Principles of Physical Training Chapter 1
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
what are the three types of muscle?
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
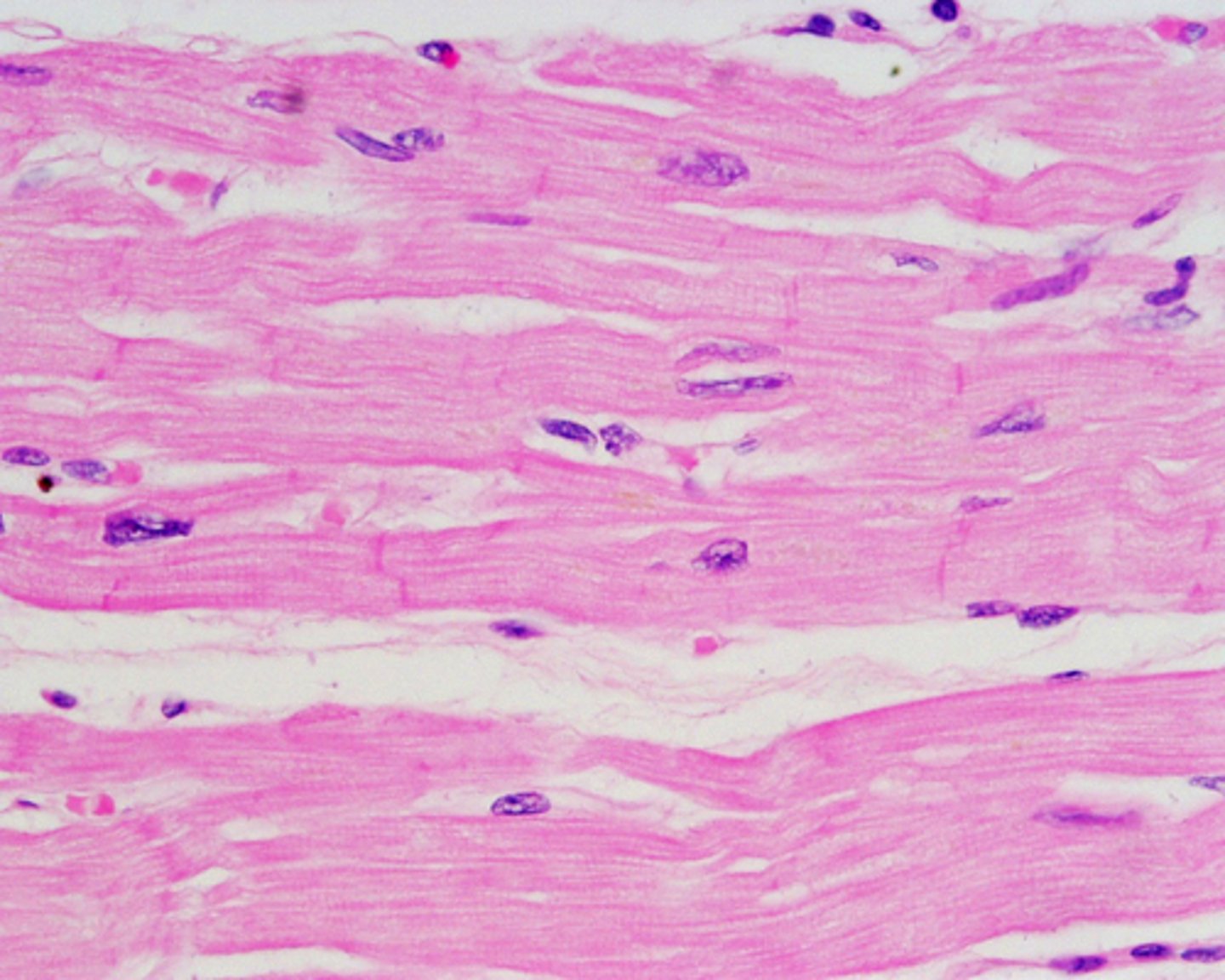
cardiac muscle
striated but smaller, branches, and uninucleated
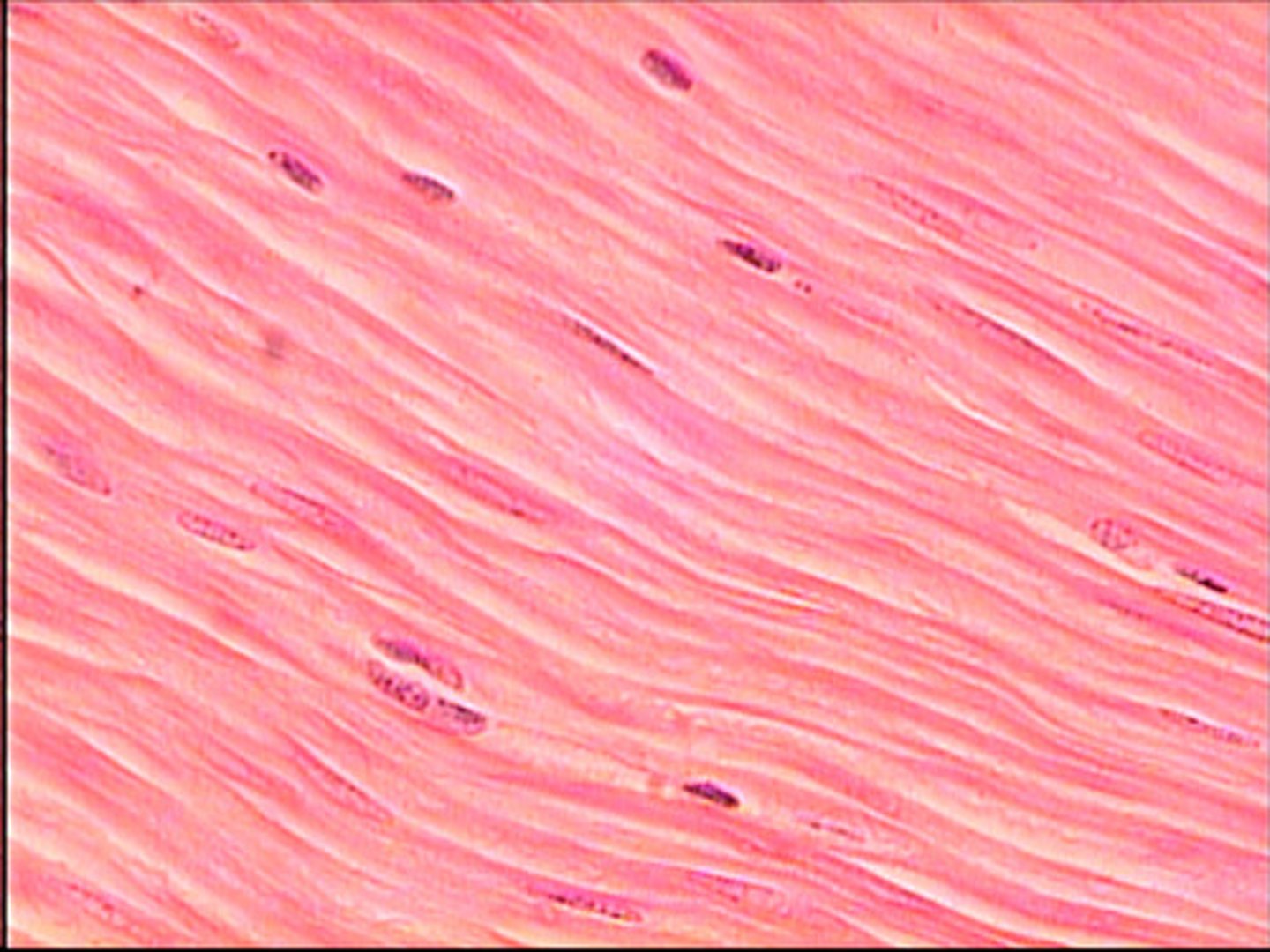
smooth muscle
lines the walls of blood vessels, stomach, ureters, and intestines
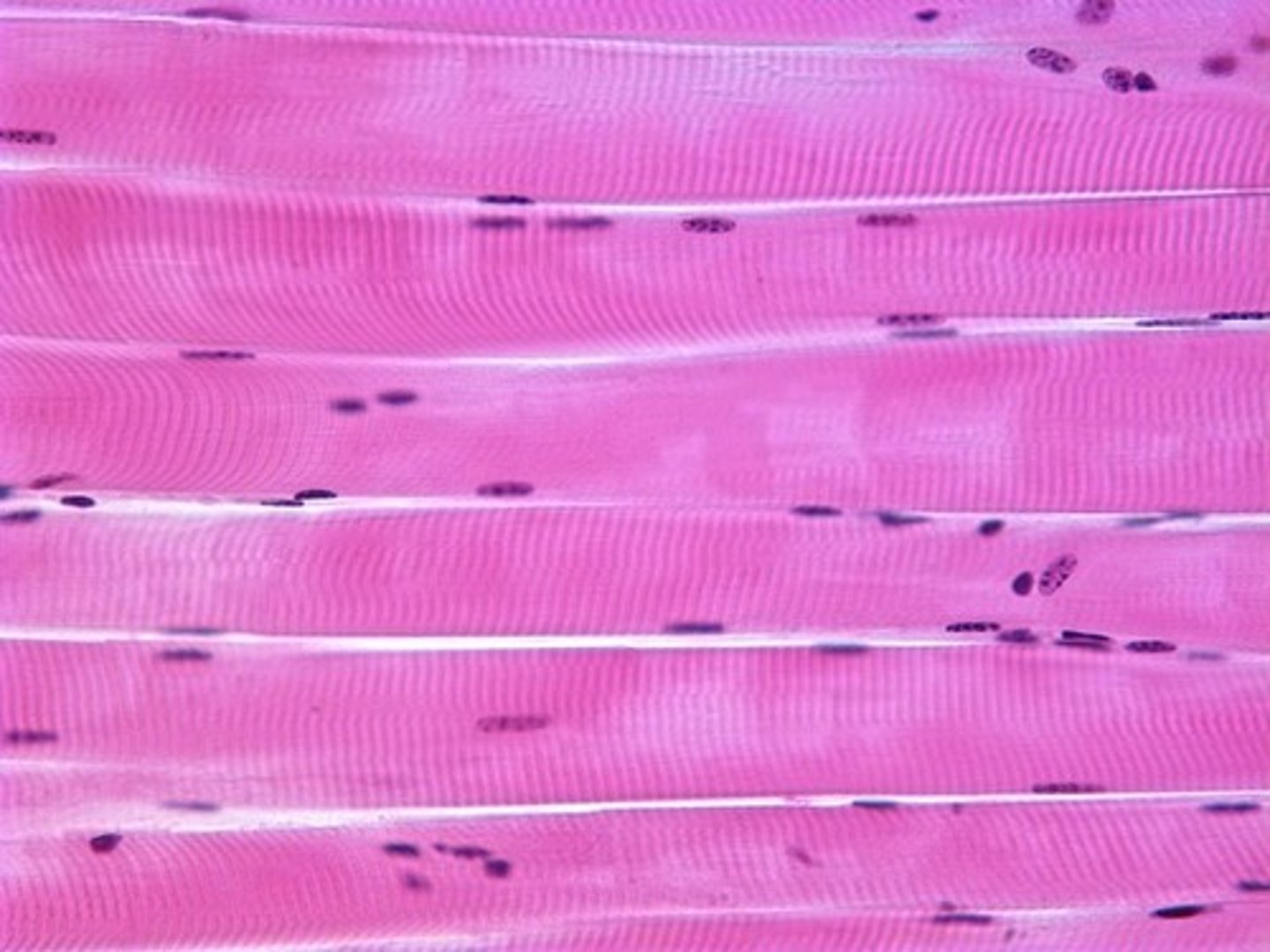
skeletal muscle
attaches to bones for movement, striped, and multinucleated
how much of the total body mass is muscular?
35-45%
tendons
attach muscle to bone allowing transfer of energy for movement
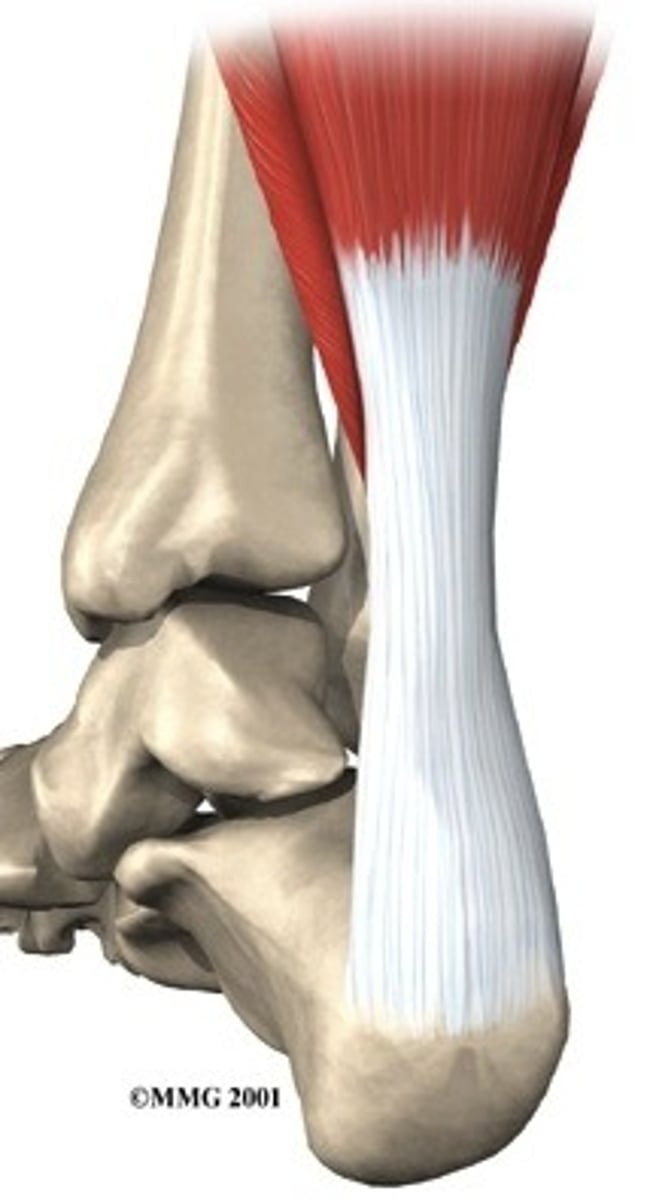
what is the primary constituent for tendons?
collagen
ligaments
Connect bone to bone
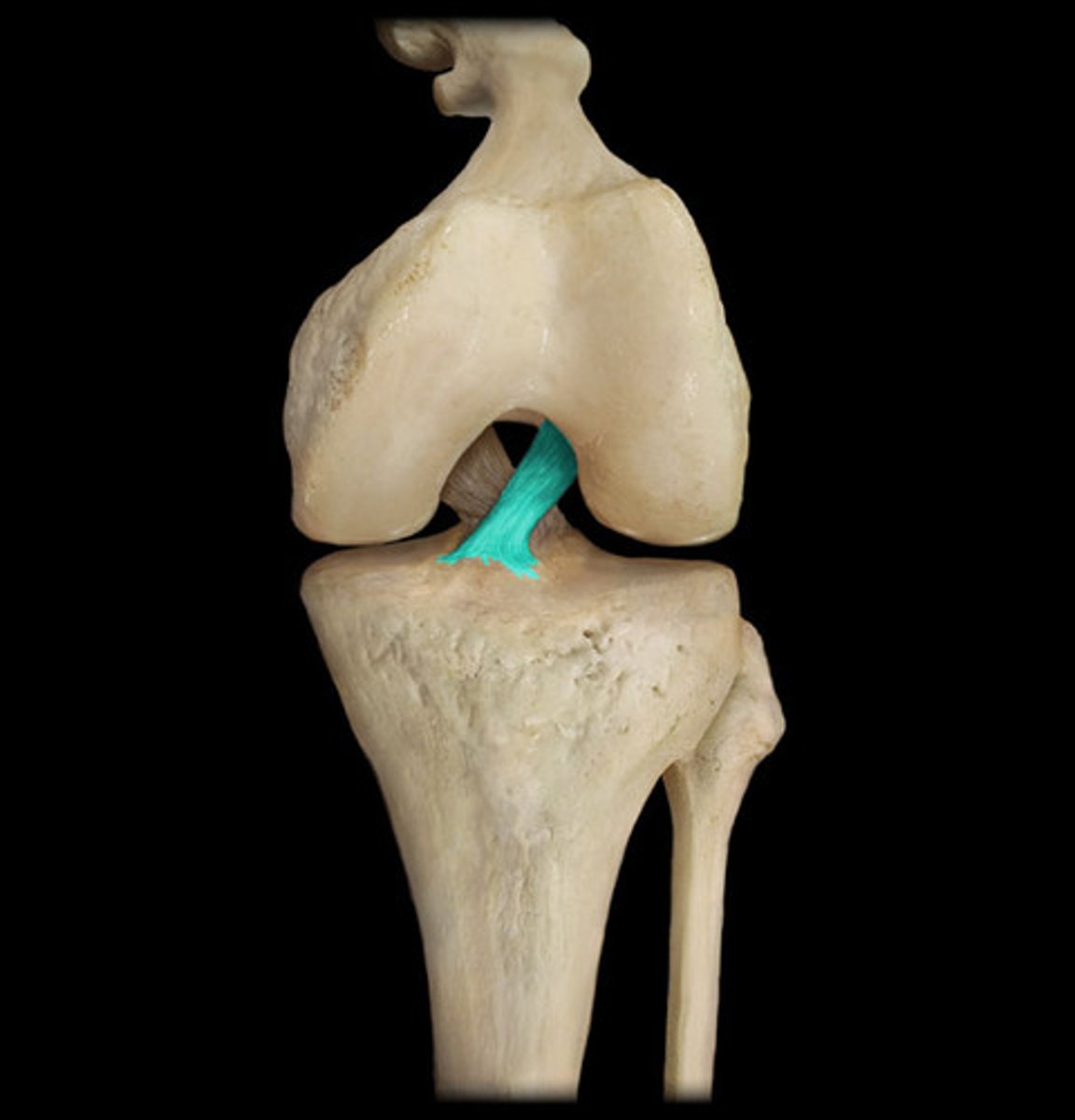
what is the primary constituent for ligaments?
collagen
what is the secondary constituent for ligamentd?
elastin
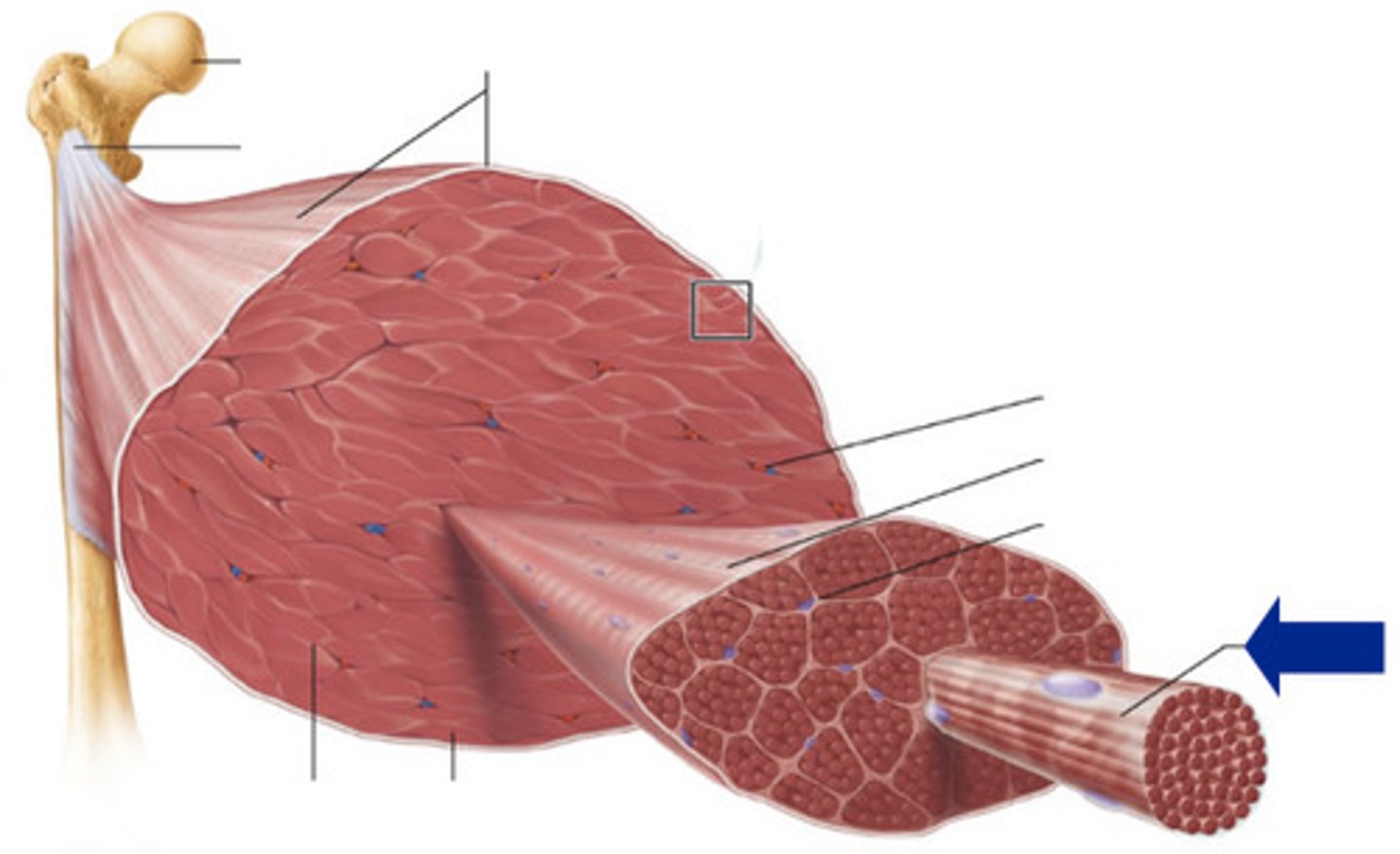
muscle organization
myofilaments → sacromere → myofibril → muscle fiber (cell) → fascicle → skeletal muscle (organ)
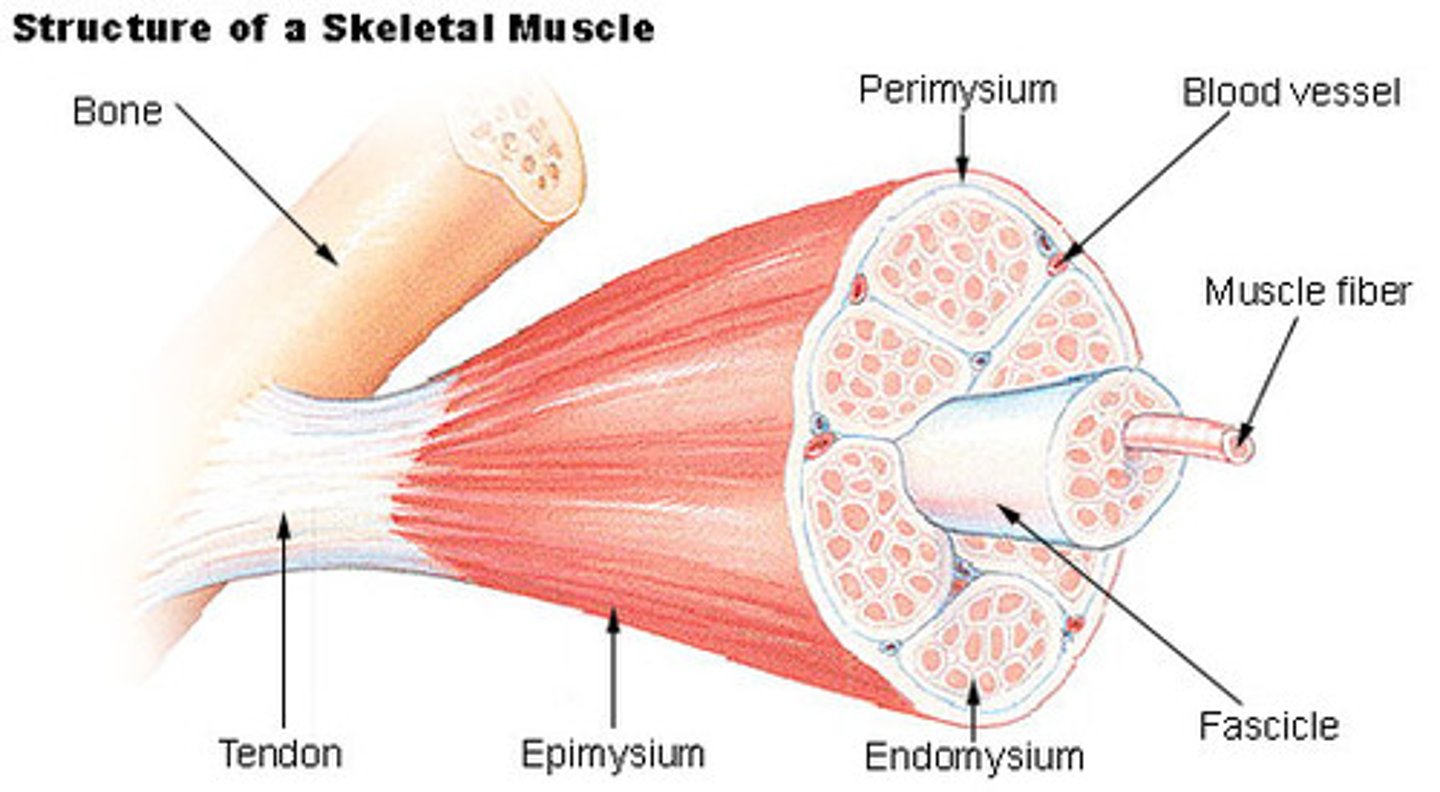
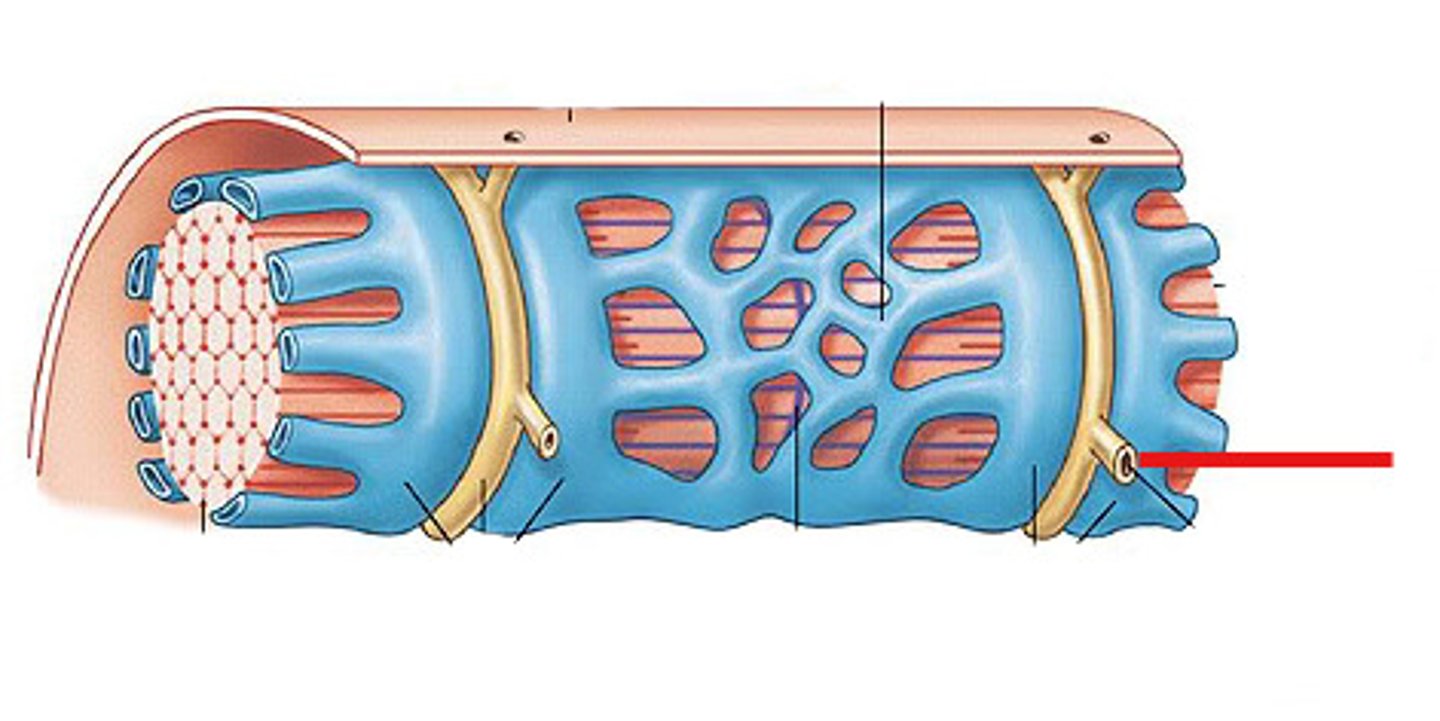
epimysium
covers the entire skeletal muscle
perimysium
Connective tissue surrounding a fascicle
endomysium
Connective tissue surrounding a muscle fiber
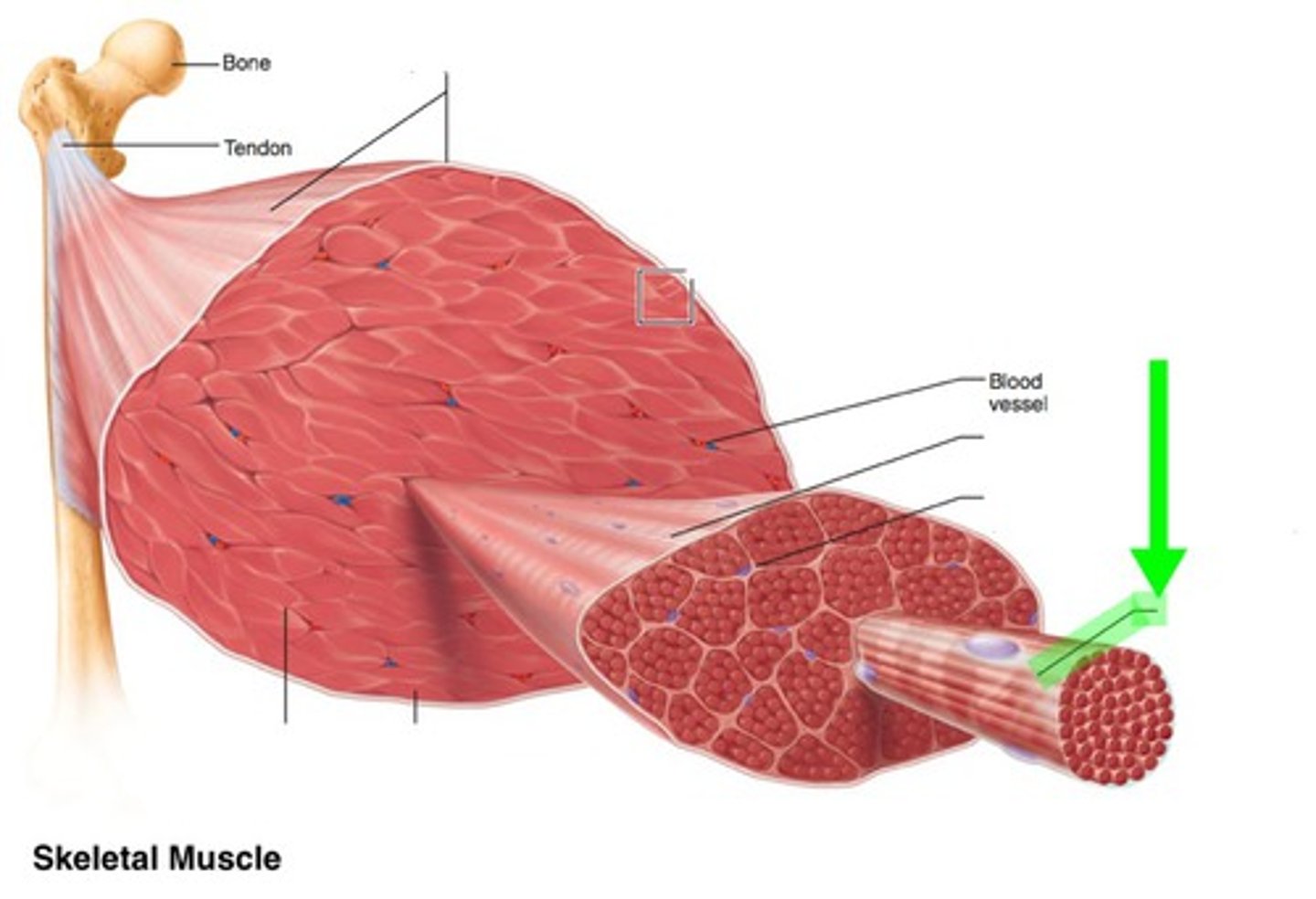
fascicle
bundle of muscle fibers, can be up to 150 fibers
muscle fiber
cylindrical cell containing hundreds of nuclei encased in endomysium
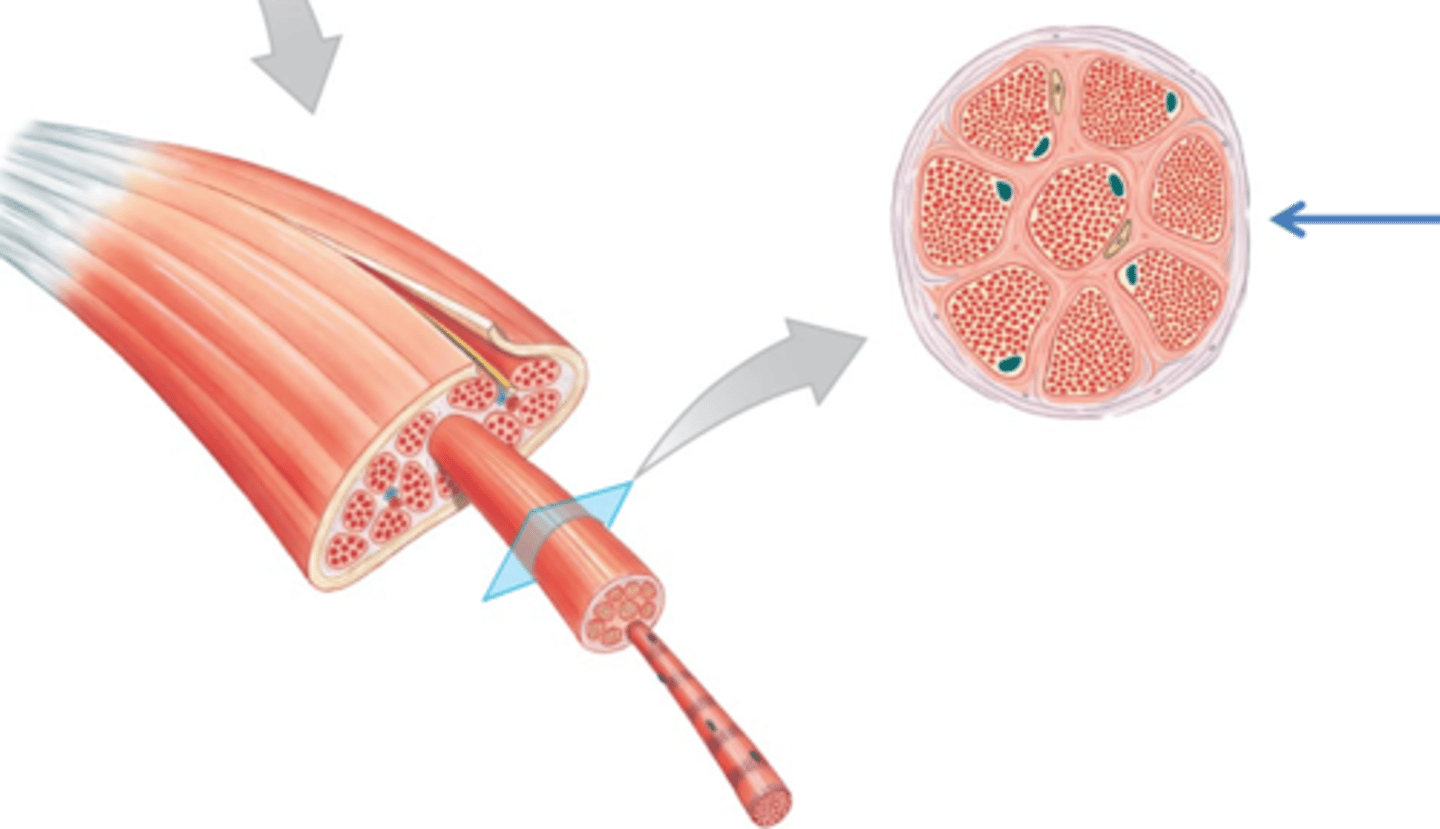
t tubules
tubular infoldings of the sarcolemma which penetrate through the cell and emerge on the other side
sarcoplasmic reticulum
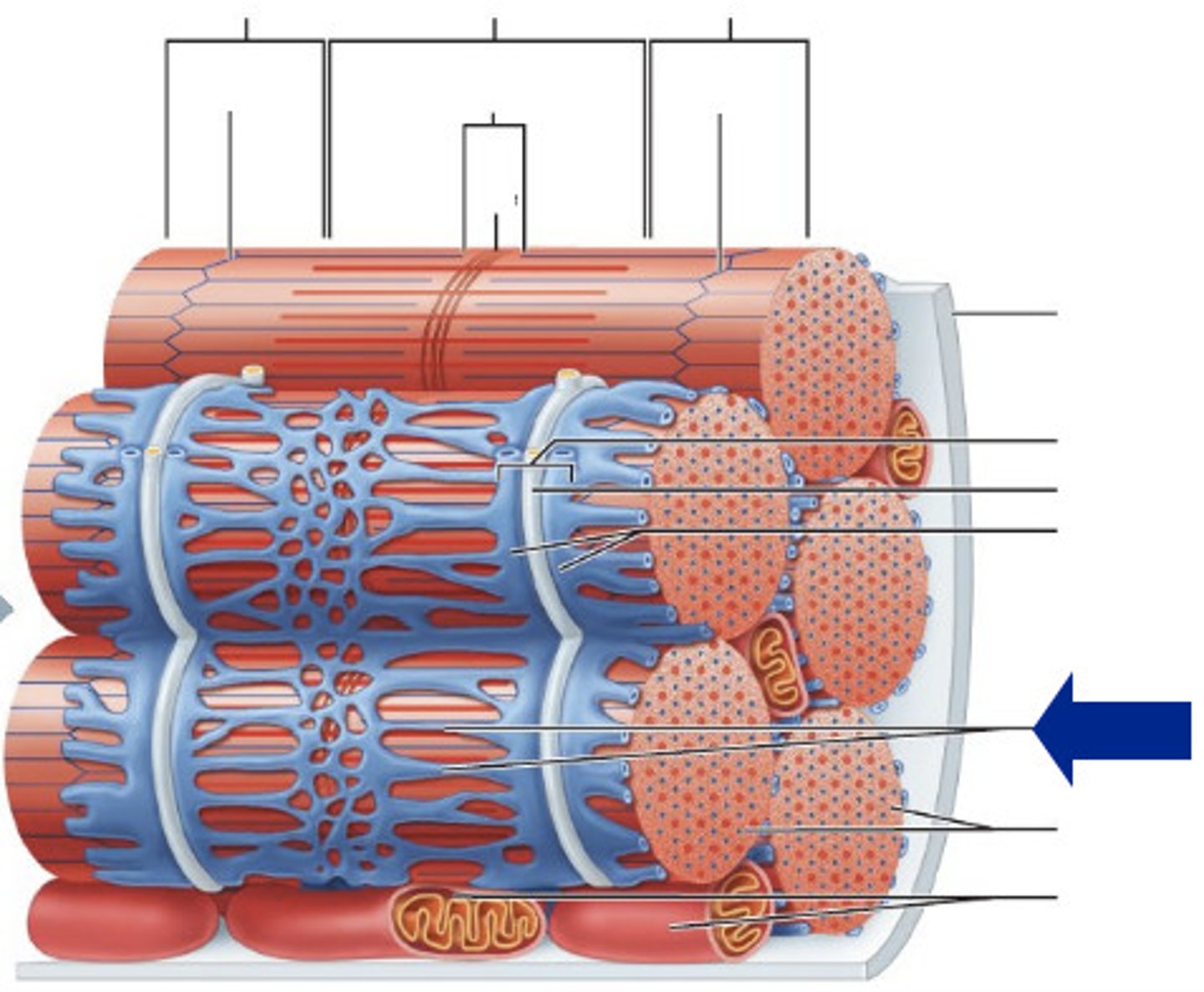
myofibril
contractile element of skeletal muscle
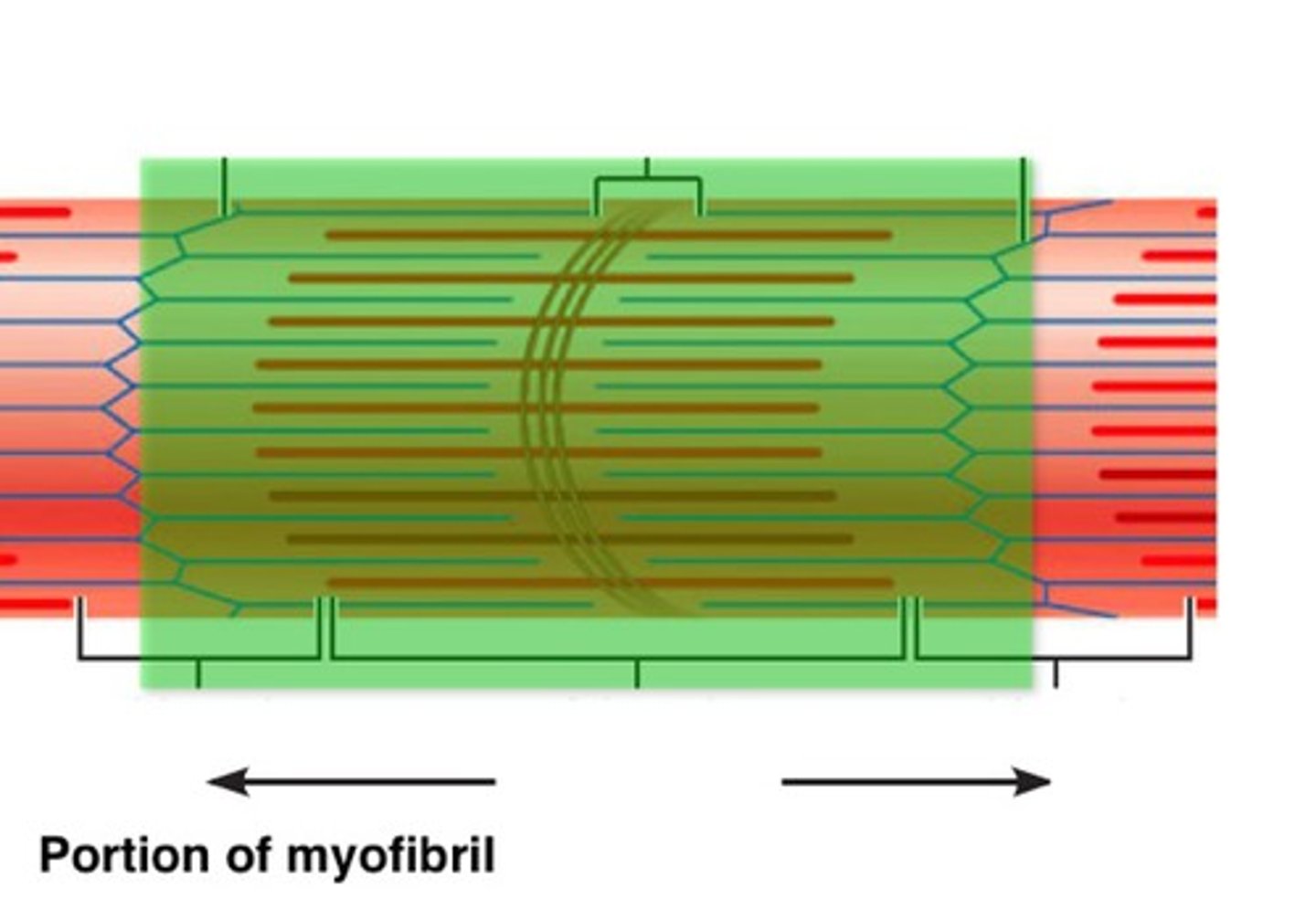
sarcomere
functional unit of muscle extending from one Z line to another
what are the 2 primary myofilaments?
actin (thin) and myosin ( thick)
A band
determines by the width of a myosin filament, anchored to the z line via titin
- provides the dark striation of skeletal muscle
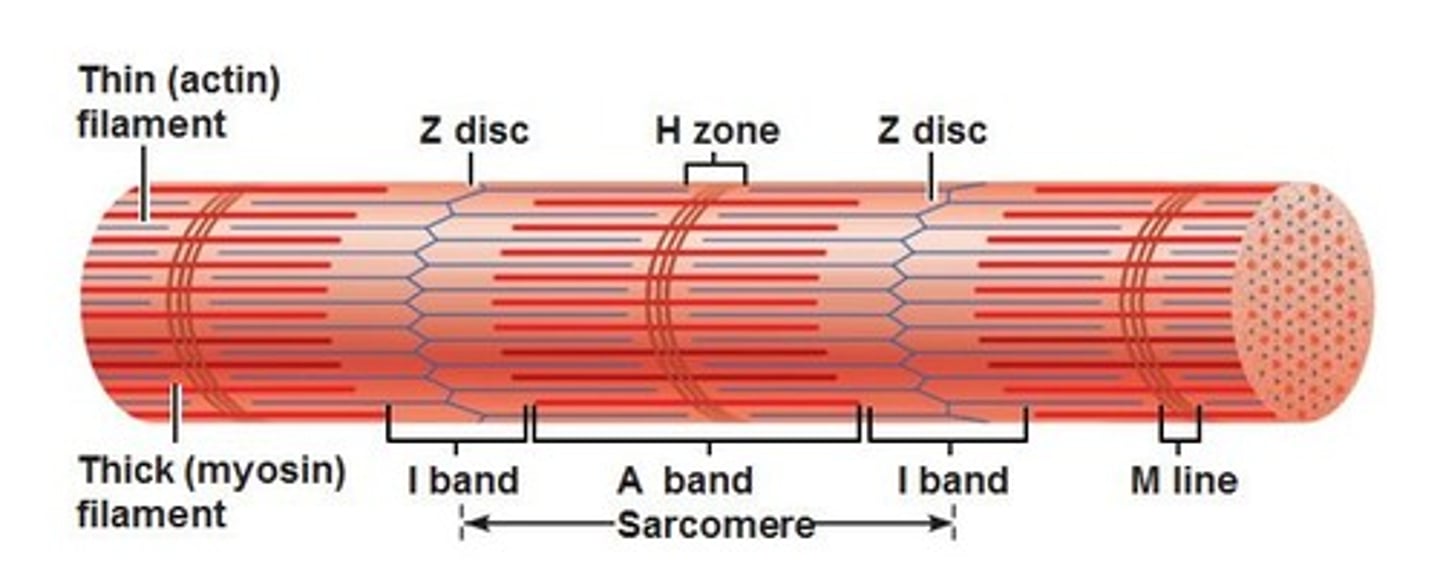
I band
spans distance between ends of adjacent myosin filaments
- gives skeletal muscles its light striation
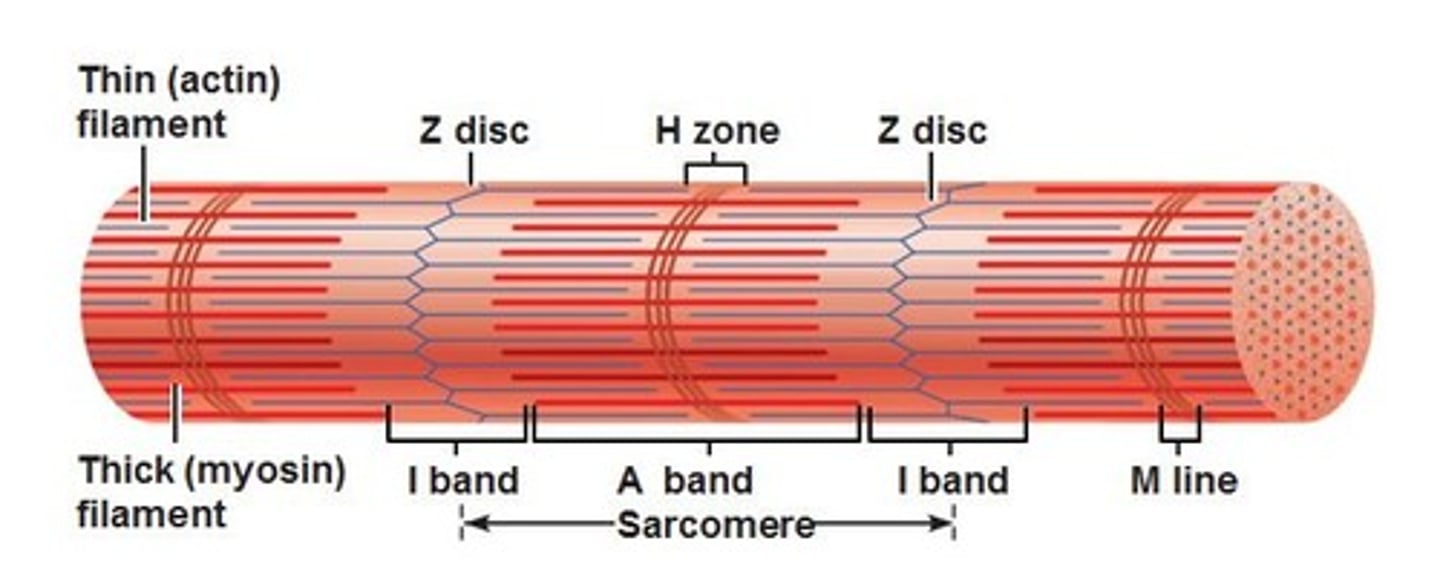
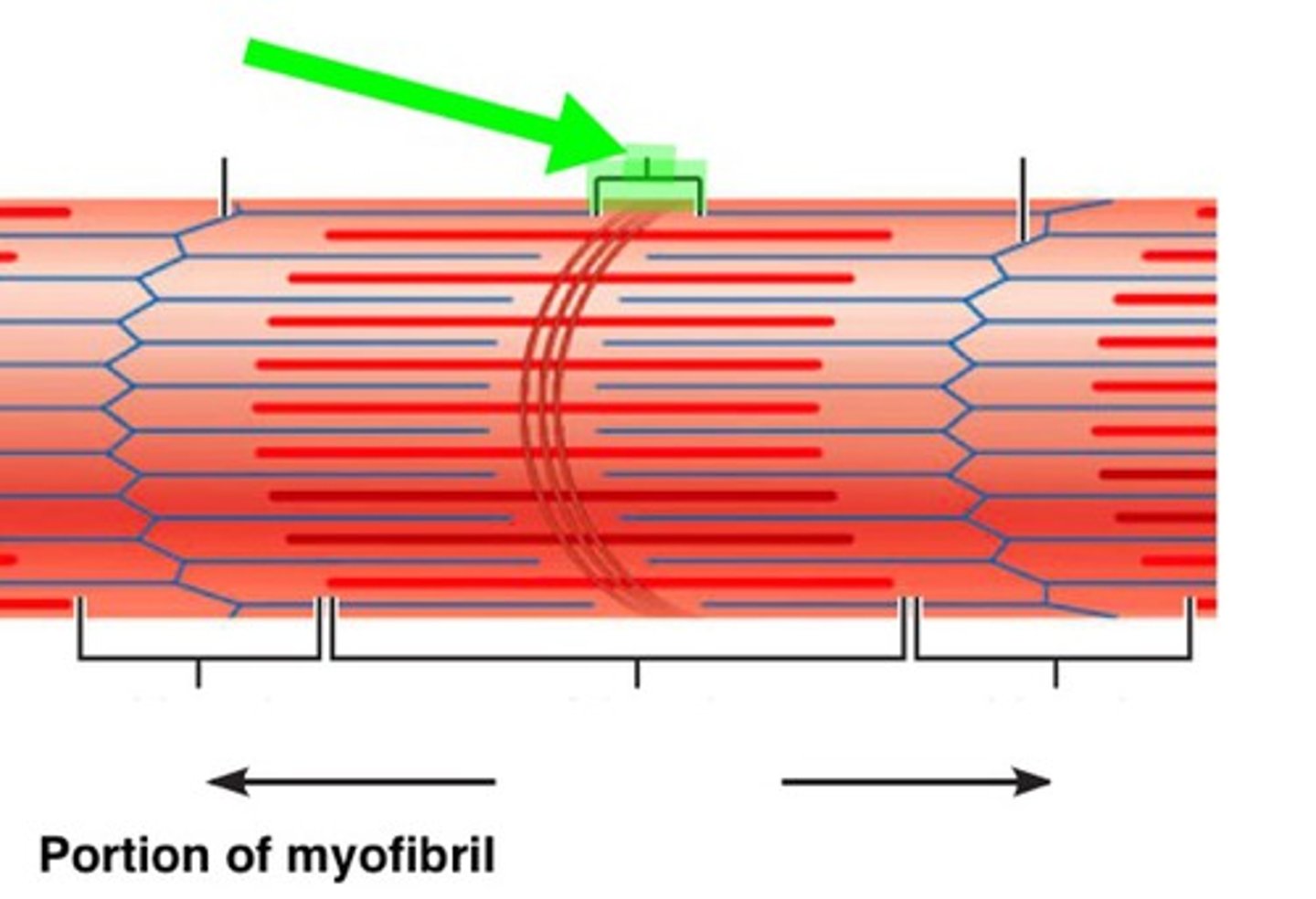
H zone
area of an A band that contains myosin not actin
M line
dark line in the middle of the H zone
- helps align adjacent myosin filaments
how is myosin filament formed?
aggregation of myosin molecules
how are actin filaments formed?
globular proteins
tropomyosin
rod like protein that covers the myosin binding sites when at rest
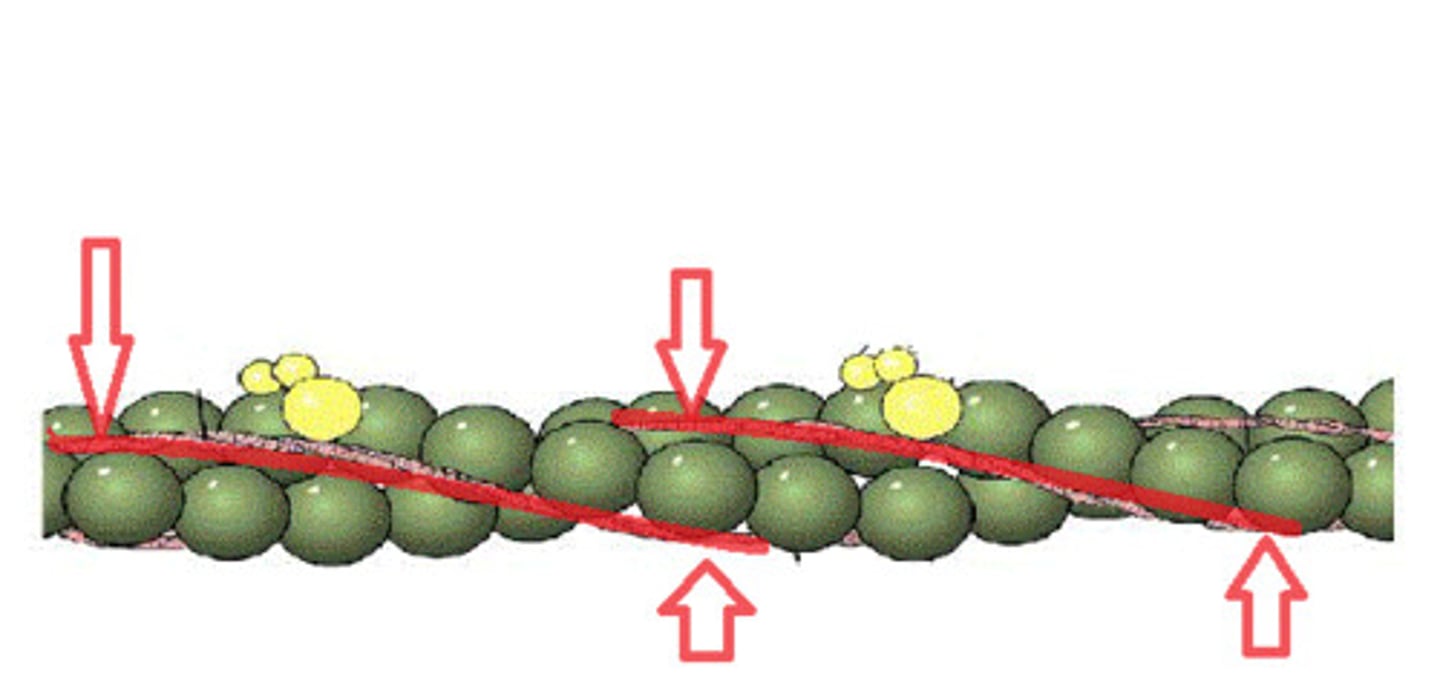
troponin
at the end of each tropomyosin
- accepts Ca2+
- reveal the active binding sites
sliding filament theory
theory that actin filaments slide toward each other during muscle contraction, while the myosin filaments are still
step 1 of sliding filament theory
1. Action Potential (AP) moves down neuron, releases Acetylcholine (ACh) into the synaptic cleft from where it is stored in synaptic vesicles of the axon terminal
step 2 of sliding filament theory
ACh crosses synaptic cleft, binds to ACh receptors on motor endplate of muscle fiber
step 3 of sliding filament theory
Ca2+ migrates to the sarcoplasm and binds to troponin
step 4 of sliding filament theory
binding results in conformation changes in troponin which results in the exposure of myosin head binding sites on actin
step 5 of sliding filament theory
myosin head attach to the binding sites on the actine filament forming a cross bridge. ADP and PI dissociate from the myosin head resulting in a power stroke action
step 6 of sliding filament theory
ATP binds to the myosin head and is quickly hydrolyzed dissociating myosin and actin filaments ( restroke)
step 7 of sliding filament theory
the process occurs in a cycle until CA2+ is actively pumped back into the SR
concentric muscle action
When a muscle is exerting force greater than the resistive force, resulting in shortening of the muscle.
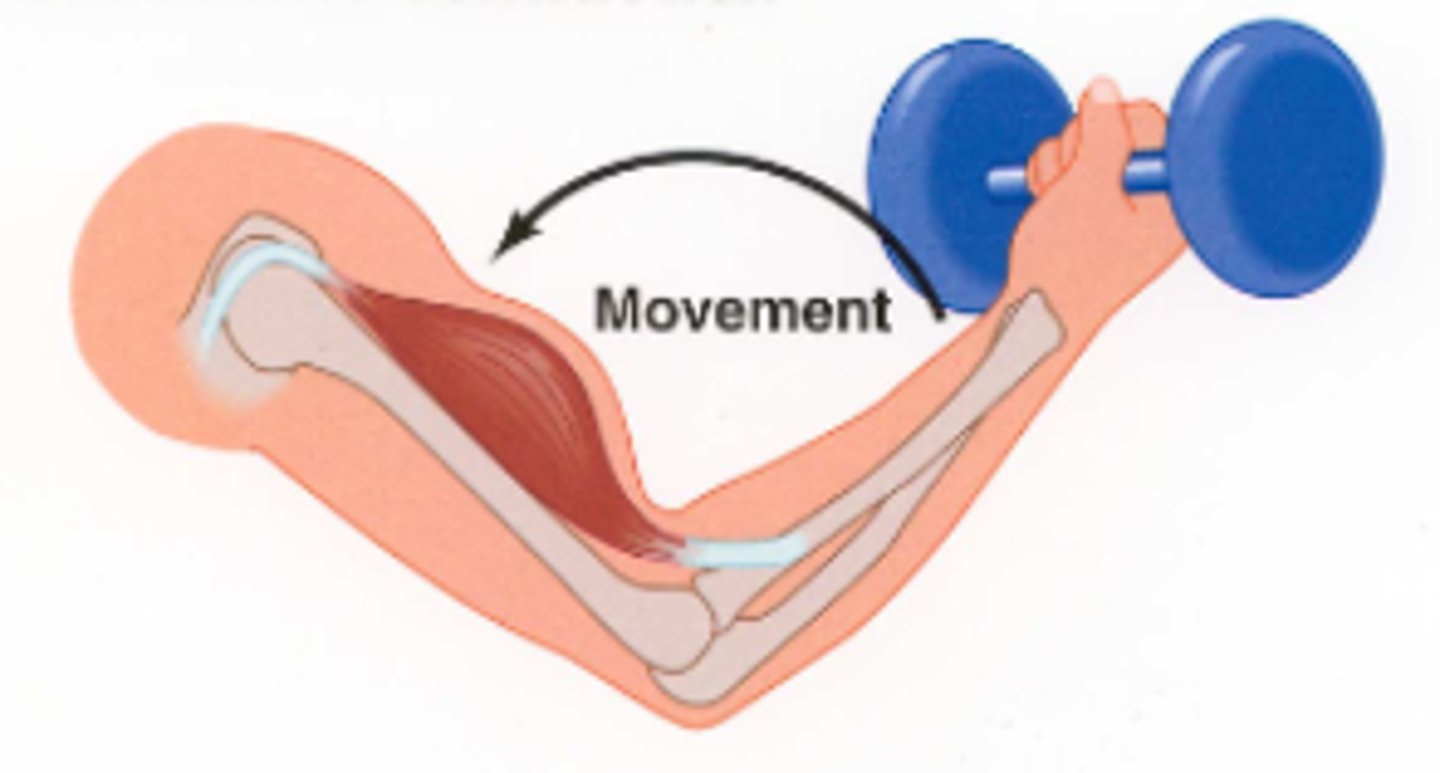
eccentric muscle action
when a muscular force is less then the external force, resulting in lengthening of the muscle
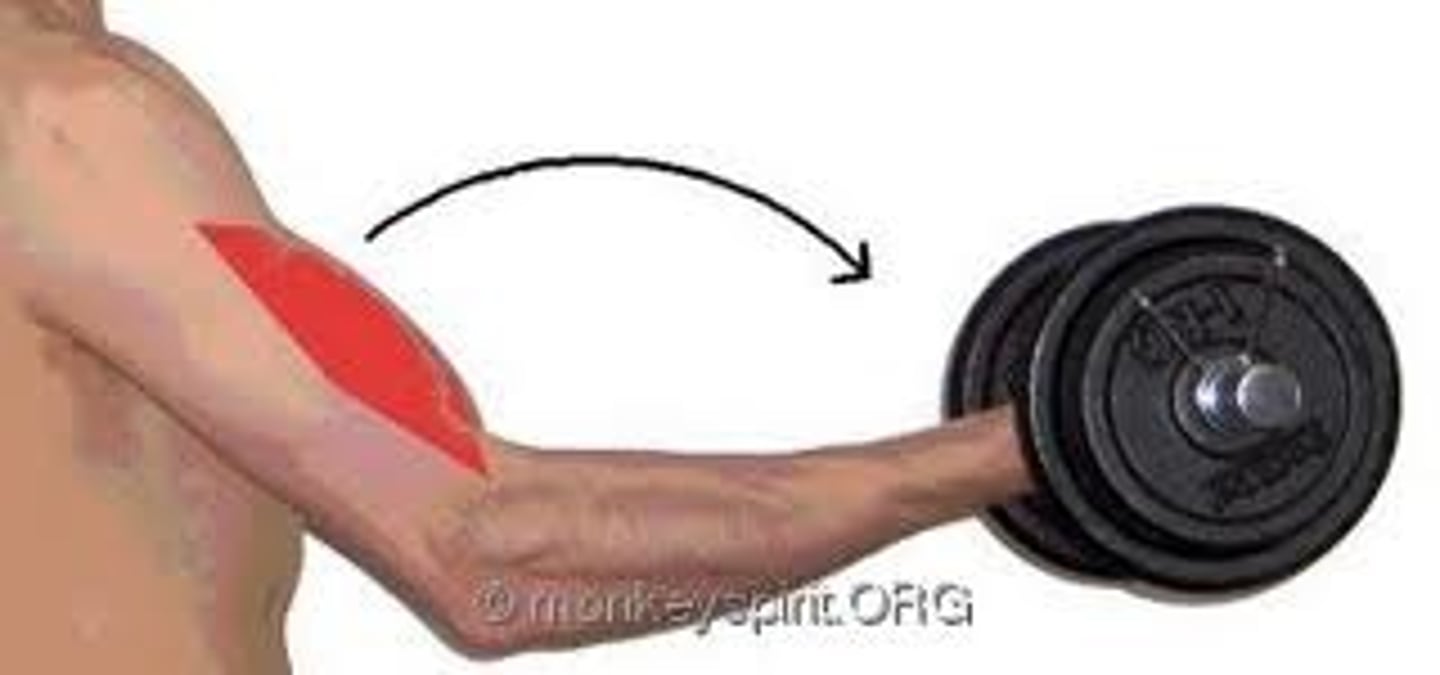
isometric muscle action
When a muscle is exerting force equal to the force being placed on it leading to no visible change in the muscle length

Type 1 muscle fibers
slow-twitch, smaller and slower to produce maximal tension, more resistant to fatigue.
how do type 1 muscle fibers generate ATP?
aerobic means
what are the features of type 1 muscle fibers?
- high oxidative capacity
- lots of mitochondria
- very dense vasculature
- contains myoglobin
type 2 muscle fibers
fast-twitch, larger in size, quick to produce maximal tension and fatigue more quickly
what are some features of type 2 muscle fibers?
- fast oxidative glycolytoc and fast glycolytic
- high ATPase activity = fast contractions
how do type 2 muscle fibers generate ATP?
through anaerobic means
type IIx
purely anaerobic and highly fatigable
type IIa
hybrid, have an increased aerobic capacity, slight resistance to fatigue
what neurotransmitter is associated with initiating muscle contraction?
acetocholin
where is the cell body and dendrites of motor neurons located?
anterior grey horn
motor units
a single motor neuron and all muscle fibers innervated by it
what are the 2 neural mechanisms responsible for force gradation?
motor unit recruitment and rate coding
motor recruitment
increasing the force of contraction of a muscle by progressively increasing the number of motor units activated
rate coding
rate at which the motor units are fired
what neural mechanism do smaller muscles use?
rate coding up to 50%
what neural mechanism do larger muscles use?
motor unit recruitment up to 80%
muscle spindles
receptors sensitive to change in length of the muscle and the rate of that change, sense stretch
golgi tendon organs
Receptors sensitive to change in tension of the muscle and the rate of that change
why are muscle spindles and golgi tendons important?
they monitor posture and balance for safety
osseous tissue
dynamic, living bone tissue
compact (cortical) bone
compact, hard, dense bone 80-90% calcified
- contain haversian system
cancellous (trabecular) bone
spongy bone
- synthesis red blood cells
- no haversian system
wolff's law
A bone grows or remodels in response to forces or demands placed upon it
osteoclasts
bone cutters, resorb bone
when are osteoclasts activated?
when calcium levels are low
osteoblasts
bone forming cells
osteocytes
mature bone cells
what are the three most common fracture sites?
hip, spine, wrist
when is peak bone mass?
around 20