DMU 3313 Unit 6 Review
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
What states of matter are materials that flow/fluids
gases and liquids
What is viscosity
resistance to flow offered by a fluid in motion
What is the unit of viscosity?
poise
What is density?
mass per volume
What is pressure?
driving force behind fluid flow
What is required for flow to occur?
pressure difference
If pressure difference is greater, what happens to flow rate?
it increases
Pressure formula
pressure = force/area
What is resistance
the opposition of flow
What does flow resistance depend on?
kinematic viscosity, tube length, and tube radius
What factor has the largest effect on resistance?
radius of tube
Resistance equation
R = 8(tube length)(viscosity)/(pi)(r )^4
What is volumetric flow rate?
the volume of blood passing a point per unit of time
What unit is used for volumetric flow rate?
mL/s
volumetric flow rate equation
Q = pressure difference/resistance
Poiseuille’s equation with radius
Q = (pressure difference)(pi)(r^4) / (8)(L)(viscosity)
Poiseuille’s equation with diameter
Q = (pressure difference)(pi)(d^4) / (128)(L)(viscosity)
For steady flow in long straight tubes, if pressure difference or diameter of tube increases, flow rate will….
increase
For steady flow in long straight tubes, if viscosity or length of the tube increases, flow rate will…
decrease
What are the spatial categories for types of flow
plug, laminar, parabolic, disturbed, turbulent
What are the temporal categories for types of flow
steady and pulsatile
What is plug flow?
the speed of the fluid is essentially constant across the tube
What is laminar flow?
streamlines are parallel to each other and flow speed is maximum at the center of the tube and minimum or 0 at tube’s walls
What is parabolic flow?
a form of laminar flow where the average flow speed across the vessel is equal to ½ the maximum flow speed (center)
What is disturbed flow?
a form of laminar flow that occurs when the parallel streamlines are altered from their straight lines
When does disturbed flow occur?
in the region of a stenosis or at a bifurcation
What is turbulent flow?
nonlaminar flow with random and chaotic speeds and directions, but forward net flow is still maintained
What is steady flow?
pressures, flow speeds, and flow patterns do not change over time
What is pulsatile flow?
non-steady flow, with acceleration and deceleration over the cardiac cycle
What direction does flow move from?
high pressure to low pressure
How does inspiration affect flow?
increased flow from abdominal cavity into thoracic cavity and decreased flow from legs into abdominal cavity
How does expiration affect flow?
decreased flow from abdominal cavity into thoracic cavity and increased flow from legs into abdominal cavity
What is a stenosis?
abnormal narrowing of a passage in the body
What does the continuity rule state?
volumetric flow rate must be constant proximal, within, and distal to a stenosis
Continuity rule equation
Q = average velocity x area
What is the Bernoulli effect?
In order for blood to accelerate within a stenosis, there must be a drop in pressure (if flow speed increases, pressure decreases)
Where does the largest pressure drop occur in the cardiovascular system?
arterioles
Why does turbulence occur distal to stenoses?
increased velocity and vessel widening
What does post-stenotic turbulence result in?
bruit (sounds on auscultation from turbulence)
What does Doppler provide information about in DMU?
presence, direction, speed, and character of blood flow of motion
What is the Doppler effect?
the change in frequency caused by motion of a sound source, receiver, or reflector
Is wavelength effected by the Doppler effect?
not directly, but it is effected as a result of frequency being effected
What possible situations result in the Doppler effect?
moving source, receiver, reflector, or more than one of these moving
What is Doppler shift?
the difference between the frequency of the received sound wave and frequency of the emitted sound wave
What is the Doppler shift if the reflector is moving toward the source?
positive shift and ascending flow
What is the Doppler shift if a reflector is moving away from the source?
negative shift and descending flow
The amount of increase or decrease in frequency in Doppler shift depends on what?
speed of reflector, angle between wave motion and direction of reflector, and frequency of wave emitted from source
What is the Doppler equation? (Doppler shift)
fD = (2/c)(v)(fT)(cos(theta))
What is Doppler angle?
the angle between the direction of sound propagation and flow direction
Where does the Doppler gate indicator line need to be lined up on the image?
as close to parallel to the flow direction
As Doppler angle increases, the % of error in speed will…
increase
Doppler angles less than what are recommended to avoid error?
less than 60 degrees
If wave propagation is directly opposite of blood flow, what shift will be obtained?
maximum positive shift
If wave propagation is directly parallel moving with flow, what shift will be obtained?
maximum negative shift
If propagation direction is perpendicular to blood flow, what shift will be obtained?
no shift will be measured
What are the types of Doppler imaging?
pulsed wave, continuous wave, and power Doppler
What are the types of display in Doppler?
color flow, spectral, duplex, triplex, and audio
What does color Doppler show?
real time blood flow or tissue motion information
What type of display is color Doppler?
duplex
In color Doppler, what does red represent? What does blue represent?
red represents positive doppler shift, blue represents negative doppler shift
What is Nyquist limit?
the highest frequency in a sampled signal that can be displayed correctly or minimum number of samples to avoid aliasing
Nyquist limit equation
Nyquist limit (fD) = PRF/2
When does aliasing occur?
when the Doppler shift exceeds the Nyquist limit (PW only)
What is aliasing?
appearance of Doppler information on the wrong side of the baseline
What are the methods of reducing or eliminating aliasing?
shift baseline, increase PRF, increase doppler angle, use lower operating frequency, use a continuous wave device
What are advantages and limitations of color Doppler?
advantages: shows blood flow, direction of flow, and nonvascular motion
limitations: angle dependent, lower frame rates, lack of detailed spectral info
How to differentiate flow reversal and aliasing?
flow reversal has dark regions between opposite colors and aliasing has bright colors with no black
What is the power of Doppler shift determined by?
concentration of moving scatterers
What does power Doppler do?
presents 2D Doppler info by color encoding the strength of the Doppler shifts
What are advantages and disadvantages of power Doppler
advantages: angle independent, no aliasing, improved sensitivity
disadvantages: no directional info, no flow speed or character info
How does continuous wave spectral Doppler work?
detects the Doppler shift within the region of overlap between the beams of transmitting and receiving transducer elements
How does pulse wave spectral Doppler work?
emits ultrasound pulses and receives echoes using a single element transducer and array
What does the vertical axis of a spectral display represent?
Doppler shift frequency
What does the horizontal axis of a spectral display represent?
time
Where are positive shifts placed on a spectral display? Where are negative shifts placed?
positive shifts are above baseline, negative shifts below baseline
What is a spectral window?
the area within or under the waveform
What happens if all the cells are moving at the same speed?
there is a narrow range of velocities present, approximately plug flow, spectral trace is thin, and open spectral window
What is spectral broadening?
filling in of the spectral window
What are features of a low resistance waveform?
forward flow during systole and diastole, perfuse organs that need continuous blood flow, typically monophasic, and gentle upstroke
What are features of a high resistance waveform?
brief flow reversal during diastole, perfuse organs that do not need continuous flow, triphasic, and rapid upstroke
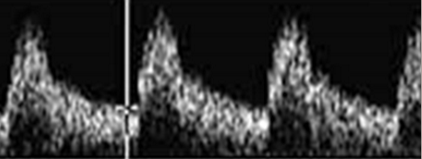
What type of waveform is shown in the image?
low resistance
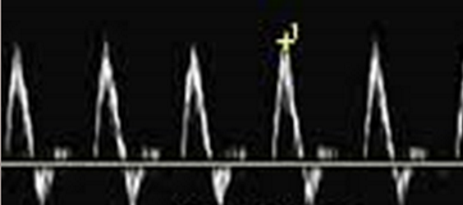
What type of waveform is shown in the image?
high resistance