A2.2 - Cell Structure
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What is cell theory?
1. Cells are the most basic unit of life
2. Cells come from prexisting cells
3. All living things are made up of cells
How does the meaning of “theory” differ in science vs daily language?
In daily language, a theory often means a guess or assumption. In science, a theory is a well-supported explanation based on evidence, repeatedly tested and confirmed.
Distinguish inductive and deductive reasoning.
Inductive reasoning: building general principles from many observations.
Deductive reasoning: predicting outcomes from general principles.
How did inductive reasoning lead to cell theory?
Scientists observed that all organisms studied were made of cells. From repeated observations, they induced the general principle that all living things are composed of cells.
How can deductive reasoning predict features of a new organism?
Since cell theory states all living things are made of cells, if a new organism is discovered, deductive reasoning predicts it will also be made of cells.
What do all cells have?
plasma membrane, cytoplasm, DNA, ribosomes
What are the two types of cells?
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
--> prokaryotic cells are unicellular, have no membrane nucleus
--> eukaryotic cells can be unicellular and multicelluar
What are the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a membrane-bound nucleus, have naked DNA in a loop, and 70S ribosomes.
Eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus with DNA bound to histones, compartmentalized cytoplasm, 80S ribosomes, and membrane-bound organelles.
What is microscopy used for in studying cells?
Microscopy allows observation of cells too small for the naked eye.
Techniques include preparing temporary mounts, staining, using eyepiece graticules for measurements, calculating magnification, and creating scale bars.
How do you calculate total magnification of a microscope?
Total magnification = ocular lens magnification × objective lens magnification.
How do you measure field of view diameter on low power?
Place a ruler on the stage and measure visible width in mm.
6. What is magnification and how is it calculated?
Magnification = Image size ÷ Actual size.
Actual size = Image size ÷ Magnification.
Measured using eyepiece graticules and calibrated with stage micrometers.
How do you calculate field of view under medium/high power?
Field of view (new) = field of view (low) × (magnification low ÷ magnification new).
Define resolution and magnification.
Resolution = ability to distinguish two close points as separate.
Magnification = enlargement of an image compared to its actual size.
Compare light vs electron microscopes.
Light microscopes: lower resolution (~200 nm), can view living cells.
Electron microscopes: higher resolution (~0.1 nm), only dead specimens.
What is a benefit of fluorescent stains?
They highlight specific structures within cells, increasing contrast and visibility.
How does immunofluorescence visualize proteins?
Antibodies with fluorescent tags bind to target proteins, making them visible under fluorescence microscopy.
How does freeze-fracture electron microscopy work?
Cells are frozen and fractured; fractures split membranes, allowing visualization of membrane structure.
How does cryo-electron microscopy work?
Samples are rapidly frozen, preserving structure without staining, enabling visualization of proteins at near-atomic resolution.
What is the nucleoid?
A dense region of DNA in a prokaryotic cell.
What is a plasmid?
circular piece of DNA
What is the cell wall?
surrounds the cell membrane of the plant cell; provides support and shape, withstands turgor pressure
What is the flagella?
Long, thin whip-like structure that helps organisms move through moist or wet surroundings
What is the capsule?
material surrounding the cell outside the cell wall consisting of polysaccharidesor protein. It serves to protect the cell.
What is the plasma membrane?
the boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings
What is the cytoplasm?
the portion of the cell outside the nucleus
What are pili?
Protein filaments on the edge of a cell wall that helps bacterial cells attach to surfaces and to one another.
What are ribosomes?
site of protein synthesis, join amino acids together to create polypeptide chains
--> prokaryotes have 70s ribosomes
--> eukaryotes have 80s ribosomes
What is “naked DNA” in prokaryotes?
DNA not associated with histone proteins, existing as a single circular chromosome.
What is the nucleolus?
where ribosomes are made inside nucleus
What is the nucleus?
double membrane bound with pores, contains the DNA
The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which has pores allowing transport of materials in and out of the nucleus.
What is the rough ER?
It is continuous with the nuclear membrane and usually is folded into a series of flattened sacs. The outer surfaw of rough ER is studded with ribosomes, the sites of protein synthesis.
What is the smooth ER?
It extends from the rough ER to form a network of membrane tubules. Unlike rough ER, smooth ER does not have ribosomes on the outer surfaces of its membrane. Synthesizes lipids
What is the golgi apparatus?
flattened stacks that process, package, and deliver proteins and lipids from the ER
What are mitochondria?
Converts glucose into ATP in the process of respiration
What are chloroplast?
where photosynthesis takes place in plant cells
What are vesicles?
membranous sacs that are used to transport materials in the cell
What is a vacuole?
A membranous sac used to store water, amino acids, sugars, or waste
What is the cytoskeleton?
a network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm which provide support and structure for cell
What are lysosomes?
Membrane-bound vesicles containing digestive enzymes.
Involved in breaking down waste materials and cellular debris (intracellular digestion).
What are microvilli?
Small finger-like projections of the plasma membrane.
Increase surface area for absorption (e.g., in intestinal cells).
What are the functions of structures common to all cells?
Plasma membrane: regulates entry/exit of materials.
Cytoplasm: site of metabolic reactions.
DNA: stores genetic information.
Ribosomes: site of protein synthesis.
What are the 8 processes of life?
1. Metabolism- chemical reactions that take place in a cell
2. Response to Stimuli- reacting to change in external environment
3. Homeostasis- the maintenance of constant internal conditions despite external changing
4. Movement- living things have some control over their place and position
5. Growth- cells can increase in size over a period of time
6. Reproduction- cells can produce offspring
7. Excretion- the removal of metabolic waste
8. Nutrition- the intake or production of nutrients
How does Paramecium carry out life processes?
Uses cilia to move (movement), contracts vacuole to expel water (homeostasis), feeds on bacteria (nutrition), excretes via anal pore (excretion).
How does Chlamydomonas carry out life processes?
Uses flagella to move, photosynthesizes for nutrition, senses light with eyespot (response), divides asexually/sexually (reproduction).
What are the differences between plant, fungal, and animal cells?
Plant cells: Have cellulose cell walls, large central vacuole, chloroplasts, no centrioles.
Fungal cells: Have chitin cell walls, small vacuoles, no chloroplasts, no centrioles.
Animal cells: No cell wall, small vacuoles, no chloroplasts, have centrioles.
Cilia and flagella present in some animal and protist cells.
What are atypical eukaryotic cells?
cells with unusual or non-standard structures, organelle numbers, or functions that allow them to perform specialized tasks.
Aseptate fungal hyphae: Multinucleate, lack septa.
Skeletal muscle fibers: Multinucleate due to cell fusion.
Red blood cells: Anucleate (no nucleus).
Phloem sieve tube elements: Anucleate, rely on companion cells.
Organelles in a eukaryotic cell
plasma membrane
cytoplasm
80S ribosomes
nucleus
mitochondria
chloroplast (plants)
ER
Golgi
vesicles
vacuoles
lysosomes
cytoskeleton.
What is the theory of endosymbiosis?
Eukaryotic cells evolved when prokaryotic cells were engulfed but not digested.
Mitochondria and chloroplasts originated this way.
Evidence: Both have 70S ribosomes, naked circular DNA, and replicate independently.
Evidence supporting endosymbiosis?
Genetic: Mitochondria and chloroplasts have circular DNA and 70S ribosomes like prokaryotes.
Structural: Double membranes and similar size to bacteria.
Behavioural: They divide by binary fission, independent of the host cell cycle.
What is cell differentiation and how does it occur?
Process where cells become specialized in structure & function.
Based on selective gene expression, often triggered by environmental signals.
What are benefits of cell specialization in multicellular organisms?
Increases efficiency; different cells perform unique functions; enables complex structures.
How did multicellularity evolve and what are its advantages?
Multicellularity is the condition where an organism is composed of more than one cell, which are specialized, physically connected, and work together to perform complex functions for the whole organism.
Multicellularity evolved independently in fungi, algae, plants, and animals.
Allows for larger body size and specialized cells performing specific functions.
Outline steps in the evolution of multicellularity.
Cell adhesion → communication → differentiation → specialized tissues and organs.
How can you distinguish between prokaryote, plant, and animal cells in micrographs?
Prokaryotes: Nucleoid region, 70S ribosomes, cell wall, plasma membrane.
Plant cells: Cell wall, chloroplasts, large vacuole, plasma membrane.
Animal cells: No cell wall, small vacuoles, plasma membrane, microvilli (sometimes).
What organelles can be identified in electron micrographs?
Nucleoid (prokaryotes), prokaryotic cell wall, nucleus, mitochondrion, chloroplast, sap vacuole, Golgi apparatus, rough & smooth ER, chromosomes, ribosomes, plasma membrane, microvilli.
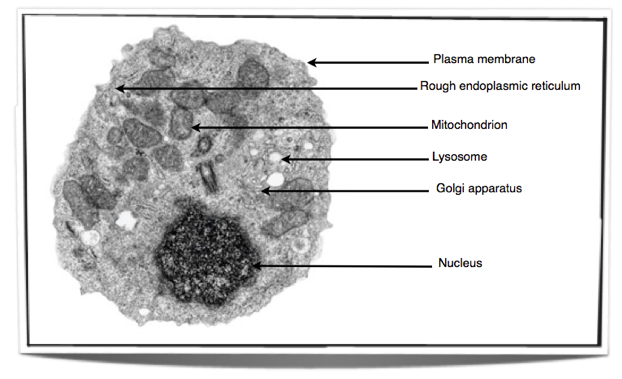
How should organelles be drawn and annotated from electron micrographs?
Diagrams should be accurate in proportion and include:
Nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplast, vacuole, Golgi apparatus, rough & smooth ER, ribosomes, plasma membrane, secretory vesicles, microvilli.
How do you draw the ultrastructure of a prokaryotic cell from a micrograph?
A: Include: nucleoid, plasma membrane, ribosomes, cell wall, pili, flagella.
How do you draw the ultrastructure of a eukaryotic cell from a micrograph?
A: Include: nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplast (plants), vacuole, Golgi, ER, ribosomes, plasma membrane.