, weight (bold, regular, light), and style (italic, oblique).
Each font within a typeface corresponds to a specific combination of these attributes.
Script Typeface
Hand-lettered look and are thought to convey an elegant feel. Often used for wedding invitations.
Cedarville Cursive
Brush Script
Lobster
Pacifico
Great Vibes
Dancing Script
Decorative Typefaces
Designed to be eye-catching and unique, often used for headlines, logos, posters, and other display purposes where you want to make a strong visual impact.
Comic Sans MS
Papyrus
Curlz MT
Chiller
Jokerman
Comic Neue
Paprika
Monoton
Fredericka the Great
Jolly Lodger
Monospace Typefaces
Each character occupies the same amount of horizontal space.
Often used for displaying codes.
Courier New
Consolas
Monaco
Lucida Console
Source Code Pro
Serif Typefaces
Often associated with a traditional or formal aesthetic.
Used for legal documents.
Times New Roman
Georgia
Garamond
Baskerville
Merriweather
Sans Serif Typefaces
Do not have decorative lines and are often thought of as a contemporary and modern.
Most recommended for web since it creates a better reading experience.
Arial
Helvetica
Verdana
Futura
Open Sans
font-family
Collection of related fonts.
Used to define the typeface of an element.
The value is declared as list of font options, arranged by priority from highest to lowest.


Generic font family
Define by the browser
Fonts will vary across devices and operating systems.

System Fonts
Can be used as a fallback or primary font option.
Used to create designs that integrate with the look and feel of the user’s operating system.
Can still include fallback fonts in the stack.

Valid Font Family Names
Names with spaces, numbers, or characters other than a hyphen should be contained in quotes.
Generic fonts must always be unquoted.


font-weight
When a weight is specified for which no font files exist., the typeface with the closest weight is used
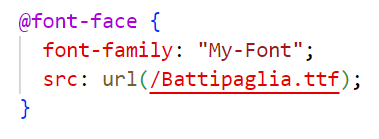
@font-face rule
allows you to specify custom fonts for your web design.
You can load fonts from either a remote server or a locally-installed font on the user’s own computer.

Media query
make it possible to selectively apply CSS based on specific conditions, such as different screen sizes of device orientation.
must start with the @media at-rule.
The media type defines the device category used to display the website.
The media features test for a specific feature of the browser or device.
media feature: width
used to test the width of the viewport.
ranges can be specified with min-width and max-width

Adding Media Query
Can be added below related CSS blocks
Can be grouped together and added to the bottom of the CSS files
Can also be written in a separate stylesheet
It must be loaded into the HTML file with
<link> and a media attribute.
JavaScript
is a programming language that plays a crucial role in web development. Together with HTML and CSS, it forms the foundation for creating interactive and dynamic web pages.
It can perform calculations, logical checking, and modify the existing CSS and HTML codes.
Focuses on the behavior of the website.
Vanilla JavaScript
also known as plain JavaScript, refers to the original, unmodified JavaScript language without any additional frameworks or libraries. It represents the pure version of JavaScript that runs directly in web browsers, relying solely on the language’s built-in methods and objects.
Arrow Functions
ES6 introduced arrow functions, which provide a concise syntax for writing function expressions.
Template Literals
allow you to embed expressions inside strings using backticks (`).
Destructuring
allows you to extract values from objects or arrays easily.
<script> tag
used to embed or reference JavaScript code within an HTML document
Usage of <script> tag
You can place the <script> tag either in the <head> section or the <body> section of your HTML document.
When placed in the <head>, the script is loaded before the page content, which ensures that it’s available for use throughout the page.
When placed in the <body>, the script is loaded after the page content, which can improve page load performance.
document.getElementById()
It is a fundamental part of the HTML Document Object Model (DOM).
Allows you to select an HTML element based on its unique ID.
It returns a reference to the element with the specified ID or null if no matching element exists.
Common scenarios include changing an element’s content, style, or behavior dynamically.
Variable
is a named container that holds a value. Variables allow you to store and manipulate data throughout your application.
You can declare a variable using the var, let, or const keywords.
Variables declared with var were commonly used in JavaScript code before 2015. However, it’s recommended to use let or const instead.
let
if you need mutable variables
is used to declare block-scoped variables
Variables declared with let are scoped to the block in which they are defined. This means they are accessible only within that block.
const
if the value should not change (especially for arrays and objects)
Also has a block scope like let
Used to declare immutable variables
Once you assign a value to a const variable, you cannot change it later.
The name “constant” can be misleading. const does not define a constant value; it defines a constant reference to a value.
You can modify properties of the object, but not reassign the entire object
var
only for older browsers that don’t support let and const.
With the introduction of let and const in ES6, it’s generally recommended to use them instead of var.
let provides block scoping and const ensures immutability for constants.
Identifier
Start with a valid character. (letter, underscore, or a dollar sign)
Avoid starting with a number
Case sensitive
Special characters are not allowed except underscore and a dollar sign.
6 Types of Operators
Arithmetic Operators
Assignment Operators
Comparison Operators
String Operators
Logical Operators
Conditional or Ternary Operator
Arithmetic Operators
These operators perform mathematical operations on numbers.
let x = 5; let y = 2; let sum = x + y; let product = x*y;
Assignment Operators
are used to assign values to variables.
Assignment (=): Assigns a value to a variable.
Addition Assignment (+=): Adds a value to a variable.
Subtraction Assignment (-=): Subtracts a value from a variable.
And more (e.g., *=, /=, %=).
Comparison Operators
These operators compare values and return a Boolean result (true or false)
String Operators
The concatenation operator (+) is used to join strings together.
Logical Operators
These operators are used for logical operations (e.g., AND, OR, NOT).


Ternary Operators
The (condition ? expr1 : expr2) allows you to write concise conditional statements.
It’s called the _____ because it takes three operands: a condition, a result for true, and a result for false.
prompt()
The ____ method shows a pop-up dialog box containing a message, an input field for the user to type their input, and two buttons: “OK” and “Cancel.”
if statement
Allows you to execute a block of code if a specified evaluates to true.
if-else statement
Allows you to execute different blocks of code based on a condition.
if-else if
When you have multiple conditions to check, you can use an if-else if chain. It allows you to test multiple conditions sequentially and execute the corresponding block of code for the first true condition.
Switch statement
provides an efficient way to handle multiple cases based on the value of an expression.
It evaluates an expression and compares it against various cases. If a match is found, the corresponding block of code is executed.
For loop
Allows you to execute a block of code repeatedly for a specified number of iterations.
While loop
Executes a block of code as long as a specified condition remains true.
do-while loop
Exit-controlled loop. It executes the code block at least once, and then continues as long as the specified condition is true.
Functions
reusable blocks of code that perform specific tasks. They help organize your code and make it more maintainable.
JavaScript functions are defined with the function keyword.
Parts of a Function
Name
unique name given by the developer
Parameters/Arguments
to pass on input values to function
Body
a block of statement(s) to be executed
Objects
a standalone entity with properties
in JavaScript it is an unordered collections of related data.
Represented by “key:value” pairs.
Are like containers that can hold multiple values at once.
These values are stored as properties of the object, each with its own key.
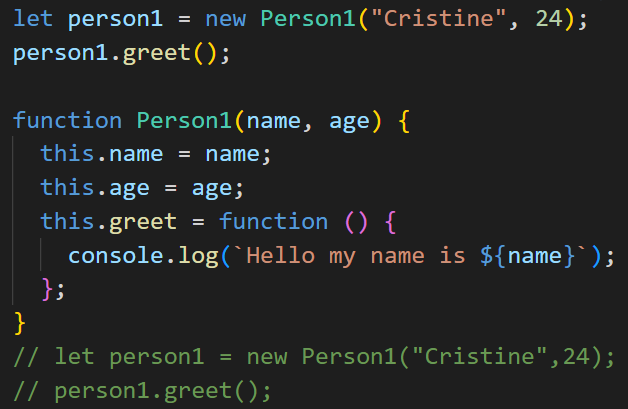
Function Declaration
Define using the ‘function’ keyword followed by the function name.
Hoisted at the top of the scope, meaning they can be called before they are defined in the code
Can be used to create objects.
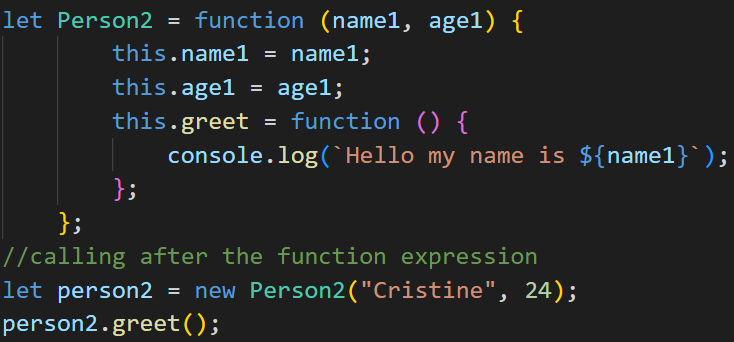
Function Expression
Created by assigning a function to a variable.
Not hoisted like function declarations, so they can only be called after they are defined.
Can be used to create objects but must be defined before they are used.
Document Object Model (DOM)
represents a web page as a tree structure, where each node corresponds to an object representing a part of the document.
allows programs to interact with and manipulate the document’s structure, style, and content.
Usage of DOM
Updating Content
Manipulating Styles
Handling Events
Events
are actions or occurrences that happen in the browser.
They can be triggered by various user interactions or by the browser itself.
Event Handler
Allow you to respond to specific events that occur in the browser.
These handlers can be attached to HTML elements using event attributes or added dynamically using the addEventListener() method.
addEventListener
method in JavaScript allows you to attach event handlers to HTML elements.
document.addEventListener(event,function);event
(without the “on” prefix). For example, use "click" instead of "onclick".
function
to run when the event occurs. An event object is passed to this function as the first parameter.
onchange
Fired when an HTML element (such as an input field) has been changed.
Useful for handling user input changes.
onclick
Triggered when the user clicks an HTML element (e.g., a button, link, or image).
Commonly used for button clicks and other interactive elements.
onmouseover
Fired when the user moves the mouse pointer over an HTML element.
Useful for creating hover effects.
onmouseout
Triggered when the user moves the mouse away from an HTML element.
Often used to revert styles after a hover effect.
onkeydown
Occurs when the user pushes a keyboard key.
Useful for capturing keyboard input.
onload
Fired when the browser has finished loading the page.
Useful for initializing scripts or fetching data.
onsubmit
Triggered when a form is submitted (e.g., by clicking a submit button).
Allows validation and form handling.
onfocus
Occurs when an element receives focus (e.g., when the user clicks inside an input field).
Useful for enhancing accessibility.
onblur
Fired when an element loses focus (e.g., when the user clicks outside an input field).
Often used for form validation.
onresize
Triggered when the browser window is resized.
Useful for responsive design adjustments.
String Manipulation
String Concatenations
Changing the given string’s case
Substring inside a String
String Concatenations
Suppose we have two strings in separate. We want these two strings to be concatenated in one. For this, we can simply use the traditional one (the + operator).
const greeting = "Hello"; const name = "Alice"; const message = greeting + "," name; //Hello, Alice
Template Literals (ES6)
Also known as template strings, use backticks ( ` ) instead of single or double quotes.
They allow you to embed expressions directly within the string using ${} placeholders.
let person = {name:"John Smith"}; let tpl = `My name is ${person.name}.`; //My naame is John Smith.
Changing the given string’s case
We can change the case of the string whenever required by using toLowerCase() and the toUpperCase() JavaScript built-in functions.
const originalString = "Hello, World!"; const lowercaseString = originalString.toLowerCase(); const uppercaseString = originalString.toUpperCase(); console.log(lowercaseString); // hello, world! console.log(uppercaseString); // HELLO, WORLD!
indexOf(substring,startIndex)
Finds the index of the first occurrence of a substring within a string.
const sentence = "JavaScript is fun"; const index = sentence.indexOf("fun"); console.log(index); //14
lastIndexOf(substring,lastIndex)
Finds the index of the last occurrence of a substring within a string.
const sentence2 = "JavaScript is fun, fun, fun!";
const lastIndex = sentence2.lastIndexOf("fun");
console.log(lastIndex); //24includes()
Checks if a string contains a specified substring.
Returns true or false
const text = "This is a test string."; const containsTest = text.includes("test"); // Returns true console.log(containsTest);
String reverse
is again the part of string manipulation. This is all about getting the string from the last index to the first index.
function reverseString(str) { let newString = ''; for (let i = str.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { newString += str[i]; } return newString; } const originalString = 'hello'; const reversedString = reverseString(originalString); console.log(`Original string: ${originalString}`); console.log(`Reversed string: ${reversedString}`);
charAt(index)
You can return the character at the specified index in a string using
const str = "Hello, world!"; const charAtIndex = str.charAt(7); // Returns "w"
trim()
Cleaning the string with the unwanted character.
For this, we can use the JavaScript trim() function. This function can be used to remove the space from the beginning and the end of the given string.
const text = " Hello World! ";
const trimmedText = text.trim();
console.log(`Original text: "${text}"`);
console.log(`Trimmed text: "${trimmedText}"`);
Original text: " Hello World! "
Trimmed text: "Hello World!"