Bacteria and Viruses
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
cytoplasmic structures:
nucleoid
plasmids
features of nucleoids
Doble stranded DNA
Circular chromosomes
Spatial organization --> super coiled
Bacterial ribosomes are a target for antibacterial drugs
16s RNA --> low mutation rate --> used in phylogenetic
features of plasmids
circular or lineal extrachromosomal DNAs
not usually essential for bacterial survival
capable of autonomous replication
often provide a selective advantage
features of flagella
circular or lineal extrachromosomal DNAs
not usually essential for bacterial survival
capable of autonomous replication
often provide a selective advantage
Long helical filament à extend outside the cell
connecting hook
Basal body à rotor to turn the flagellum
features of pili and fimbriae
Protein spikes that extend from surface
Pili are longer than fimbriae
Fimbriae are normally more abundant per cell
function of fimbriae and pili
Functions = adhesion --> T1 fimbriae required for pathogenic strains to adhere
T4 pili used in extension and retraction of pili, help move along a solid surface
Sex pilus involved in DNA transfer in conjugation
what are capsules
Amorphous polysaccharide slime surrounding cells
Tightly bound to the bacterial cell wall
Can be present in both Gram-positive & Gram-negative bacteria
Features of Capsules
Barrier to toxic hydrophobic molecules (e.g. detergents)
Contain water à prevents desiccation
presence and composition are strain-specific
e.g streptococcus pneumoniae --> meningitis, pneumonia, sepsis
non capsulated strains are mainly
antivirulent
active transport - group translocation
Substrate modified, generally phosphorylated, during transport
E.g. phosphotransferase system (PTS system)
The energy is provided by the PEP passed along chain of enzymes
Modification of the sugar à maintains concentration gradient
regulation of metabolism in bacteria
Adaption to varying supply of carbon sources in different niches
Gluconeogenesis and TCA cycle --> essential when E.coli infects the urinary tract
Glycolysis and Entner-Duodoroff pathway --> growth in the intestinal trac
features of listeria
Gram positive rods
Found in coils, farms, dust and intestinal tact
Use of host sugar phosphates via specific transporter activated in hosts
Promote rapid intracellular growth
listeria monocytes
Major human food borne pathogen
Can cause septicaemia abortion and meningoencephalitis
Direct cell to cell spread causes avoidance of extracellular defences
what type of ribosomes are in bacteria
70s
why are bacterial ribosomes targets for antibacterial drugs
very different from eukaryotic ribosomes = more specific
features of bacterial cell membrane
lipid bilayer structure
similar to eukaryotic but no steroids such as cholesterol
features of bacterial cell wall
rigid layers around cytoplasm
peptidoglycan - mucopeptide or murein
polysaccharide chains with peptide cross links
resists osmotic pressure and determines cell shape
signals to innate cells of bacterial presence
Gram positive basteria cell wall
chains of glycerol phosphate/ribitol phosphate
bound covalently to peptidoglycan
provide rigidity
cell wall - gram negative
more complex than G+
thinner peptidoglycan than G+
absence of teichoic and lipoteichoic acids
periplasmic space of Gram negative contains:
transport systems for iron, proteins, sugars
hydrolytic enzymes —> breakdown of large macromolecules
virulence factors such as collagenases, proteases and beta-lactamase
what makes electron transfer possible in aerobic respiration
presence of components that exist in oxidised or reduced forms, e.g Fe-S clusters
what is the final electron accepter in aerobic respiration
molecular oxygen
what are the key components of aerobic respiration in bacteria
Dehydrogenases, quinones, cytochromes and one or more terminal oxidases
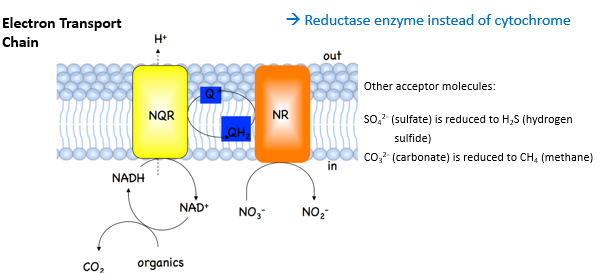
what is the final electron acceptor in anaerobic respiration
an inorganic compound that is’t O2
what happens in anaerobic respiration in bacteria
NO3- (nitrate) is reduced to NO2 (nitrite) via nitrate reductase
Total ATP yield less as only part of Krebs cycle
features of fermentation
Releases energy from oxidation of organic molecules
Does not use the Krebs cycle or the electron transport chain
Derive ATP from substrate-level phosphorylation
Does not require oxygen (anaerobic process)
Recycle NADH back to NAD+
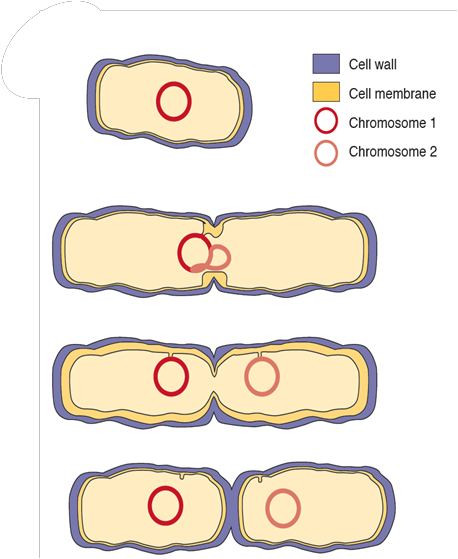
process of binary fission
Elongation of cell wall, cell membrane and overall volume, starts chromosome duplication
Septum wall grows inward, chromosomes are pulled towards opposite ends
Septum is synthesised and cell membrane starts to separate into chamber
fermentation - dental disease
Diets with high sugar content
Lactic acid bacteria --> ferments sugar --> lactic acid
Dissolve calcium phosphate
Bacterial proteolytic enzymes --> degrades supporting matrix
use of energy and metabolism in TB
Host cells lipids are essential carbon sources during infection
Switch from carbohydrate based metabolism of lipid substrates via glyoxylate shunt enzymeisocotrate lyase --> avoids carbon loss during oxidation in TCA cycle
Specific substrates are used at different stages of infection
Can survive under energetically unfavourable and poorly oxygenate conditions
what is an FTS protein
filamentous temperature sensitive
act to form the divisome —> a cell division apparatus that forms a septal ring and defines division plane
FtsZ
tubulin-like GTPasesZ
ZipA
ftsZ anchor
Ftsl
peptidoglycan biosynthesis protein
FtsK
help in chromosome separation
FtsA
similar to actin, ATPase activity
What triggers endospore formation
survival mechanism —> triggered by adverse conditions
Bacterial genome is sequested in a safe place until environmental conditions improve
how is the spore protected
Mother cell secretes protein coat (calcium dipicolinate) to protect spore à then lyses to release spore
what is in the core of the spore
DNA, RNA, protein
what is in inner membrane of spore
lipids/proteins
what is endospore wall made of
peptidoglycan
Diplicolinic acid
form complex with calcium --> bind water --> spore become drier and compact
obligate oxygen requirements
yes
aerobic respiration
facultative oxygen requirements
can use with or without
aerobic/anaerobic/fermentation
microaerophilic
work in low oxygen
aerobic respiration
aerotolerant
work with or without oxygen
fermentation/anaerobic
signal
environmental change, signalling molecule
sensor
usually ligand binding, able to change protein confirmation for protein-protein interactions
regulator
usually specific DNA binding protein - binds in control region
regulon
group of genes controlled by a common regulator
Two component system
Consist of a sensor kinase (detects signal) and a response regulator (activates gene expression).
PhoP/PhoQ in Salmonella, which responds to magnesium levels and triggers expression of virulence factors.
Environmental regulation - 2cs —> gene regulation
Interaction with transcription protein activator/repressor
Effects on RNA-polymerase sigma factors
DNA binding regulator
biofilm
a structured community of bacterial cells enclosed in a self produced polymeric matrix
quorum sensing
When population density is high enough, they turn on genes together — including toxins, enzymes, and biofilm factors.
role of quorum sensing
Control of virulence gene expression
Facilitate dispersion of biofilm
HHQ and PQS modulate inflammatory and immune response in mammals
Attenuates LPS induced inflammation and allows for establishment of infection
Toxin production increases inflammation
How do gene regulatory circuits work together for colonization & pathogenesis?
Bacterial pathogens use cascades and feedback loops to time their actions:
Early genes: Adhesins, pili/fimbriae → for attachment to host.
Mid-phase genes: Toxins, invasion systems (like T3SS) → for invasion and immune evasion.
Late genes: Nutrient acquisition, evasion, stress survival → for long-term survival.
How is gene expression managed at a community level (biofilms)?
Biofilm matrix genes (like EPS production) are upregulated.
Virulence genes may be suppressed or timed depending on the stage of biofilm development.
Stress resistance genes (e.g., oxidative stress, antibiotic resistance) are highly expressed.
Bacteria deep in the biofilm get less oxygen/nutrients, so gene expression varies by position
role of bacterial cell envelope
modulates bacterial interactions with their environment
effect of secreted proteins from mutualistic and pathogenic associations
modify host physiology → necessary for bacterial survival → e.g. promote colonization of host (toxins and effector proteins)
what are secretion systems
Protein export machinery outside the cells & into other cells.
Difference in export depending on Gram -positive or –negative bacteria
features of SEC
general secretion
Requires signal peptide leader sequence
moves unfolded proteins
features of TAT
twin arginine translocation
moves folded proteins that have twin arginine motif in signal sequence
how many layers of lipids in gram negative cell wall
2
how does cholera cause diarrhoea
Cholera toxin (CTX) --> binds to GM1 ganglioside receptor
CTX endocytosed and trafficked to EPR
Activates adenyl cyclase system, increasing cAMP levels
cAMP triggers inhibition of reabsorption of Na+/K ions and hypersecretion of chloride ions
Osmotic gradient causes movement of H2O into intestinal lumen --> diarrhoea
features of T1SS
One-step system: Transports proteins directly from cytoplasm to outside the cell.
Doesn’t require a periplasmic intermediate.
Substrates: Toxins, enzymes (like proteases).
Common in Gram-negative bacteria.
function of T3SS
Known as the “injectisome”.
One-step system: Directly injects proteins (effectors) into host cell cytoplasm.
Highly associated with virulence.
Found in bacteria like Salmonella, Shigella, Yersinia, and E. coli.
Regulation of T3SS gene expression
TTSS contains >20 proteins
gene expression coupled to secretion
signals, regulators and networks vary from one system to another
Salmonella typhimurium is …
gram negative
T3SS-1
Early phase invasion of enterocytes and M cells
Activation of pro-inflammatory responses
T3SS - 2
Later phase of infection
Intracellular survival and replication within macrophages
features of T4SS
Transfers both proteins and DNA.
Can target other bacteria or host cells.
Used in conjugation (DNA sharing) and pathogenesis.
features of T6SS
A contractile nanomachine, like a molecular crossbow.
Injects toxic proteins into other bacteria or host cells.
Involved in bacterial competition and virulence.
cholera
what are dynamic firing cycles in T6SS
expulsion of a cell-puncturing device loaded with multiple toxins
T7SS
Used by TB
ATPase driven export
specialised to export proteins across thick cell wall
role of Tir
triggers actin polymerisation and pedestal formation underneath attached bacterium
How to distinguish between commensal and pathogenic E. coli?
Intestinal cells can sense the T3SS present in pathogenic E. coli
Trigger NF-KB activation in a non-TLR dependent mechanism
T3SS recognition by the immune response to differentiate between pathogen & commensal
pathogenic
disease causing bacteria, affects all normal host defences
non-pathogenic
organisms invade an individual without causing any obvious detectable symptoms
commensal
an organism that is found normally on those parts of the body that are exposed or communicate to the external environment
changes in normal flora - hormonal physiology and development
Female genital tract and lactobacilli
changes in normal flora - antibiotics select for a resistant flora
Candida overgrowth in mouth/vagina
C diff - antibiotic associated colitis
changes in normal flora - new organisms
Neonate from maternal tract during birth
bacteria need…
iron
to adhere to host mucosa
adherence in gram positive bacteria
adherence to host cells e.g pili, fimbriae
prevents bacteria from being washed off by significant fluid flow
formation of a microcolony
relevance to pathogenicity
exotoxin
secreted by a bacterium into the environment
endotoxin
LPS of gram negative bacteria
enterotoxin
an exotoxin only active in GI tract
iron sequestering
Iron is essential
Limiting in host
Sequestration is critical for in vivo success
Produce iron binding compounds called siderophores
Capture from the host
defensive factors - polysaccharides capsule
negatively charged
Slime
Biofilm
defensive factors - immunologic mechanisms
LPS - cytokine stimulation --> septic shock
Outer membrane proteins
stages of viral replication
adsorption
entry
uncoating
genome replication and transcription
synthesis of virus components
assembly
release and maturation
features of attachemetn
random collision
not all cells carrying a receptor for a particular virus can be infected by that virus
most neutralising antibodies are specific for virion attachment proteins
what is the influenza virus receptor
sialic acid
What are the 2 mechanisms of entry
endocytosis
fusion of virus envelope with cell membrane
what is uncoating
release of viral genome
lysosomes strip off the virus protein coat
virion can no longer be detected - eclipse period
HIV attachment and entry
SU protein attached to CD4 on target cell
CD4 isn’t sufficient —> co-receptor required e.g chemokines
Influenza entry and uncoating
low pH in the endosome
causes conformation change in HA
allows fusion of viral envelope with endosomal membrane
SARS CoV attachment and entry
S glycoprotein cleaved by TMPRSS2
facilitates viral activation
essential host factors for SARS-coV-2 pathogenicity
TMPRSS2 is a potential target for antiviral drugs
Non-enveloped virus entry and uncoating
e.g polio
after receptor attachment, protein taken into endosome
conformational changes to the viral structural proteins results in:
formation of a pore in the endosomal membrane
viral RNA released into cytoplasm