topic 3: membranes
1/17
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
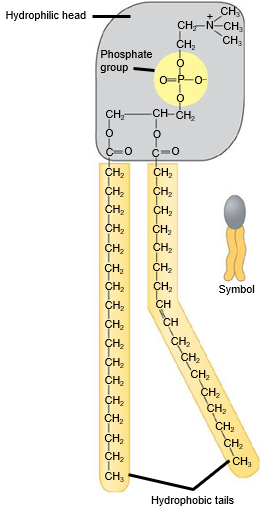
fluid mosaic model
describes teh plasma membrane as a polar/hydrophilic head and a nonpolar/hydrophobic tail
what is the plasma membrane primarily comprised of?
lipids (phospholipids + cholesterol)
carbohydrates
proteins
phospholipids
a molecule consisting of glycerol, two fatty acids, and a phosphate linked head group
where are phospholipids hydrophilics?
the head
where are phospholipids hydrophobic?
the tails
integral proteins/integrins
proteins that integrate completely into the membrane structure, they are found in the tail
glycoproteins
located on the membranes exterior surface, basically carbohydrates attach to proteins
cholesterol
made of 4 fused carbon rings, located next ti the phospholipids on the tails, these lower the temperature and organize proteins
diffusion
net flow of a substance down its concentration gradient until it reaches equilibrium, this is a form of passive transport
facillitated diffusion
diffusion with the help of a transport protein which acts as a carrier or a channel (channels are specific to the substance)
aquaporins
transport/channel proteins that helps water cross membranes (water has difficulty crossing bc its so polar)
osmosis
net flow/diffusion of water down its concentration gradient across a differentially permeable membrane, deals with an aqueous solution
aqeuous solution
water (solvent) + a solute
hypotonic solution
solute is low
ex. .45% NaCl for dehydration
hypertonic solution
solute is high
ex. .9% NaCl + .5% glucose for low blood sugar
isotonic solution
solution is in equilibrium
ex. .9% NaCl for comatose people
active transport
requires energy in the form of ATP
solute binds to the binding site
ATP phosphorylates the transport protein
the transport protein changes shape and releases the solute on the other side
phosphate group detaches and the transport protein changes back to its original shape
Na+ K+ Pump
basically cells need high K and low Na inside them to do stuff so Na’s gradient drives into the cell and the K’s gradient also goes down into the cell but this causes the K to go out of the cell