Urticaria and Angioedema, anaphylaxis
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is urticaria and angioedema
Same process, different levels of skin
Where does urticaria occur
Dilation of vascular structure in SUPERFICIAL dermis, last for <24h and intesnely pruritic
Where does angioedema occur
Deeper dermis and subcutaneous tissue
Acute urticaria
Exposure to food, environment, drug or viral infection
Chronic urticaria
Idiopathic
Dermatographism
Linear wheal with erythema
Physical urticaria
Pressure: response to stimulus, cholinergic, solar, cold, aquagenic, contact, vibratory
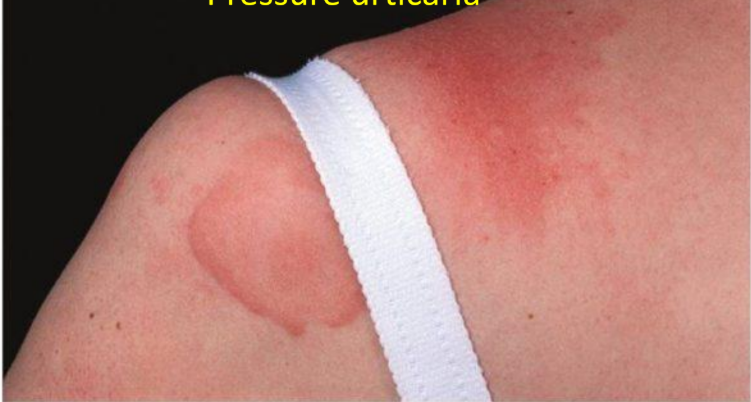
Pressure urticaria
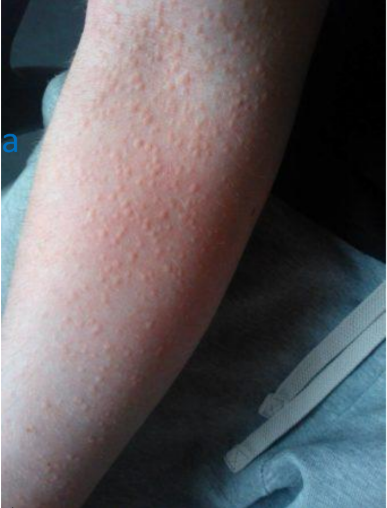
Cholinergic urticaria
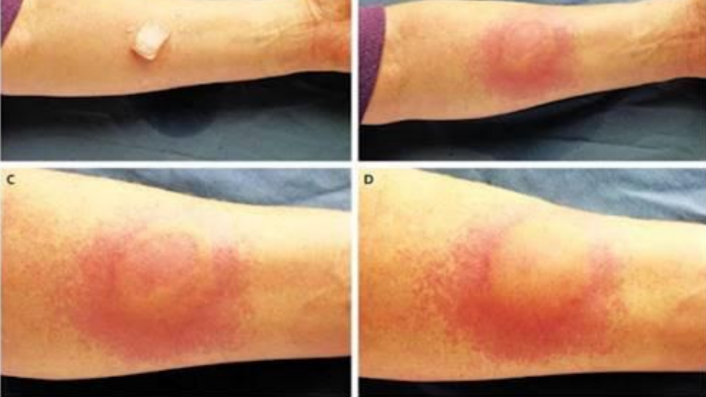
Cold urticaria
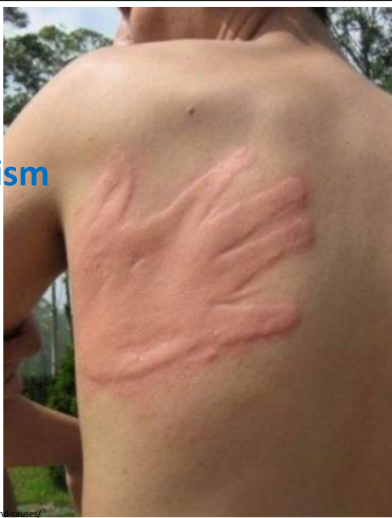
Dermatogarphism
What is isolated angioedema
Autosomal dominant mutation; idiopathic or from bradykinin generation
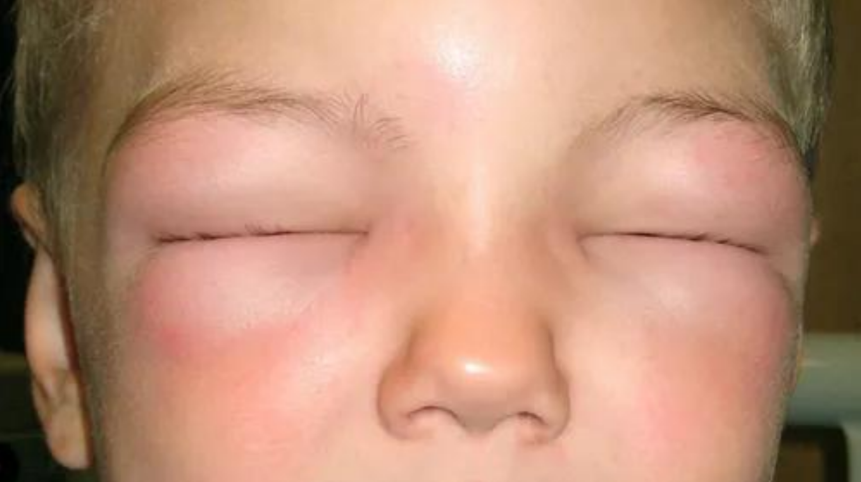
Angioedema
What is anaphylaxis
Medication and stinging insects leading trigger in adults; systemic allergic reaction
Anaphylaxis cause
IgE binding and cross linking on surface of mast cell and basophil
Biphasic anaphylaxis
Recurrent anaphylaxis occurs 1-72 hours after first episode; <1%-20% of patients
Anaphylaxis criteria
Sudden onset of illness with skin, mucosal involvement or both (respiratory and BP symptoms)
Augmentation anaphylaxis reaction
Physical exertion, infection, mental stress, drug, alcohol
Concomitant disease in anaphylaxis
Bronchial asthma, cardiovascular disease, mastocytosis, thyroid disease