MCAT Biology Review 2025-26
1/296
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
297 Terms
1665 Robert Hooke
assembled microscope and found cells
1674 Leewenhock
1st man to view living cells
Tenets of Cell Theory
All living things are composed of ccells
cell is the most basic unit of life
cells arise only from pre-exisiting cells
cells carry genetic information in DNA form to be passed onto daughter cells
What tenets of cell theory do viruses violate that make them non-living?
cells arise only from pre-exisiting cells
cells carry genetic information in DNA form to be passed onto daughter cells
Eukaryotic Cells
in multi cell orginisms
nucleus enclosed in membrane
membrane bound organelles=> compartmentalization of function
reproduced by mitosis
cytosol
liquid that allows diffusion of molecules through cell
nucleus
Function: holds the genetic material encoded in DNA which is organized into chromosomes
surrounded by nucleus membrane
nuclear pores in membrane allow for selective material to enter and leave
DNA has coding regions called genes wound against proteins called histomes
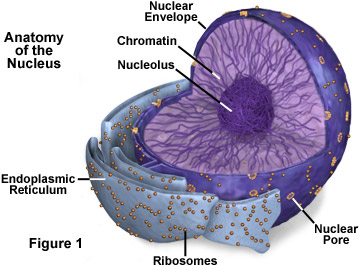
nucleolus
Function: Rrna Synthesis
25% of the colume of nucleus, the darker spot
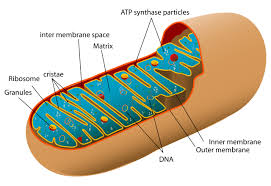
mitochondria
Function: provides energy for the cell and performs apoptosis
orginated in prokoyatic cell
semi autonomous
has its own genes
replicates independently
cytoplasmic inheritance
outer-membrane → The Matrix → inner-membrane (contains Electron Transport Chain material)
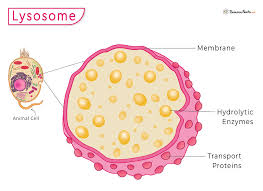
Lysosomes
Function: causes apoptosis when hydrolytic enzymes are released
works with endosomes to break down many substrates
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
series of interconnected membranes that are actually contiguous with the nuclear envelope
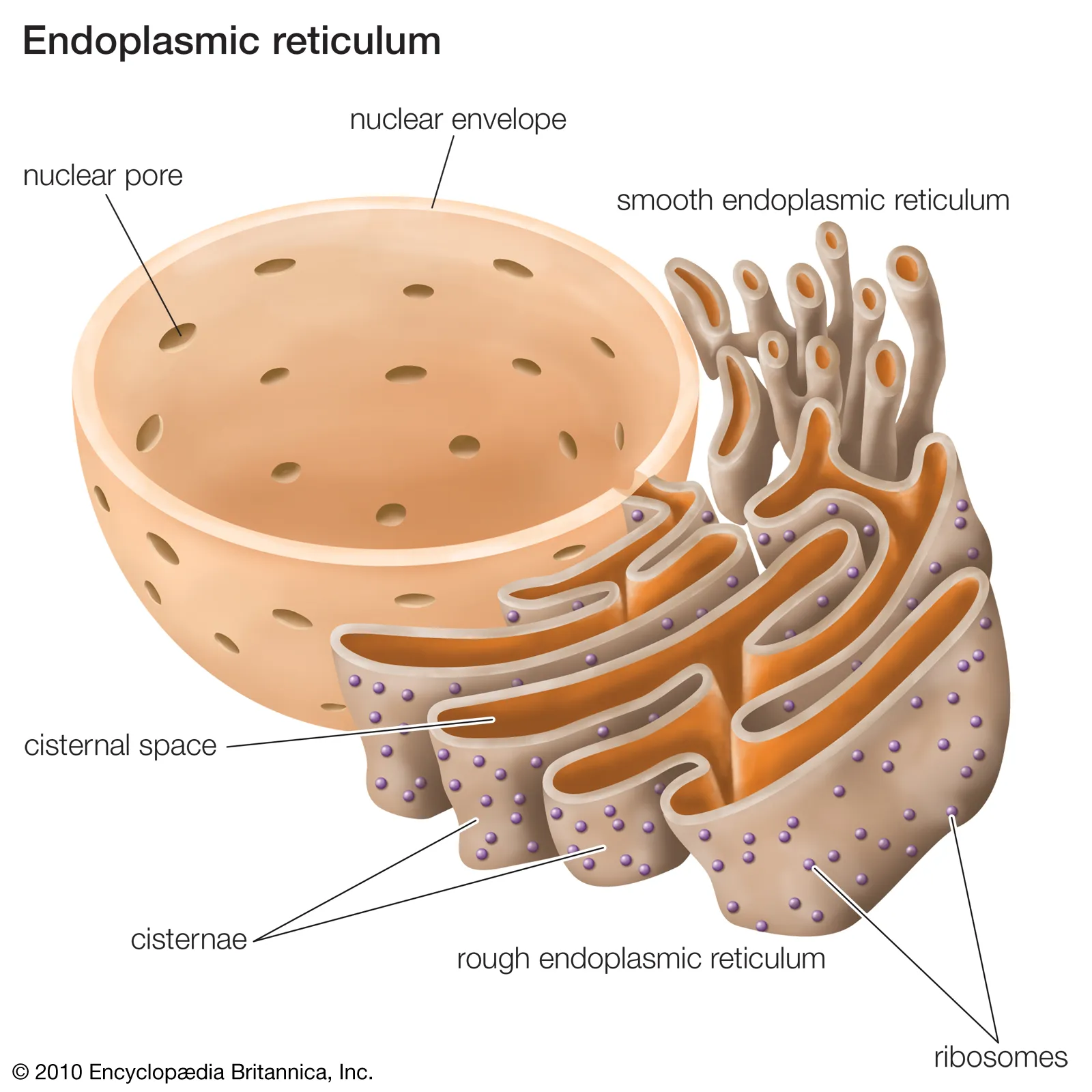
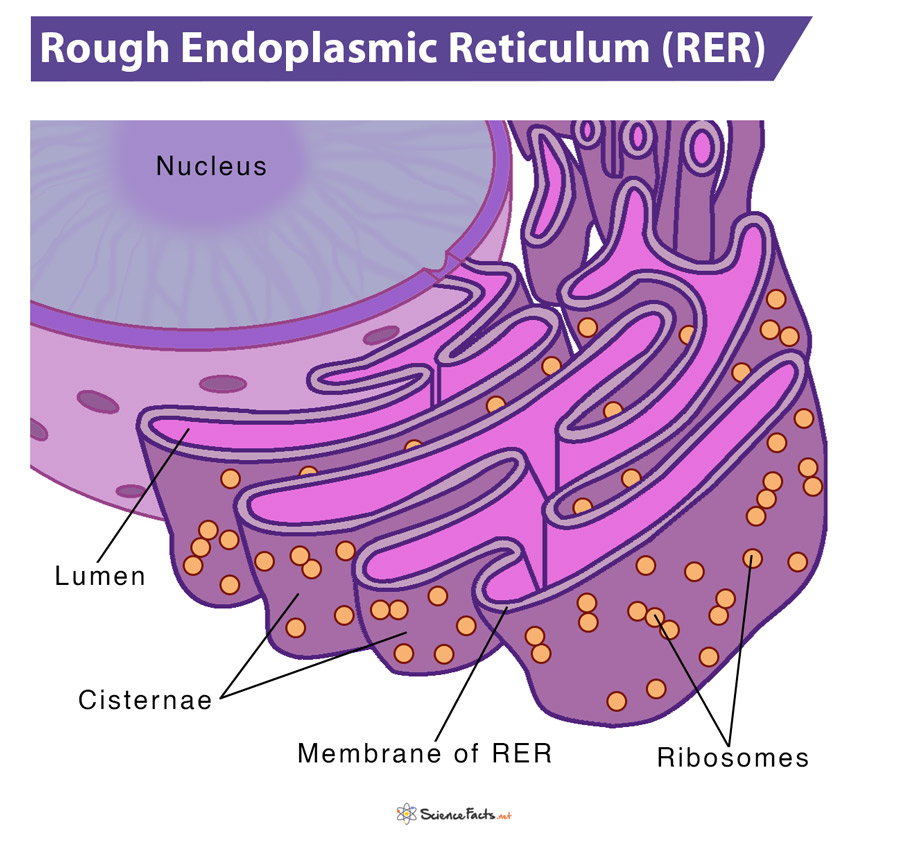
Rough ER
Function: permits the translation of proteins desired for direct secretion into the lumen
studded with ribosomes
Smooth ER
Function: lipid synthesis and detox, transports proteins to the golgi
Golgi Apparatus
Function: proteins are modified, repackage products in vesicles, exocytosis
Peroxisomes
Function: contains hydrogen peroxide, breaks down fatty acid chains, sythesis of phosphlipids and enzymes
Cytoskeloton
Function: structure of cell and shape maintenance
Microfilaments
Function: cytokinesis and forms cleavage furrow
made of actin (resistant to compression and fracture) which provides protection for the cell
actin filaments can also use ATP
Predominant Protein: actin
Microtubles
Function: provides primary pathways for motor proteins kinesin and dynein to carry vesicles (cilla and flagella)
hallow polymers of tublin proteins
Predominant Protein: tublin
Flagella
projections from cell involved of the movement of material inside the cell
Cilla
projections from cell involved of the movement of material outside the cell
9 + 2 structure
Flagella and Cilla Both have
9 pairs of microtubles in outer ring and two microtubles inside
centrioles
found in centrosome (cell region) and organizing cneters for microtubles and have a hallow center
Intermediate filaments
cell to cell adhesion or maintenance of the cytoskeleton; anchors organelles
Predominant Protein: keratin and desmin
Epithelial Tissue
Function: provides protection against pathogens & desecration, absorbtion, secretion, and sensation (constitutes the parenchyma or the functional part of the organ)
polarized (one side facing the lumen or hallow cavity and one side facing outside world)
different classifications
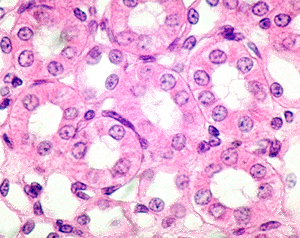
simple epithelia
one layer of cells
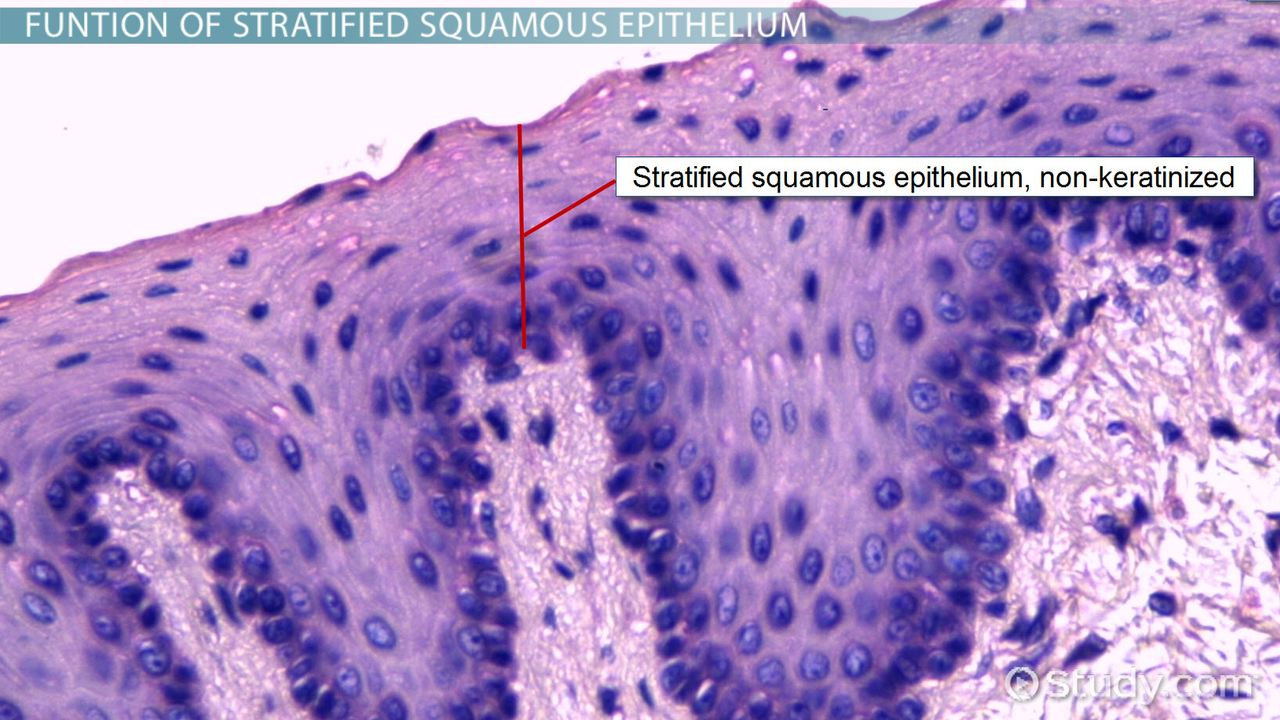
stratified epithelia
multiple layers
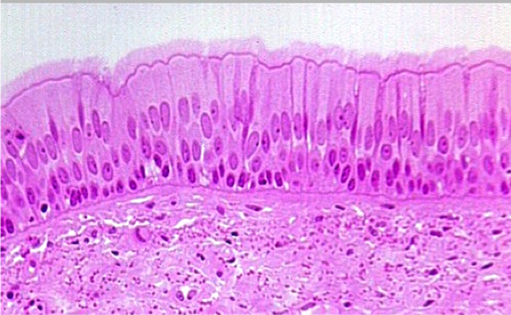
psedostratified epithelia
appear to have multiple layers but actually have one
cubidol
cube shaped
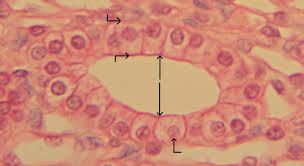
columnar
long and thin
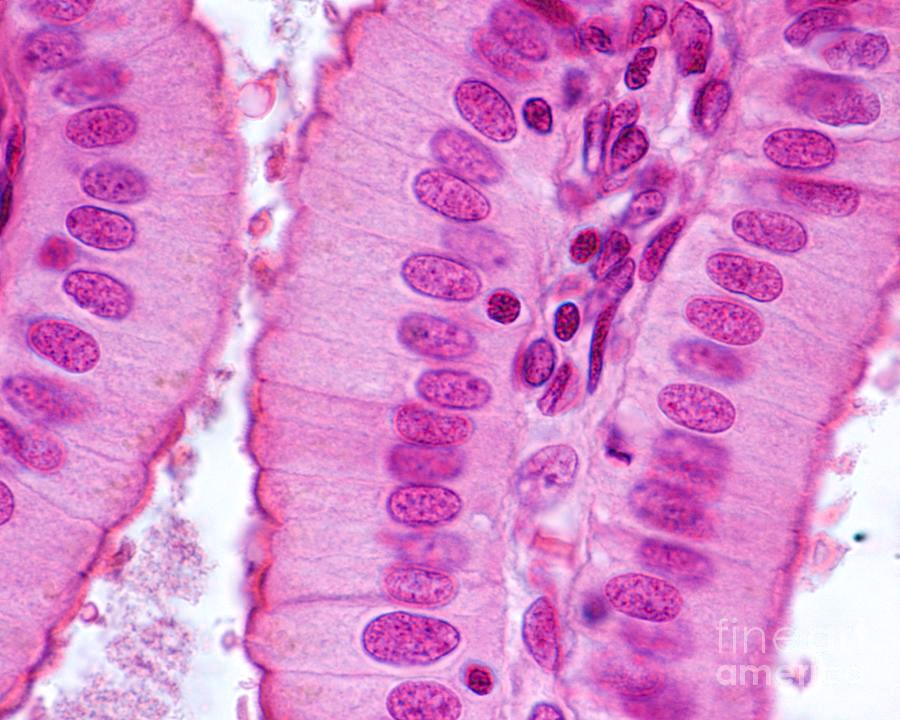
squamous
flat and scale like
Basement Membrane
the connective tissue that allows epithelial tissue to be joined together
Connective tissue
suppports the body and provides the framework for the epithelial cells to carry out their functions
forms the extracelleur matrix
prokaryotes
cells that do not contain membrane bound organelles; they contain their genome in a single circular molecule of DNA located in the nucleoid region
archaea
extremophiles (mostly), often use chemosythesis and similar to both eukaryotes (translation, RNA polymerases, histones) and bacteria (single circular chromosomes, divide by binary fission or budding)
bacteria
similar structures to eukaryotes, complex relationships with humans including mutualistic symbiosis and pathogenesis
Eukarya
is the only non prokaryotic domain
Cocci
spherical bacteria
Bacilli
rod shaped bacteria
Spirilli
spiral shaped bacteria
Obligate aerobes
require oxygen for metabolism
obligate anaerobes
cannot survive in oxygen containing enviroments and can only carry out anaerobic metabolism
facultative anaerobes
can survive in environments with or without oxygen containing environment
aerotolerant anerobes
cannot use oxygen for metabolism, but can survive in oxygen-containing environments
Gram positive bacteria
have a thick cell wall composed of peptidoglycan and lipoteichoic acid
Gram Negative Bacteria
thin cell wall composed of peptidoglycan and an outer membrane containing phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides
Diploid (2n)
cells that have two copies of each chromosomes
Haploid (n)
cells have one copy
interphase
G1, S, G2 phases that is where DNA is uncoiled in the form of chromatin
G1 stage
pre-synthetic gap, cells create organelles for energy and protein production, and increase their size
Restriction point: during which the DNA is checked for quality, must be passed for the cell to move into the S stage
S (synthesis) stage
further cell growth and replication of organelles in preparation for mitosis, quality checkpoint before mitosis
M stage
mitosis and cytokinesis occurs
G0 stage
the cell performs its functions without preparing for divsion
p53
plays a role in the two major checkpoints of the cell cycle
Cyclins and Cyclin Dependent Kinases (CDKs)
rise and fall during the cell cycle, cyclins bind to CDKs which activate transcription factors for next stage of cycle
Cancer
when cell cycle control becomes deranged which allows damaged cells to replicate; these type of cells will release factors that allow them to delocalize and invade nearby tissues (metastasize)
Somatic Cell
where mitosis produce two genetic identical diploid daughter cells from a single cell
Prophase
the chromosomes condense, the nuclear membrane dissolves, nucleoli dissapear, centrioles migrate to opposite sides of the cell and the spindle appratus begins to form
— kinetochore of each chromosome is contacted by a spindle fiber
Metaphase
chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate
Anaphase
sister chromatids are separated and pulled to opposite poles
Telophase
the nuclear membrane reforms, spindle apparatus disappears, and cytosol and organelles split between daughter cells through cytokinesis
mieosis
occurs in gametocytes and produces up to four haploid gametes
Meiosis
one round of replication and two rounds of division
Meiosis I
homologous parts of chromosomes are separated from each other
Homologues
are chromosomes that are given the same number, but are of opposite parental origin
Prophase I
same events occur EXCEPT:
homologues come together and intertwine in a process called synapsis
Four chromosomes called tetrad have crossing over that occurs to exchange genetic materal
Mendels Second Law of Independent Assortment
Mendels Second Law of Independent Assortment
crossing over that occurs in prophase I
Metaphase I
homologous chromosomes line up on opposite sides of the metaphase plate
Anaphase I
homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite pole of the cell; account for Mendels First Law of Segregation
Mendels First Law of Segregation
during the formation of reproductive cells (gametes) of Anaphase I , the two alleles for each trait separate, so that each gamete receives only one allele
Telophase I
the chromosomes may or may not fully decondence and the cell may enter interkinesis after cytokinesis
Meiosis II
sister chromotids are seperated from each other in a process that is functionally identical to mitosis
Sister Chromotids
are copies of the same DNA held together at the centromere
X Chromosome
X linked genes are sex linked disorders
males are hemizygous with respect to the unpaired genes on the X chromosome so they will express sex linked disorders even if they have one recessive allele while females will not
Y chromosome
carries little genetic information, but does contain SRY gene which cause the gonads to differentiate into testes
Sperm
develop in the seminferous tubiles in the testes; norished by sertoli cells
interstitial cells of Leydig
in the testes, secrete testosterone and other male sex hormones
scrotum
where the testes are located which hangs outside of the abdominal cavity and has a temperature 2 to 4 degrees celcius lower than the rest than the rest of the money
epididymis
sperm gain mobility here once formed and are stored there until ejaculation
Path of ejaculation
Vas Deferens —→ ejaculatory duct —→ uretha —→ penis
seminal vesicles
contribute fructose to nourish sperm and produce alkaline fluid
prostate gland
produces alkaline fluid
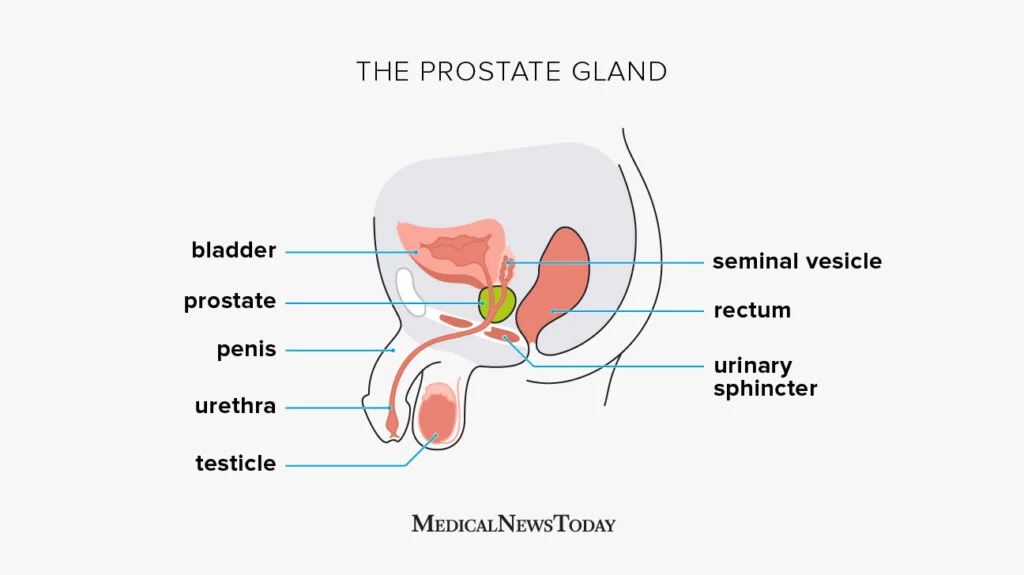
bulbourethral glands
produce a clear viscous fluid that cleans out any remnants of urine and lubricates the urethra during sexual arousal
semen
is composed of sperm and seminal fluid from the glands above
spermatogenesis
four haploid sperm are produced from a spermatogonium
Primary Spermatocytes
after S stage, the germ cells are called….
secondary spermatocytes
after meiosis I, the germ cells are called…
spermatids
after Meiosis II, the germ cells are called…
spermatozoa
after maturation, the germ cells are called…
head of sperm
contains the genetic material and is covered with an acrosome (modified Golgi apparatuss that contains enzymes that help sperm fuse with and penetrate the ovum)
mid-piece of sperm
generates ATP from fructose and contains many mitochondria
flagellum of sperm
promotes motility
Ova
are produced in follicles in the ovaries
Ovulation
once each moth, the eggs are ovulated into the peritoneal sac and is drawn into the fallopian tube or ovidact
Uterus
fallopian tubes are connected; the bottom is called the cervix
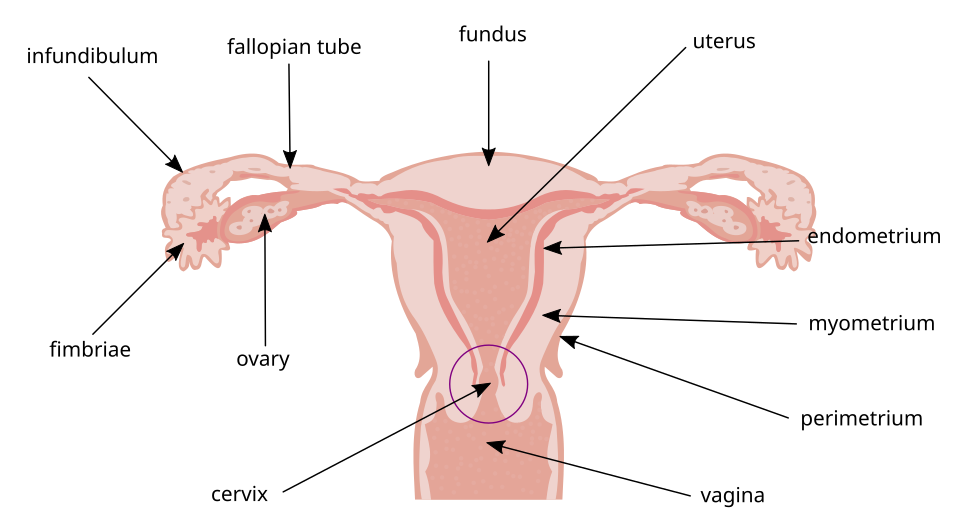
Vaginal Canal
lies below the cervix and is the site where sperm are deposited during intercourse; site of childbirth
Vulva
the external parts of the female genital
Oogenesis
one haploid ovum and a variable number of polar bodies are formed from an oogonium
Primary oocytes
at birth, all oogonia have already undergone replication and are considered…
Secondary oocytes
the ovulated egg each month and is arrested in metaphase II
Polar Body
Cytokinesis is uneven in oogenesis; the cell receiving very little cytoplasm and organelles