Unit 2 population
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for Demography Lecture Review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Demography
The statistical study of populations, especially human beings.
Census
A complete enumeration of a population.
Population
The number of people living in a particular area.
Population Distribution
The arrangement of a population across a geographic area.
Ecumene
The portion of the Earth's surface that is permanently inhabited by humans.
Non-ecumene
The uninhabited or sparsely populated areas of the world.
Metacity
A very large conurbation, typically one with more than 10 million people.
Megacity
A very large city, typically one with a population of more than 10 million people.
Developed Country
A country with a high level of industrialization and a high standard of living
Developing Country
A country with a relatively low level of industrialization and a lower standard of living.
Population Density
The number of people per unit of area.
Arithmetic Density
The total number of people divided by the total land area.
Agricultural Density
The number of farmers per unit area of arable land.
Physiological Density
The number of people per unit area of arable land.
Overpopulation
A situation in which a population exceeds the carrying capacity of its environment.
Carrying Capacity
The maximum number of individuals that an environment can support without significant negative impacts.
Population composition
The structure of a population in terms of age, sex, and other properties.
Dependency Ratio
The number of people who are too young or too old to work, compared to the number of people in their productive years.
Youthful/Young Dependents
The number of people below the age of 15 who are dependent on the working population.
Aging/Older Dependents
The number of people above the age of 64 who are dependent on the working population.
Population Pyramids
A graphical illustration that shows the distribution of various age groups in a population.
Sex Ratio
The ratio of males to females in a population.
Baby Boom
A period of increased birth rates.
Baby Bust
A period of decreased birth rates.
Echo Boom
A period of increased birth rates following a baby bust.
Demographic equation
The change in population size over time, considering births, deaths, and migration.
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
The average number of children a woman will have during her childbearing years.
Replacement Fertility Rate
The average number of children a woman needs to have to replace herself and her partner in the population.
Gender Roles
The social and cultural expectations about how men and women should behave.
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
The total number of deaths in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
The number of deaths of infants under one year old per 1,000 live births.
Natural Increase Rate (NIR)
The difference between the number of births and deaths in a population.
Zero Population Growth (ZPG)
A condition in which the population of a country does not grow or decline.
Doubling Time
The number of years it takes for a population to double in size.
Rule of 70
A method for calculating doubling time by dividing 70 by the growth rate.
Mortality
The state of being subject to death.
Life Expectancy
The average period that a person may expect to live.
Demographic Transition Model
A model that describes the historical shift of population growth in countries from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates.
Industrial Revolution
A period of major industrialization that took place during the late 1700s and early 1800s.
Medical Revolution
Advancements in medical technology and practices that have increased life expectancy.
Epidemiological Transition Model
A model that describes the changes in mortality patterns due to disease.
Thomas Malthus
An English scholar who argued that population growth would eventually outstrip food production.
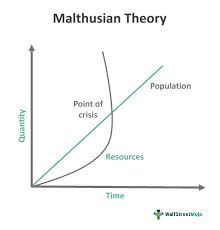
Neo-Malthusians
People who believe that Malthus's theory is still relevant today.
Pronatalist Policies
Government policies that encourage people to have more children.
Anti Natalist policies
Government policies that discourage people from having children.
Immigration Policies
Government policies that regulate the flow of people into and out of a country.
Contraceptives
Methods used to prevent pregnancy.
Family Planning
The practice of controlling the number of children in a family and the intervals between their births.
"Graying" Population
A population that is aging, with a growing proportion of elderly people.
Elderly Dependency Ratio
The ratio of elderly dependents to the working-age population.