Study Guide Ch 11,16,37,45 Fill out and maintain accurate and thorough patient records is the most ____for a Medical Assistant important duty Pt medical history and present condition is found where? Medical record also known as charts Patient care management, patient records are used for ? Continuity/Quality of care, communication tool, research, and legal documentation The medical assistant may help _________ about his condition or its management, as requested by ___________. Educate the patient, the physician Pt illness and reason for visit is found in the ___________. History of Present Illness (HPI) Hospital Discharge Summary generally includes? Admission/Discharge dates, HPI, diagnosis, treatment, follow-up care instructions, physician’s signature, complications (if any) The first document found in a pt’s financial record is? Patient Registration Form Initialing imaging reports helps ? To show who is responsible for the entry also to see if practitioner has reviewed them Where should you interview a patient? Private area to have confidentiality You need to distinguish between signs and symptoms. An example of a sign is ________ A fever, rash, or swelling (what other people can tell) You need to distinguish between signs and symptoms. An example of a symptoms is ________ Headache or Nausea (how you feel inside) Signs are External factors that are seen or measured by others Symptoms are Internal factors that are stated by the patient What does each letter of SOAP stands for Subjective, Objective, Assessment, Plan Blue ink is recommended to ensure what? Originality, readability, and fraud prevention Test results should be record ____________ Immediately and accurately Typical time for an CPE is? 30-60 minutes Typical time for f/u appt is? 5-15 minutes The disadvantage of an open-hours scheduling system is? Uneven patient flow (inefficient downtime for office staff) & long wait times What is time-specified scheduling? Where patients arrive at regular, specified intervals, ensuring the practice of a steady stream of patients Wave scheduling is? Several patients seen in the same hour, seen in order they arrived; determined by dividing the hour by the length of the average visit and then giving that number of patients appointments with the doctor at the beginning of each hour Double-booking? 2 or more patients are scheduled at same time slot, assuming both will be seen within the period Advance scheduling is useful in __________ or __________in which a pts are generally booked wks or months in advance. Annual checkups or consultations Advantages of computerized scheduling? Blocks time for emergency or last-minute visits. Lets staff see the schedule from anywhere in the office. Shows which patients cancel or don’t show up often. Helps find and schedule follow-up appointments easily. Makes reports to track how scheduling is going. Uses colors to organize different types of appointments. Lets you search for open days or times quickly
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Fill out and maintain accurate and thorough patient records is the most __ for a Medical Assistant
important duty
Patient medical history and present condition is found where?
Medical record also known as charts
Patient care management, patient records are used for?
Continuity/Quality of care, communication tool, research, and legal documentation
The medical assistant may help _________ about his condition or its management, as requested by ___________.
Educate the patient, the physician
Patient illness and reason for visit is found in the __.
History of Present Illness (HPI)
Hospital Discharge Summary generally includes?
Admission/Discharge dates, HPI, diagnosis, treatment, follow-up care instructions, physician’s signature, complications (if any)
The first document found in a pt’s financial record is?
Patient Registration Form
Initialing imaging reports helps?
To show who is responsible for the entry also to see if practitioner has reviewed them
Where should you interview a patient?
Private area to have confidentiality
You need to distinguish between signs and symptoms. An example of a sign is __.
A fever, rash, or swelling (what other people can tell)
You need to distinguish between signs and symptoms. An example of a symptom is __.
Headache or Nausea (how you feel inside)
Signs are
External factors that are seen or measured by others
Symptoms are
Internal factors that are stated by the patient
What does each letter of SOAP stands for?
Subjective, Objective, Assessment, Plan
Blue ink is recommended to ensure what?
Originality, readability, and fraud prevention
Test results should be recorded .
Immediately and accurately
Typical time for a CPE is?
30-60 minutes
Typical time for follow-up appointment is?
5-15 minutes
The disadvantage of an open-hours scheduling system is?
Uneven patient flow (inefficient downtime for office staff) & long wait times
What is time-specified scheduling?
Where patients arrive at regular, specified intervals, ensuring the practice of a steady stream of patients
Wave scheduling is?
Several patients seen in the same hour, seen in order they arrived; determined by dividing the hour by the length of the average visit and then giving that number of patients appointments with the doctor at the beginning of each hour
Double-booking is?
2 or more patients are scheduled at the same time slot, assuming both will be seen within the period
Advance scheduling is useful in or _ in which patients are generally booked weeks or months in advance.
Annual checkups or consultations
Advantages of computerized scheduling?
Blocks time for emergency or last-minute visits; Staff can see the schedule from anywhere in the office; Shows which patients cancel or don’t show up often; Helps find and schedule follow-up appointments easily; Makes reports to track how scheduling is going; Uses colors to organize different types of appointments; Lets you search for open days or times quickly.
Appointment reminders include?
Cards, Reminder mailing, Confirmation calls, Recall Notices, and E-mail
When scheduling a patient who is fasting for a procedure, what are some things to consider?
Early morning and confirm fasting instructions such as the need to fast and when fasting should begin since the test might not be accurate
What does fasting mean?
No food or drinks
What patient requires extra consideration when scheduling and should not be scheduled for late morning?
Diabetic and fasting patients
Why would a diabetic patient who takes insulin eat meals or snacks at regular times?
To prevent low blood sugar/from blood sugar dropping low
Best way to handle routinely late patients?
Schedule them later in the day/end of the day
Define No-Show? Why is documenting no-shows important especially when in the office or phone calls?
No-shows are patients who miss appointments without notice; documentation protects the office legally and tracks liability
Why are some reasons you may change the route of temperature?
Age of patient, Patient condition, Safety/infection risk, Accuracy needed, Patient comfort or cooperation
Why would it benefit the office to have a POL?
Faster results, better care, and convenient for office staff
Procedure for weighing a toddler?
Weigh parent + child, then subtract parent’s weight
What is Microbiologic Testing?
Identifies microorganisms that are present
Hematologic testing?
Testing of blood to identify problems with count, size, or number of blood cells
Toxicologic test?
Testing to identify poisons or other chemicals in the body
Cytology Test?
Microscopic examination of cells to diagnose
Immunology Test?
Testing to identify disorders and disease of the immune system
Blood Banking?
Lab department responsible for processing and storing blood and blood products for transfusion and blood disorder treatments
Urinalysis Test?
Testing urine for kidney disease and other disorders and certain metabolic disorders
Histology Test?
Microscopic evaluation of tissues to make a diagnosis
Serology Test?
Testing the liquid part of the blood for antibodies against specific microorganisms
Chemistry Test?
Testing for certain substances in the blood, urine or other body fluids
What is the purpose of using an autoclave?
To sterilize instruments with pressurized steam to clean instruments
A centrifuge is?
Spins samples to separate components
Optical Microscope uses
Light that is concentrated through a condenser and then focused through the object being examined
Ocular is?
The eyepiece you use to view an image and also contains a magnifying lens called a 10x lens
Glucometer is used for?
To check blood glucose levels
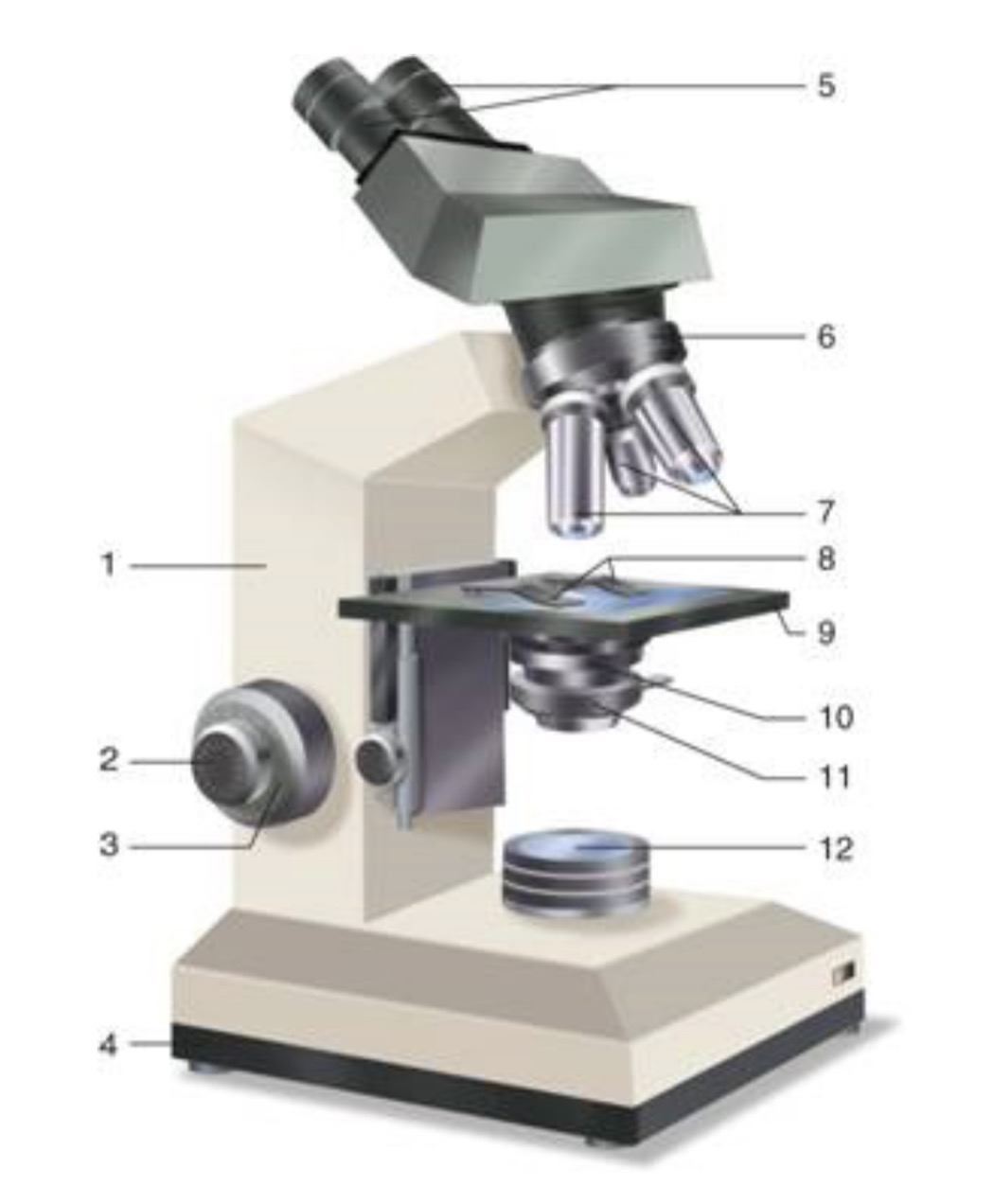
What is #1?
Arm
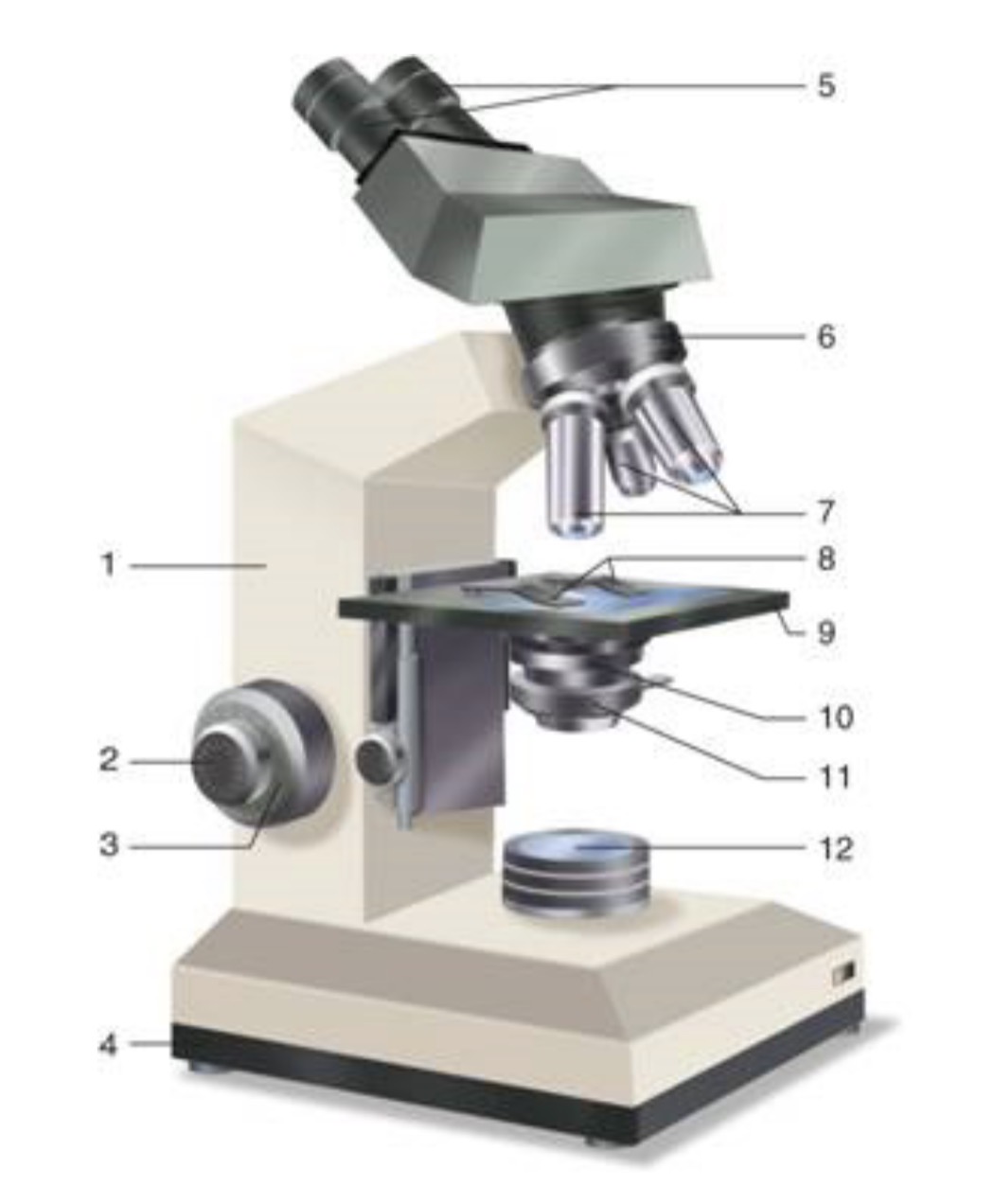
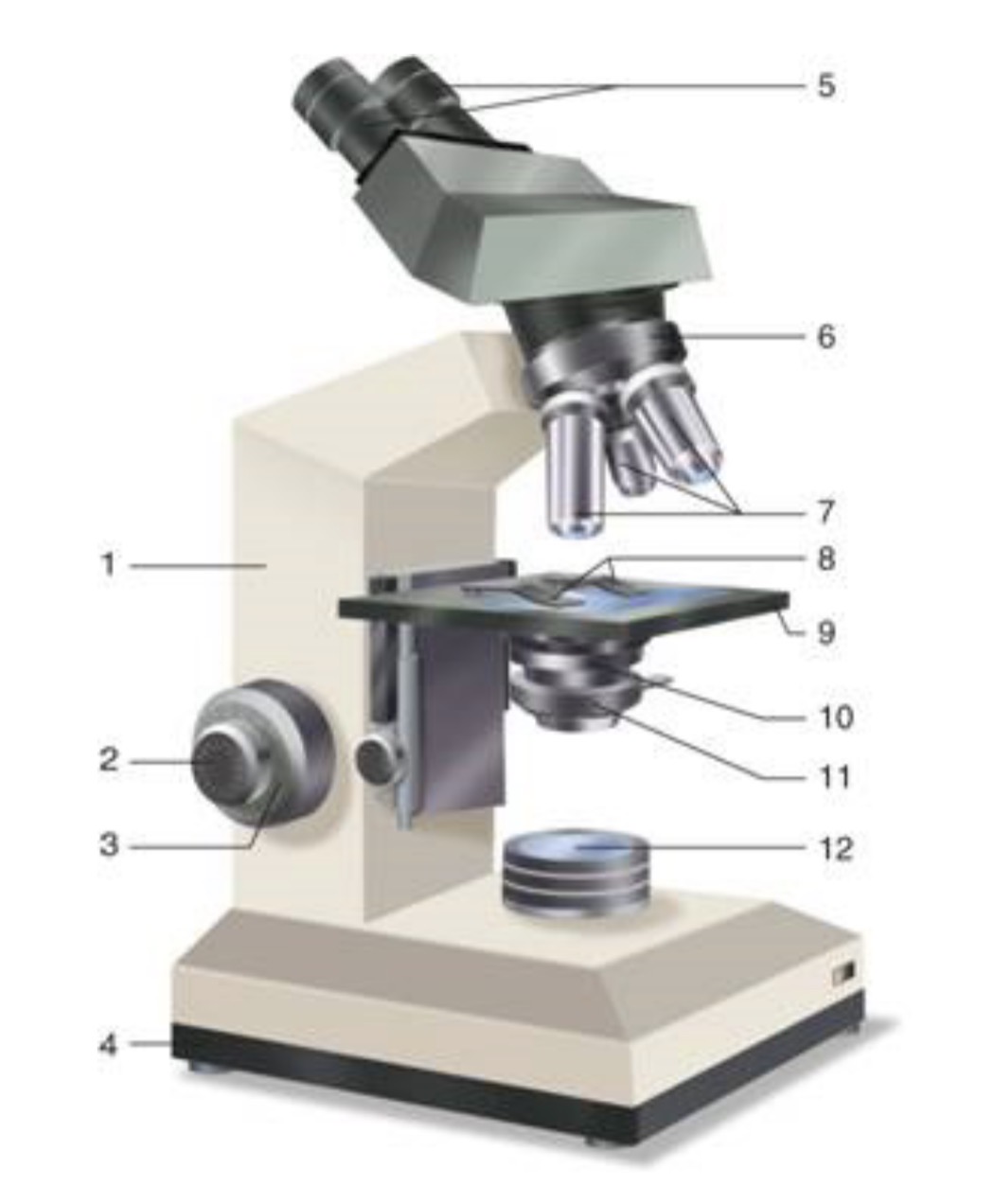
What is #2?
Fine Adjustment Knon
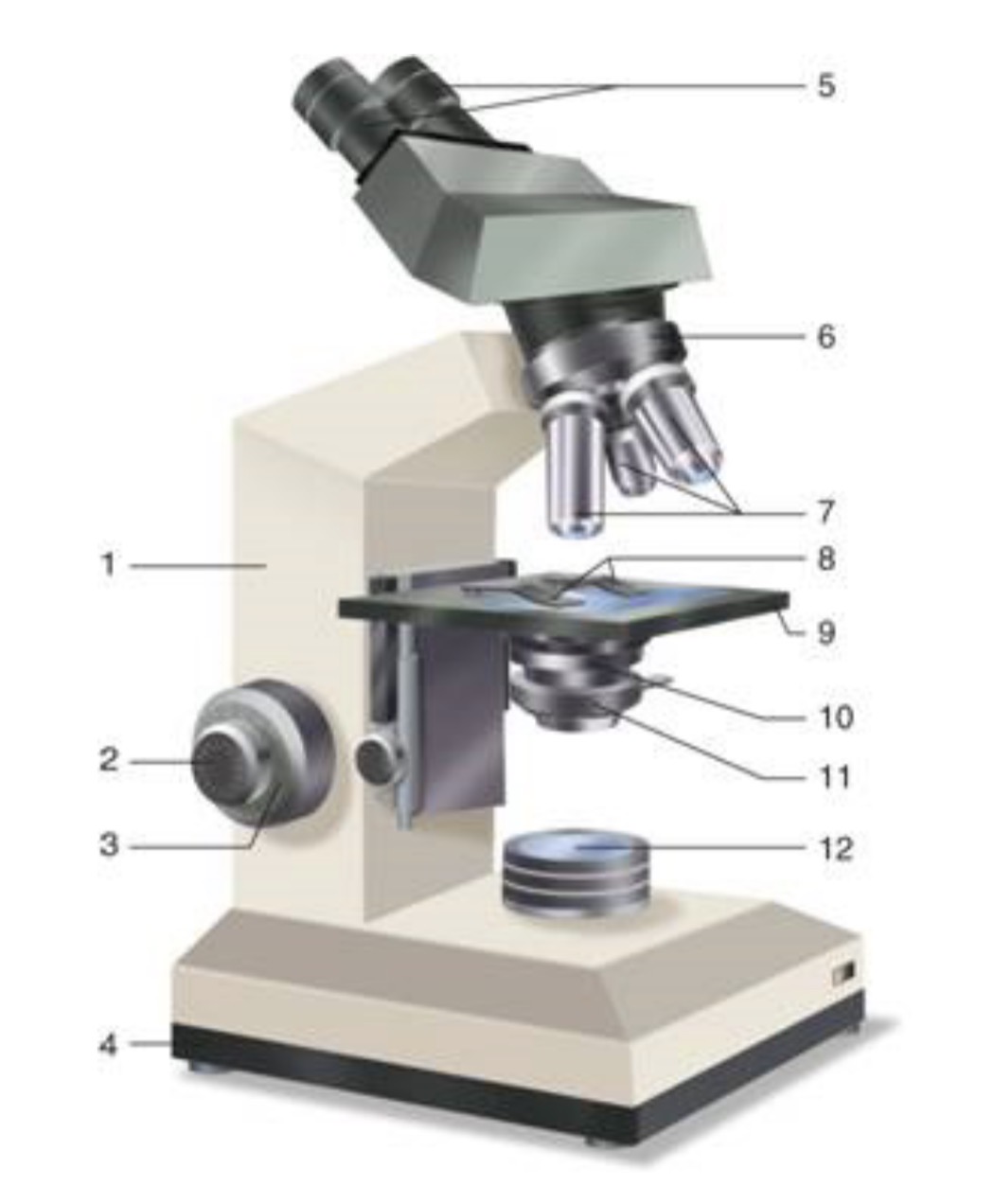
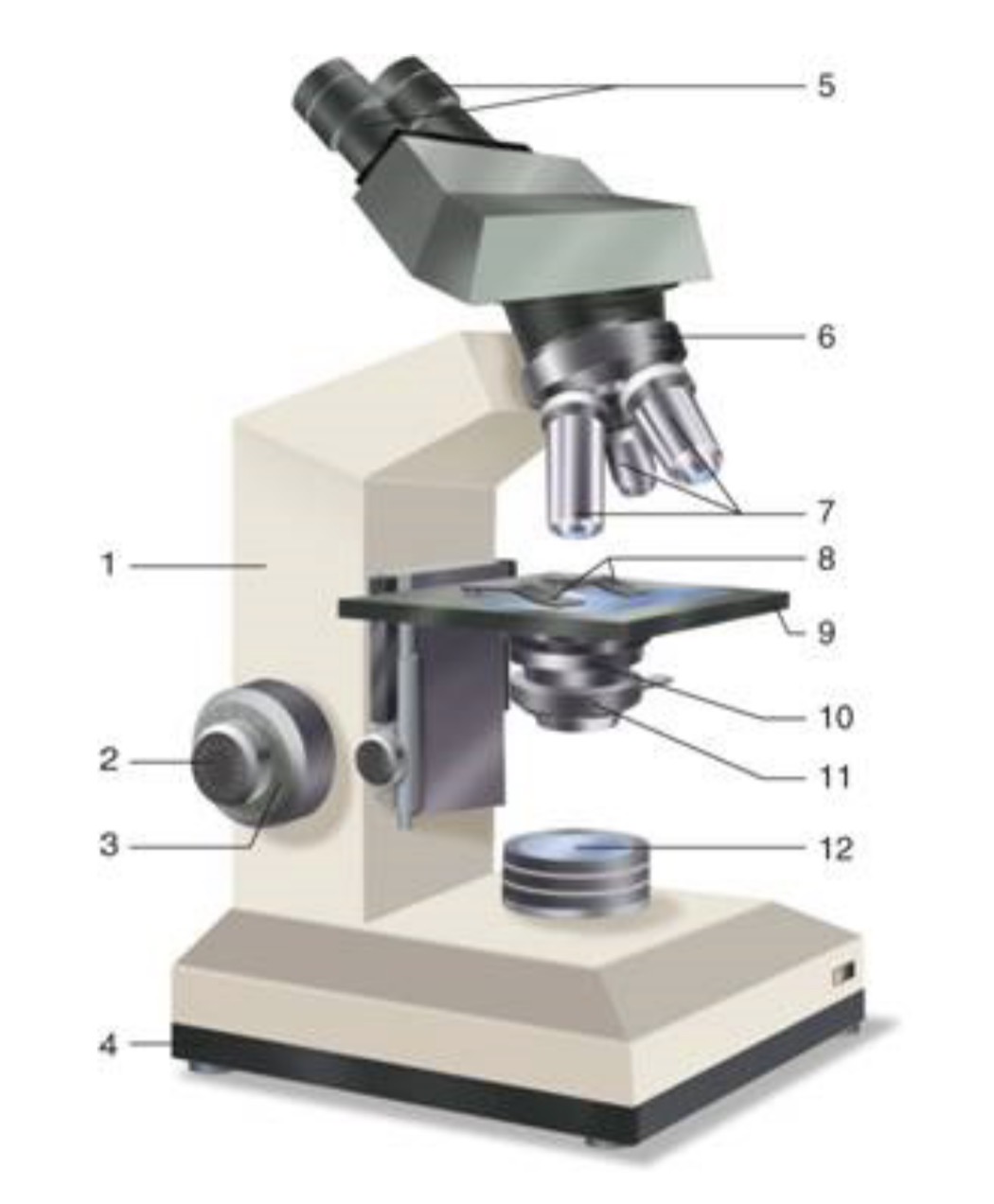
What is #3?
Coarse Adjustment Knob
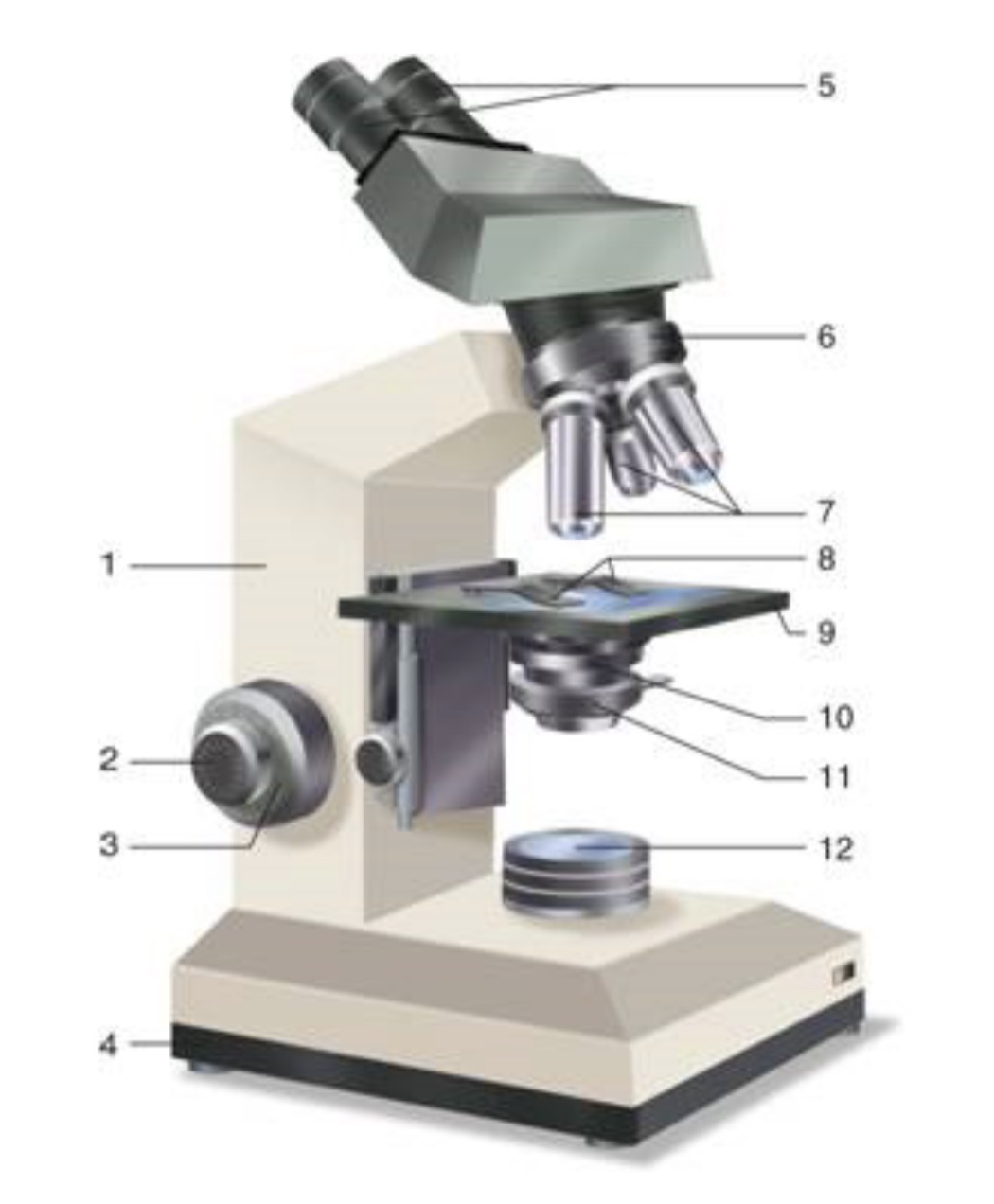
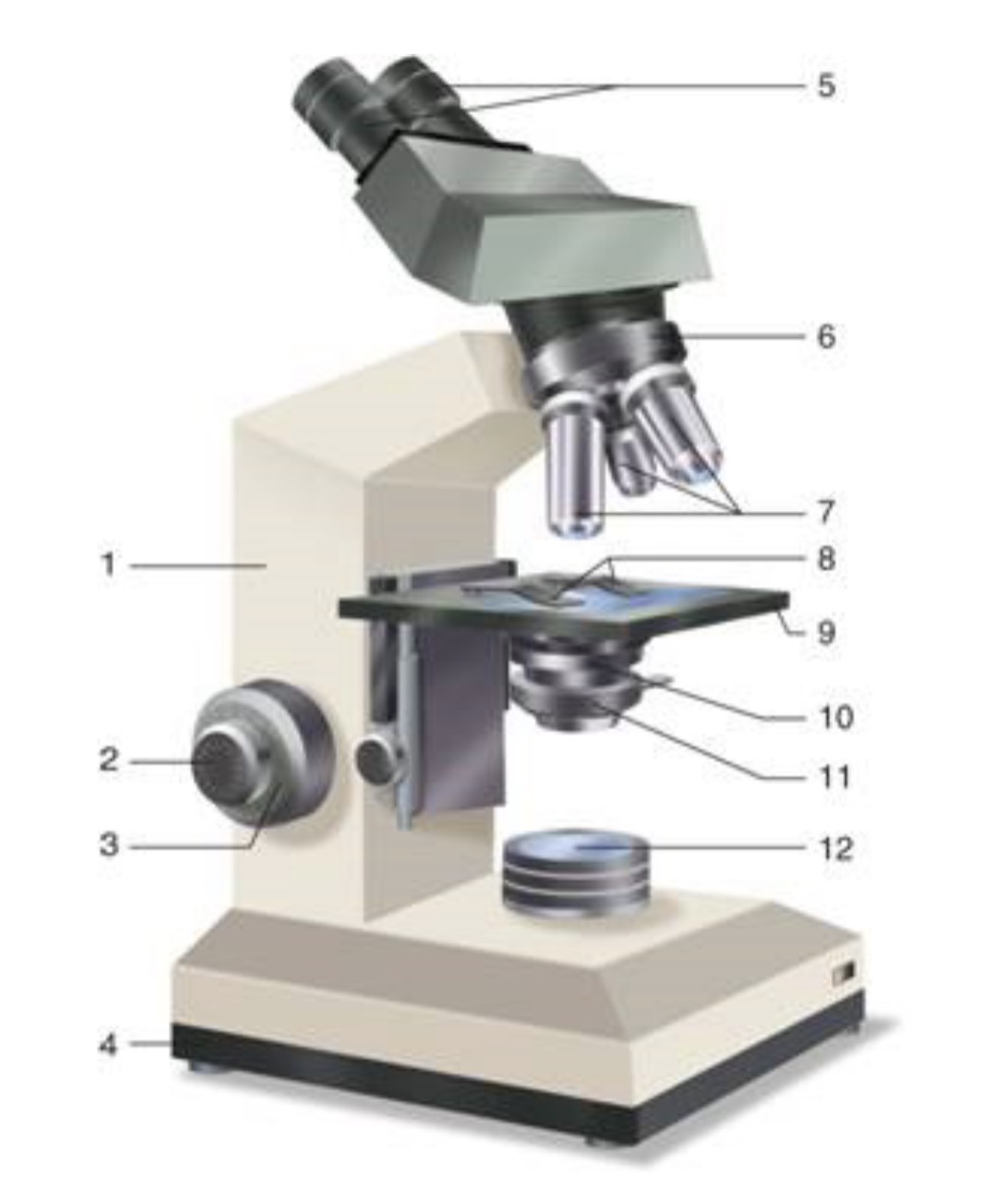
What is #4?
Base
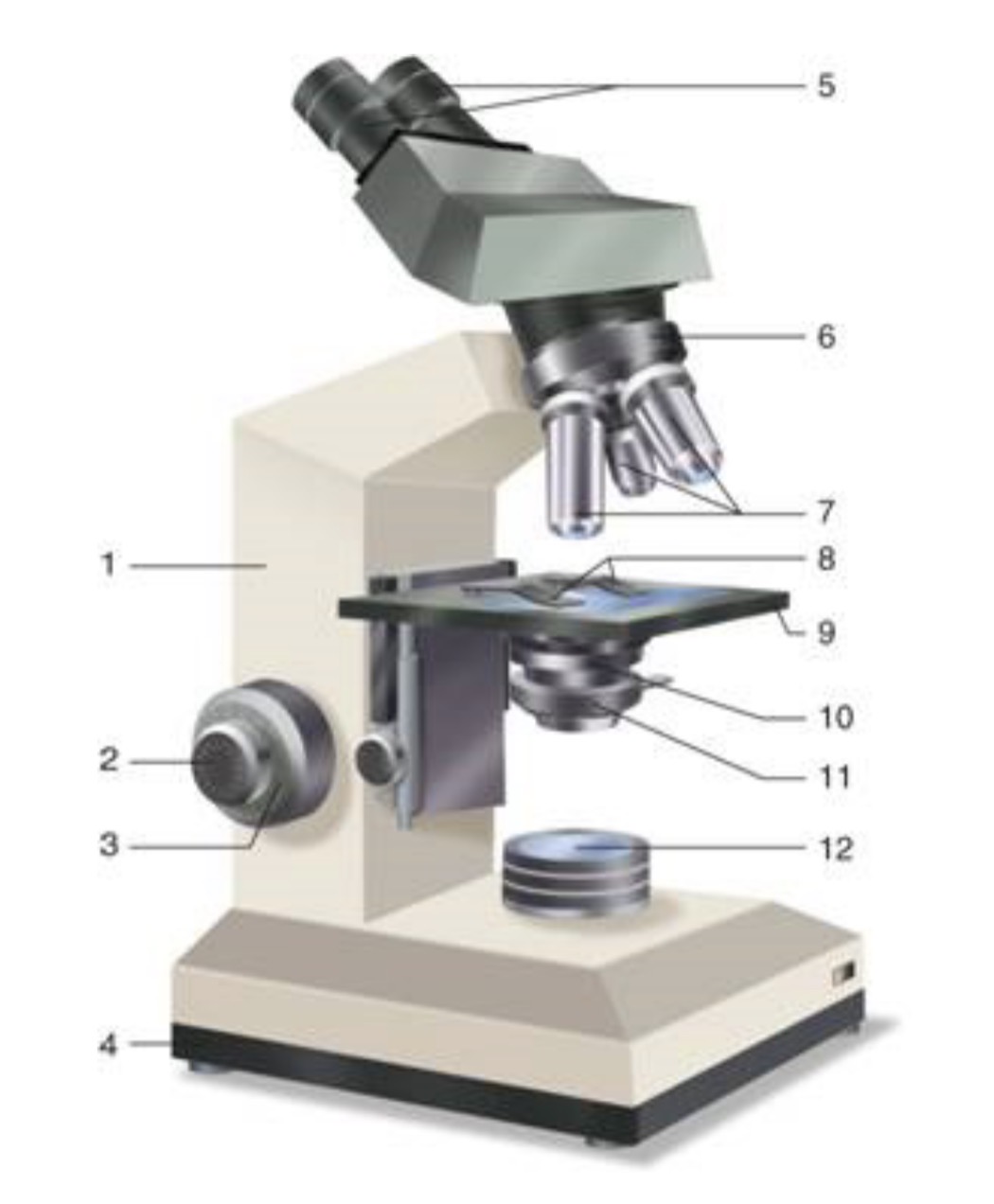
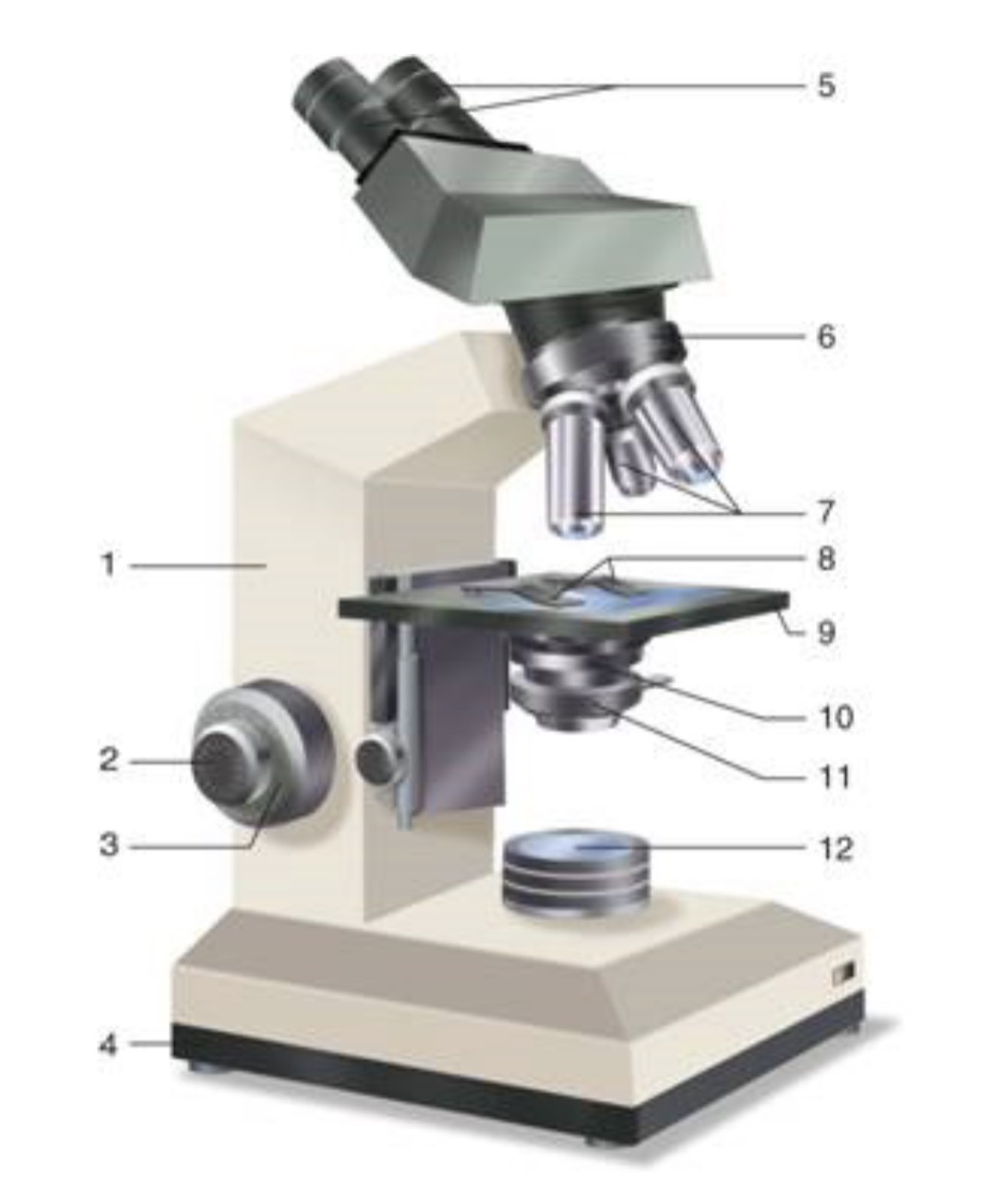
What is #5?
Ocular (eyepiece)
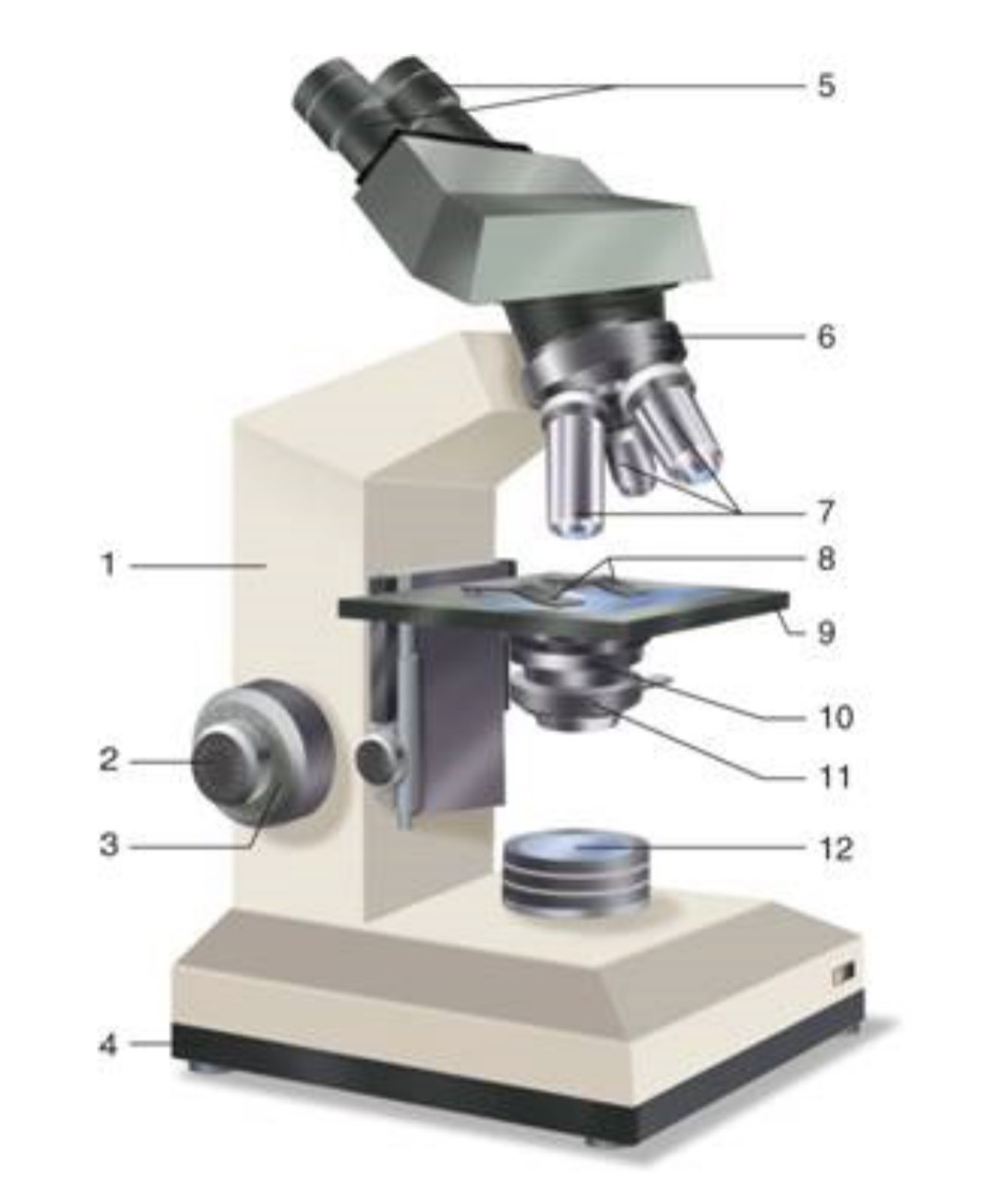
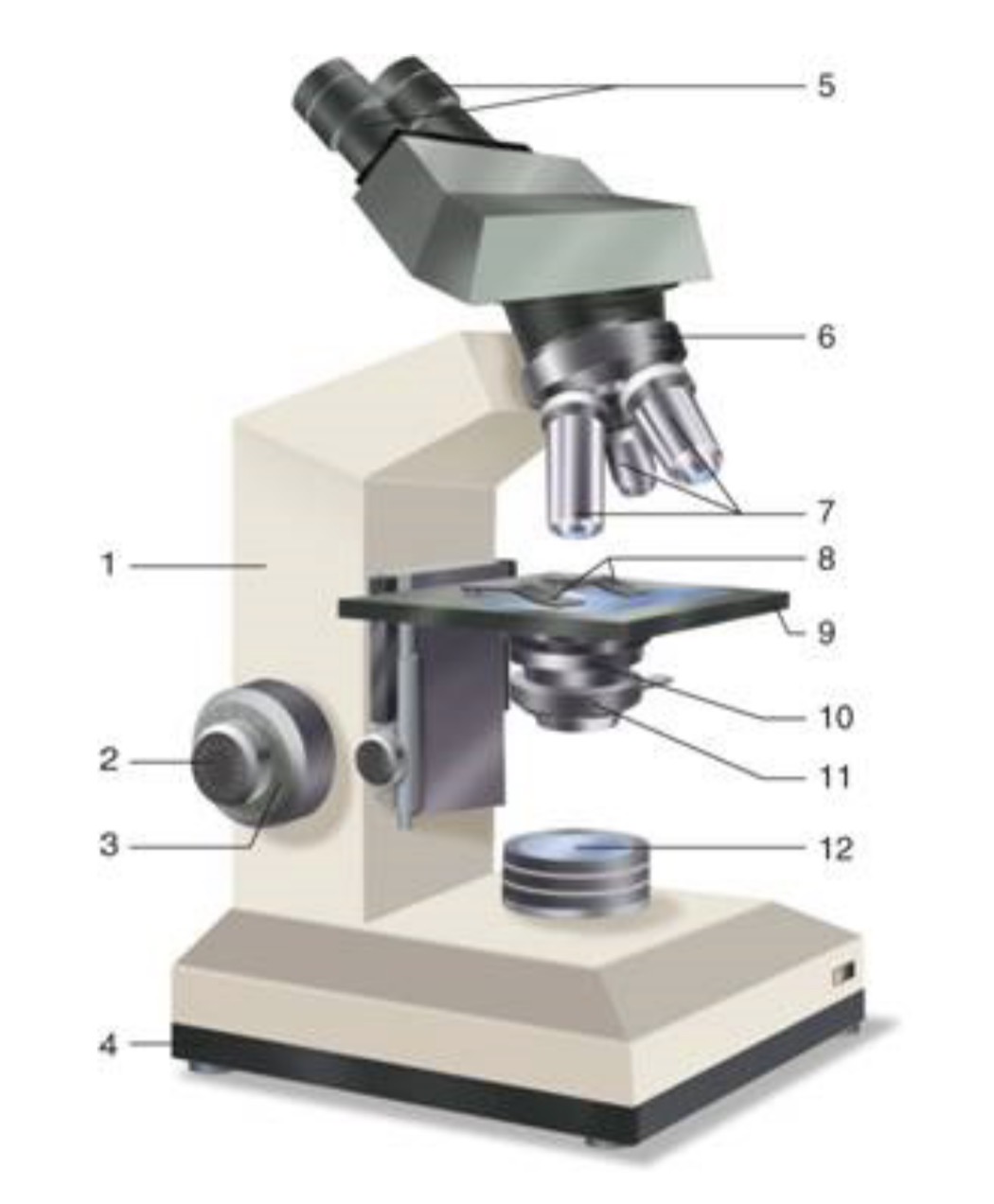
What is #6?
Nosepiece (Resolving turret)
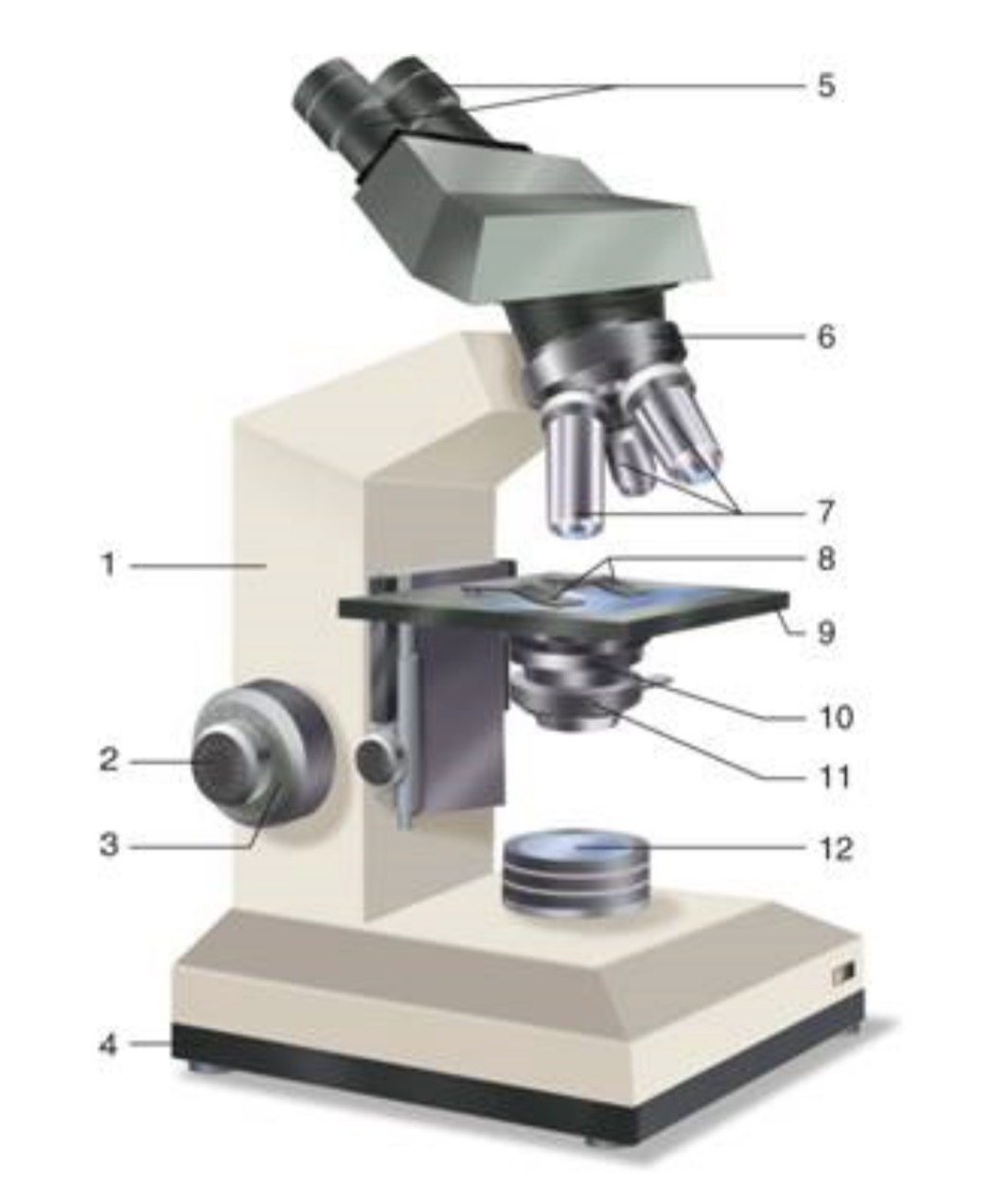
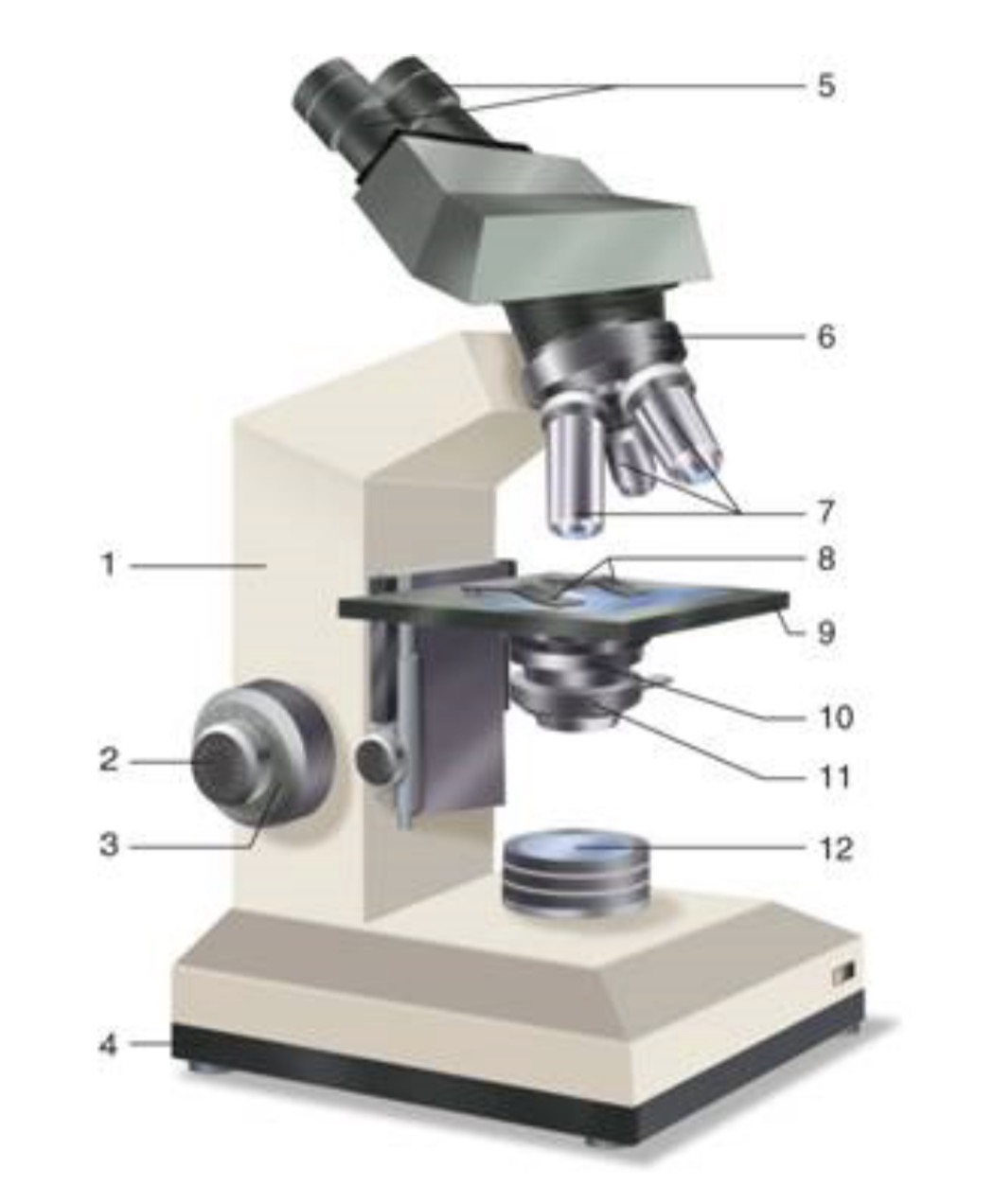
What is #7?
Objectives
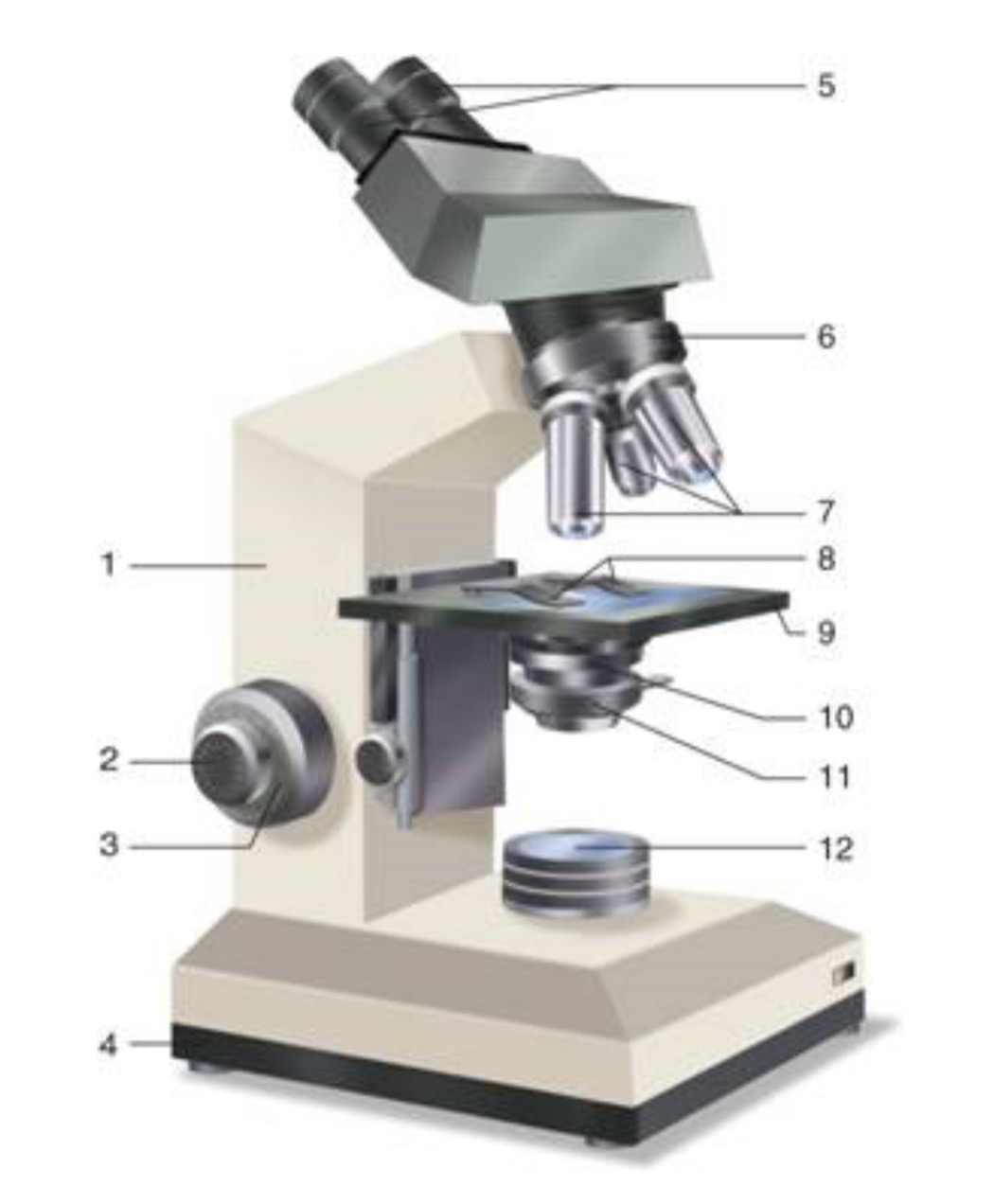
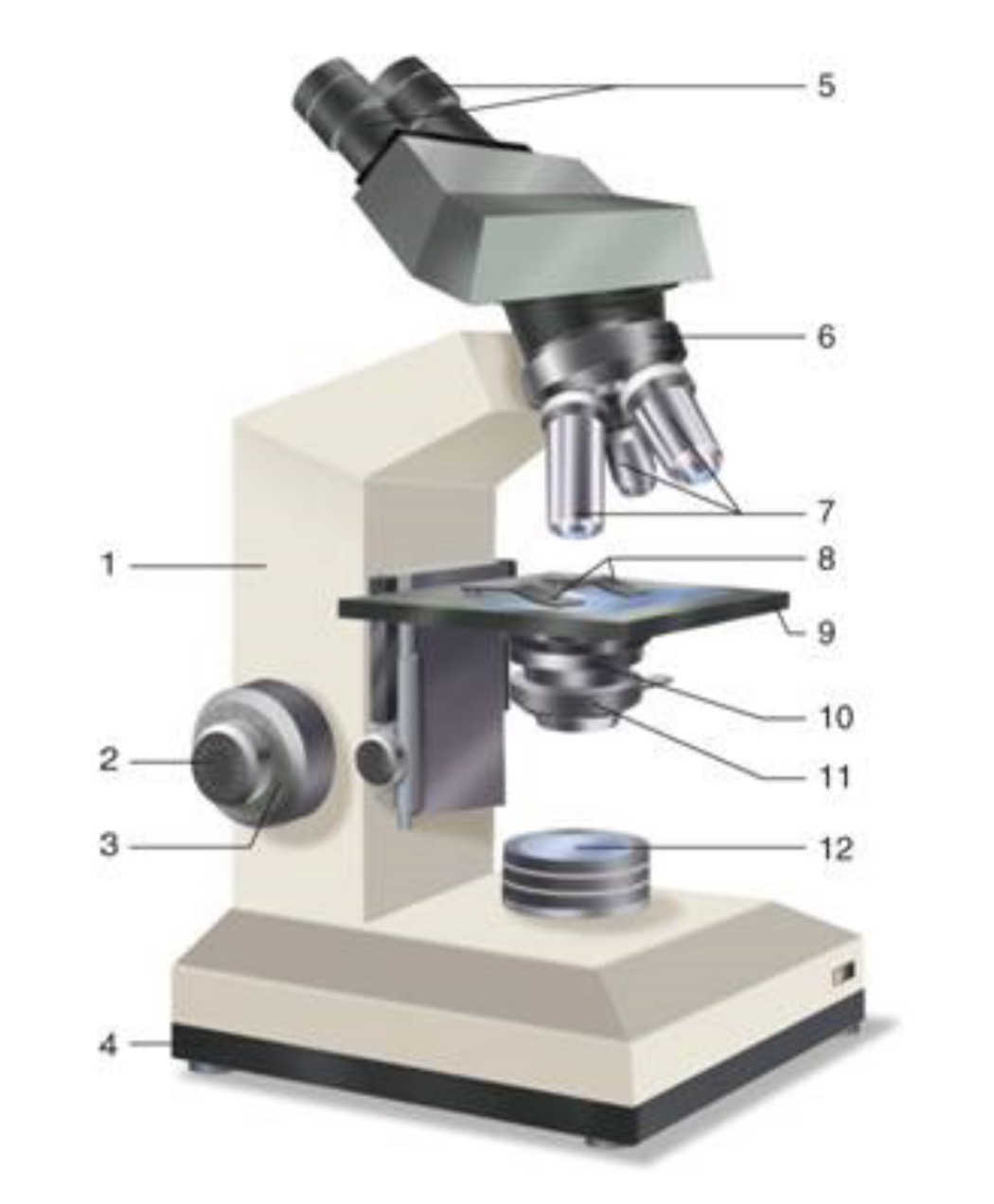
What is #8?
Stage Clips
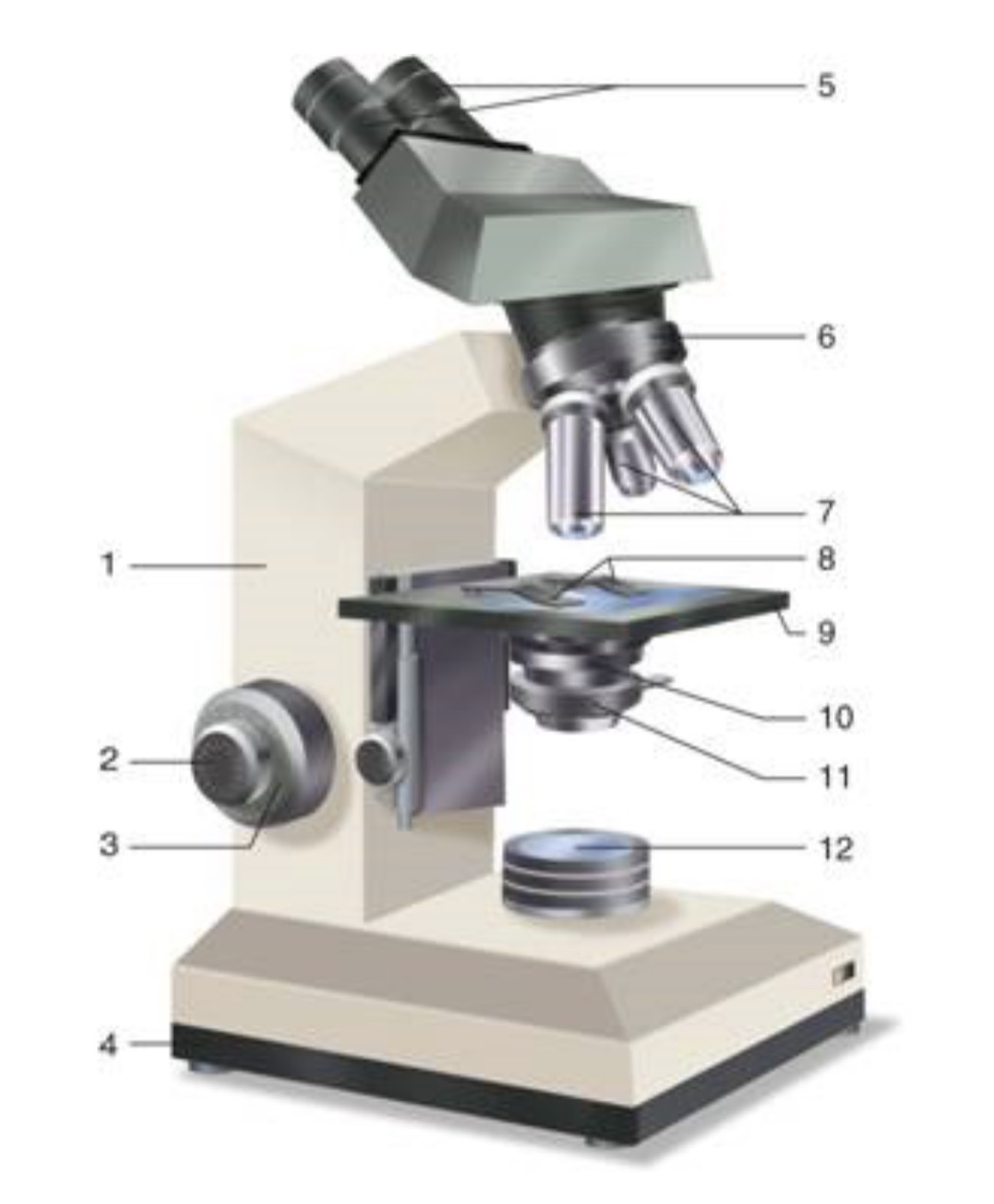
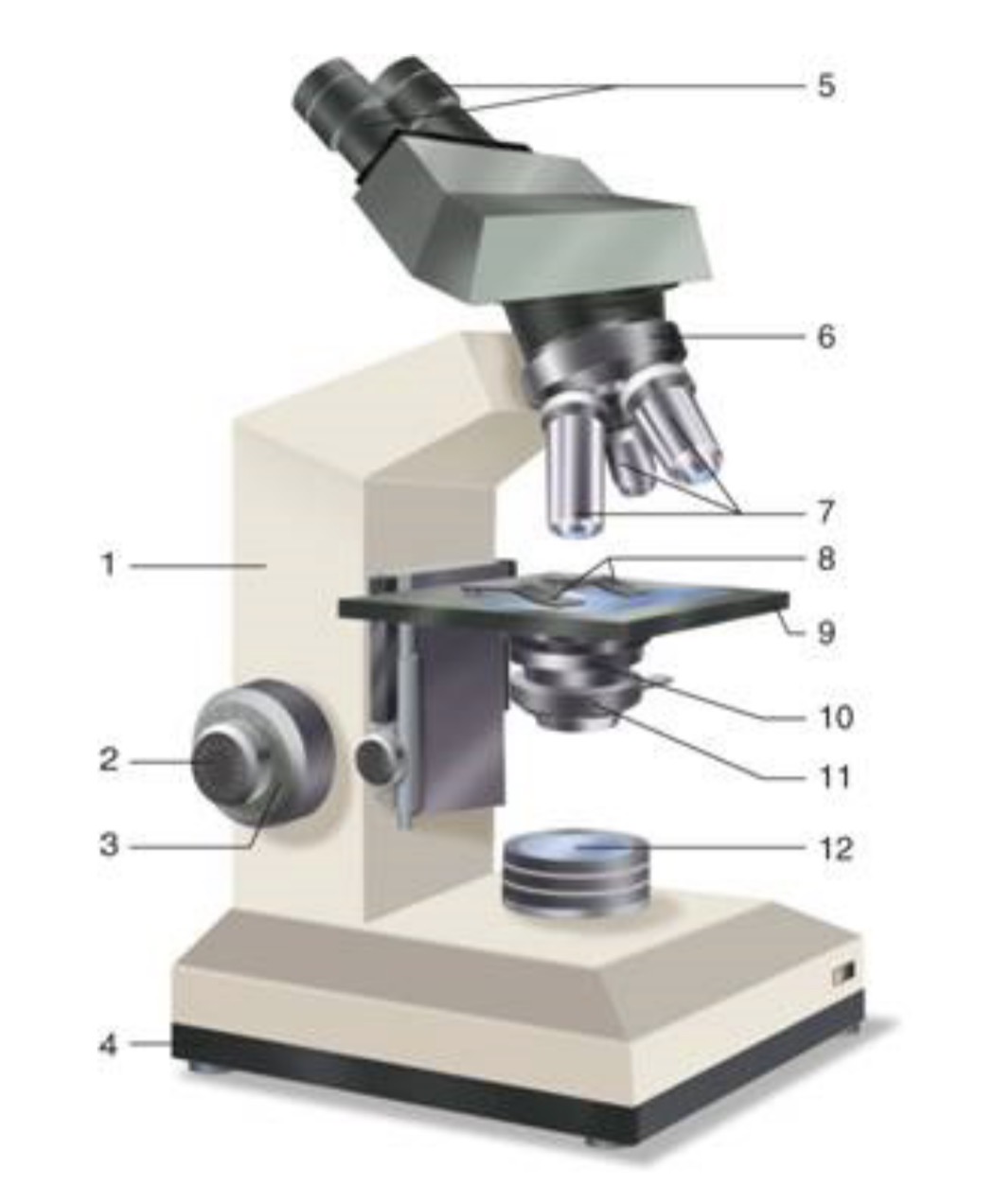
What is #9?
Stage
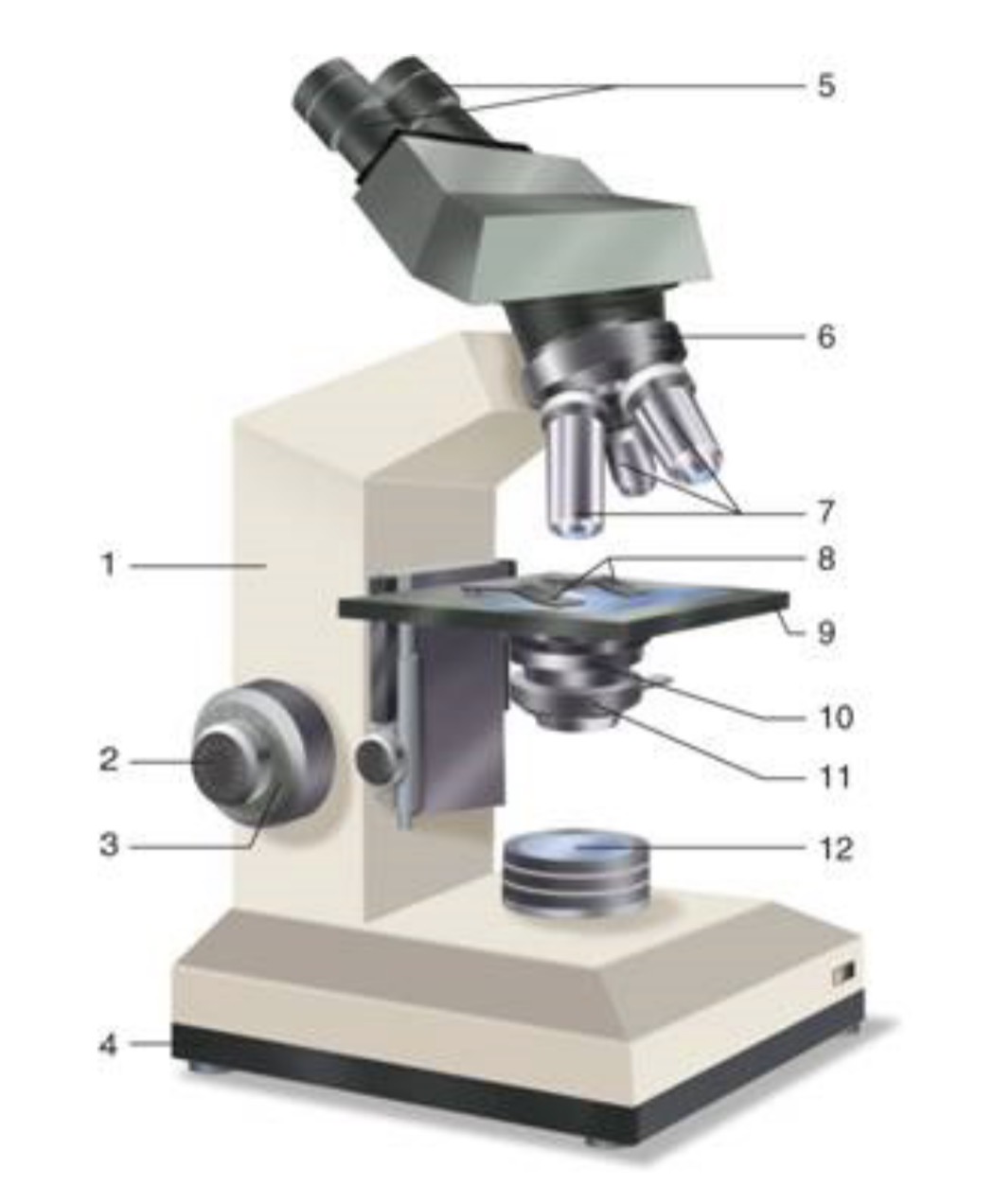
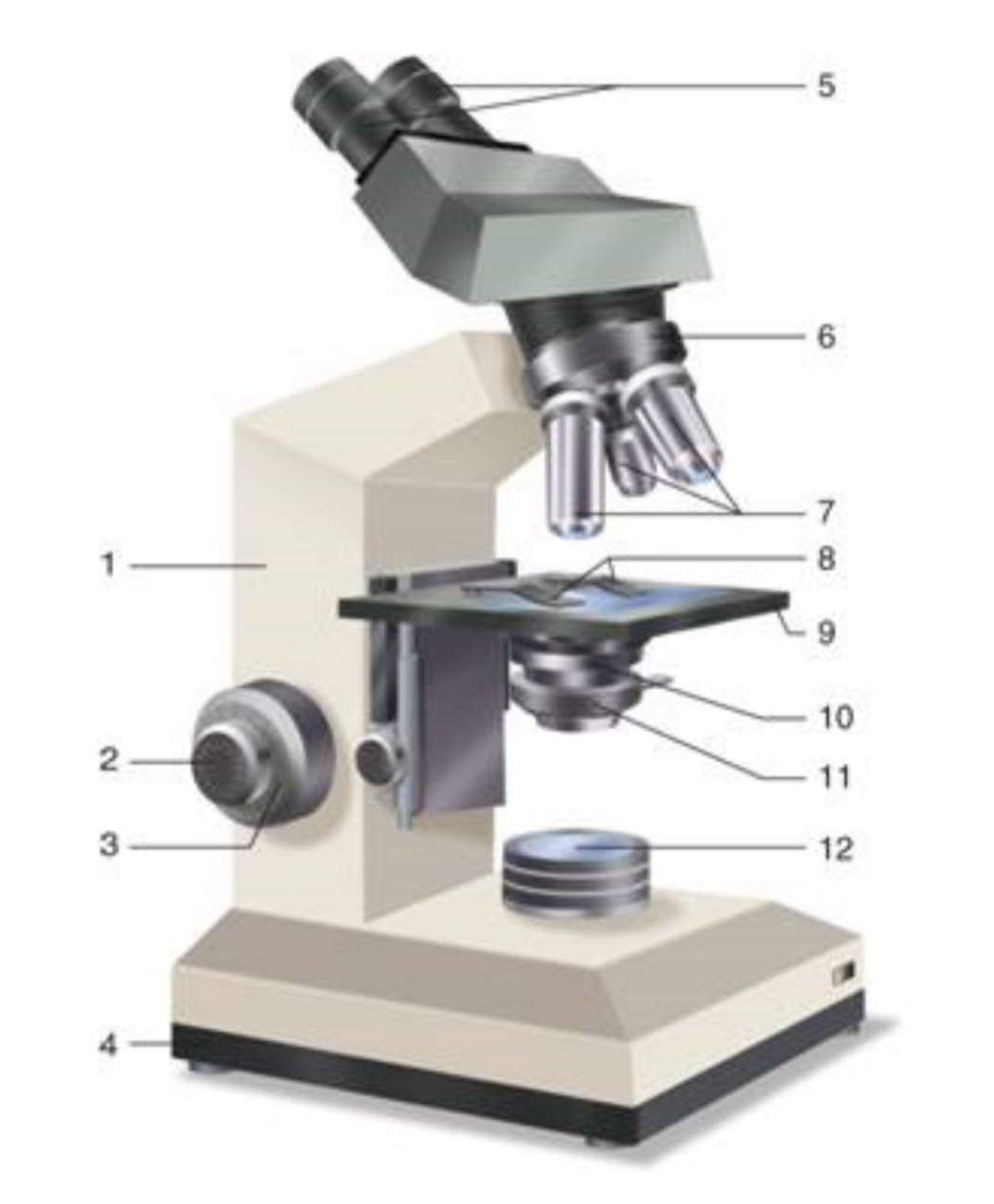
What is #10?
Condenser
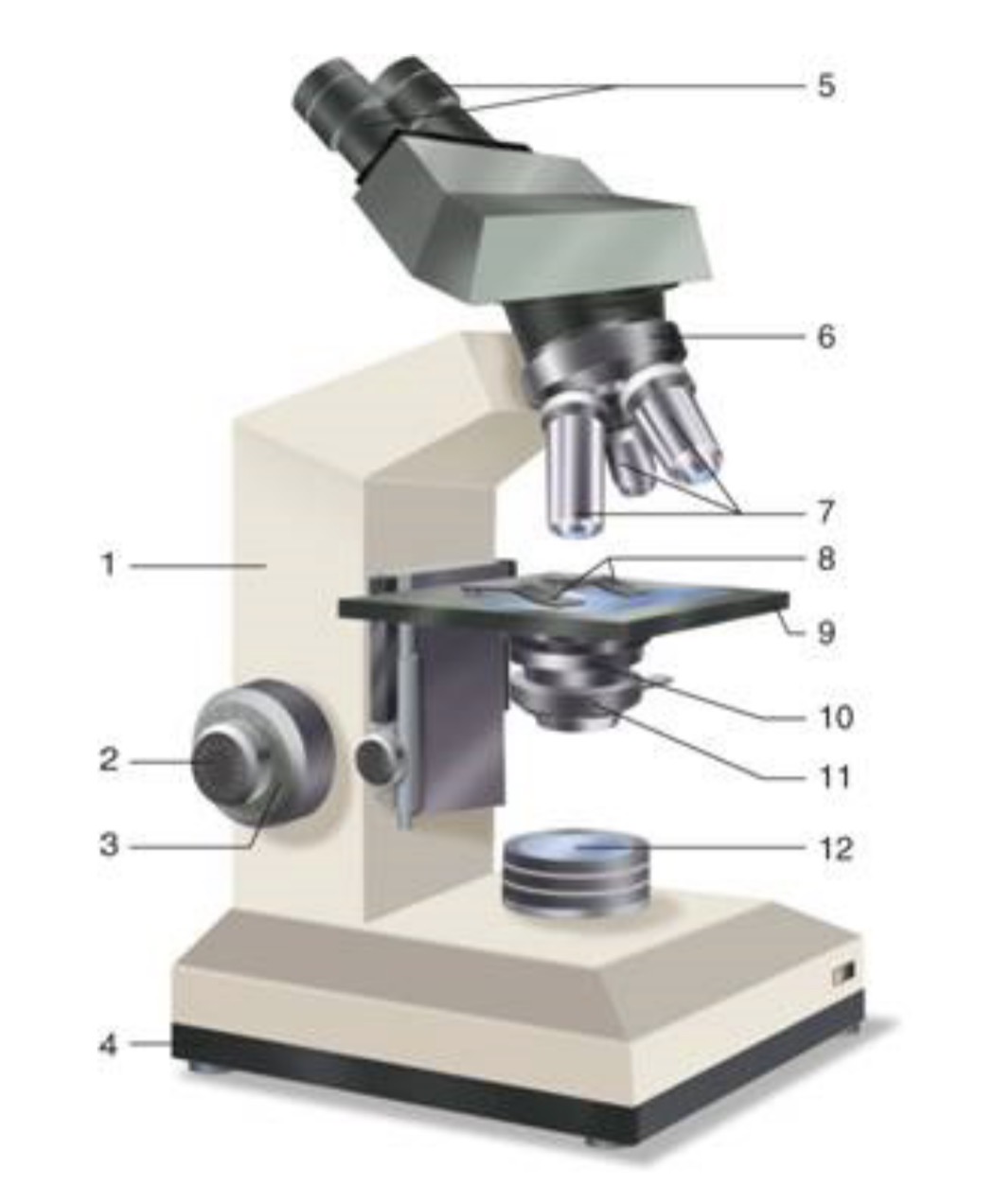
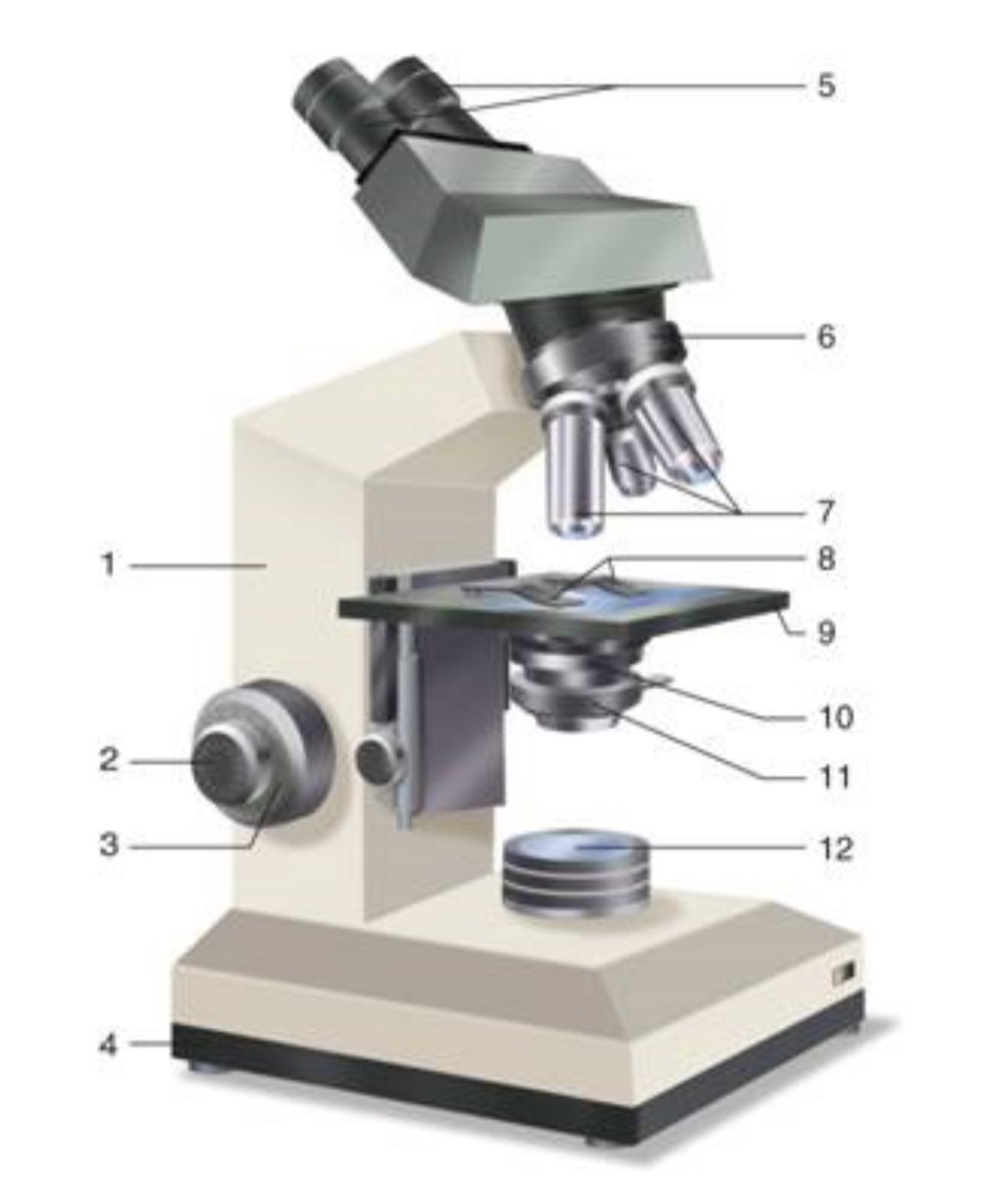
What is #11?
Iris
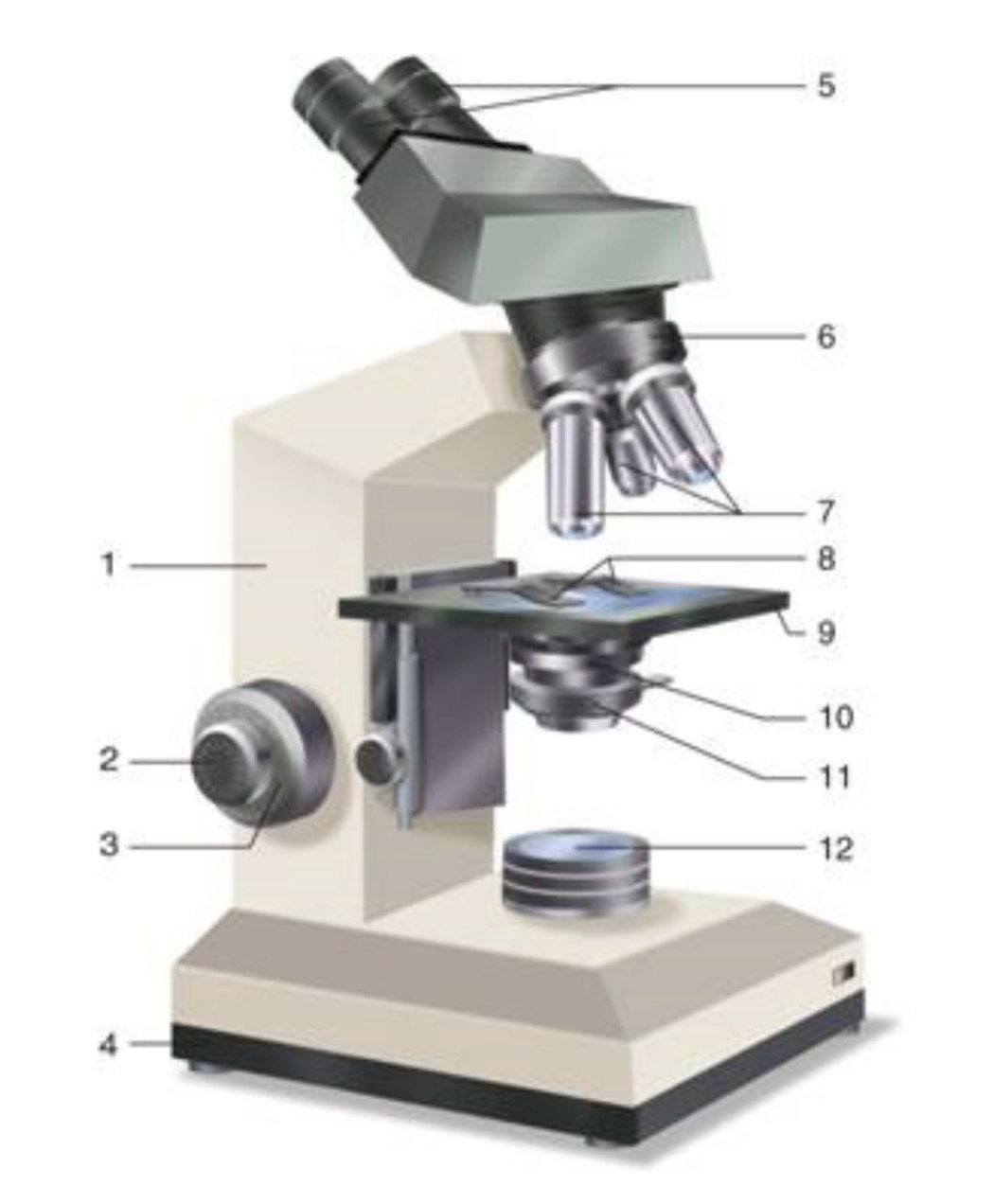
What is #12?
Light Source
List the Guidelines for Standard Precautions
Wear gloves for all body fluids
Change gloves between patients
Wash hands after removing gloves
Wear mask/eye protection if splashing possible
Avoid needle sticks and sharp injuries
Never use mouth pipettes
Prevent spills and splashes
Clean spills with 10% bleach
Remove PPE before leaving the lab
A pipette is
Tool to measure small amounts of liquid
What directions are given for a pt when fasting for a blood test?
To refrain them from eating or drinking especially beginning the night before
Accurate measurement of body Temp?
Rectal is most accurate but to get accurate results use the proper thermometer and follow directions
Urine dipstick is part of
POL
Pap Smear is part of
Reference
Blood banking is apart of
Reference
Drug testing is apart of
Reference
Wound Cultures is apart of
Reference
Rapid Influenza is apart of
POL
Electrolytes is apart of
Reference
Lipid Panel is apart of
Reference