Overview of REBT, CBT, SFBT, and DBT Therapies
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
REBT
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy; focuses on rational thinking.
ABC Model
Framework: Activating event, Beliefs, Consequences.
Activating Event (A)
Situation triggering emotional or behavioral reaction.
Beliefs (B)
Thoughts about the activating event; can be rational or irrational.
Consequences (C)
Emotional and behavioral outcomes from beliefs.
Disputation (D)
Challenging irrational beliefs to replace with rational ones.
Cognitive Disputation
Questions irrational thoughts using logical techniques.
Behavioral Disputation
Tests irrational beliefs through real-life experiences.
Emotive Disputation
Uses emotional techniques to reinforce rational beliefs.
Shame-Attacking Exercise
Homework to promote self-acceptance without others' approval.
Unconditional Acceptance
Acceptance of clients as fallible beings for open discussion.
DIBS
Dispute Irrational Beliefs using disputing questions.
Cognitive Distortions
Thought patterns leading to irrational thinking.
Absolutistic Musts
Rigid demands causing cognitive distortions.
Awfulising
Exaggerating negative outcomes beyond reality.
I-can't-stand-it-itis
Belief that one cannot tolerate discomfort.
People-Rating
Judging oneself and others negatively.
Rational Emotive Imagery
Imagining positive emotional responses to challenges.
Humor in Therapy
Using humor to challenge irrational beliefs.
Role-Playing
Practicing scenarios to reinforce rational beliefs.
Ultimate Goals of REBT
Teach rational thinking, appropriate feelings, adaptive behavior.
Active Therapy
REBT involves direct and confrontational techniques.
Cognitive, Emotive, Behavioral Methods
Combined approaches to facilitate client change.
Cognitive Distortions
Irrational thought patterns causing emotional distress.
REBT
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy focusing on changing beliefs.
ABC Model
Framework for understanding emotional responses in REBT.
Emotional Distress
Negative feelings resulting from cognitive distortions.
Maladaptive Behaviors
Actions that are counterproductive to emotional well-being.
Teaching in REBT
Structured education to identify and challenge irrational beliefs.
Core Beliefs
Deeply held beliefs influencing thoughts, feelings, and actions.
Negative Core Beliefs
Beliefs that undermine self-worth and capability.
Positive Core Beliefs
Beliefs that enhance self-esteem and confidence.
Intermediate Beliefs
Attitudes and rules derived from core beliefs.
Automatic Thoughts
Spontaneous thoughts triggered by specific situations.
Schemas
Frameworks formed by core beliefs influencing automatic thoughts.
Coping Strategies
Developed methods to avoid negative core beliefs.
Diathesis Stress Model
Model explaining mental disorders through predisposition and stress.
Socratic Dialogue
Technique for exploring thoughts and beliefs through questioning.
Awfulising
Cognitive distortion exaggerating negative outcomes.
Change Process in REBT
Steps to facilitate cognitive and emotional transformation.
Reinforce Change
Strengthening new beliefs and behaviors post-therapy.
Beck's View of Human Nature
Humans can control thoughts but may distort them.
Automatic Images
Mental visuals arising spontaneously in response to triggers.
Critical Thinking
Encouraging rational thought and self-reflection.
Homework Importance
Reinforces skills and promotes independent improvement.
Thought-Stopping
Replacing negative thoughts with positive alternatives.
Reframing
Changing perception to find a balanced perspective.
Diathesis-Stress Model
Explains mental disorders via vulnerabilities and stressors.
Solution Focused Therapy
Focuses on client strengths and future goals.
Preferred Goal Questions
Inquire about client's desired future outcomes.
Evaluative Questions
Assess effectiveness of client's current actions.
Exception-Seeking Questions
Identify instances when problems did not occur.
Coping Questions
Explore past coping strategies of the client.
Solution-Oriented Questions
Visualize life without the current problem.
Amplification
Encouraging discussion of client's successful solutions.
Customers
Clients ready to define outcomes and solve problems.
Complainants
Clients agree on issues but struggle with solutions.
Visitors
Clients exploring therapy without commitment.
Client as Expert
Clients recognized as experts in their own lives.
Not Knowing Posture
Therapist encourages exploration by withholding answers.
Therapeutic Alliance
Constructed through rapport, empowerment, and goal co-construction.
Irreverent Communication
Provocative and direct communication in therapy.
Wise Mind
Balanced state between logic and emotion.
DBT Stages
Four stages focusing on safety and emotional stability.
Stage I
Prioritizes safety and stabilization of the client.
Stage II
Addresses behaviors causing misery from past trauma.
Stage III
Focuses on everyday living and contentment.
Stage IV
Focus on deeper meaning and spiritual fulfillment.
Third Wave of Behavior Therapy
Integrates behavior, biology, and environmental context.
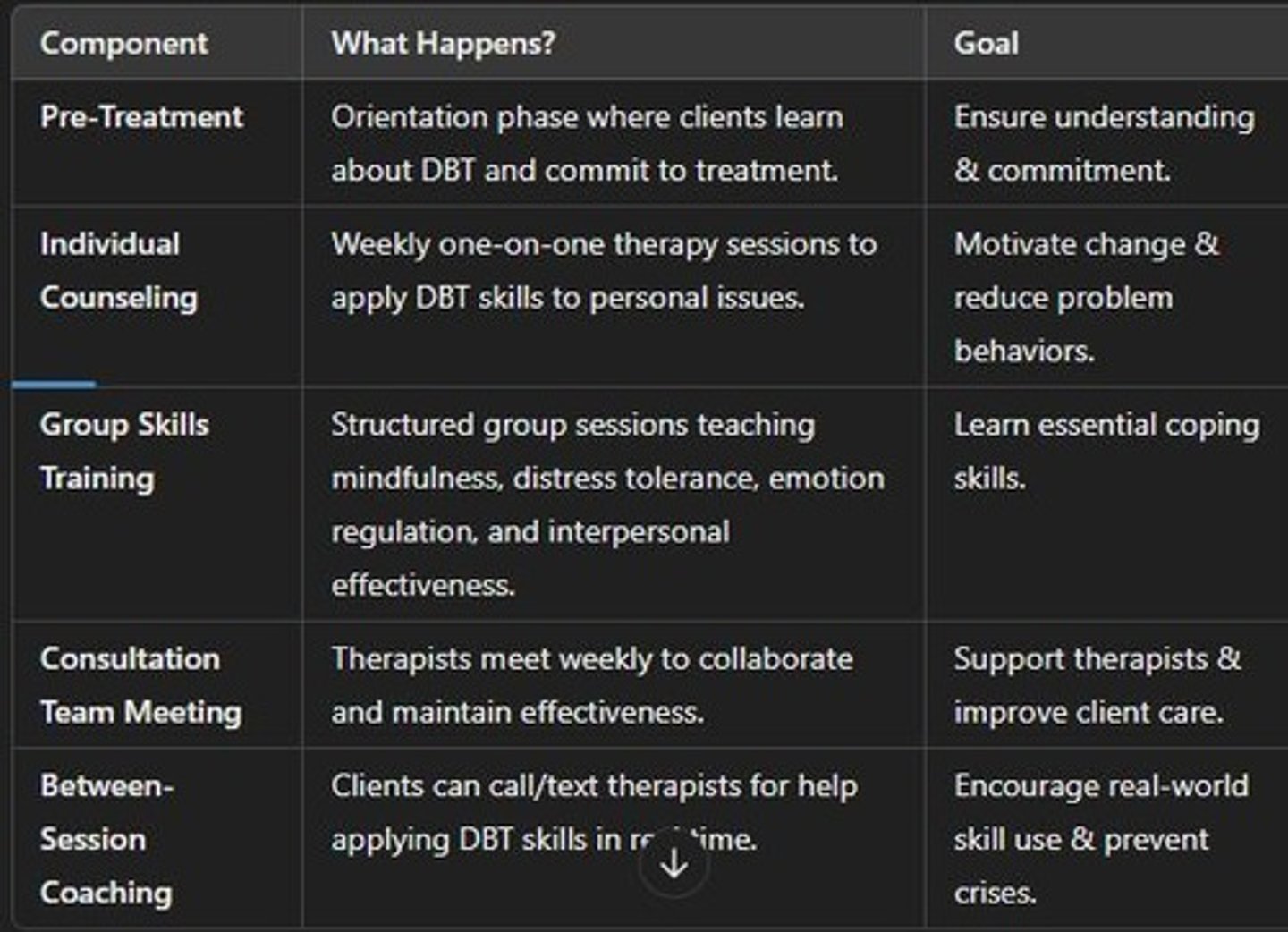
DBT
Dialectical Behavior Therapy emphasizing mindfulness and acceptance.
Emotional Vulnerability
Constitutional factors leading to heightened emotional sensitivity.
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)
Characterized by unstable relationships and emotional instability.
Diagnostic Criteria for BPD
Five or more symptoms required for diagnosis.
Frantic Efforts to Avoid Abandonment
Intense fear of being abandoned by others.
Identity Disturbance
Unstable self-image or sense of self.
Impulsivity
Engaging in risky behaviors without forethought.
Suicidal Behaviors
Thoughts or actions related to self-harm or suicide.
Emotional Instability
Rapid mood swings and emotional responses.
Chronic Feelings of Emptiness
Persistent sense of void or lack of fulfillment.
Inappropriate Anger
Intense anger disproportionate to the situation.
Stress-Related Paranoid Ideation
Paranoia triggered by stress or anxiety.
Dialectical Concept
Balancing acceptance and change in therapy.
Unconditional Positive Regard
Accepting clients without judgment or conditions.
Seven Basic Assumptions of DBT
Core beliefs guiding the practice of DBT.
People are Doing Their Best
Individuals act to the best of their ability.
Motivation to Change
Desire for improvement drives therapeutic progress.
Responsibility for Problems
Individuals must solve their own issues.
Behavioral Generalization
New behaviors must apply across various contexts.
Causal Nature of Behaviors
All behaviors have underlying causes.
Chain Analysis
Technique identifying triggers and consequences of behaviors.
Challenging Communication
Techniques to provoke thought and perspective shifts.
Irreverent Communication
Direct and confrontational communication style.
Devil's Advocate
Presenting opposing viewpoints to stimulate discussion.
Problem Behavior
Behavior identified as problematic in therapy.
Diary Card
Tool for tracking problem behaviors over time.
Prompting Event
Trigger that initiates problem behavior.
Chain of Events
Sequence linking prompting event to problem behavior.
Consequences
Outcomes resulting from problem behavior, positive or negative.
Vulnerability Reduction
Strategies to lessen susceptibility to problem behavior.
Event Prevention
Methods to stop prompting events from recurring.