Chapter 23: The Digestive System Overview
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
Gastrointestinal Tract
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, intestines.
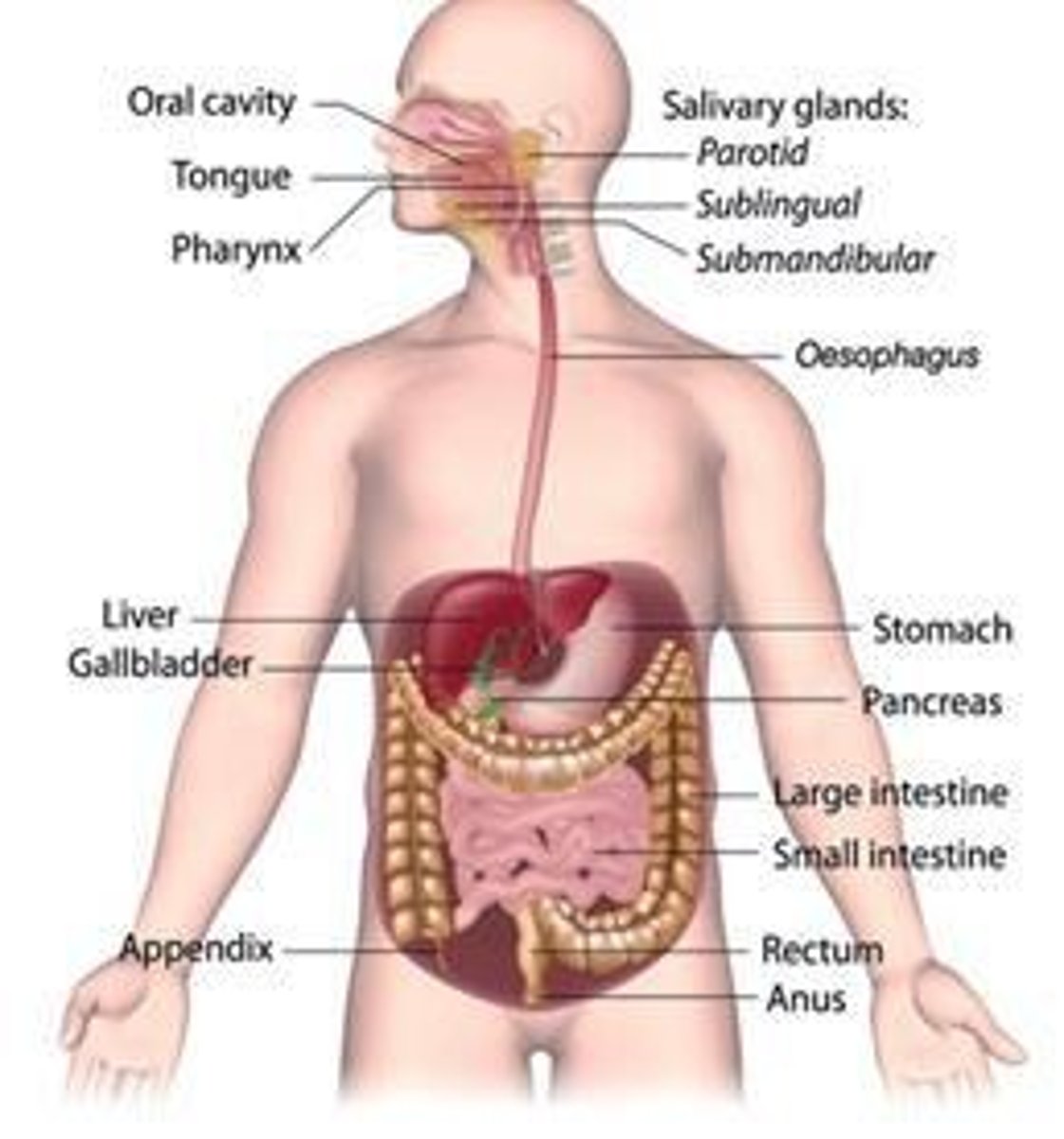
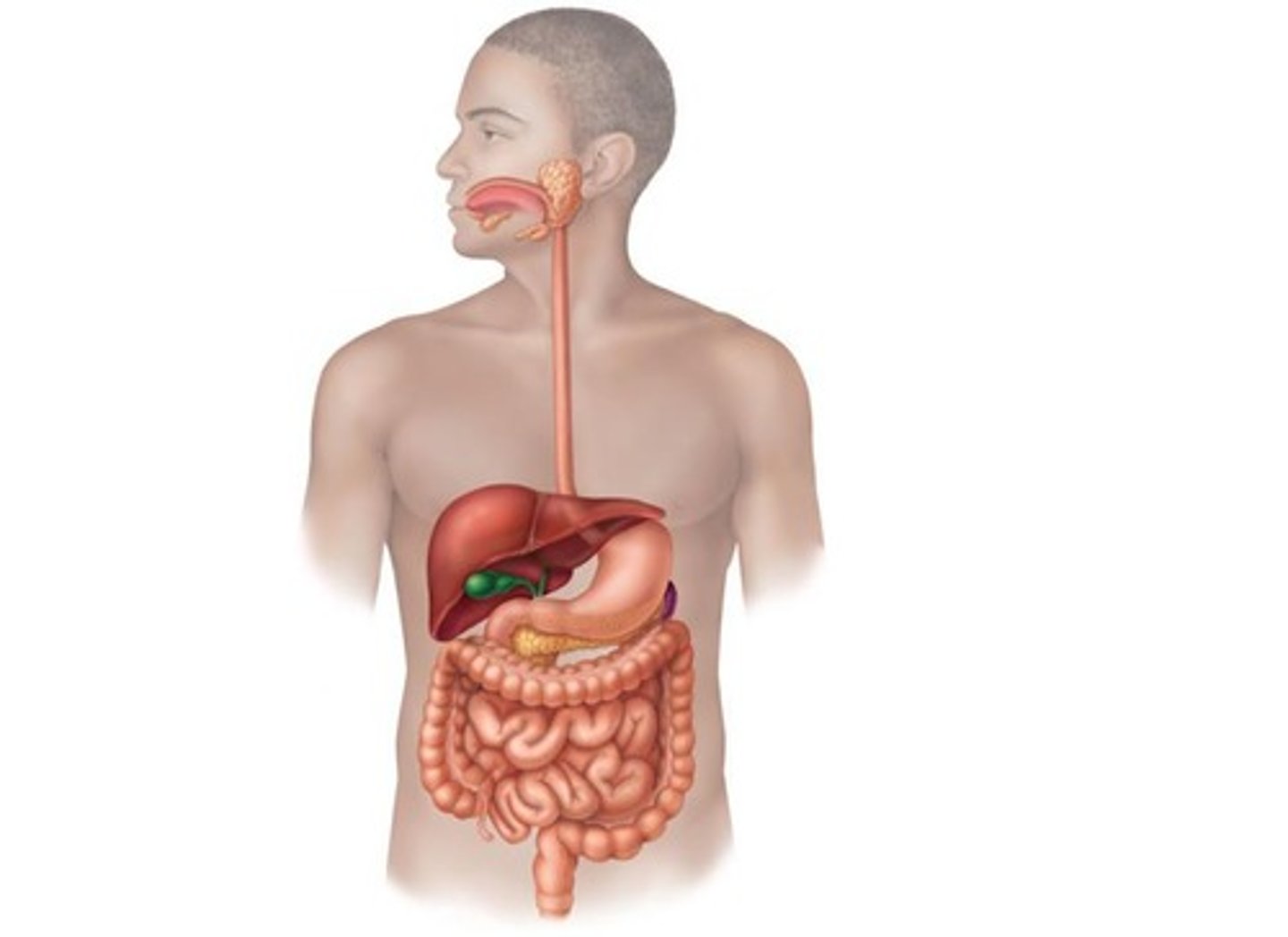
Accessory Digestive Organs
Organs aiding digestion: salivary glands, liver, pancreas.
Ingestion
Intake of food into the digestive system.
Mechanical Digestion
Physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces.
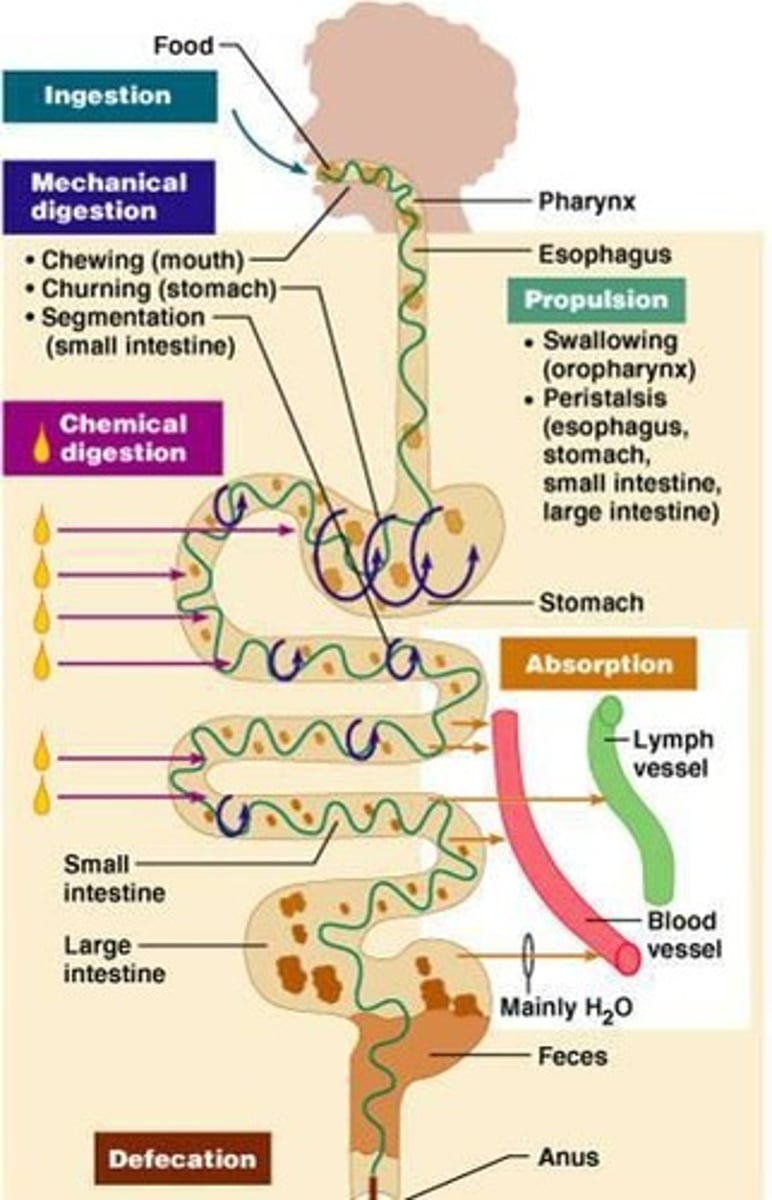
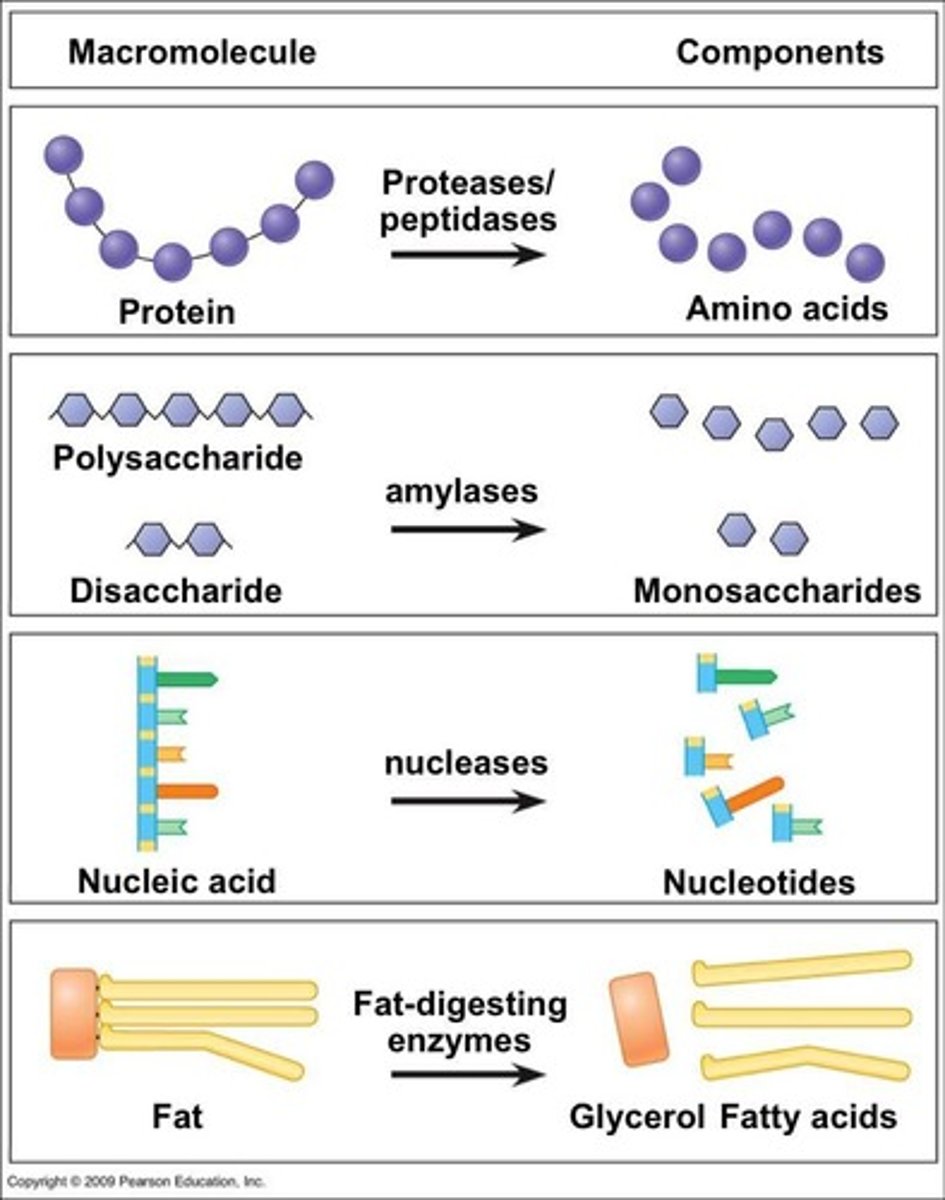
Chemical Digestion
Enzymatic breakdown of food into molecules.
Absorption
Nutrients taken into blood or lymph from intestines.
Defecation
Elimination of indigestible substances as feces.
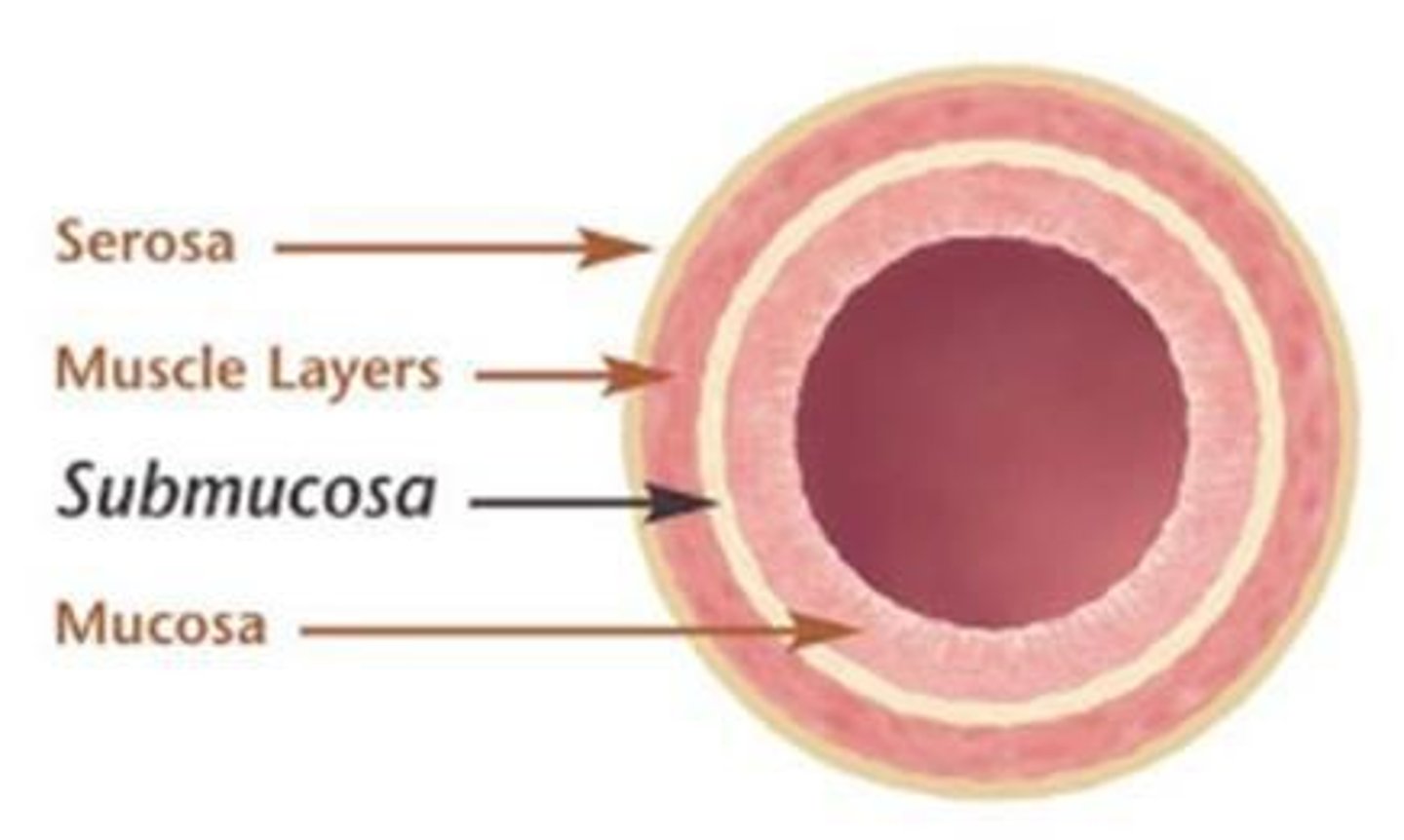
Mucosa
Innermost layer of the gastrointestinal tract.
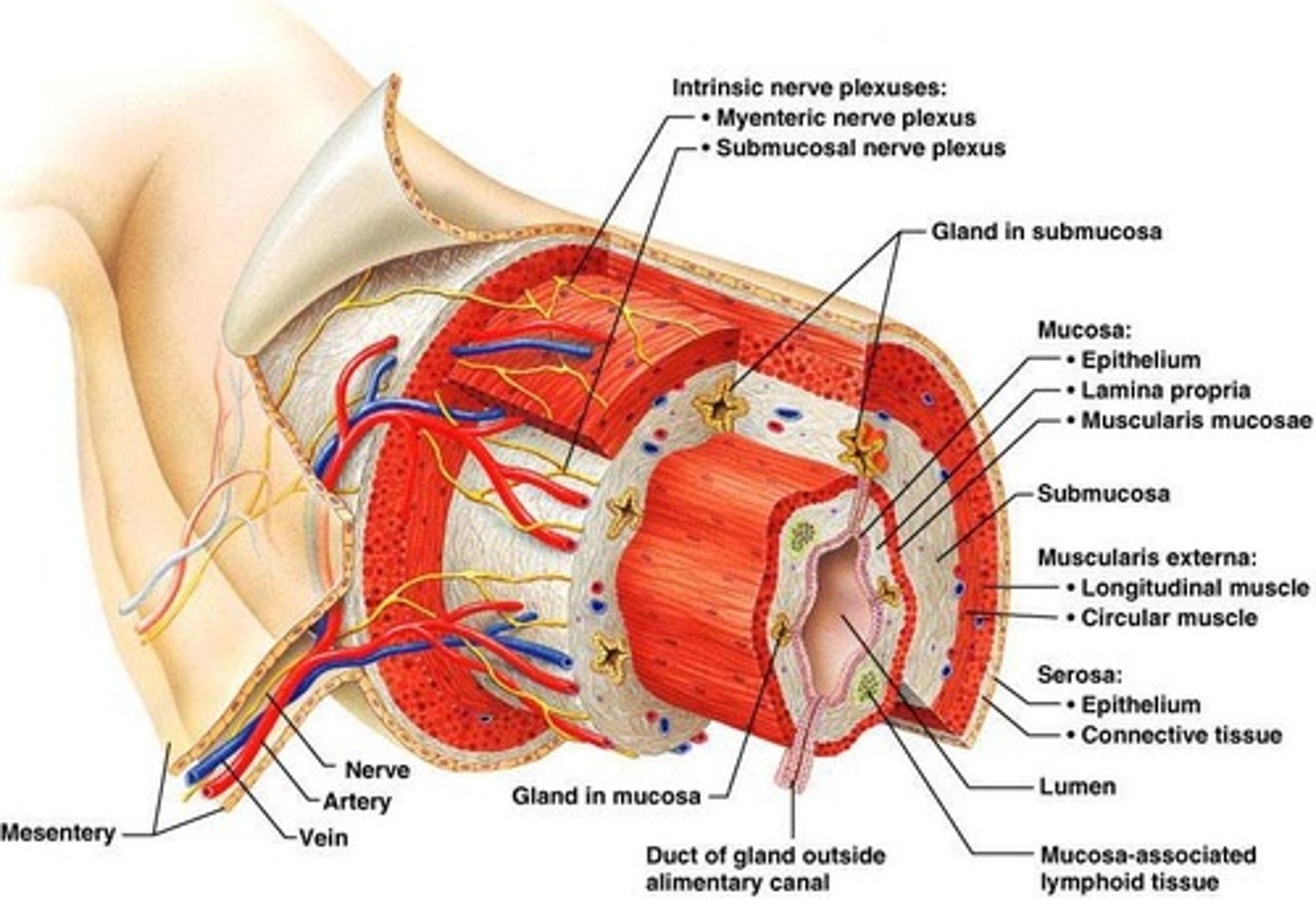
Submucosa
Layer containing blood vessels and nerve plexus.
Muscularis
Layer responsible for peristalsis and food movement.
Serosa
Outer layer covering abdominal organs.
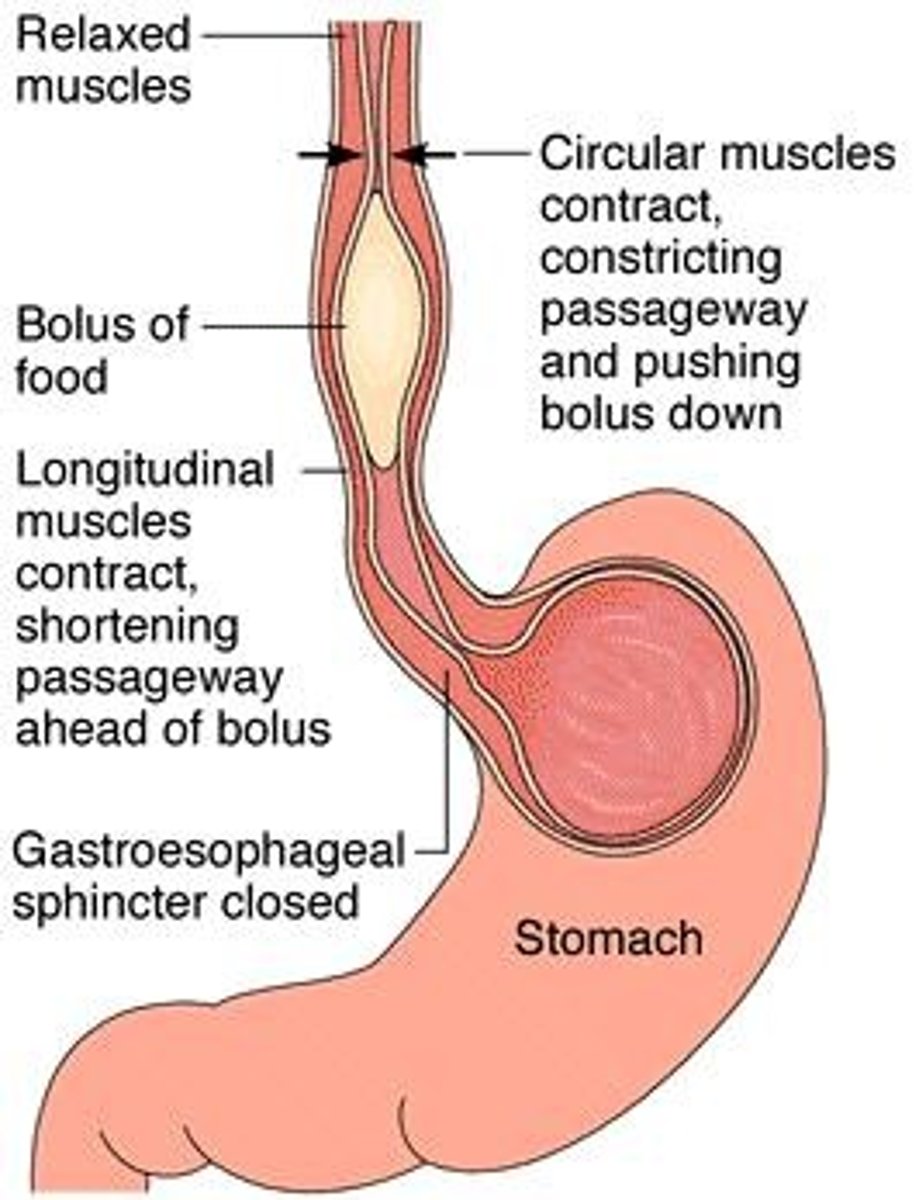
Peristalsis
Involuntary muscle contractions moving food through GIT.
Salivary Glands
Produce saliva to aid digestion and lubrication.
Parotid Gland
Largest salivary gland, secretes saliva into mouth.
Sublingual Gland
Salivary gland located under the tongue.
Submandibular Gland
Salivary gland located beneath the jaw.
Tongue
Muscular organ aiding in taste and food manipulation.
Palate
Roof of the mouth, separates oral cavity from nasal.
Uvula
Projection from soft palate, aids in swallowing.
Pharynx
Muscular tube connecting mouth to esophagus.
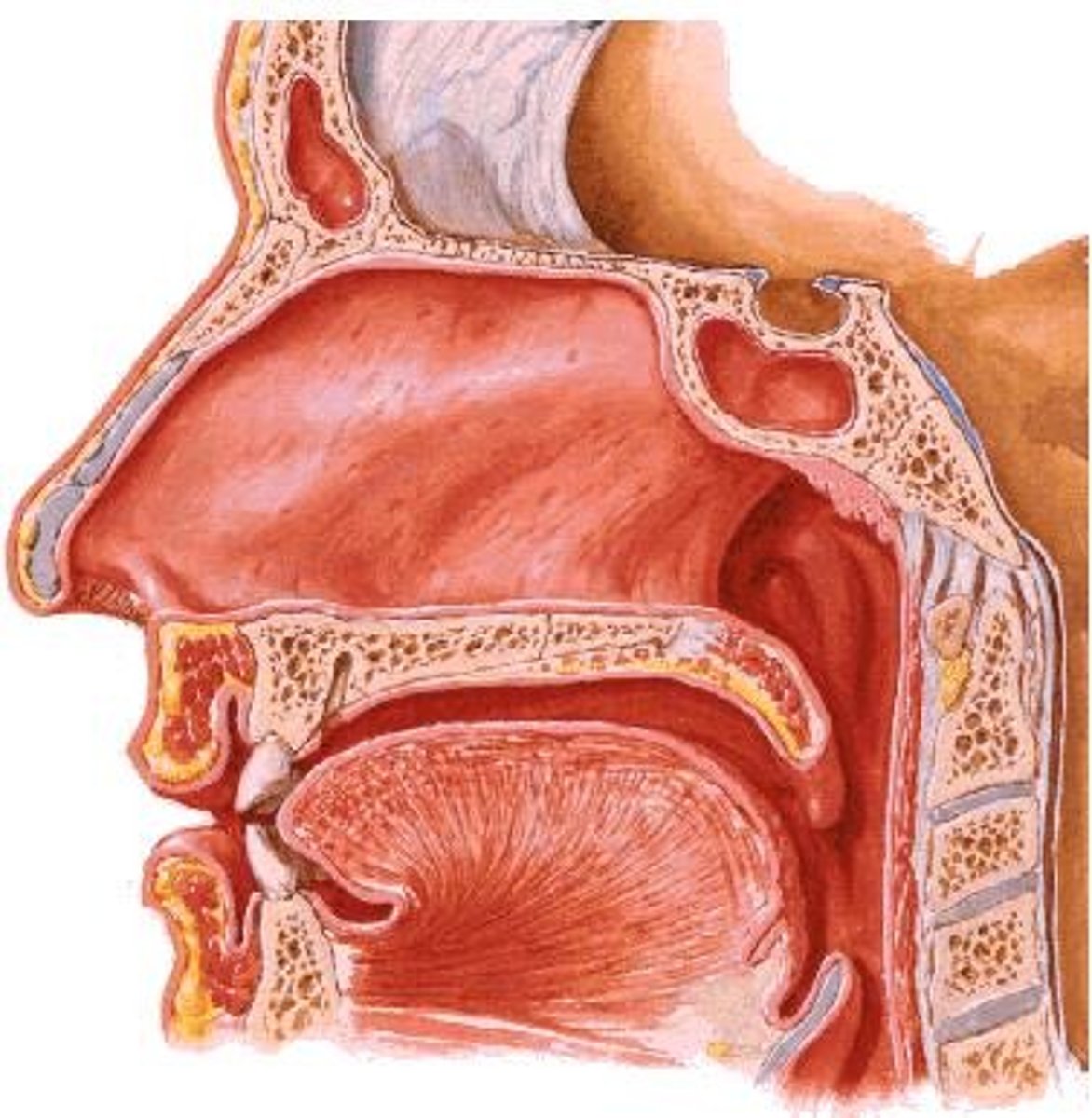
Esophagus
Tube transporting food from pharynx to stomach.
Stomach
Organ for food storage and initial digestion.
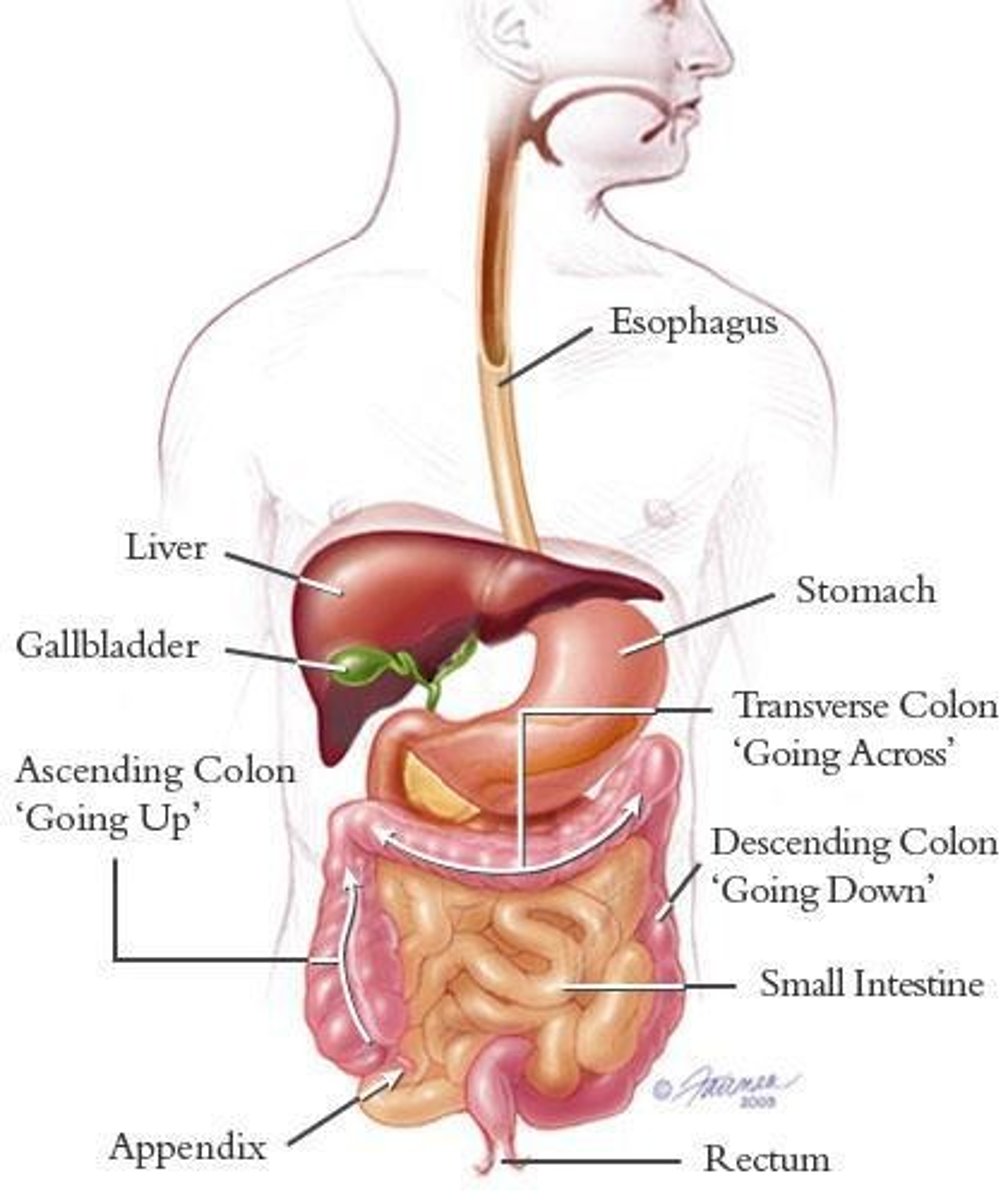
Small Intestine
Site for most digestion and nutrient absorption.
Large Intestine
Absorbs water and forms feces from indigestible waste.
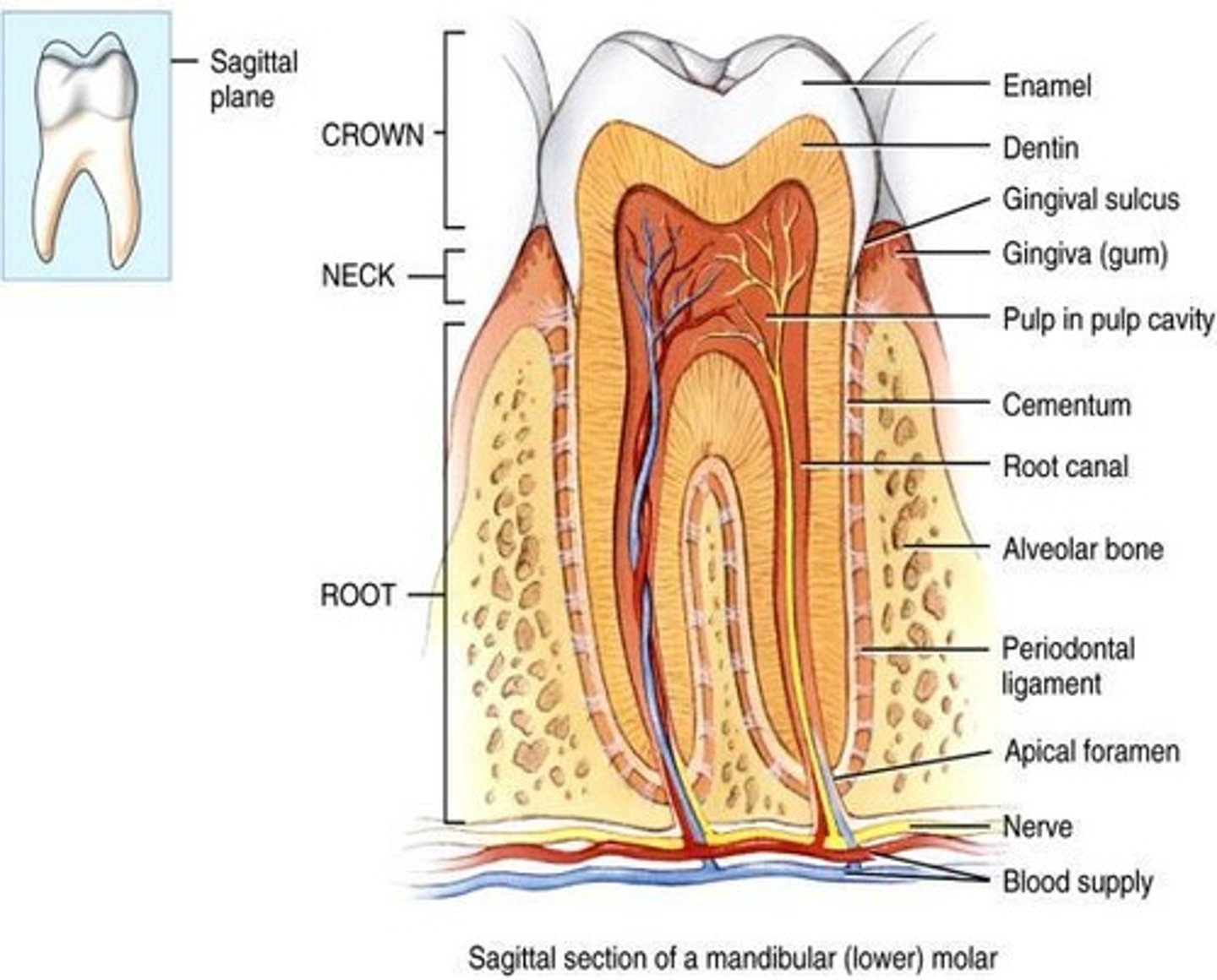
Teeth
Mechanical breakdown of food into smaller pieces.
Crown
Top part of the tooth above the gum line.
Root
Part of the tooth embedded in the jawbone.
Neck
Region between the crown and root of a tooth.
Enamel
Hardest substance in the body covering the crown.
Maxillary Teeth
Upper set of teeth in the mouth.
Mandibular Teeth
Lower set of teeth in the mouth.
Deciduous Teeth
Temporary teeth, 20 total in children.
Permanent Teeth
Adult teeth, 32 total in adults.
Incisors
8 teeth adapted for cutting food.
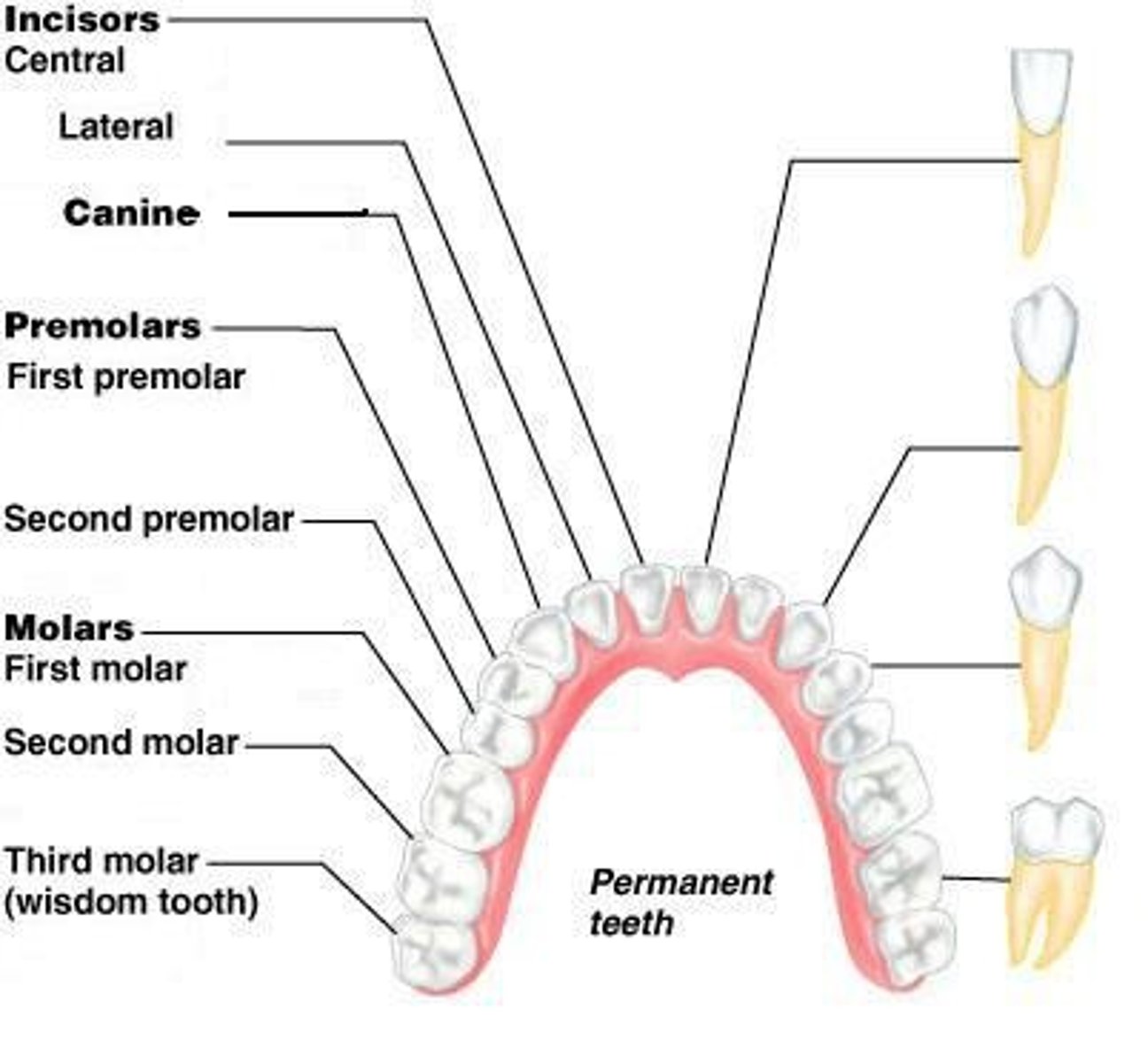
Canines
4 teeth adapted for tearing food.
Premolars
8 teeth adapted for grinding food.
Molars
12 teeth adapted for grinding food.
Saliva
Fluid that lubricates and begins digestion.
Salivary Amylase
Enzyme in saliva that digests carbohydrates.
Lingual Lipase
Enzyme that begins fat digestion in the mouth.
Upper Esophageal Sphincter
Regulates food entry into the esophagus.
Lower Esophageal Sphincter
Regulates food movement into the stomach.
Swallowing Phases
Two phases: voluntary and involuntary.
Bolus
Mass of food swallowed into the esophagus.
Gastroesophageal sphincter
Muscle controlling food entry into the stomach.
Cardia
Upper region of the stomach near the esophagus.
Fundus
Dome-shaped upper region of the stomach.
Body of stomach
Main central region of the stomach.
Pylorus
Canal-like lower part of the stomach.
Rugae
Folds in the stomach lining when empty.
Greater curvature
Left border of the stomach.
Lesser curvature
Right border of the stomach.
Chyme
Semi-liquid mixture of gastric juice and food.
Mucous neck cells
Cells secreting mucus in the stomach lining.
Parietal cells
Cells secreting HCl and intrinsic factor.
Chief cells
Cells secreting pepsinogen and gastric lipase.
G cells
Endocrine cells secreting gastrin hormone.
Acid reflux
Backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus.
Gastric juice
Digestive fluid containing HCl and enzymes.
Intrinsic factor
Essential for vitamin B12 absorption.
Pepsinogen
Inactive enzyme converted to pepsin in stomach.
Gastric lipase
Enzyme that digests fats in the stomach.
Cephalic phase
Initial response to food sight, smell, or taste.
Gastric phase
Hormonal response to food in the stomach.
Intestinal phase
Inhibition of gastric activity by duodenal hormones.
Ileocecal valve
Valve between ileum and cecum.
Bile duct
Duct delivering bile to the duodenum.
Pancreatic duct
Duct delivering pancreatic juice to the duodenum.
Villi
Finger-like projections enhancing absorption surface area.
Microvilli
Epithelial cell extensions increasing absorption capacity.
Lacteals
Lymphatic capillaries absorbing large fat molecules.
Absorptive cells
Cells with microvilli secreting digestive enzymes.
Goblet cells
Secrete mucus for lubrication and protection.
Paneth cells
Immune cells secreting antimicrobial lysozymes.
Enteroendocrine cells
Secrete hormones regulating digestive processes.
Gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP)
Inhibits stomach, stimulates insulin secretion.
Secretin
Stimulates bicarbonate and bile secretion; inhibits stomach.
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Stimulates pancreatic enzymes and bile release.
Brush border enzymes
Digestive enzymes secreted by absorptive cells.
Enterokinase
Activates trypsinogen into trypsin for protein digestion.
Amylase
Enzyme that digests starch into sugars.
Trypsinogen
Inactive form activated to digest proteins.
Chymotrypsinogen
Inactive form activated to digest proteins.
Carboxypeptidase
Enzyme that digests proteins into amino acids.
Lipase
Enzyme that digests lipids into fatty acids.
Bicarbonate ion
Neutralizes gastric acidity in small intestine.
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars absorbed into blood capillaries.
Fat-soluble vitamins
Vitamins A, D, E, K absorbed with fats.
Cecum
Blind pouch receiving ileum and appendix.
Ascending Colon
Vertical section on right side of abdomen.
Right Colic Flexure
Bend between ascending and transverse colon.
Transverse Colon
Horizontal section connecting right and left colic flexures.
Left Colic Flexure
Bend between transverse and descending colon.
Descending Colon
Vertical section on left side of abdomen.
Sigmoid Colon
S-shaped segment entering the pelvis.
Rectum
Final section of large intestine before anus.
Anal Canal
Passage leading to the anus, guarded by sphincter.
External Anal Sphincter
Skeletal muscle controlling voluntary defecation.
Functions of Large Intestine
Absorbs water and salts, forms feces.
Fermentation
Metabolic process converting sugars into acids or gases.