Gram Positive Organisms Part 1A & 1B
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
What are the Gram-Positive Organisms?
Cocci
Staphylococcus
Streptococcus
Enterococcus
Bacilli
Bacillus
Clostridium spp
Listeria spp
Corynebacterium spp
A 53-year-old farmer presents for evaluation of a growth on his arm. This began as a blister about a week ago and then ruptured developing into an ulcer. He also had fever along with the blister. He has had no ill contacts. He takes care of the cows, buffaloes and sheep on his farm. On examination he has a 4.5-cm circular black eschar surrounded by vesicles and edema. He also has tender lymph nodes in his arm pit. A gram stain of the eschar pus shows Gram Positive Bacilli.
What is this disease likely to be?
Anthrax
A 53-year-old farmer presents for evaluation of a growth on his arm. This began as a blister about a week ago and then ruptured developing into an ulcer. He also had fever along with the blister. He has had no ill contacts. He takes care of the cows, buffaloes and sheep on his farm. On examination he has a 4.5-cm circular black eschar surrounded by vesicles and edema. He also has tender lymph nodes in his arm pit. A gram stain of the eschar pus shows Gram Positive Bacilli.
What led to the infection?
contact with animals
A 53-year-old farmer presents for evaluation of a growth on his arm. This began as a blister about a week ago and then ruptured developing into an ulcer. He also had fever along with the blister. He has had no ill contacts. He takes care of the cows, buffaloes and sheep on his farm. On examination he has a 4.5-cm circular black eschar surrounded by vesicles and edema. He also has tender lymph nodes in his arm pit. A gram stain of the eschar pus shows Gram Positive Bacilli.
Describe the likely pathogen?
Bacillus anthracis
A 53-year-old farmer presents for evaluation of a growth on his arm. This began as a blister about a week ago and then ruptured developing into an ulcer. He also had fever along with the blister. He has had no ill contacts. He takes care of the cows, buffaloes and sheep on his farm. On examination he has a 4.5-cm circular black eschar surrounded by vesicles and edema. He also has tender lymph nodes in his arm pit. A gram stain of the eschar pus shows Gram Positive Bacilli.
What is the virulence factor responsible?
capsular polypeptide and anthrax toxin
A 53-year-old farmer presents for evaluation of a growth on his arm. This began as a blister about a week ago and then ruptured developing into an ulcer. He also had fever along with the blister. He has had no ill contacts. He takes care of the cows, buffaloes and sheep on his farm. On examination he has a 4.5-cm circular black eschar surrounded by vesicles and edema. He also has tender lymph nodes in his arm pit. A gram stain of the eschar pus shows Gram Positive Bacilli.
What is the mode of action of the virulence factor?
inhibiting phagocytosis and activation of neutrophils
Anthrax and Bacillus anthracis
Infections of ______
_____ infection
Infections of herbivores
zoonotic infection
Anthrax and Bacillus anthracis
Possible _____ agent
Possible bioterrorism agent
Anthrax and Bacillus anthracis
Gram ______
Gram-positive rod
Anthrax and Bacillus anthracis
Spore-forming
_________ of bacterial cell
______ survival under harsh conditions
Protective, dormant form of bacterial cell
increases survival under harsh conditions
B. anthracis
Microscopy
Gram stain= ______
Capsule = _____
Spores = _____
Gram stain= long GPR/ GPB; single paired or long serpentine chains (box cars)
Capsule= only in clinical specimens; made of polypeptides
Spores= old culture- not in clinical specimens; malachite green stain
B. anthracis
Culture = _____
Culture= Blood agar
large nonhemolytic adherent colonies
Cutaneous anthrax
90-95% of cases
Eschar produced at entry site
Inhalation anthrax
Woolsorter’s disease
Inhalation of spores from animal hair and wool
Bioterrorism event
Gastrointestinal anthrax
Rare in humans
Common in herbivores
B. anthracis Virulence Factors:
Spore= ___
Capsule = ____
Exotoxins= _____
Spore = the infectious particle
Capsule - poly-D-glutamic acid
antiphagocytic
capsule genes on plasmid
Exotoxins- Anthrax toxin is a tripartite toxin.
edema factor (EF): adenylate cyclase
lethal factor (LF): kills cells
protective antigen (PA): mediates entry of EF or LF into eukaryotic cells
nontoxic individually, but pathogenic when combined
PA + EF = edema toxin Æ edema
PA + LF = lethal toxin Æ tissue necrosis
all toxin genes are on pX01 plasmid
How anthrax toxins work?
EF= _____
EF = adenylate cyclase —> ↑ intracellular cAMP —→ ↑ efflux of fluids and ions —→ Edema
How anthrax toxins work?
LF= _____
EF = mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPKK) protease —> ↓ disrupts cell signaling —→ Cell death and tissue necrosis
Anthrax-Diagnosis:
Microscopy:
Gram stain = _____
Spores = ____
Capsule= ____
Gram stain= GPR, boxcars
Special stains for Capsule
Spores: seen in malachite green stain
Anthrax-Diagnosis:
Culture on blood agar plate:
________
Large, non-hemolytic adherent colonies
Anthrax-Diagnosis:
Molecular assays:
_____
PCR
Anthrax treatment =
Ciprofloxacin
Anthrax prevention:
Toxoid vaccine used for high-risk persons
Vaccination of animals to control disease
Eradication unlikely because of spore production
What is the causative agent for Botulism?
Clostridium botulinum
What is Botulism?
rare poisoning caused by toxins by Clostridium botulinum
Can be fatal and requires emergency medical care
can occur in infants, be spread in food, or infect a wound
Symptoms:
difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) or speaking (dysarthria), facial weakness and paralysis
Botulism- Clostridium botulinum
Gram stain = ___
Large GPR
Strict anaerobic
Spore forming
Found in soil, river and sea water; Animal gut
Botulism- Clostridium botulinum
Common sources = ____
For older children and adults- contaminated canned vegetables/ canned meats (canned foods with low acidity)
For infants- contaminated honey/ formula feed
Which type of botulism is best described below:
Due to ingestion of foods contaminated with spores of C. botulinum
a) Food botulism
b) Infant botulism
c) Wound botulism
d) Iatrogenic botulism
e) Inhalation botulism
b)
Which type of botulism is best described below:
Due to ingestion of foods contaminated with preformed toxins of C. botulinum
a) Food botulism
b) Infant botulism
c) Wound botulism
d) Iatrogenic botulism
e) Inhalation botulism
a)
Which type of botulism is best described below:
Due to wound contamination with soil containing spores of C. botulinum
a) Food botulism
b) Infant botulism
c) Wound botulism
d) Iatrogenic botulism
e) Inhalation botulism
c)
Which type of botulism is best described below:
Rare, due to inadvertent injections of medications contaminated with spores (Botox therapy)
a) Food botulism
b) Infant botulism
c) Wound botulism
d) Iatrogenic botulism
e) Inhalation botulism
d)
Which type of botulism is best described below:
Rare, due to inhalation of soil containing spores of C. botulinum
a) Food botulism
b) Infant botulism
c) Wound botulism
d) Iatrogenic botulism
e) Inhalation botulism
e)
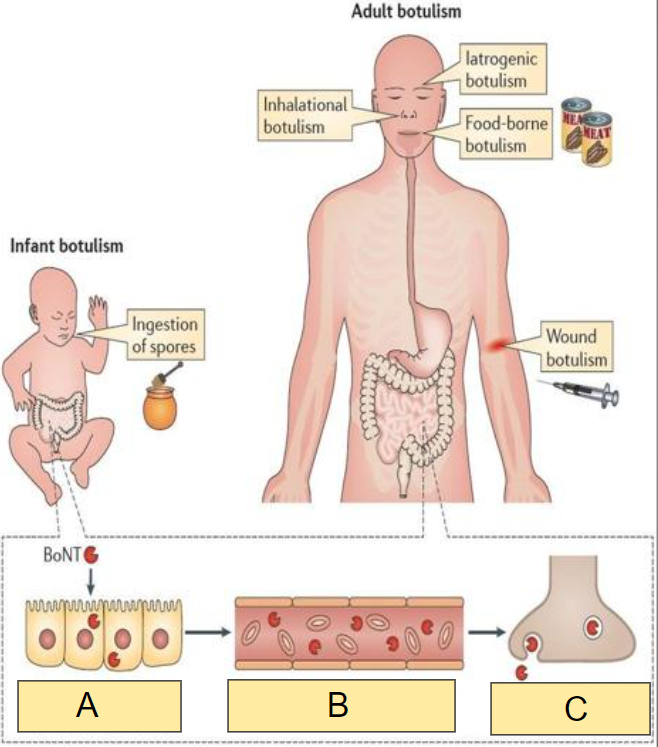
In the image, what occurs at:
A
a) Spread in general circulation
b) Entry into peripheral nerve terminals
c) Transcytosis across intestinal epithelium
c)
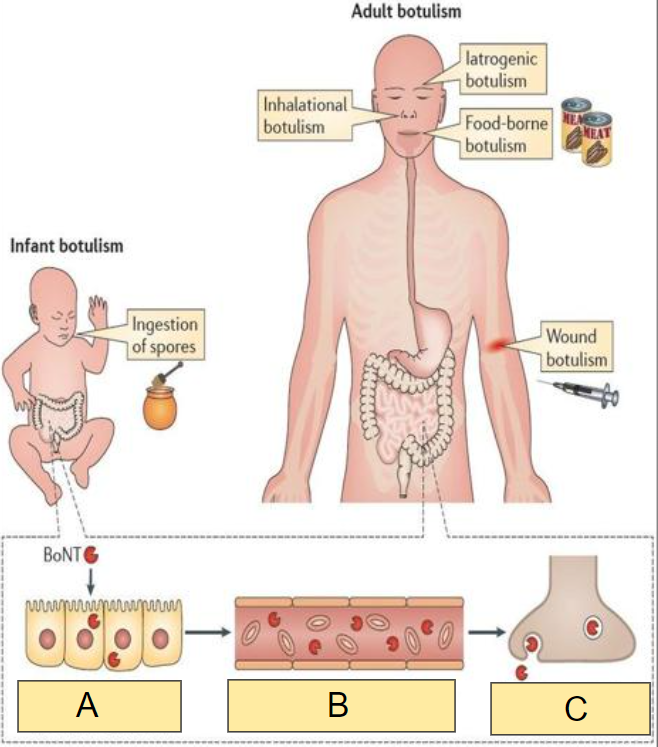
In the image, what occurs at:
B
a) Spread in general circulation
b) Entry into peripheral nerve terminals
c) Transcytosis across intestinal epithelium
a)
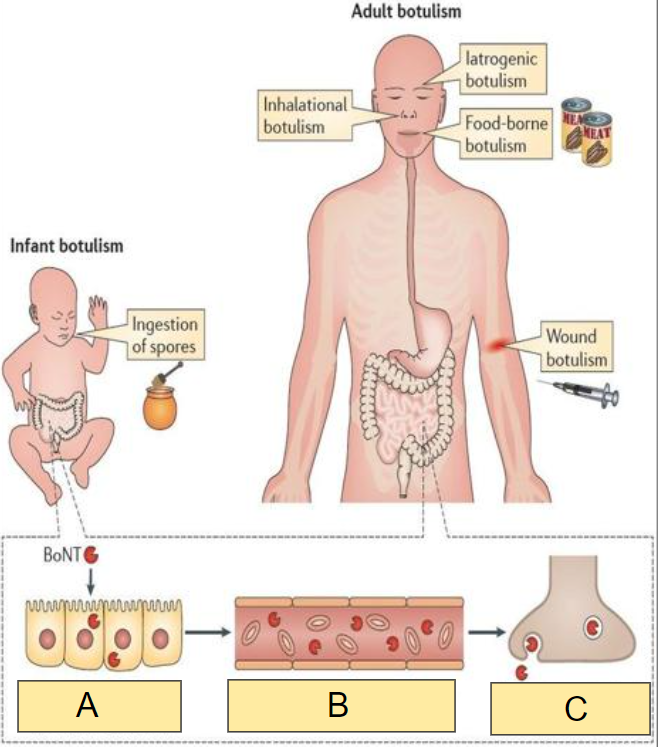
In the image, what occurs at:
C
a) Spread in general circulation
b) Entry into peripheral nerve terminals
c) Transcytosis across intestinal epithelium
b)
Botulism:
Is there constipation or diarrhea?
a) Constipation, no diarrhea
b) Diarrhea, no constipation
a)
Botulism:
Flaccid paralysis and ultimately death due to respiratory paralysis
a) True
b) False
a)
Floppy Baby Syndrome
Ingestion of C. botulinum spores = Infant botulism
Features include:
weak cry
constipation
inability to hold head or feed well, failure to thrive
C. Botulinum Exotoxin:
C. botulinum forms ____
Neurotoxin
Mode of action = _____
Forms a very potent heat labile toxin coded for by lysogenic prophage
Neurotoxin
Mode of action=
Blocks release of acetylcholine from peripheral nerves
Leads to flaccid paralysis, double/ blurred-vision, muscle weakness
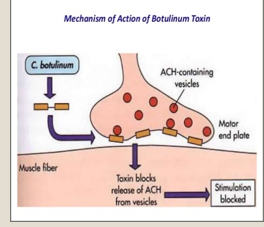
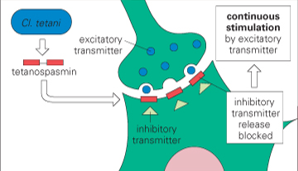
Clostridium tetani Exotoxin:
Intracellular-acting toxins = ____
Mode of Action = ____
Intracellular-acting toxins= Neurotoxin
Mode of action=
blocks release of inhibitory neurotransmitters Æ unopposed firing of the motor neurons —→ constant contraction
Food Botulism
Lab diagnosis = ______
toxin detection in food
Infant Botulism
Lab diagnosis = ______
toxin detection in serum or feces
Botulism
Treatment = ______
Treatment = Mechanical ventilatory support, antitoxin
Food Botulism
Prevention = ______
Prevention= Proper sterilization of canned foods
Infant Botulism
Prevention = ______
Prevention= avoid honey in children < 1 year of age
Listeriosis
serious infection caused by the ingestion of food contaminated with the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes
Listeria monocytogenes:
Characteristics= _____
Small, nonsporting gram-positive bacilli or cocco-bacilli
Facultative intracellular pathogen
Grow at 4°C (cold enrichment) -35°C
Show characteristic tumbling motility at 25°C
Weak beta hemolysis on Blood agar, Catalase positive
Found in animal gut and colonizes human gut or genital tract
Listeria monocytogenes:
Pathogenesis = ______
Virulence factors = _____
Lab test = ____
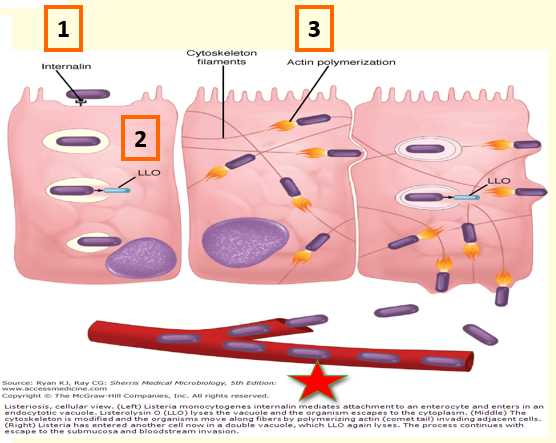
Pathogenesis =
Attach to host cell receptors like Enterocytes, M cells, phagocytes, etc.
Virulence factors =
Internalins= attachment and entry into nonphagocytic cells
Listeriolysin O= Beta-hemolysin (pore forming exotoxin) allowing escape from phagosome into cytoplasm
ActA= actin polymerization —> lateral propulsion and involvement of adjacent cells
Lab test =
Gram stain and culture of body fluids, such as CSF or placenta
Treatment=
Antibiotics- Ampicillin/ Ampicillin + Gentamicin
Prevention=
Avoid unpasteurized cheese/ unwashed salads esp. in pregnancy and old age
Which virulence factor of Listeria monocytogenes is best described?
Attachment and entry into nonphagocytic cells
a) Internalins
b) Listeriolysin O
c) ActA
a)
Which virulence factor of Listeria monocytogenes is best described?
Beta-hemolysin (pore forming exotoxin) allowing escape from phagosome into cytoplasm
a) Internalins
b) Listeriolysin O
c) ActA
b)
Which virulence factor of Listeria monocytogenes is best described?
Actin polymerization —> lateral propulsion and involvement of adjacent cells
a) Internalins
b) Listeriolysin O
c) ActA
c)
What is the principle of the Coagulase Test:
Coagulase enzyme converts plasma fibrinogen into fibrin clots
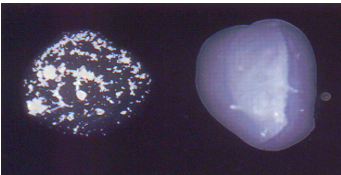
In the image, which is the positive Coagulase test?
a) Left
b) Right
a)
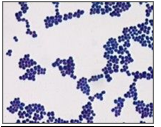
Which of the following is best described below?
Normal flora of skin and mucous membrane
May cause disease (clinically significant)
Hands and nares of 20-40% of population (higher in hospital personnel)
Most clinically significant staphylococcus species
Gram-positive cocci, catalase positive, coagulase positive
Beta-hemolytic with golden pigment
a) Staphylococcus epidermidis
b) Staphylococcus aureus
c) Streptococcus pyogenes
d) Streptococcus pneumoniae
b)
Which of the following is best described below?
Gram-positive cocci, catalase positive, coagulase positive
Beta-hemolytic with golden pigment
Pathogenesis:
Forms a host of virulence factors and causes a variety of diseases
a) Staphylococcus epidermidis
b) Staphylococcus aureus
c) Streptococcus pyogenes
d) Streptococcus pneumoniae
b)
S. Aureus causes diseases through _______ or ______ (2)
Direct invasion -with abscess formation or Production of exotoxins
Staphylococcus aureus —→ Direct invasion-with abscess formation —→ ______
Pyogenic disease:
Folliculitis, furuncles
Staphylococcus aureus —→ Production of exotoxins—→ ______
Toxin-mediated diseases:
Toxic shock syndrome
Food poisoning
Scalded skin syndrome
What are the virulence factors for:
Staphylococcus aureus (Pyogenic Disease)
Capsule: produced by some strains
Adhesion and Protection:
Surface adhesins
Coagulase and Clumping factor
fibrinogen —> fibrin clot —> abscess
Protein A- binds Fc receptor of IgG —> prevents antibody-mediated immune clearance
Damage:
Enzymes: Lipases (degrades skin lipids), hyaluronidases
Teichoic acids: inflammatory response
Cytolytic toxins:
Alpha toxin= pore forming toxins
Panton-Valentine leuckocidin= lyses white blood cells
Of the following cytolytic toxins given which is found in Staphylococcus aureus (Pyogenic Disease)*
a) Protein A
b) Pyrogenic exotoxins
c) Panton-Valentine Leukocidin
d) Pneumolysin
c)
Which of the following is best described below:
____ = pore-forming toxin
a) Teichoic acids
b) Panton-Valentine leukocidin
c) Lipases
d) Alpha toxin
d)
Which of the following is best described below:
____ = lyses white blood cells
a) Teichoic acids
b) Panton-Valentine leukocidin
c) Lipases
d) Alpha toxin
b)
Which of the following best describes:
Coagulase and Clumping factor = _________
a) binds Fc receptor of IgG —> prevents antibody-mediated immune clearance
b) fibrinogen —> fibrin clot —> abscess
b)
Which of the following best describes:
Protein A = _________
a) binds Fc receptor of IgG —> prevents antibody-mediated immune clearance
b) fibrinogen —> fibrin clot —> abscess
a)
20-yr old Jane is brought to the hospital by her friend as she complained of fever, a headache, diarrhea and weakness. There was a steady deterioration in her condition over the last 24 hours and this morning she was confused and very ill. On examination she has high temperature and a low blood pressure. There is a widespread erythematous rash over the trunk and peeling of skin on the palms and soles. Further questioning reveals that she was menstruating and usually used tampons.
What condition is Jane likely suffering from?
Toxic shock syndrome
20-yr old Jane is brought to the hospital by her friend as she complained of fever, a headache, diarrhea and weakness. There was a steady deterioration in her condition over the last 24 hours and this morning she was confused and very ill. On examination she has high temperature and a low blood pressure. There is a widespread erythematous rash over the trunk and peeling of skin on the palms and soles. Further questioning reveals that she was menstruating and usually used tampons.
What led to Jane’s infection?
Contaminated tampons
20-yr old Jane is brought to the hospital by her friend as she complained of fever, a headache, diarrhea and weakness. There was a steady deterioration in her condition over the last 24 hours and this morning she was confused and very ill. On examination she has high temperature and a low blood pressure. There is a widespread erythematous rash over the trunk and peeling of skin on the palms and soles. Further questioning reveals that she was menstruating and usually used tampons.
Describe the likely pathogen?
GPC in clusters
20-yr old Jane is brought to the hospital by her friend as she complained of fever, a headache, diarrhea and weakness. There was a steady deterioration in her condition over the last 24 hours and this morning she was confused and very ill. On examination she has high temperature and a low blood pressure. There is a widespread erythematous rash over the trunk and peeling of skin on the palms and soles. Further questioning reveals that she was menstruating and usually used tampons.
What is the virulence factor responsible?
TSST- a superantigen
What is TSST-1?
Virulence Factor- Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin
TSST-1 binds directly to MHCII on macrophages
Interact with T cell receptors
Nonspecific proliferation of T cells and massive release of cytokines
What is best described below:
Sudden onset: fever, vomiting, diarrhea
Red rash resembling a sunburn and desquamation 1-2 weeks later
Occasional deaths
a) Listeriosis
b) Botulism
c) Toxic Shock Syndrome
d) Anthrax
c)
Staphylococcus aureus can also cause food poisoning
a) True
b) False
a)
Explain how Staphylococcus aureus can also cause food poisoning?
Enterotoxin
Intoxication usually associated with potato salad, dairy products, and ham
No detectable odor of food appearance change
Nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramping and diarrhea within 1-6 hours of ingestion
Resolves within 24 hrs
No fever
S. aureus Infections-Treatment
Superficial lesions and food poisoning are usually _______
self-limiting
S. aureus Infections-Treatment
______ and ______ for extensive or deeper infections
a) Superficial lesions and food poisoning
b) Surgical drainage and superficial lesions
c) Surgical drainage and food poisoning
d) Surgical drainage and antibiotic therapy
d)
S. aureus Infections-Treatment
Antibiotic resistance is a big problem
Give example of S. aureus that is resistant to an antibiotic = _______
Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA)
S. aureus Infections-Treatment
Antibiotic resistance is a big problem
Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA)
Explain the mechanism?
Organism acquires a gene, mecA, that alters binding site for penicillins
PBP2 —> PBP2A
What is the treatment for Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA)
Vancomycin or linezolid
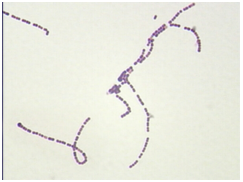
Which of the following is best described below?
A few species are normal flora of skin and mucous membranes, especially in the oral cavity
May cause disease (clinically significant)
GPC in chains
Catalase negative
Growth on blood agar
a) Staphylococcus
b) Streptococcus
c) Enterococcus
b)
How are Streptococci classified?
Alpha hemolytic strep
Beta hemolytic strep
Gamma hemolytic strep

_____ hemolytic strep = Partial
a) Alpha hemolytic strep
b) Beta hemolytic strep
c) Gamma hemolytic strep
a)

_____ hemolytic strep = Complete
a) Alpha hemolytic strep
b) Beta hemolytic strep
c) Gamma hemolytic strep
b)

_____ hemolytic strep = None
a) Alpha hemolytic strep
b) Beta hemolytic strep
c) Gamma hemolytic strep
c)
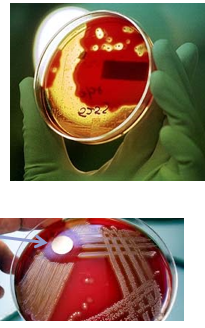
Which of the following is best described below:
Group A strep, Beta Strep
Beta-hemolytic colonies
Small, pinpoint colony
Big zone of hemolysis
GPC, catalase neg
Bacitracin susceptible
a) Staphylococcus epidermidis
b) Staphylococcus aureus
c) Streptococcus pyogenes
d) Streptococcus pneumoniae
c)
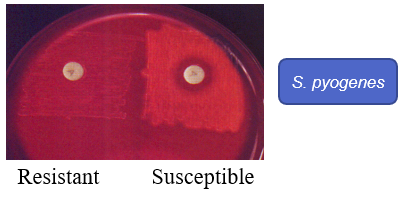
What are the physiological characteristics of:
Bacitracin disc (A disc)
Bacteria streaked onto plate
Filter paper disc containing bacitracin dropped
Incubate and observe for growth inhibition
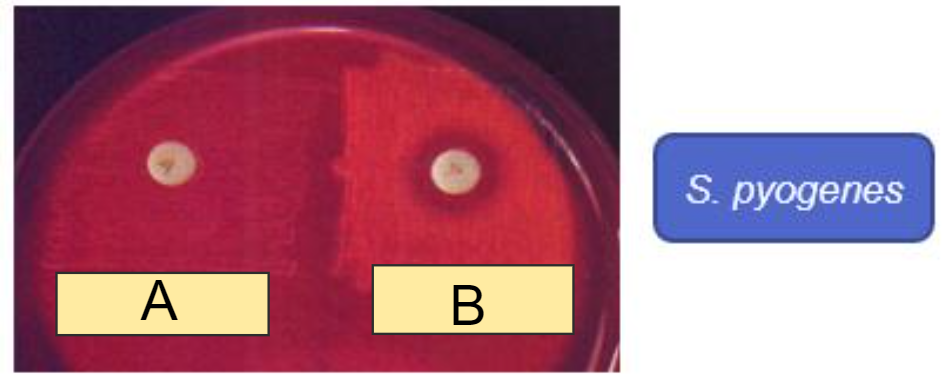
In the Bacitracin disc (A disc) image, which shows resistance?
a) A
b) B
a)
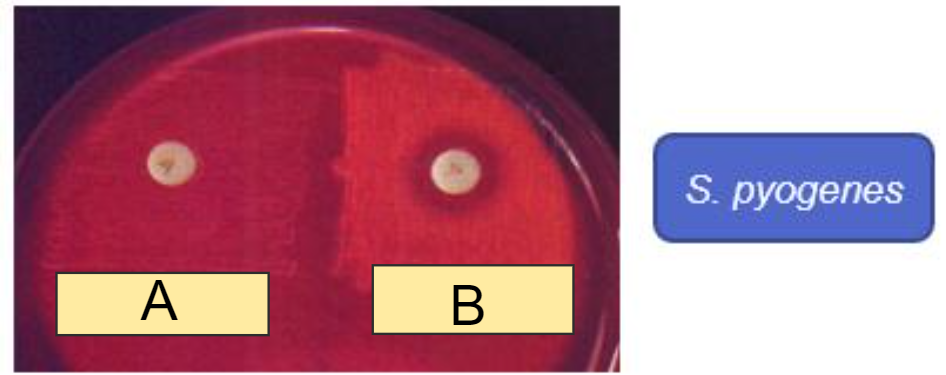
In the Bacitracin disc (A disc) image, which shows Susceptible?
a) A
b) B
b)
What are the virulence factors of:
Streptococcus pyogenes
Adhesion & Protection
M-protein– binds to fibronectin and is antiphagocytic
F-protein – binds fibronectin
Hyaluronic acid capsule– non-immunogenic, antiphagocytic
Spreading factors & Damage
Exoenzymes – DNase, hyaluronidase, hemolysins
Teichoic acids – Inflammatory response
Toxins
Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins – superantigens
Streptolysin O and S pore forming —> hemolysins
Which virulence factor of Streptococcus pyogenes is best described:
_______ = binds to fibronectin and is antiphagocytic
a) F-Protein
b) A- Protein
c) M- Protein
d) Hyaluronic acid capsule
c)
Which virulence factor of Streptococcus pyogenes is best described:
_______ = binds fibronectin
a) F-Protein
b) A- Protein
c) M- Protein
d) Hyaluronic acid capsule
a)
Which virulence factor of Streptococcus pyogenes is best described:
_______ = non-immunogenic, antiphagocytic
a) F-Protein
b) A- Protein
c) M- Protein
d) Hyaluronic acid capsule
d)
Strep Throat diagnosis =
Diagnosis from throat swab
Rapid strep enzyme immunoassay
Culture
Sequelae
Scarlet Fever
Cross-reacting antibodies
Acute streptococcal glomerulonephritis
Rheumatic fever
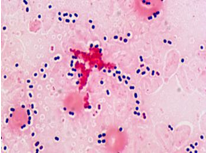
Which of the following is best described below:
Also k/a Pneumococcus
Lancet-shaped GP diplococci
Alpha hemolytic colonies
Catalase negative
Susceptible to Optochin
a) Staphylococcus epidermidis
b) Staphylococcus aureus
c) Streptococcus pyogenes
d) Streptococcus pneumoniae
d)
What are the virulence factors found in:
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Polysaccharide capsule
90 pneumococcal serotypes, 23 responsible for most diseases
IgA protease
Colonization
Pneumolysin
Pore-forming toxin
Pneumococcal Pneumonia = Typical Lobar Pneumonia
Rapid onset
Chills & fever
Chest pain
Productive cough + blood in the sputum (rusty sputum)
Damage of epithelium stimulates outpouring of fluid, red blood cells, and leukocytes from alveoli Æ productive cough with blood
Treatment for Streptococcal infections
Penicillin or Amoxycillin
Ceftriaxone in very ill patients of pneumonia
Drug sensitivity is good
Prevention for Streptococcal infections
Avoiding contact with sick patients
Handwashing and cough etiquette