CPU and Memory Basics
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
How is CPU and Memory connected
Every instruction executed by the CPU requires memory access
Primary memory
holds program instructions and data
Secondary storage
Used for long term storage
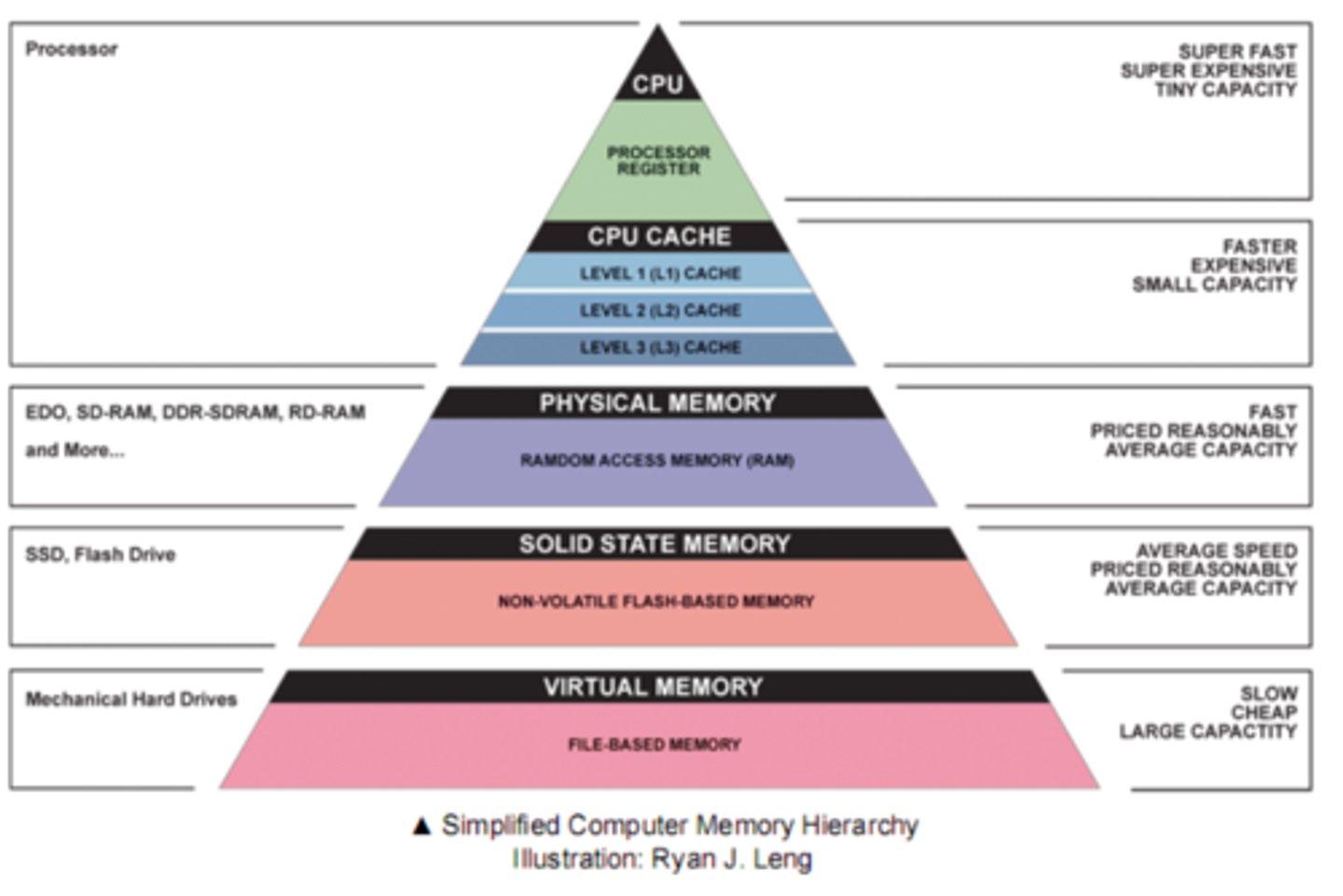
Memory Hierarchy
Can be thought of as a pyramid
CPU Architecture Designs
Complex Instruction Set Computers
Reduced Instruction Set Computers
CISC
Larger vocabulary, uses less steps to complete a task
RISC
Smaller Vocabulary, uses fewer unique instructions
Arithmetic Logic Unit
Performs calculations and comparisons
Control Unit processes (3)
Performs fetch/execute cycle
Accesses program instructions and issues commands to the ALU
Moves data to and from CPU registers and other hardware components
Control Unit Subcomponents (2)
Memory management unit
I/O Interface
Memory Management Unit
Supervises fetching instructions and data from memory
I/O Interface
sometimes combined with memory
management unit as Bus Interface Unit
Stored Program Computer
Computer that store their programs in electronic memory
Von Neumann Architecture
Computer has a single storage system for storing data as well as program to be executed and there is a single set of address/data buses between CPU and memory
Von Neumann Bottleneck
Processor can process an instruction faster than it can be transferred in from memory, therefore processor is left idle, waiting for transfer
Harvard Architecture
Two separate memory and data buses for data and instructions.
Registers
Small, permanent storage locations within the CPU used for a particular purpose
What directly manipulates Registers?
Control Unit
What size do registers hold?
bits or bytes
What can registers hold? (3)
data, address, instruction
General Purpose Register
Hold intermediate results or data values, e.g. loop counters
How many general purpose registers are in a CPU
Typically several dozen
Instruction Register
Stores instruction fetched from memory
IP
Instruction Pointer
MAR
Memory Address Register
Memory Address Register
Stores address of memory source
MDR
Memory Data Register
Memory Data Register
Stores data from memory
Status Registers
Status of CPU and currently executing program
Flags to track conditions like arithmetic carry and overflow, power failure, internal computer error
Where is the address from an instruction copied to?
the MAR
What does transfer take place between
MDR and memory
T/F MDR is a two-way register
True
Fetch
Decode/find instruction, load from memory into register and signal ALU
Execute
Performs operation that instruction requires and moves/transforms data
What is used for timing purposes for each step of the instruction cycle?
Computer Clock
Bus
The physical connection that makes it possible to transfer data from one location in the computer system to another
Bus Signal Types (4)
Data
Address
Control
Power
Parallel Bus
All bits of a word are transmitted simultaneously
Serial Bus
1 bit transmitted at a time
Parallel Bus Disadvantages (2)
Expensive and requires lots of space
Subject to radio-generated electrical interference
why is serial throughput typically higher for many applications than parallel?
Lack of electrical interference
When is parallel Buses typically used
for short distances
Blocks
between 8 and 64 bytes
Cache Line
Unit of transfer between storage and cache memory
Tags
Pointer to location in main memory
Cache Controller
Hardware that checks tags to determine if in cache
Hit Ratio
ratio of hits out of total requests
Principle of Locality
Once a byte is accessed, it is likely that a nearby data element will be needed soon
Three forms of locality
Temporal
Spatial
Sequential
Temporal Locality
Recently-accessed data elements tend to be accessed again
Spatial Locality
Accesses tend to cluster
Sequential Locality
Instructions tend to be accessed sequentially