national 5 biology unit 1
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
nucleus
controls cell activity
cell membrane
controls entry + exit of substances
cell wall
supports + strengthens the cell
cytoplasm
site of chemical reactions
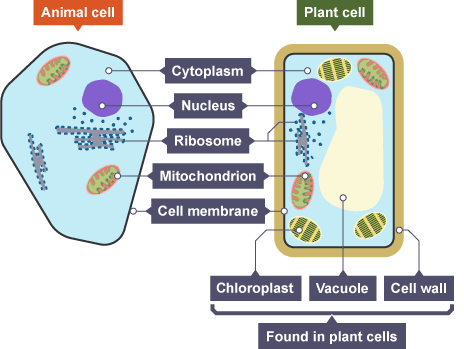
vacuole
water storage
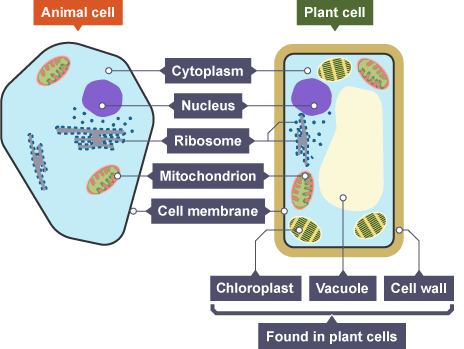
chloroplast
site of photosynthesis
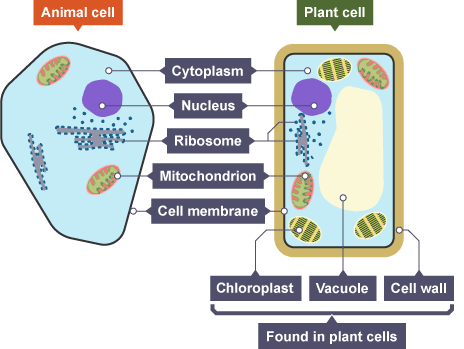
mitochondria
site of aerobic respiration
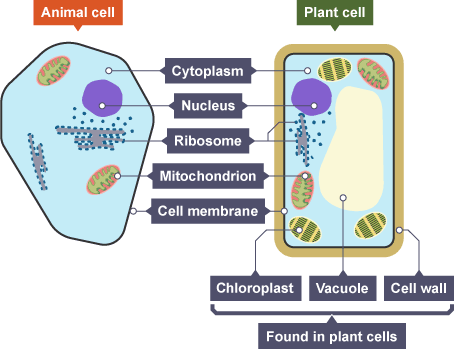
ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
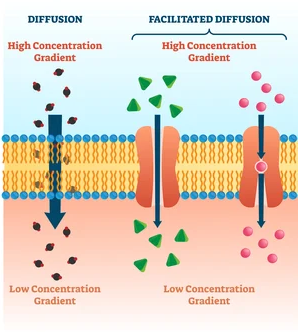
passive transport
movement of molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration without energy (osmosis/diffusion)
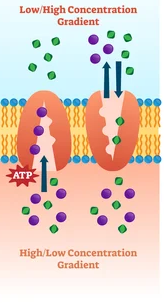
active transport
movement of molecules from a low concentration to a high concentration against the concentration gradient
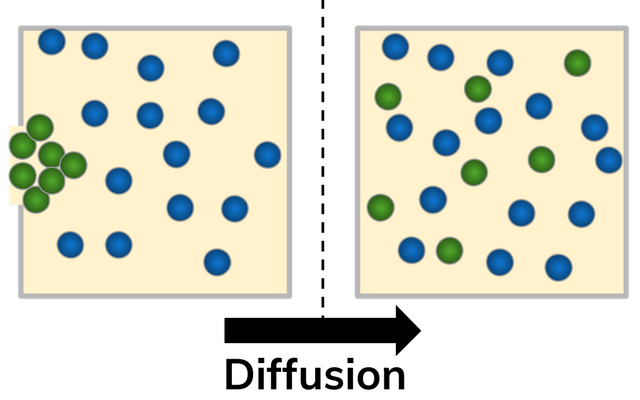
diffusion
movement of molecules down a concentration gradient from a higher to a lower concentration
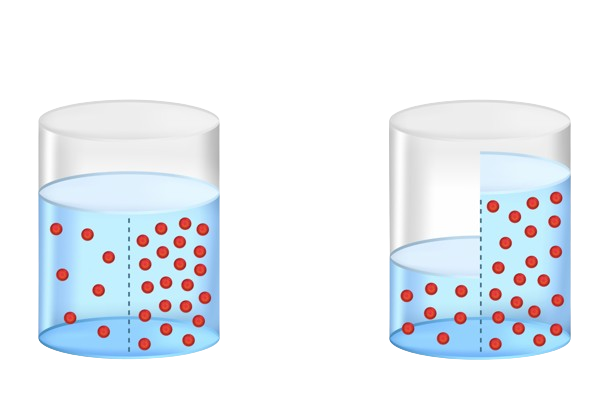
osmosis
movement of water from a high concentration to a low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane
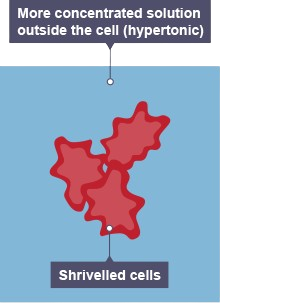
animals cells in 1.7% salt solution
lose water by osmosis and shrink
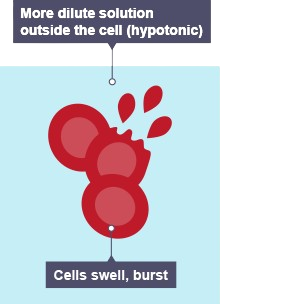
animal cells in high water concentration
gain water by osmosis and burst
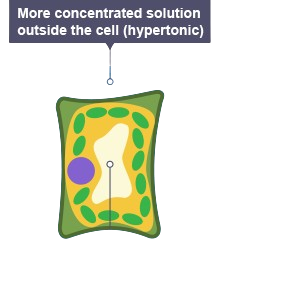
plant cells in low water concentration
lose water by osmosis and become plasmolysed
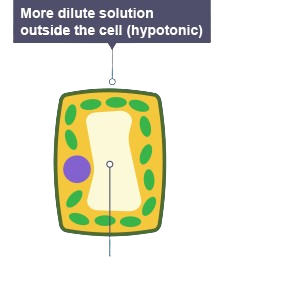
plant cells in high water concentration
gain water by osmosis and become turgid
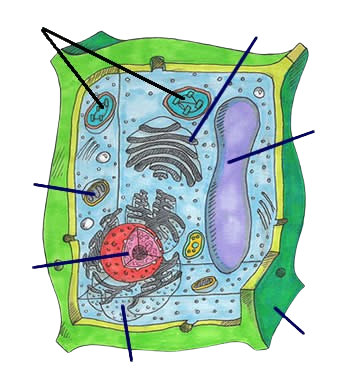
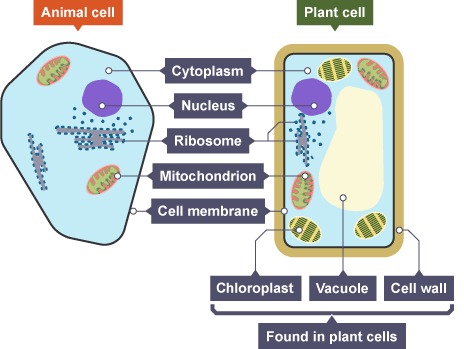
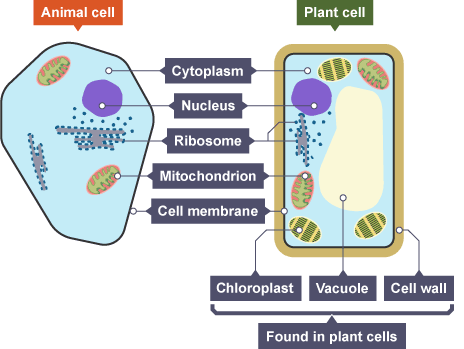
plant cell
cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, chloroplasts, vacuole, mitochondria, ribosomes
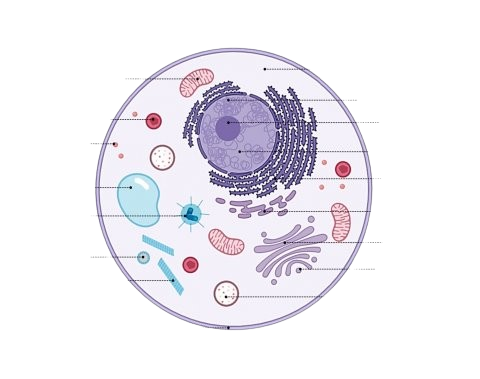
animal cell
cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus mitochondria, ribosomes
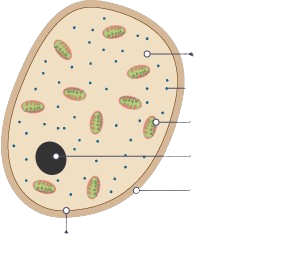
fungus cells
cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, vacuole, mitochondria, ribosomes
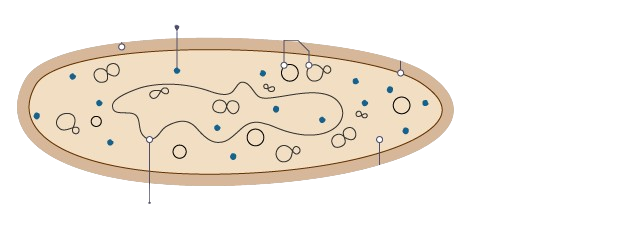
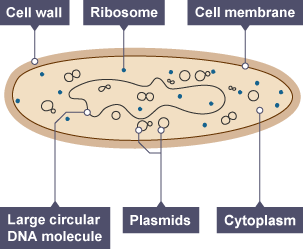
bacterium cell
cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, plasmids
what do all cells share?
cell membrane, ribosomes
gene
section of DNA that codes for a protein
sequence of bases
sequence of amino acids which determines function and structure of the protein
DNA
molecule made of nucleotides containing genetic information
protein synthesis
double helix dna unwinds + unzips along a gene
mRna creates complementary copy on DNA code
mRna seperates from DNA, leaving through holes in the membrane
mRna atatches to ribosome to create proteins
enzymes
biological catalysits that speed up chemical reactions in cells
factors affecting enzyme activity
temperature, pH, concentration
types of proteins
structural, elastin, enzyme, hormone, antibodies
structural protein
collagen
elastin protein
elasticity to skin
enzyme protein
amylase
hormone protein
insulin
antibodies protein
fight infection
activation energy
energy required for a chemical reaction to occur
protein synthesis definition
build up of small to large molecules
protein synthesis equation
glucose -(amylase) -> starch
protein degradation equation
starch -(amylase) -> maltose
protein degradation definition
large molecules broken down to small molecules
genetic engineering
transfer of genes to another organism of a different species
stages of genetic engineering
extract plasmid from bacteria
open plasmid with enzymes
identify + remove gene from chromosome
insert gene into plasmid
insert plasmid into a bacterium
grow large numbers of bacteria
aerobic respiration
respiration where oxygen is present
anaerobic respiration
respiration where oxygen is not present
which type of respiration is the most efficient?
aerobic respiration as glucose is completely broken down and a lot of ATP is produced
basic equation for respiration
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
fermentation in plant/yeast cells
glucose -> pyruvate -> ethanol + carbon dioxide
effect of lactate on muscle tissues
muscle fatigue
similarities / differences between fermentation in plant and animals cells
both types of fermentation have anaerobic conditions
fermentation is reversible in animal cells and irreversible in plant cells
2ATP produced in both
fermentation in animal cells
glucose -> pyruvate -> <- lactate
fermentation
breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen