PoB Week2 Genes in families & linkage mapping
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Sex generates new genetic combinations
Independent segregation of 2 pairs of homologous chromosomes:
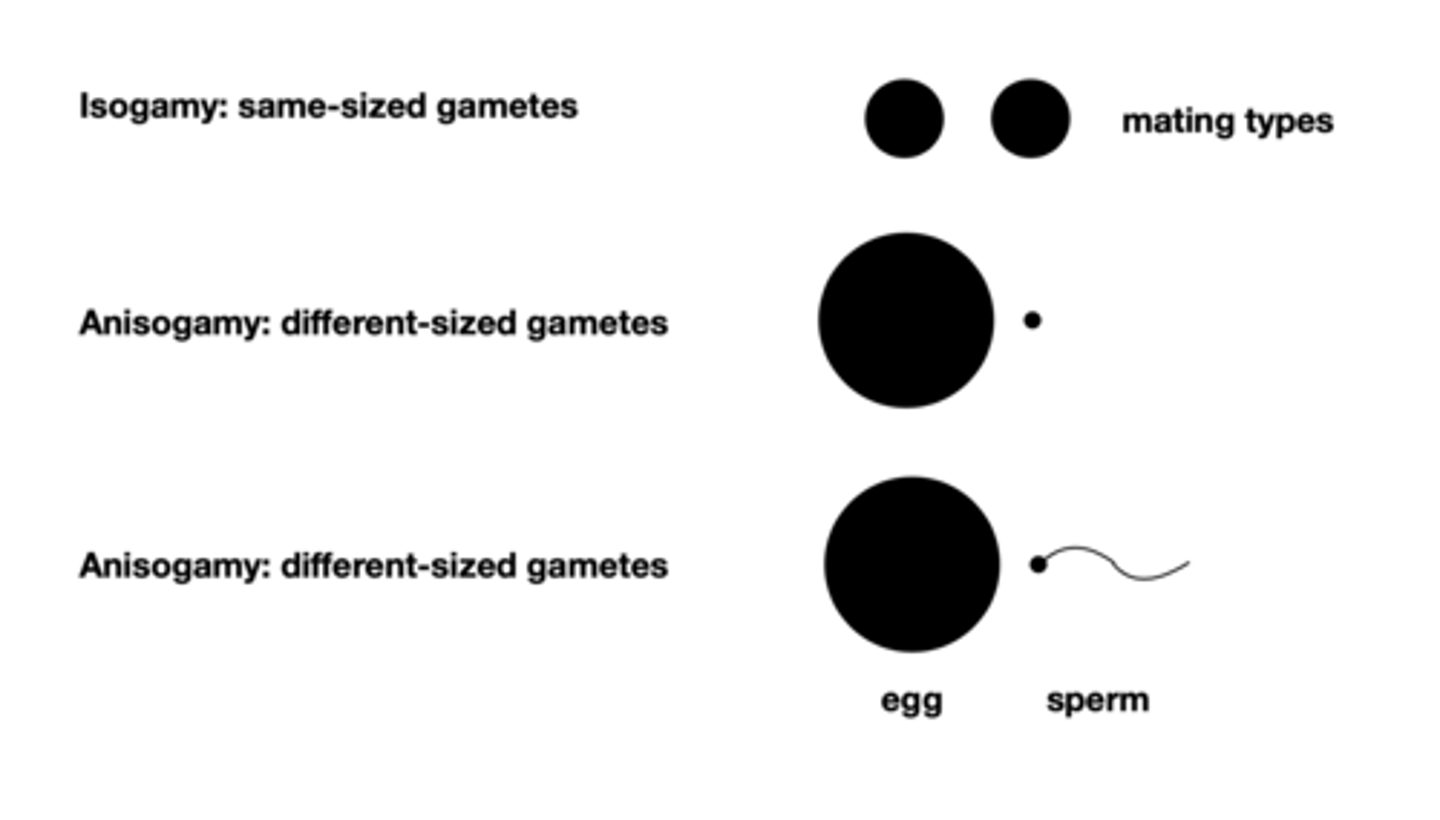
gametes of different types fuse
Isogamysame-sized gametes
Anisogamy: different-sized gametes
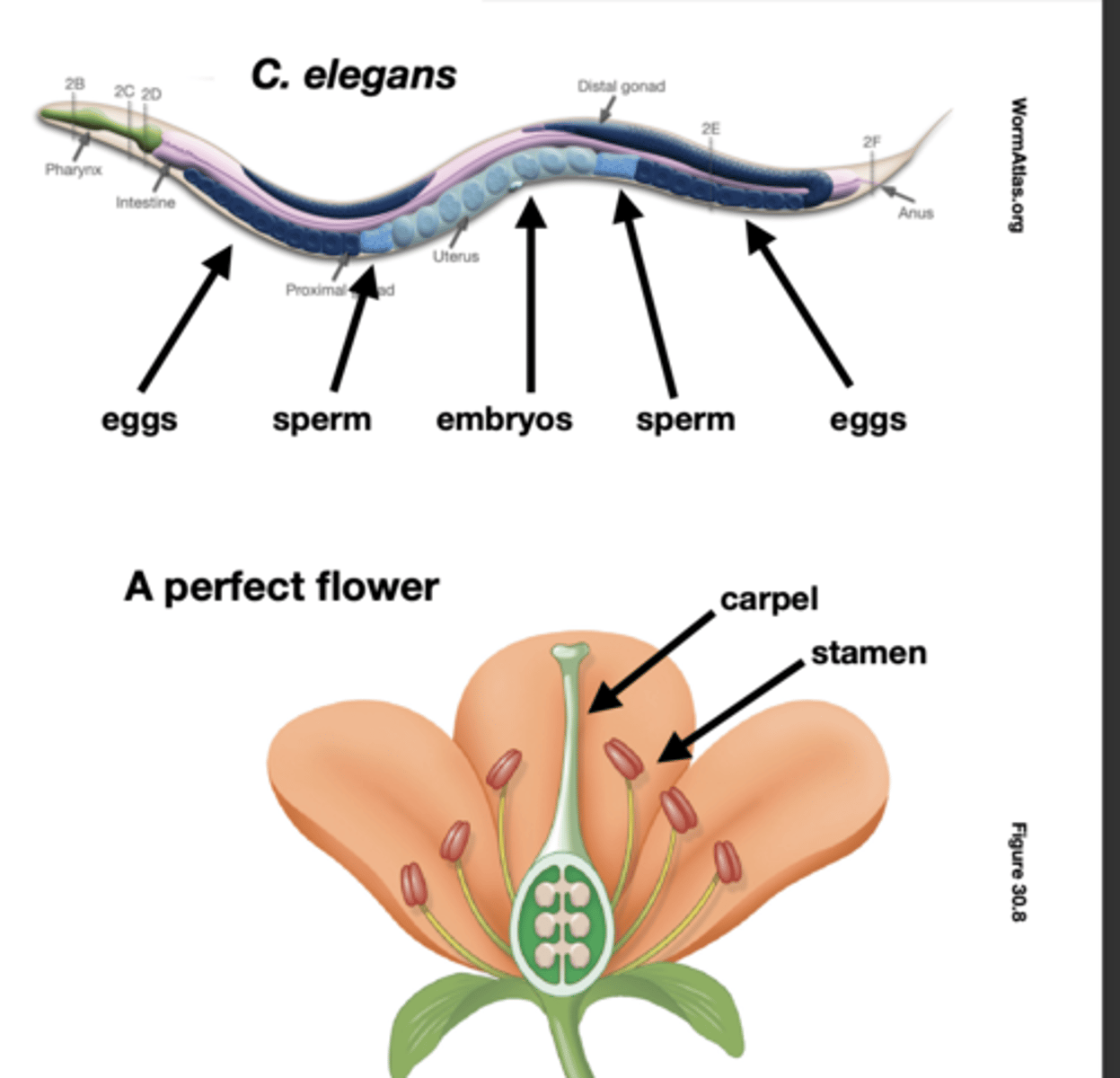
C. elegans and a perfect flower are
Individual organisms can make multiple gamete types
Sex determination
Some cue: temperature; presence of an individual making one class of gamete; genes; haplo-diploid polygenicsex chromosomes
Crepidula fornicata: newly-born => male; old ones => female; they are constantly mating
haplo-diploid polygenicsex chromosomes
Copidosoma floridanum polyembryonic wasps
if fertilized => females;
if not fertilized => males;
third sex: nonreproductives can be haploid or diploid
Sex chromosomes
ananema rhodensis
if XX crowded => hermaphrodite
if not =>
chromosomal sex determination systems
Y chromosomes => developmental biology => testes(gonadal sex) => male characteristics(phenotypic sex)
No Y =>
Y chromosomes => SRY gene => SRY proteins => lots of other genes and proteins => los of cellular phenotypes => testes => lots of hormonal stuff => lots of other genes and proteins => lots of cellular phenotypes => male characteristics
No Y, but with SRY gene => also male;
With Y, but lacking SRY gene => also female;
pathway change can cause different sex determination results
Linkage mapping
use crossover frequency to position loci along a chromosome
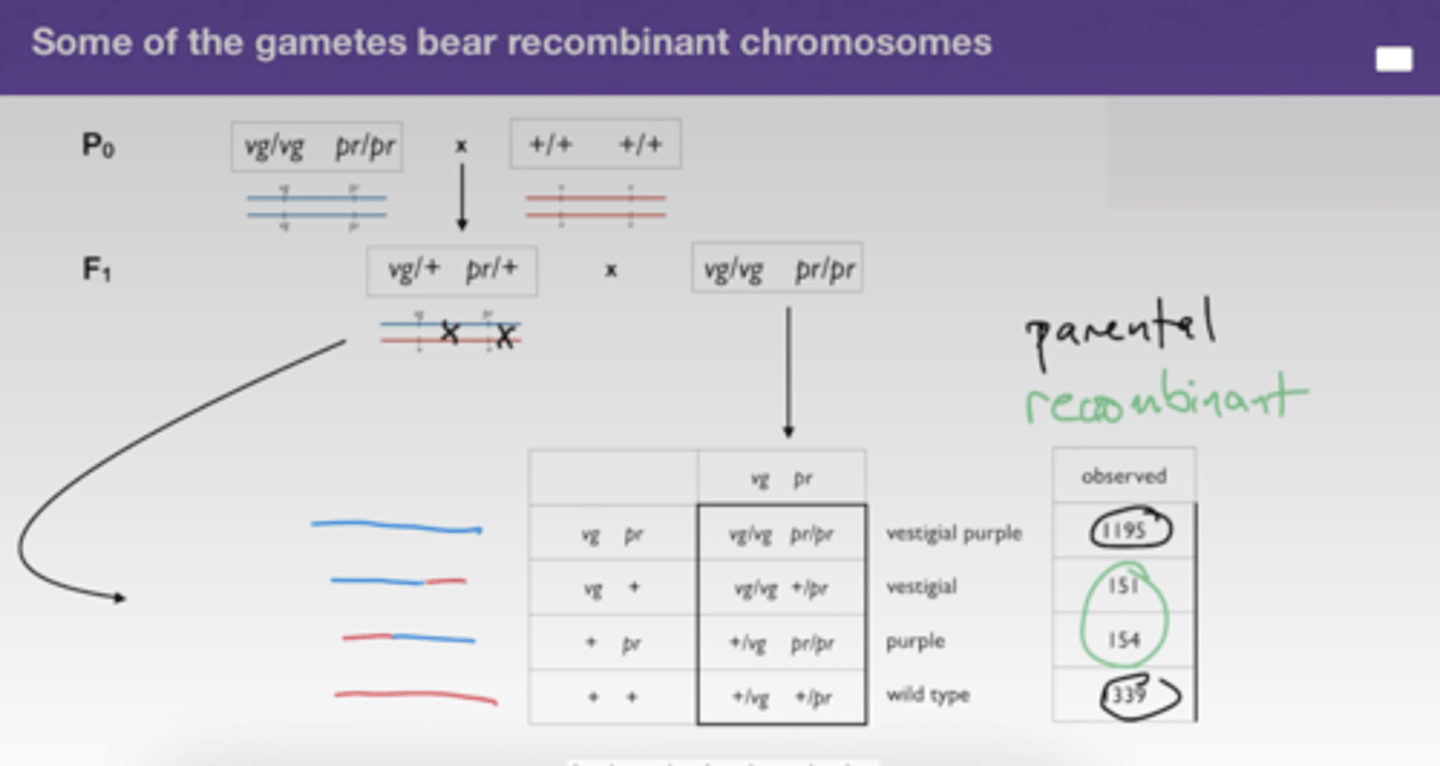
Morgan's Genetic Notation:
+: wild type, the form typical in nature genes are named for the mutant phenotype

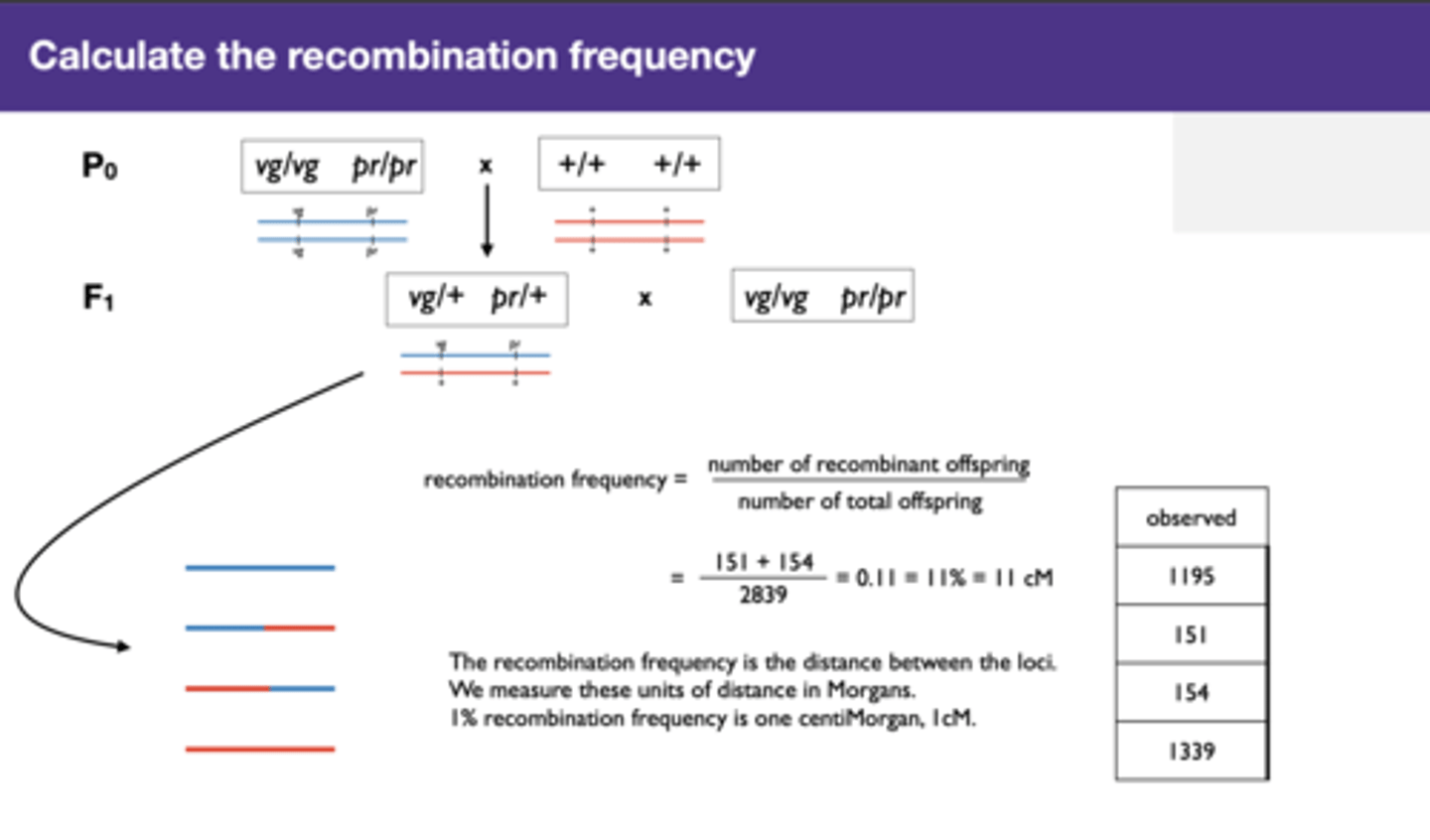
Calculate the recombination frequency
recombination frequency =
number of recombinant offspring number of total offspring
= 151+154/2839 =0.11=11%=11cM
if genes are right next to each other
the recombination frequency is low(close to 0);
very far apart => 50%:50%
The recombination frequency is the distance between the loci. We measure these units of distance in Morgans.
1% recombination frequency is one centiMorgan, 1cM.
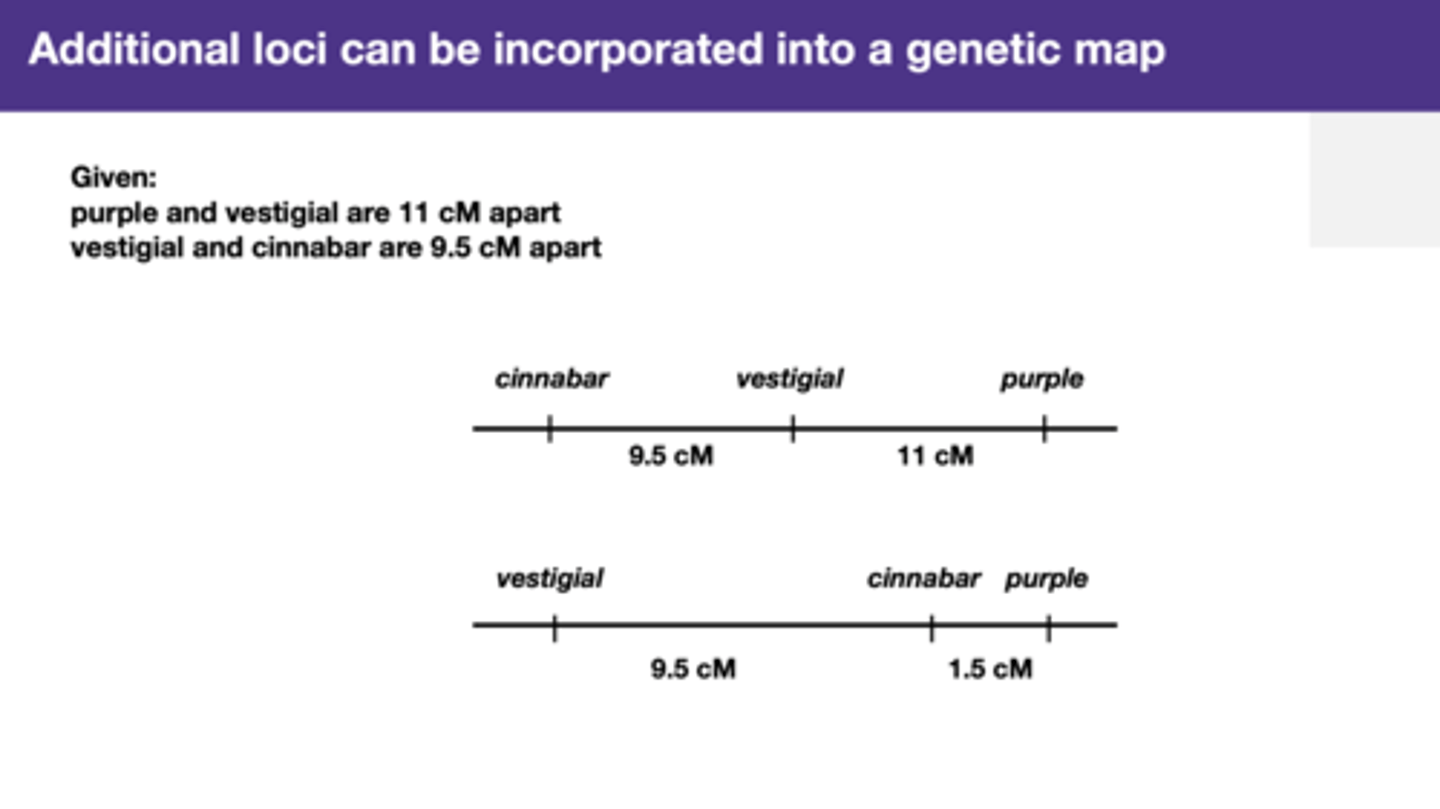
loci can be incorporated into a genetic map
position these things all the way along the chromosome and to end up with a linear representation of the chromosome where the distances are not base pairs or microns, but recombination frequencies.
Figure 15.12
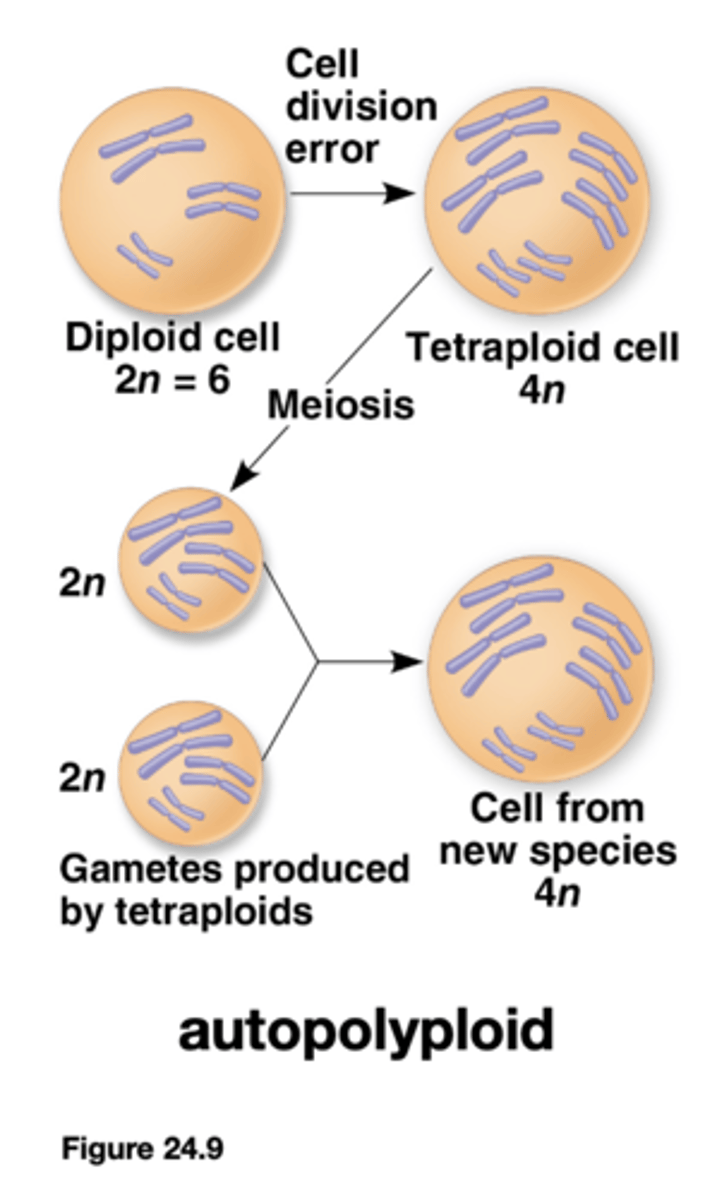
Autopolyploid
Having more than two sets of chromosomes from a single species.
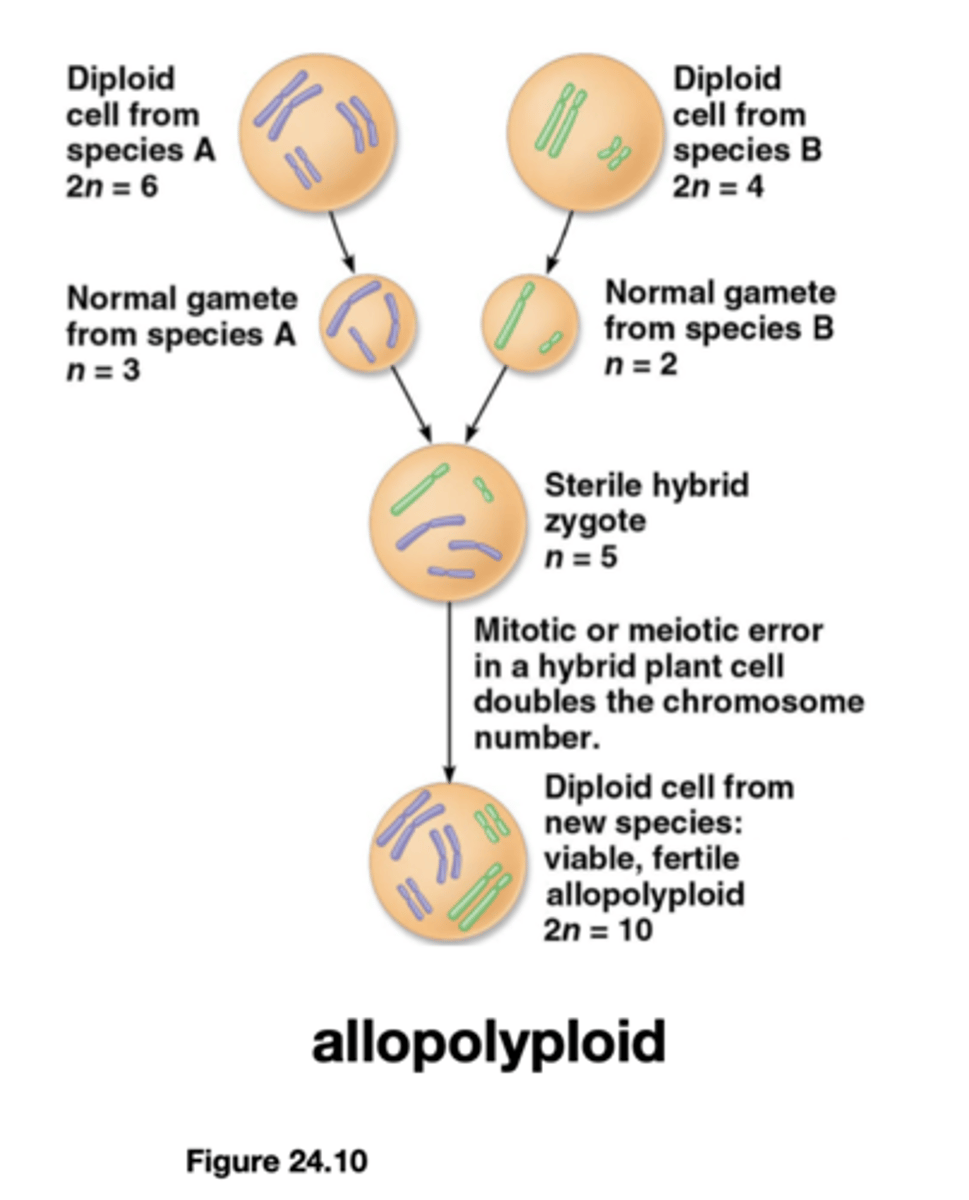
Requirements for chromosomes in sexually reproducing species:
1. Ability to pair and segregate in meiosis
2. Provide each gene in a dosage compatible with cellular processes
Ploidy
the number of sets of chromosomes Haploid, Diploid, Triploid, Tetraploid, etc
Polyploid: n > 2
allopolyploid
A fertile individual that has more than two chromosome sets as a result of two different species interbreeding and combining their chromosomes.
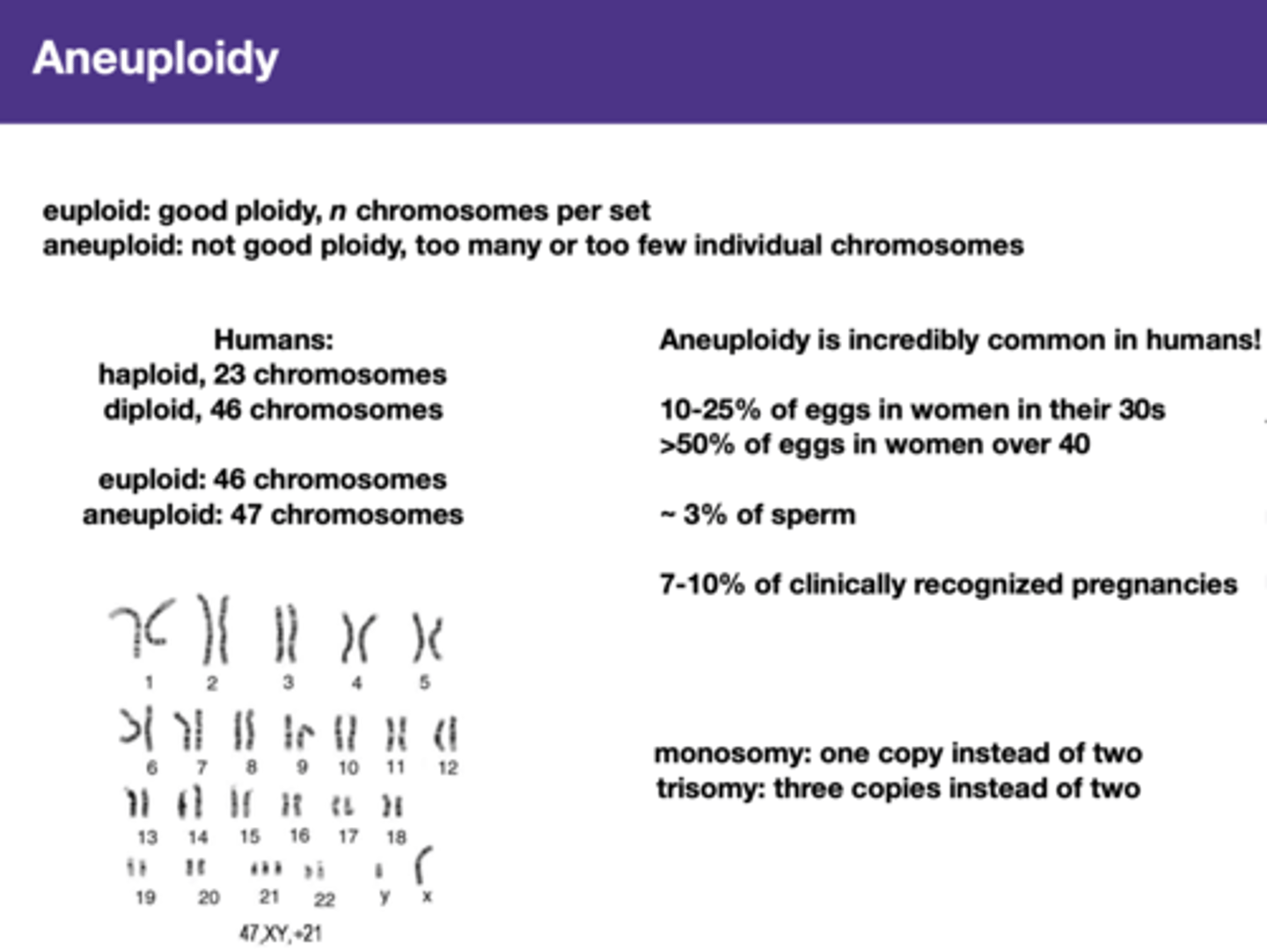
Aneuploidy
Abnormal number of chromosomes.
not good ploidy, too many or too few individual chromosomes
Aneuploidy is incredibly common in humans!
monosomy: one copy instead of two
trisomy: three copies instead of two
euploid
good ploidy, n chromosomes per set
cause of aneuploidy
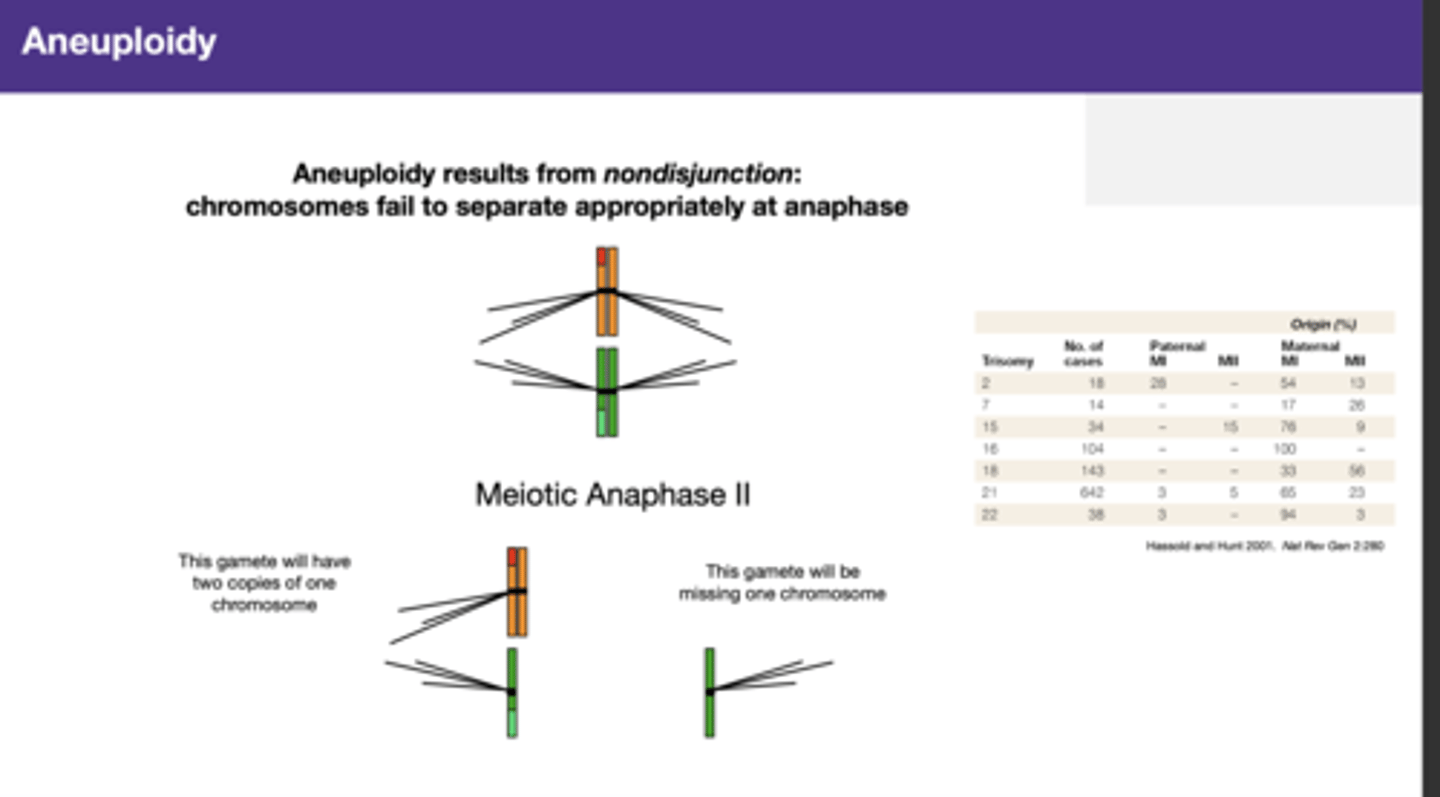
non-disjunction in meiosis I or meiosis II: chromosomes fail to separate appropriately at anaphase
Autosomal non-disjunction most often occurs during maternal meiosis I
Sex-chromosome aneuploidy
Trisomy X
Turner Syndrome
Klinefelter Syndrome
XXY

dosage compensation
Mechanism in which X chromosome inactivation/over-activation equalize gene expression between males and females.
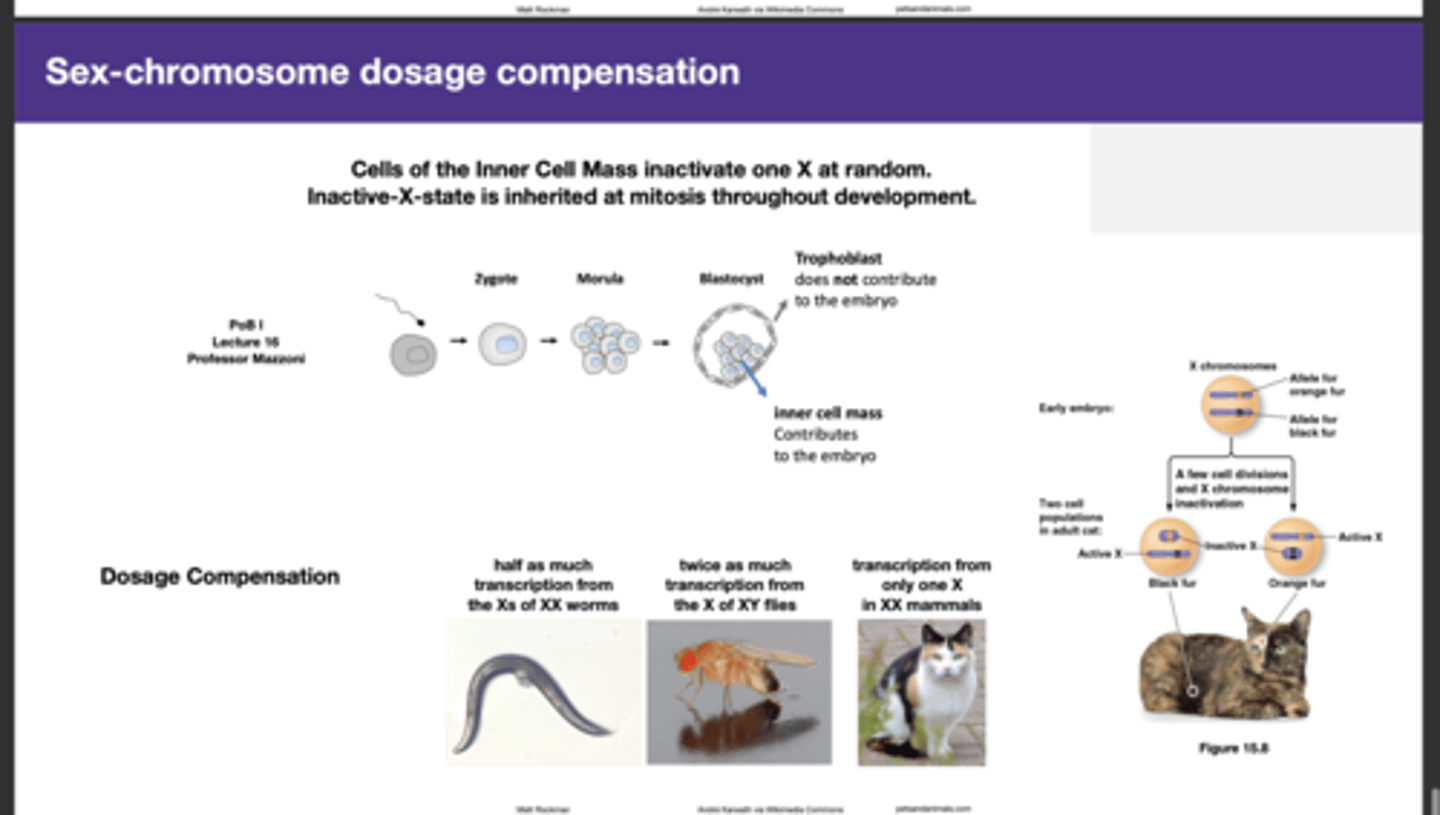
Why some female mammals are mosaic in color
Cells of the Inner Cell Mass inactivate one X at random.
=> duplicated through the process
=> Inactive-X-state is inherited at mitosis throughout development.
how to determine mutation on a small loci
1. senger sqeucning
2. PCR and see the gel difference
3. use restriction enzyme
Heterogametic
sex chromosomes are of different types(XY, ZW, X0)
Y-linkage
Genes for about 25 distinct proteins on the human Y; Includes:
SRY = proteins required for sperm development components of seminal fluid
Only one known Y-linked condition not related to male fertility(because mutation on the Y will result in sterility
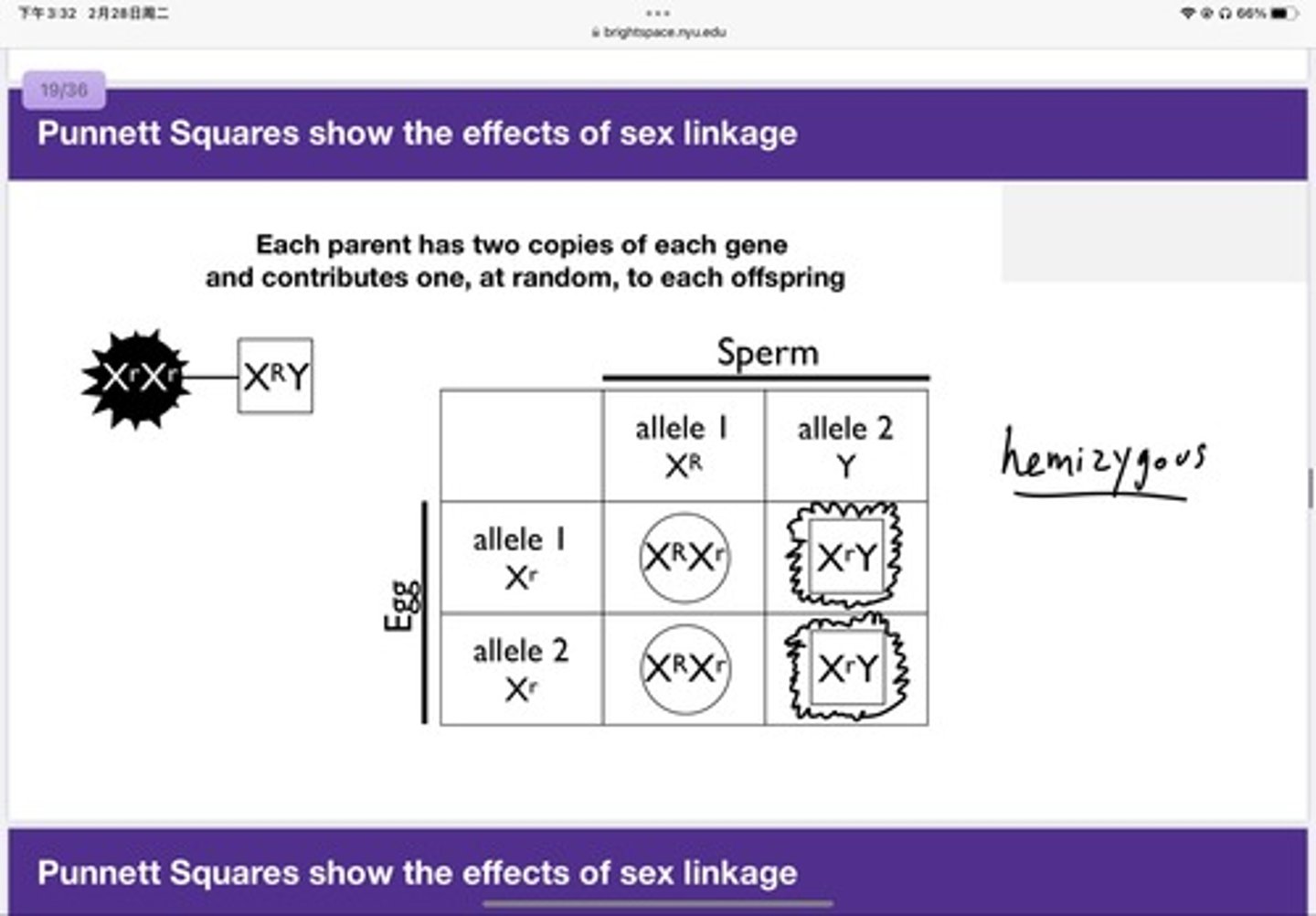
Hemizygous
the presence of only one allele for a characteristic, as in X-linkage; hemizygosity makes descriptions of dominance and recessiveness irrelevant(no X-R to conceal the X-r)*
The son cannot get the X chromosome from his father
consanguineous mating
mating between relatives(double lines)
bacteria-like circular genome different genetic code
mitochondria chloroplasts apicoplasts
Maternal Inheritance
The mitochondrial genome is passed only along the maternal lineage
The Y chromosome is passed only along the paternal lineage
(in most species)
There are exceptions to everything! Mussels have double-uniparental mitochondrial inheritance
Heteroplasmy
: multiple mitochondrial genotypes within a single cell
polymorphism
The coexistence of two or more distinct forms(of neuocleotide) in the same population.
SNPs
single nucleotide polymorphisms