arteries
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
bp cuff should be ____% of arm circumference
40%
a 30% of arm circumference bp cuff width will…
overestimate bp
*narrow cuff=overestimate bp
*wide cuff=underestimate bp
when to NOT use arm for bp
side of post-mastectomy or dialysis fistula
minimum inflation pressure to assure complete cessation of flow
20-30mmHg
LE pulse point that is most difficult to palpate
pop A
4 main pulse points:
CFA/SFA
pop A
PTA
DPA
calf vessels best seen w posterolateral approach
peroneal
where is retrograde flow normal in relation to distal anastomosis (@vessel end)?
just prox to it
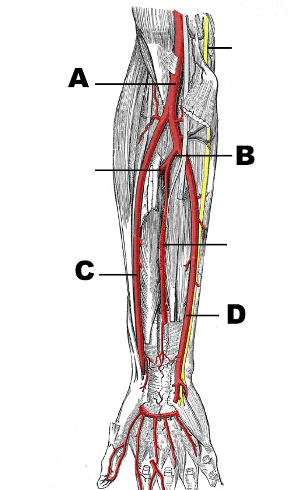
A: brachial artery
B: common interosseous artery (branch of ulnar @prontaor teres)
C: radial artery
D: ulnar artery
artery mc used for arterial line placement
radial
artery renamed at lower teres major muscle
brachial
*from axillary artery at lower teres major
artery that gives rise to deep palmar arch is ___
artery that gives rise to superficial palmar arch is ___
radial (deep)
ulnar (sup)
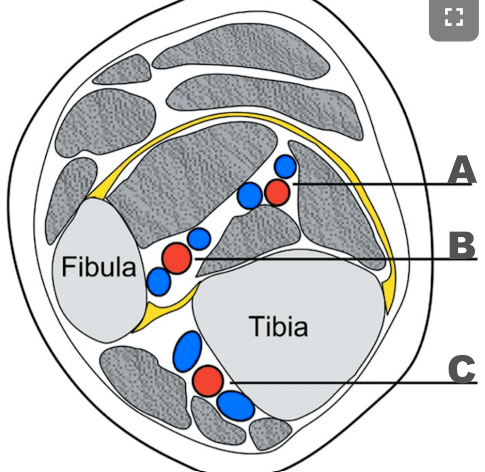
A: PTA
B: Peroneal artery
C: ATA
only vascular structure post to IVC
RRA
layers
tunica intima:
inner, endothelial cells
permeability, antithrombogenic, vasoreactivity
tunica media:
middle, thicker, smooth muscle, circular
regulate size
tunica externa:
outer, fibrous connective tissue, longitudinal
contains vasa vasorum
EVAR
TCAR
endartectomy
EVAR: stent in AAA
TCAR: stent in carotid
endartectomy: clear out plaque
mc site of pseudoaneurysm
CFA/groin
endoleak types after AAA EVAR
*flow outside EVAR graft
type I: incomplete seal at ends
type II: sac fill via branch vessel (retrograde)
type III: stent defect/tear
type IV: porous graft
type V: AAA expansion w/out leak site
SMA feeds
intestines (lower duodenum)
transverse colon
pancreas
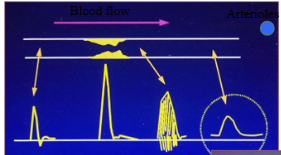
phasic flow…
pulsatile flow…
phasic: fluid movement that changes over time w breathing
pulsatile: fluid movement that changes over time from heart beating
IIA feed…
pelvic wall, gluteal, thigh, peritoneum
amount of blood ejected per beat
SV
high contractility=high SV
*CO=SVxHR
BP is controlled by…
CO & peripheral resistance
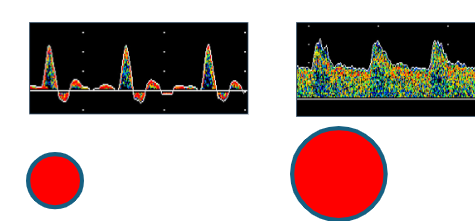
large vs small SV
large SV: spectral broadening
parabolic flow
diastole
small SV: open spectral window
plug flow
systole
do dilated arterioles have lots or little diastolic flow?
lots
*in exercise bc high demand distally (high flow volume)
normally…what happens to ankle P post exercise?
stays same or slight increase
**take P every 2min post exercise if drops
moderate steonsis
severe stenosis
PAD RF
genetic
HLD, HTN, DM
PAD
manifestation of atherosclerotic process
reduced flow bc narrowed arteries
claudication
pain of LE during exercise & relieved w rest
bc inadequate flow
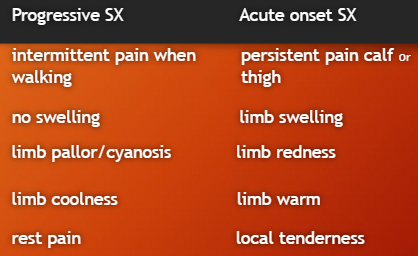
S&S:
cyanosis/pallor/rubor, cold, pain
raynauds
small vessel vasospasm
primary: bc arterial spasm; intermittent ischemia of fingers & toes
normal at ‘rest’ (w no irritant)
secondary: bc arterial obstruction; constant ischemia & rest pain
bc underlying disease
dependent rubor
limb elevation causes pallor & limb lowering returns to normal color
P’s of acute arterial disease
pain, pallor, pulselessness, paresthesia (numb), paralysis, poikilothermia (cold)
palpable pulse points
AO
fem, pop
DP, PTA
**0=no pulse; 4=bounding
atherosclerosis
thick intima (wall)
RF:
HLD, HTN, DM
genetics, male, smoking
mc @bif, intrarenal origin, brachiocephalic origin, pop trifurcation
buergers disease
“thromboangiitis obliterans”
small vessel thrombosis; ‘fixed’ occlusive disease
spares vessel walls
mc arteritis
men, <40yo, smoker
rest pain, ulcerations
types of aneurysms
true: at least 50% dilation of all wall layers
dissecting: small tear in intima; flow in new lumen
psuedo: hole in wall allows blood to escape & form hematoma pocket; always communication ‘neck’ of flow present
mc aneurysm locations
thoracic AO (infrarenal)
fem, pop
carotid
renal, splenic
entrapment syndrome
mc in pop
bc pop a compression by gastrocnemius muscle
young men
calf pain in exercise
interosseous artery runs…
off ulnar artery and runs btwn radius & ulna
UE atherosclerotic occlusive disease in which vessels?
subclavian & innominate arteries
thoracic outlet syndrome TOS
intermittent pain/numbness based on arm position
may lead to thrombosis or subclavian aneurysm
female
pain/paresthesia in hand
cold immersion test
*episodic vasospasm
submerge hand for 1-2min
waveform will decrease & should return to baseline w/in 5min
reduced amplitude >8-10min = vasospasm
hand warming test
*vasospasm vs small vessel disease
warm hand for 5min
no waveform improvement = fixed occlusive disease
allen test
*palmar arch patency
should be no drop in PPG amplitudes
compress RA & UA to determine patency or dominance
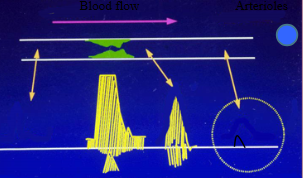
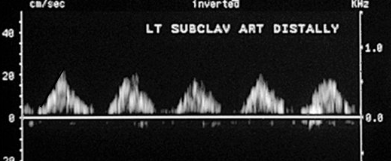
abnormal subclavian artery distal to stenosis
delayed rise time
arterial symptoms vs venous symptoms
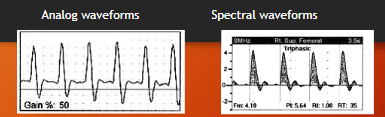
analog vs FFT
analog: zero-crossing frequency
FFT: spectrum analyzer
displays ALL freq & amp
more sensitive bc more freq
AT
normal: <133m/sec
prolonged AT if obstruction prox to probe
no prolonged AT w obstruction distal to probe
pulsatility index PI
quantify waveform in high resistance beds
normal:
CFA > 5.5
Pop = 8

bladder width should be…
20% wider than limb diameter
40% wider than limb circumference
segmental P (can NOT/can)…
can NOT determine exact location of disease
can NOT differentiate stenosis v occlusion
can be falsely elevated w calcified arteries (DM)
compare 3 cuff & 4 cuff methods to brachial P
3 cuff: thigh P = brachial P
4 cuff: prox thigh P 30mmHg > brachial P
do not exceed _____mmHg w segmental P
220mmHg
diabetics ankle P & toe P
ankle: very different P than non-diabetics
toe: lil P difference than non-diabetes
for ABI do you use the higher or lower brachial P?
higher
resting ABI values
(>1.35) probable calcified
(0.9-1.34) normal
(<0.9) stress test
(<0.8) probable claudication
(<0.5) multi-level disease
(<0.3) ischemic rest pain/pallor/severe disease
TBI values
normal: >0.75
abnormal: <0.66
*toe P more reliable than ankle P
*normal for toe P to vary 60-80% of ankle P
P drop btwn segments (PPG) that is significant
drop 30mmHg
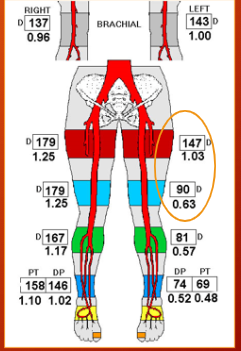
where is the problem?
LT inflow disease & fem-pop disease
ankle P for single vs multilevel disease
single: ankle P recover 2-6min post exercise
multi: ankle P recover 12min post exercise
*do NOT exercise w rest pain or ulcers
reactive hyperemia
body’s own way of increasing flow after ischemia
procedure type alt for exercise:
inflate thigh cuff 30 above brachial P for 5min…ischemia…vasodilation
pulse volume plethysmography PVR
measure changes in extremity volume
combo w doppler waveforms & segmental P to determine vascular origin or other
can NOT:
tell btwn major artery & collateral
be specific to single vessel
is UE stenosis common or uncommon?
uncommon
prox to UE occlusion w PW…
‘thump’ can be heard
significant stenosis in LE occurs at…
level of adductor canal in distal SFA & prox Pop A
%stenosis ration w PSV
prestenotic PSV:stenotic PSV
increase >100% (2:1) is 50% d reduction
(4:1) is 75% d reduction
normal finger/brachial value
0.8-0.9
where is fem artery pulse best felt?
femoral triangle
ABIs (PPG v PVR v segmental P)
look at presence & severity of disease, NO location
PPG: toes (esp w calcified)
PVR: obtains waveforms w P (inflate 65mmHg)
segmental P: looks at level of disease (old way)
mc location of LE arterial lesions
distal SFA
ATA
feeds anterior leg & dorsal surface
passes ant to popliteus muscle…btwn tib/fib...interosseous muscle
runs anterolateral leg
PTA
feeds foot sole
down medial posterior leg; posterior to medial ankle
divides into med/lat plantar a
PERO A
feeds lat lower leg & calcaneus
down lateral posterior leg, along fib
into ant/post perforators
plantar arch
feeds digits, skin, foot muscle
deep plantar a (from DPA) + lat plantar a (from PTA)
arteries around knee
genicular branches
muscle branches
sural arteries
axillary artery originates at…
lateral margin of 1st rib (from subclavian a)
radial a into…
ulnar a into…
(radial)…deep palmer arch
(ulnar)…superficial palmar arch
flow type in AO
plug
**other arteries have laminar flow
most arterial disease is due to…
atherosclerosis
common locations of cardio-emboli
AO bif
iliacs
fem bif
Pop a
mc location for pseudoaneurysm
groin
pseudoaneurysm US
*US w doppler is best method
to-and-fro flow
high V bruit
‘yin-yang’ color sign
takayasu’s arteritis
affects large vessels, AO & branches
brachiocephalic, CCA, sbclvn a
young, asian women
HTN, low peripheral pulses, AR
most patients w calf claudication have…
stenosis or occlusion of SFA
leriche’s syndrome
bilateral thigh/butt claudication w ED
impotence bc low flow thru hypogastric a (IIA)
w/ AO-iliac disease
where is ischemic rest pain most often felt?
metatarsal heads of feet
*pain lessens w dependency (hanging)
difference from diabetic neuropathy
*needs immediate attention
loss of palpable pulse indicates…
prox occlusion
*pulse grading
0: no palpable pulse
4: excessive pulse
arterioles have _____ flow
steady (rather than pulsatile in arteries)
are P drops in arterial disease more apparent at rest or exercise?
exercise (bc increased flow)
**severe disease can be diagnosed @rest
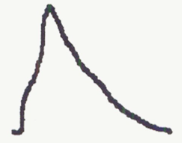
normal arterial tracing PVR
rapid upstroke
sharp peak
dicrotic notch
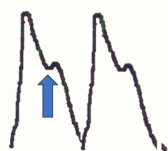
mildly abnormal arterial tracing PVR
rapid upstroke
sharp peak
absent dicrotic notch
bowed downslope
moderately abnormal arterial tracing PVR
flat peak
upslope=downslope
absent dicrotic notch

severely abnormal arterial tracing PVR
low amplitude
no pulsatility

waveforms at rest vs in exercise
(at rest) high resistance, triphasic
(in exercise) low resistance
arterial claudication
**walking, bike, abnormal pulses
(postural changes) not cause pain
(walking) symptoms
(standing) relieves
(sitting) relieves
(stationary bike) symptoms
(pulses) abnormal
neurogenic claudication
**postural changes, walking, standing
(postural changes) more pain
(walking) symptoms
(standing) symptoms
(sitting) relieves
(stationary bike) relieves symptoms
(pulses) normal
flow distal to stenosis is…
low resistance & monophasic
popliteal entrapment syndrome
popliteal a compressed by gastrocnemius
bc repetitive trauma, pop a stenosis/thrombosis
<30yo male
PAD mc symptom
intermittent claudication
leriche syndrome
“AO iliac occlusive disease”
bc severe atherosclerosis of distal AO, iliac a, fem-pop
claudication
impotence
absent fem pulse