Unit 7 - [P2] Benign Pathology of the GB
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Part Two
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What is Cholelithiasis?
Gallstones
Gallstones can be a range of sizes, what sizes cause the most problem?
Tiny stones —> may lead to duct obstruction
What are the clinical findings of Cholelithiasis?
RUQ pain
Radiating to right shoulder
Back & chest pain
What lab work may be increased by Cholelithiasis?
Bilirubin
Amylase
Alkaline Phosphatase
What are the differential diagnoses for Cholelithiasis?
Gas in duodenum
Porcelain GB
Surgical clips
Sludge
Polyps
What are the 5 F’s that correspond with Cholelithiasis?
Female
Fat
Forty
Fertile
Fair
What are the US finding for Cholelithiasis?
Bright reflector(s) with posterior acoustic shadowing
With Cholelithiasis, how does it respond to different positions?
Moveable
Dependent
Floating
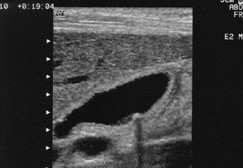
What is this image showing?
Small gallstone
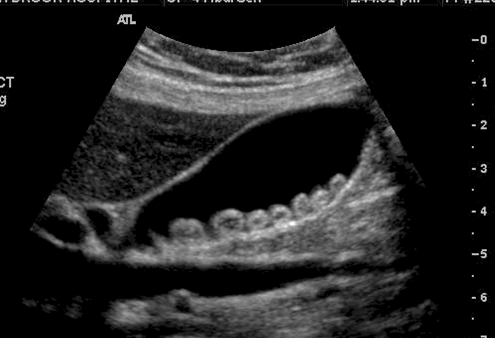
What is this image showing?
Gallstones
Floating stones are made up of _______
Cholesterol
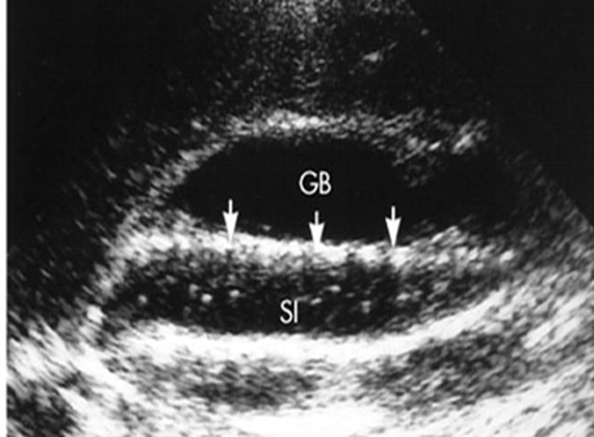
What is this image showing?
Longitudinal GB with a layer of “floating” stones along a thick layer of bile sludge
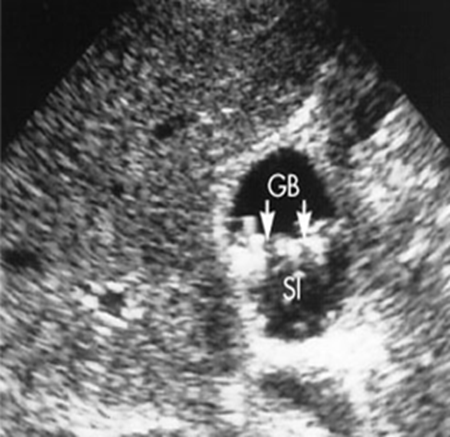
What is this image showing?
Transverse GB with a layer of “floating” stones along a thick layer of bile sludge
What does the WES sign stand for?
Wall echo shadow
WES sign can be described as a …
GB packed with stones
What are the false positives when diagnosing Cholelithiasis?
Polyp
Adenomyomatosis
Sludge Ball
Duodenal gas
Surgical clips
Biliary air
Porcelain GB
GB agenesis
What are the false negatives when diagnosing Cholelithiasis?
Contracted GB
Stone in duct/neck
Very small stones
Geographic location/technique
Sludge Ball
Gallstones in fundal cap
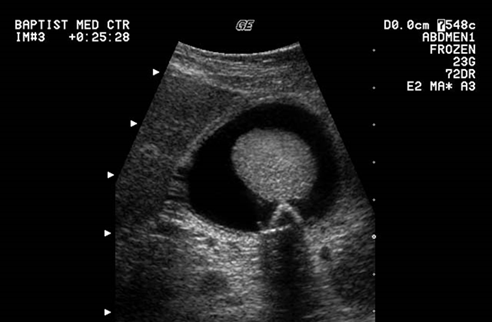
What is this image showing?
GB sludge ball
What is a Porcelain Gallbladder?
Calcium incrustation of GB wall
A Porcelain Gallbladder is associated with _________
Gallstones
Porcelain Gallbladder is more common in _________ over __________.
Women > men
What are the symptoms for a Porcelain Gallbladder?
Often asymptomatic
In a Porcelain Gallbladder __% develop _________ of the GB wall.
25%, cancer
What are the US findings of a Porcelain Gallbladder?
GB wall thickly calcified with shadowing
What are the differential diagnoses for Porcelain Gallbladder?
Gallstones with Emphysematous Cholecystitis
WES sign
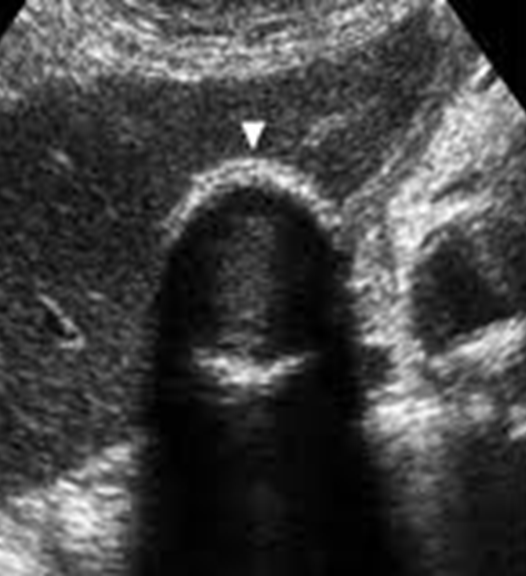
What is this image showing?
A Porcelain Gallbladder
What is Hyperplastic Cholecystosis?
A disease entity characterized by a functional abnormality of the gallbladder without specific anatomic changes
What are the two different types of Hyperplastic Cholecystosis?
Cholesterolosis
Adenomyomatosis
What is Cholesterolosis?
Cholesterol is deposited under lining of mucosa membrane
What is another title for Cholesterolosis?
Strawberry GB
What may Cholesterolosis be associated with?
Cholesterol polyps
GB polyps
What do Cholesterol polyps look like when associated with Cholesterolosis?
Attached by a stalk
< 10mm
Usually multiple
Do not shadow
Remain fixed to wall
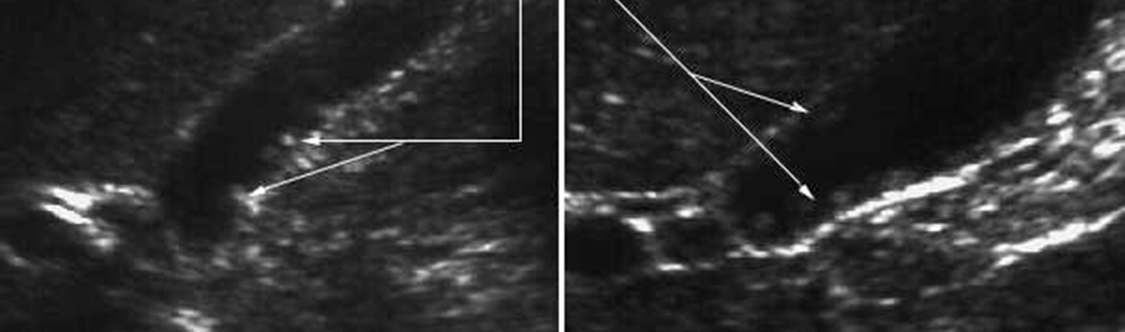
What is this image showing?
Non-mobile, non-shadowing, echogenic irregularity of the GB wall
What are Papillomas?
Noncancerous, outward-growing lumps that might cause problems in some locations
What is Adenomyomatosis?
Benign papilloma’s in the GB wall
Single or in a group
What are the US findings of Adenomyomatosis?
Small echogenic structure(s) in GB wall
Ring down or comet tail artifact
Do not move with change in positions or compression
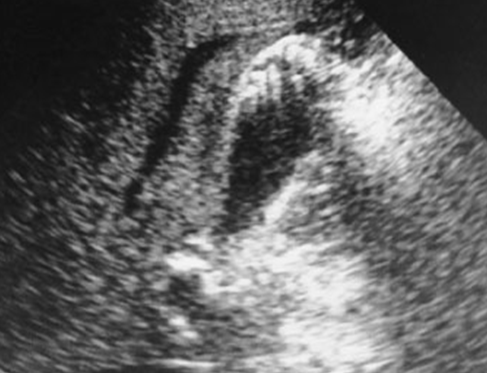
What is this image showing?
Adenomyomatosis in sagittal of the GB
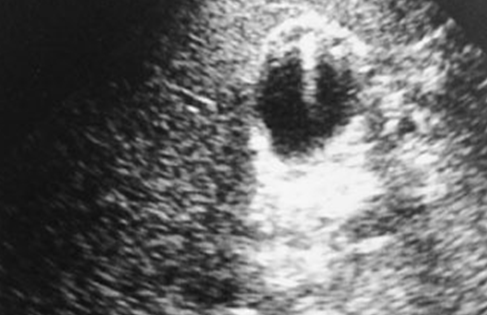
What is this image showing?
Adenomyomatosis in transverse of the GB
What is the most common pseudotumor of the gallbladder?
Polyp
What is the US findings of a polyp?
Adherent to wall of GB
No shadowing
Will not move with change in pt. positions
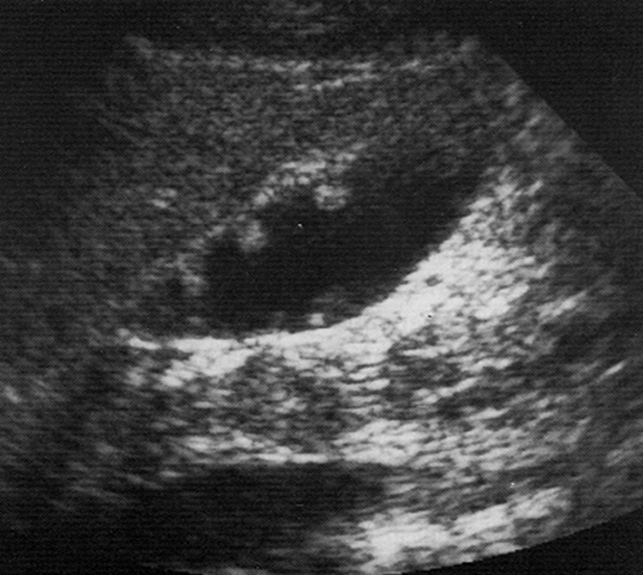
What is this image showing?
Polyps
What is an Adenoma?
Benign neoplasm with premalignant potential
What are the US findings of an Adenoma?
Usually solitary
Almost always near fundus
Homogeneously hyperechoic
GB wall may be thickened
If the GB wall is thickened adjacent to an Adenoma, what should you suspect?
Malignancy
What is a differential diagnosis for an Adenoma?
Adenomyomatosis
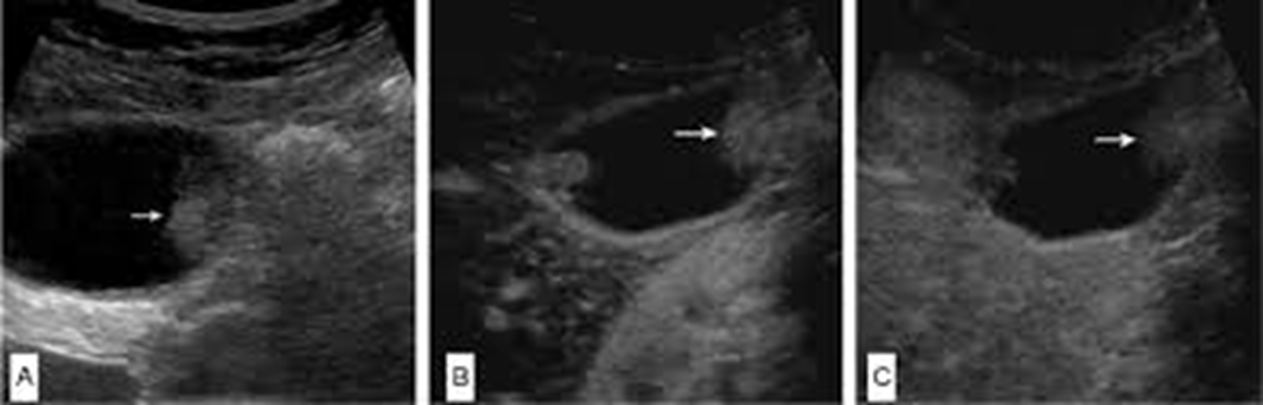
What are these images showing?
An Adenoma