Biology Exam 2 Terms (Units 4 & 5)
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Oligosaccharides
Has 2 or more monosaccharides
Polysaccharides
Has many sugars
Monosaccharides
Has single sugars either pentoses or hexoses.
Disaccharides
Has 2 sugars
Hydrogeneration
A process when hydrogen is added to a liquid fat to turn it into a solid fat at room temperature.
Hydration
The process of providing an adequate amount of water to body tissues.
Dehydration synthesis
The creation of larger molecules from smaller monomers where a water molecule is released.
Monomer
An organic molecule that can be used to form a larger molecule (polymer) consisting of many repeating units of the monomer.
Polymer
A large molecule formed by linking many smaller molecules called monomers.
Saturated
When all of the carbons in a fatty acid are linked by single covalent bonds.
Unsaturated
The property of certain lipids that contain one or more C=C double bonds.
Carotenoids
A type of photosynthetic or protective pigment found in plastids that impacts a color that ranges from yellow to orange to red.
Triglyceride
A molecule composed of 3 fatty acids linked by ester bonds to a molecule of glycerol, known as triacylglycerol.
Hexose sugar
Any of a class of sugars containing 6 atoms of carbon, including glucose and fructose.
Fat
A subgroup of components known as lipids that are found in the body and have the general property of being hydrophobic.
Pentose sugar
A component of nucleotides that contain 5 carbon atoms in a molecule
Cellulose
The main macromolecule of the cell wall of plants and many algae; a linear polymer made of thousands of glucose monomers.
Starch
A polysaccharide composed of repeating glucose units that is produced by the cells of plants and some algae protists.
Protein
A functional unit composed of one or more polypeptides. Each polypeptide is composed of a linear sequence of amino acids.
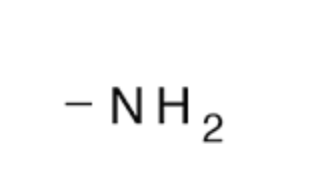
Amino group
A functional group consists of a single nitrogen atom bonded to 2 hydrogen atoms.
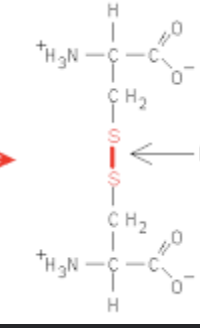
Disulfide Bridge
Covalent chemical bond formed between 2 sulfhydryl groups on cysteine side chains in a protein; important in the tertiary structure of proteins.
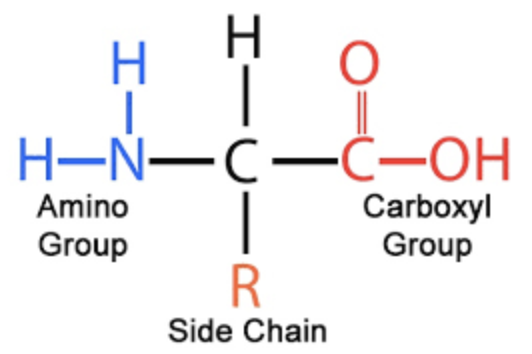
Amino acid
Any of the monomers that are linked to form a protein with a carbon atom, called the alpha-carbon, linked to an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxyl group (-COOH), as well as to a hydrogen atom and a side chain that distinguishes the particular amino acid.
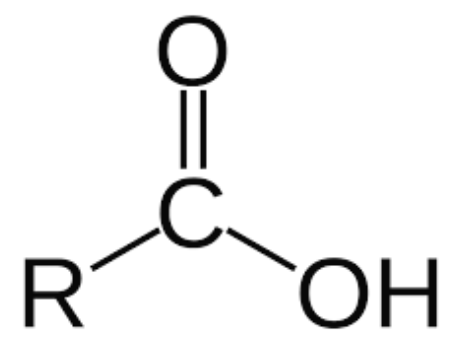
Carboxyl group
A combination of 2 functional groups attached to a single carbon atom, namely, hydroxyl (single-bond OH) and carboxyl (double bonded O) groups.
Mutagen
An agent known to cause mutation
Polypeptide
A molecule consisting of a linear sequence of amino acids, the term denotes structure.
Dehydration synthesis
A type of condensation reaction in which a molecule of water is lost
Translation
The process of synthesizing a specific polypeptide on a ribosome.
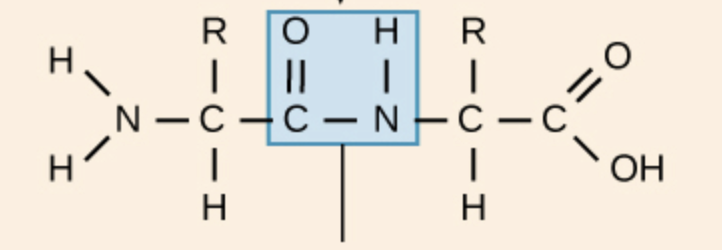
Peptide bond
The covalent bond between a carboxyl and amino group that links amino acids in a polypeptide.
Intron
Intervening DNA sequences that are found in between the coding sequences of genes.
Triplet Code
A group of 3 bases that functions as a codon.
Primary peptide structure
A linear chain of amino acids
Exon
A portion of RNA that is found in the mature mRNA molecule after splicing is finished.
Codon
A sequence of 3 nucleotide bases that specifies a particular amino acid or a stop codon; codons function during translation.
Secondary peptide structure
Comprised of regions stabilized by hydrogen bonds between atoms in the polypeptide backbone.
Denaturation
The unfolding or breaking up of a protein, modifying its standard 3D structure
Anti-codon
A three-base sequence in tRNA that is complementary to a codon in mRNA.
Alpha helix
The coiled structural arrangement of many proteins consisting of a single chain of amino acids stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
Quaternary protein structure
The fourth (and highest) classification level of protein structure.
tRNA (transfer RNA)
An RNA that carries amino acids and is used to translate mRNA into polypeptides.
Beta pleated sheet
A series of anti-parallel chains of covalently-linked animo acids with adjacent chains linked by hydrogen bonds.
Ribosome
A structure composed of proteins and rRNA that is the site where translation of mRNAs and synthesis of polypeptides occur.
rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
An RNA that forms part of ribosomes which provide the site where translation occurs
Tertiary protein structure
The overall 3D arrangement of its polypeptide chain in space
Polyribosome
A cluster of ribosomes linked together by a molecule of messenger RNA and forming the site of protein synthesis.
mRNA (messeger RNA)
Contains the information for the amino acids sequence of a polypeptide according to the genetic code.
Peptide
A strong string of 2 to 50 amino acids formed by a condensation reaction, joining together through a covalent bond.
Silent mutation
Do not alter the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide, even though the nucleotide sequence chnaged.
Missense mutation
Is a base substitution that changes a single amino acid in a polypeptide sequence
Nonsense mutation
Involves a change from a normal codon to a stop, or termination codon.
Frameshift mutation
Involves the addition or deletion of a number of nucleotides that is not a multiple of three.
Carbohydrates
a carbon-containing organic molecule, carbohydrates include starches, sugars, and cellulose.
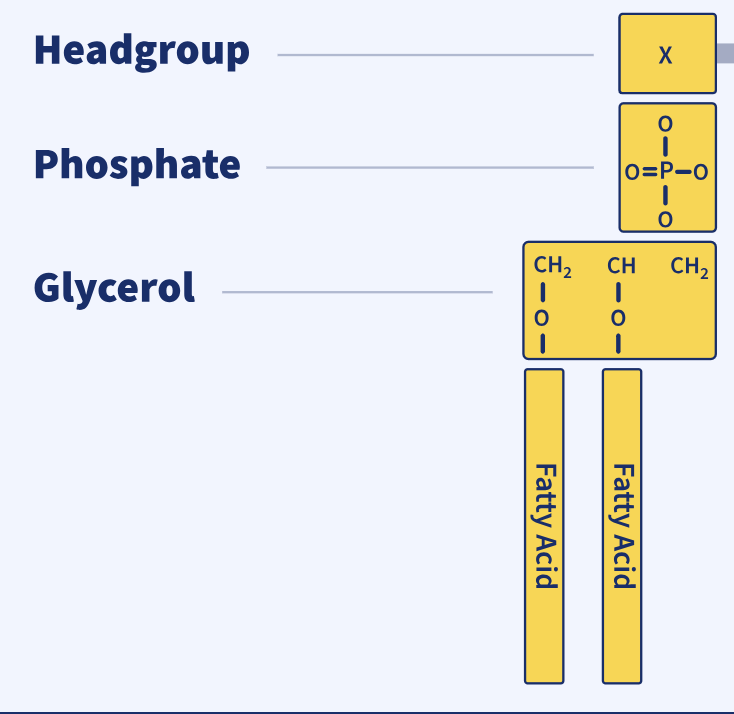
Phospholipid
a lipid with a third hydroxyl group of glycerol linked to a phosphate group instead of a fatty acid; a key component of biological membranes.
Monosaccharide
A simple sugar, such as a pentose or hexose.
Steroid
A lipid containing 4 interconnected rings of carbon atoms; functions as a hormone in animals and plants.
Wax (nonpolar)
Complex lipids that prevent water loss from organisms.
Chitin
A tough nitrogen-containing polysaccharide polymer that forms the external skeleton of many insects and crustaceans and is found in the cell walls and fungi.
Aldose sugar
A monosaccharide (a simple sugar) whose carbon skeleton has an aldehyde group.
Glycogen
A polysaccharide found in animal cells (liver and skeletal muscles) and sometimes called animal starch, also, the major carbohydrates storage of fungi.
Disaccharide
A carbohydrate composed of 2 monosaccharides.
Ketose sugar
Acids your body makes when its using fat instead of glucose for energy.
Polysaccharides
A long carbohydrate polymer formed of many monosaccharides linked together.