CHROMATOGRAPHY - HPLC AND GC
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is HPLC?
high-performance liquid chromatography
= uses high pressure to push a mobile phase (solvent+drug) through stationary column separation - refinement of column chromatography.
What are the main difference between HPLC and column chromatography?
- A solvent is passed through a metal tube under high pressure, rather than being allowed to pass through gravity.
The particle size of the stationary phase is much smaller, which allows for better separation of the components.
- The sample is injected into the column.
- The components are detected after passing through the column, usually by their absorption of ultraviolet radiation.
- The whole process is automated and the results are quickly available on a computer display.
- It has retention time rather than a retention factor.
Apparatus for HPLC
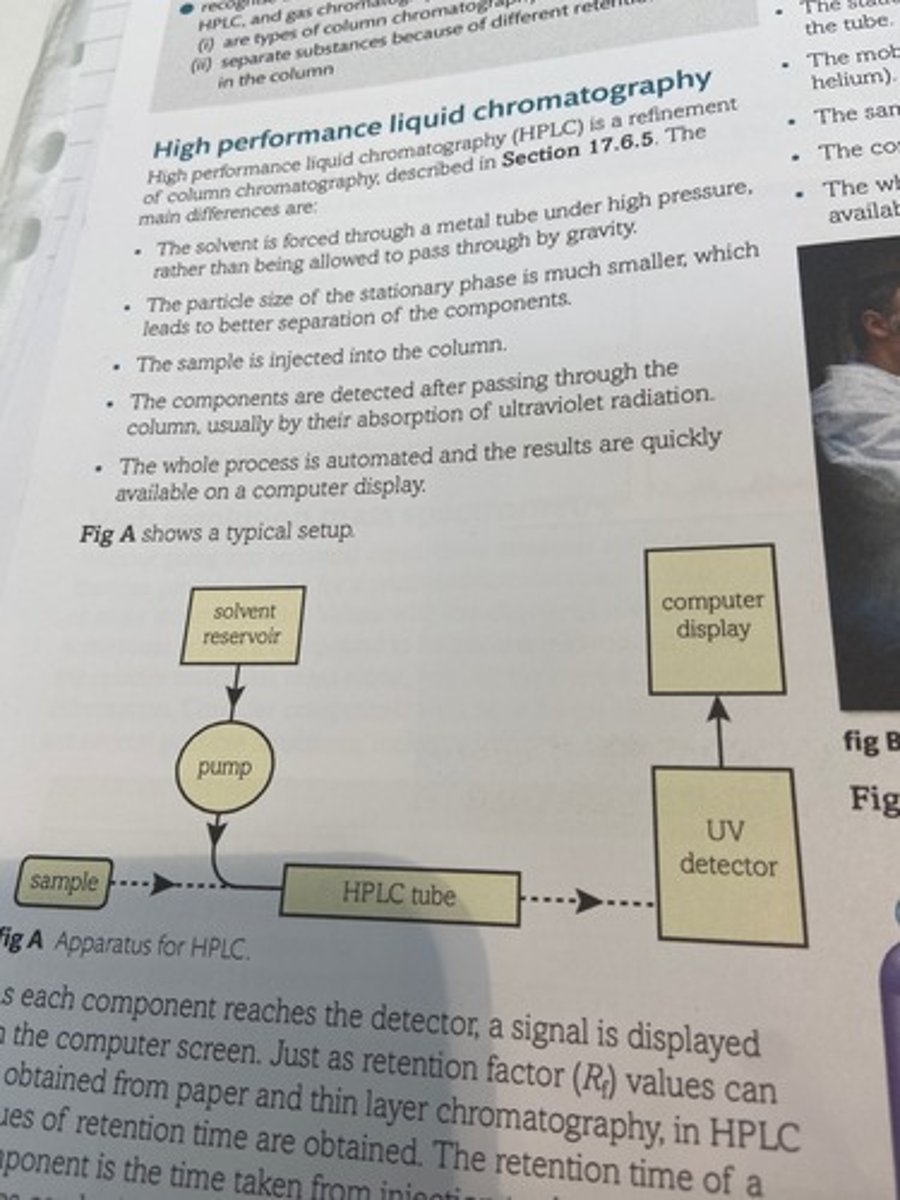
What is retention time?
Time taken from injection to detection
Retention time depends on several variables:
- The nature of the solvent
- The pressure used
- The temperature inside the column
What is gas chromatography (GC)?
useful for analysis of small amounts of compounds that have vapor pressures high enough to allow them to pass for a column. It is another refinement of column chromatography.
What are the main difference between GC and column chromatography?
- The metal tube can be several metres long and is coiled to save space
- The stationary phase is a solid or liquid coated on the inside of the tube.
- The mobile phase is an inert carrier gas (often nitrogen or helium).
- The sample is injected into the column, as in HPLC
- The components passing through the column are detected.
- The whole process is automated and the results are quickly available on a computer display.
Apparatus for GC
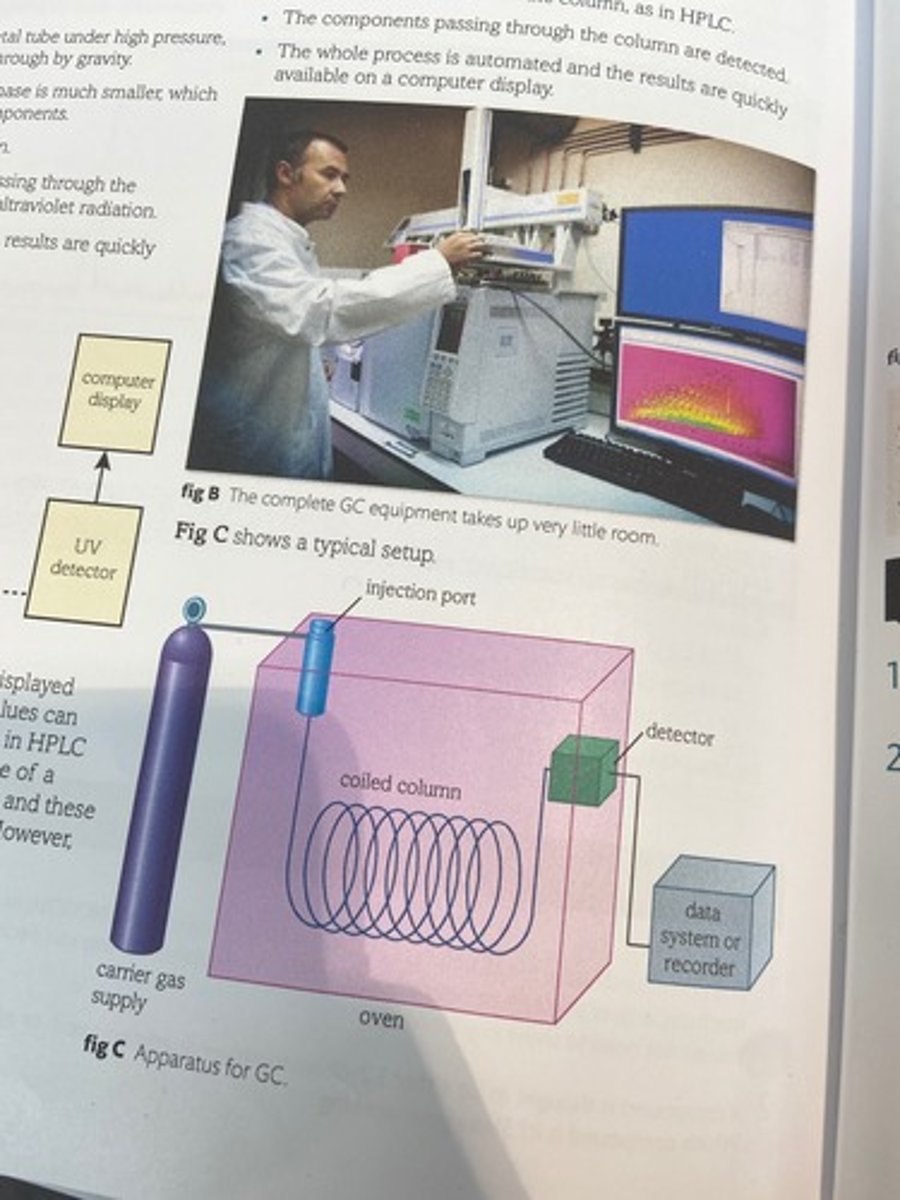
What happens after the sample injected in GC?
The components vaporise and move through the coiled tube with the carrier gas. They move at different speeds, depending on how strongly they are attracted to the stationary phase. Those with weaker attractions move more quickly and have shorter retention times.
The relative concentrations of different components are often displayed on a graph like this:
LOOK IN TEXTBOOK
Limitations of GC and HPLC
They are not very good at positively identifying them. This is partly because of the difficulty in controlling all of the variables (such as solvent, pressure and temperature) and partly because different substances may have the same retention times. Components are often identified by reference to a database of the retention times of known substances. However, if a component has a retention time for which there is no reference, then these techniques provide no useful information
Two areas in which the results of these chromatography methods have to be exactly correct:
- In providing forensic evidence (for use in a court of law)
- In detecting banned drugs in sportsmen and women and racehorses
- Analysis of pollutants in the environment
- Detecting explosives in airport baggage, and in space probes on other planets.
What is HPLC-MS and GC-MS?
Because HPLC and GC do not give results that are beyond doubt, they are often combined with a different technique known as mass spectrometry (MS), a technique that cannot separate a mixture but which can provide information about the structures of compounds. The combinations of these techniques are often abbreviated to HPLC-MS and GC-MS.
Stages in GC-MS
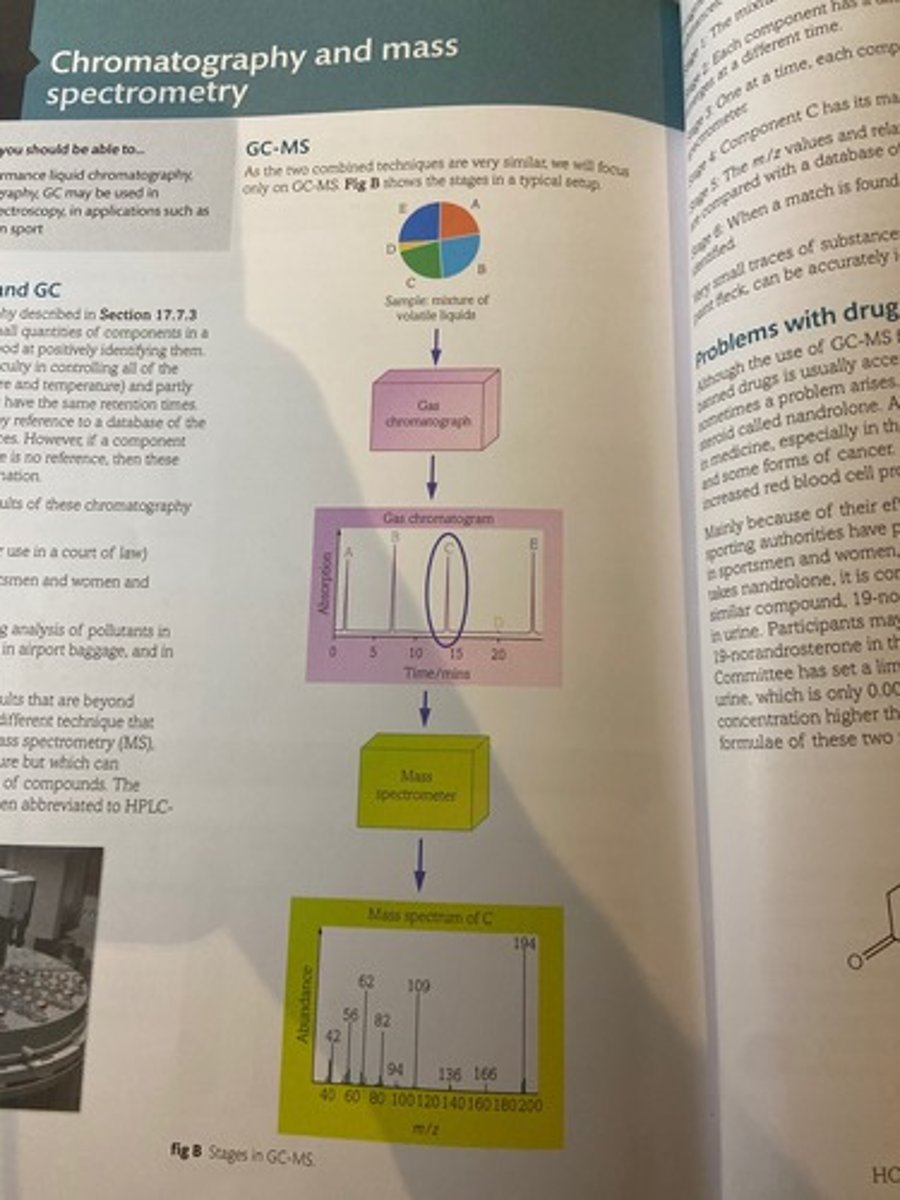
What is stage 1 in GC-MS?
The mixture is injected into a gas chromatograph.
What is stage 2 in GC-MS?
Each component has a different retention time, so emerges at a different time.
What is stage 3 in GC-MS?
One at a time, each component enters the mass spectrometer.
What is stage 4 in GC-MS?
Component C has its mass spectrum displayed
What is stage 5 in GC-MS?
The m/z values and relative abundances of components are compared with a database of known substances.
What is stage 6 in GC-MS?
When a match is found, component C has been positively indentified.
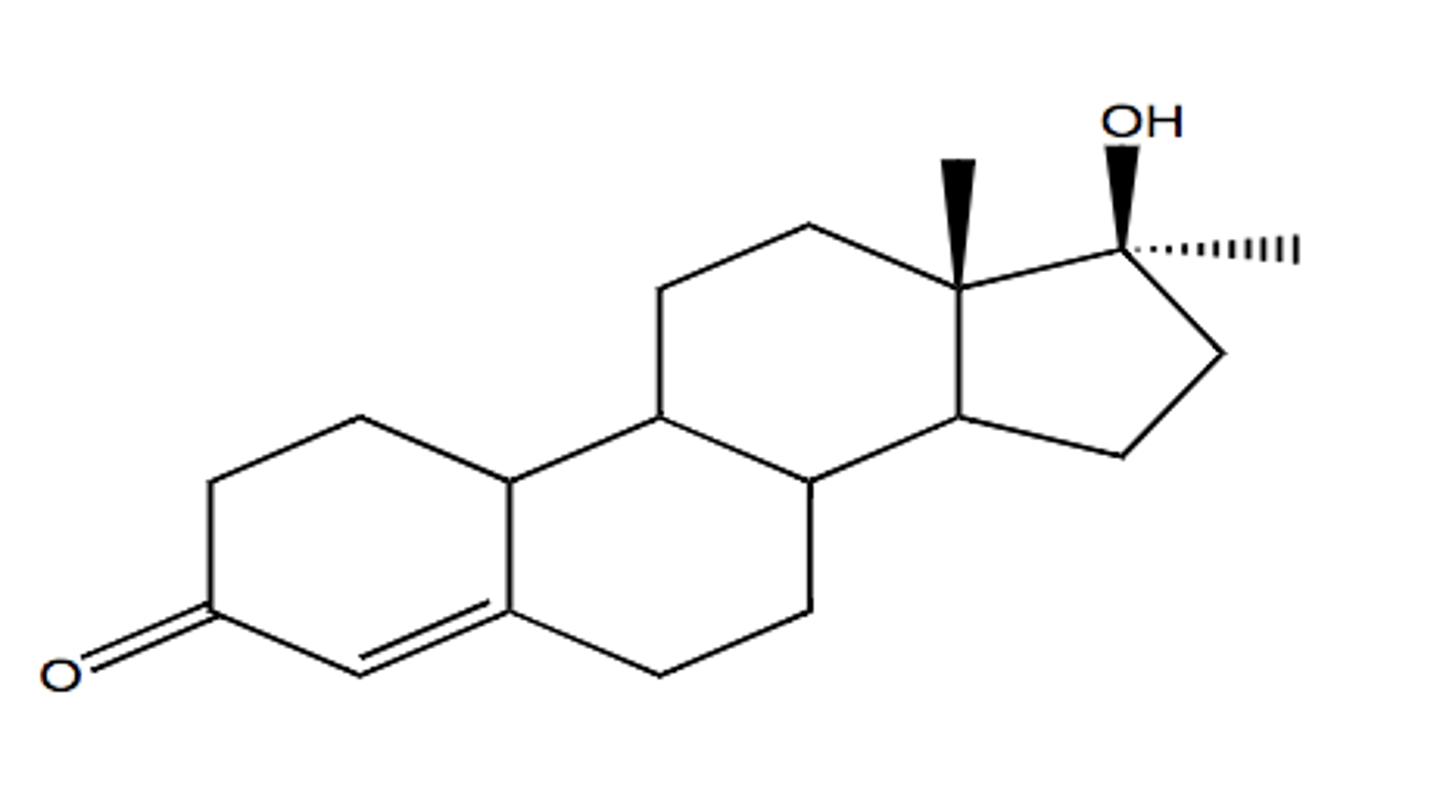
Structure of nandrolone
Structure of 19-norandrosterone
LOOK AT TEXTBOOK