Product design process and management
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Product design process
Companies continuously bring new product to market
Product design is integral to success
Product design differs significantly depending on the industry
Companies often outsource major functions
Contract manufacturer
An organization that performs manufacturing and/or purchasing needed to produce a product or device not for itself but as a service to another firm.
Core competence: the one thing a company can better than its competitors
It provides potential access to a wide variety of markets
It increases perceived customer benefits
It is hard for competitors to imitate
6 phases of the generic development process
Planning
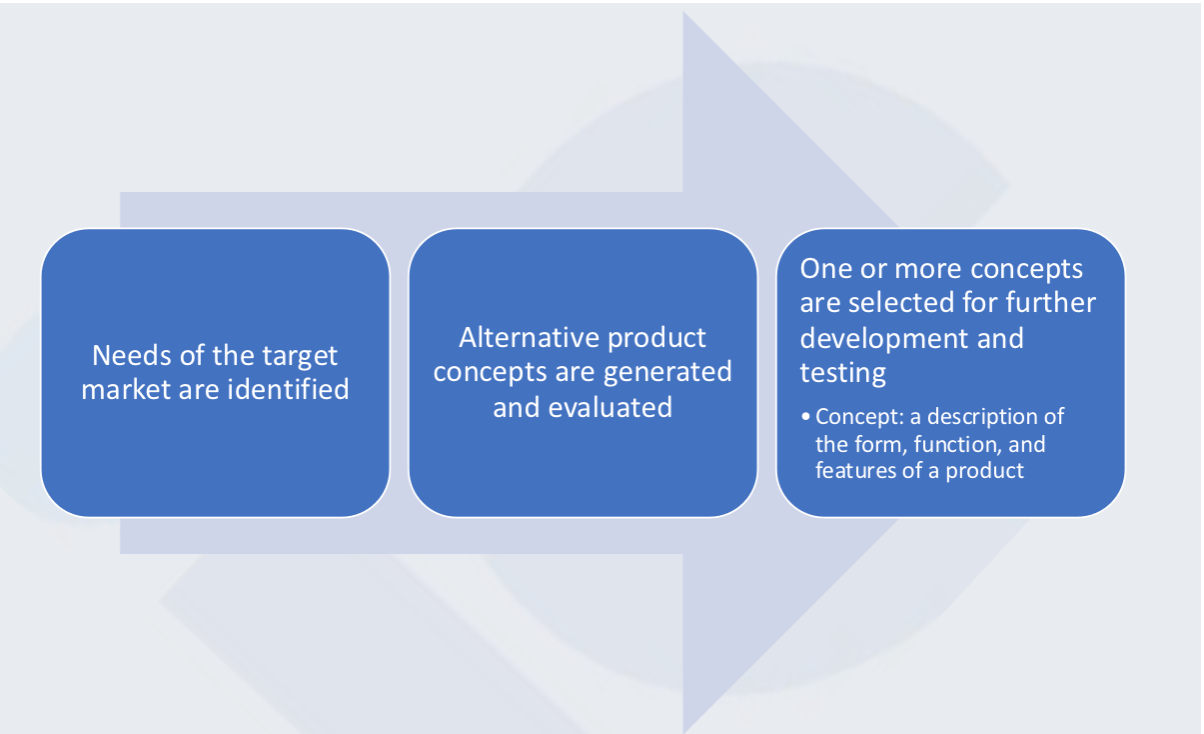
Concept development
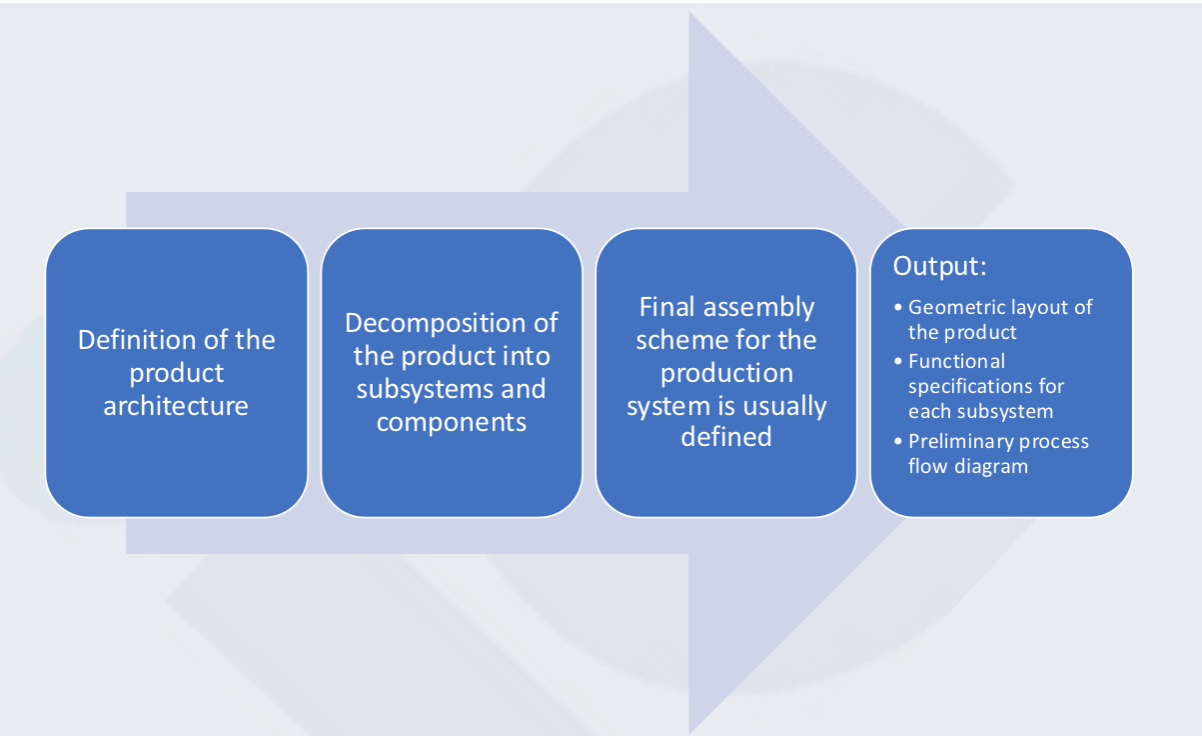
System level design
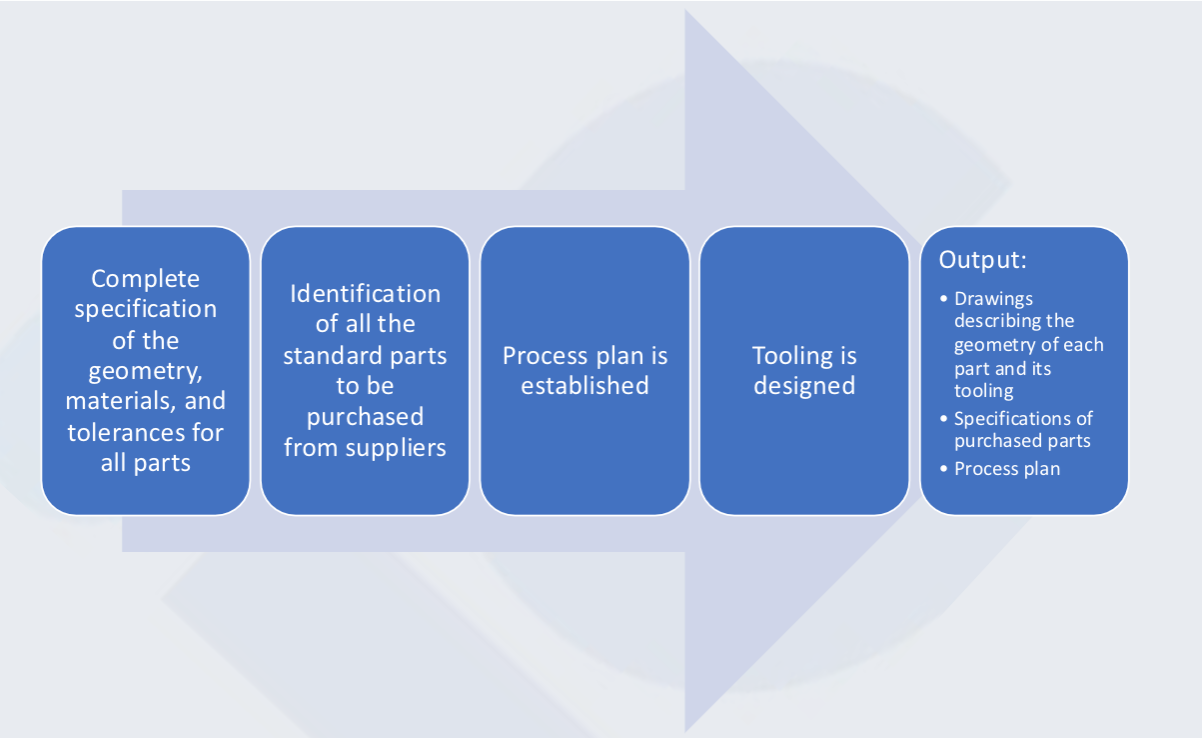
Design detail
Testing and refinement
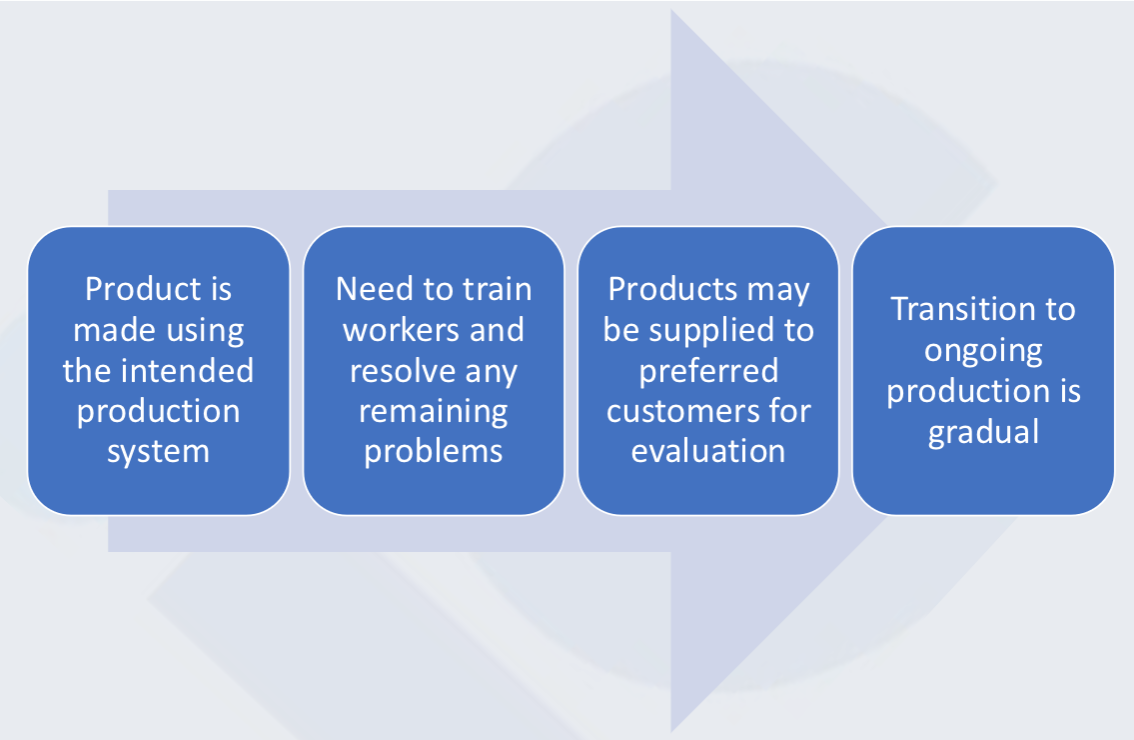
Production ramp up
0. Planning
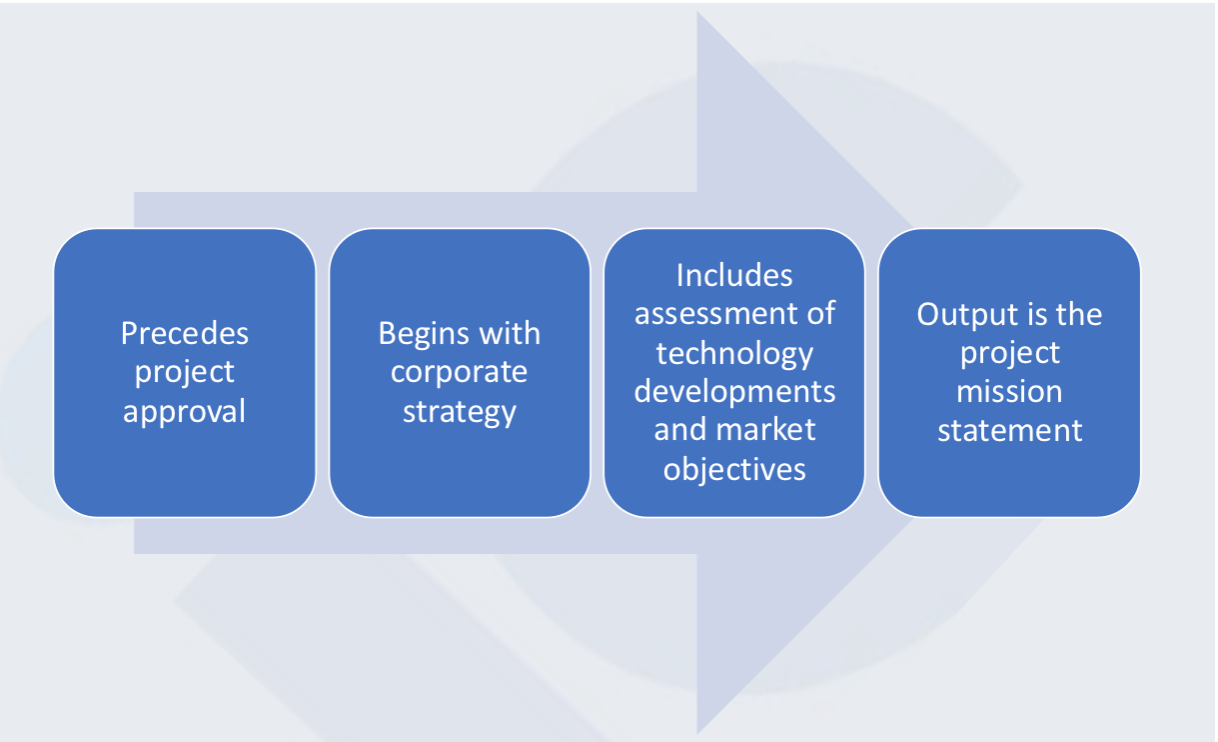
1. Concept Development
2. System Level Design
3. Design Detail
4.Testing and Refinement

5.Production Ramp Up
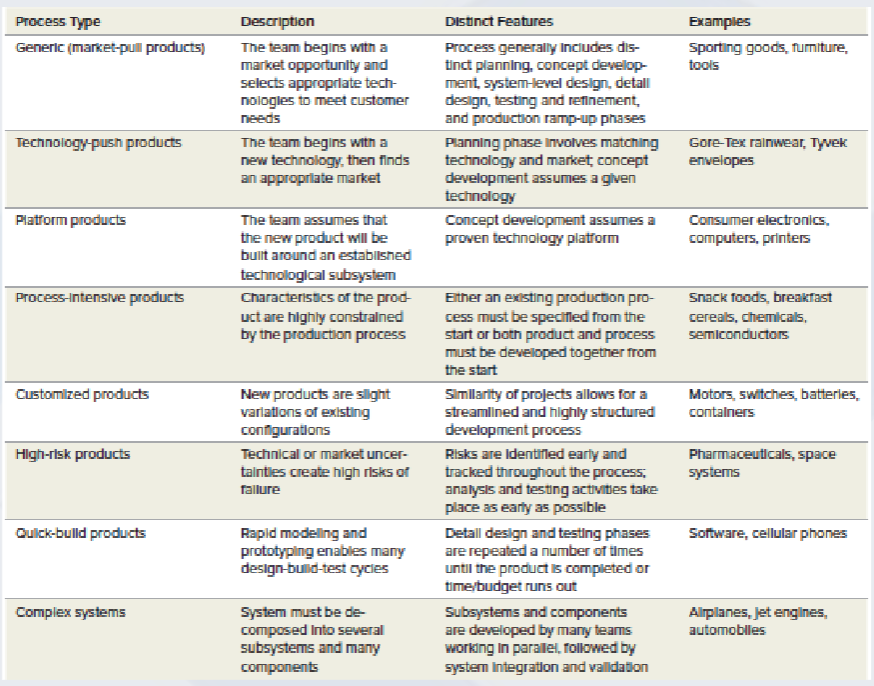
Variants of generic product development process
Technology push products
Platform products
Process intensive products
Customised products
High risk products
Quick build products
Complex systems
Technology push products
Firms begins with new technology and looks for a market
Platform products
Built around a preexistent technological subsystem
Process intensive products
Production process has an impact on the properties of the product
Product design cannot be separated from process design
Customised products
New products are slight variations of existing configuration
High risk products
Technical or market uncertainties create high risks of failure
Quick build products
Rapid modeling and prototyping enables may design build test cycle
Complex systems
Systems must decomposed into several subsystems and many components
Variant of Generic Product Development Process
Quality Function Deployment
Interfunctional teams from marketing, design engineering, and
manufacturingBegins with listening to the customer
Uses market research
Converts the expectations and demands of customers into clear
objectivesThese are then translated into specifications
Customer requirements forms the basis for the house of quality
Value Analysis/ Value Engineering (VA/VE)
Purpose is to simplify products and processes
Objective is to achieve better performance at a lower cost while
maintaining all functional requirements defined by the customerInvolves brainstorming such questions as:
Does the item have any design features that are not necessary
Can two or more parts be combined into one?
How can we cut down the weight?
Are there nonstandard parts that can be eliminated?
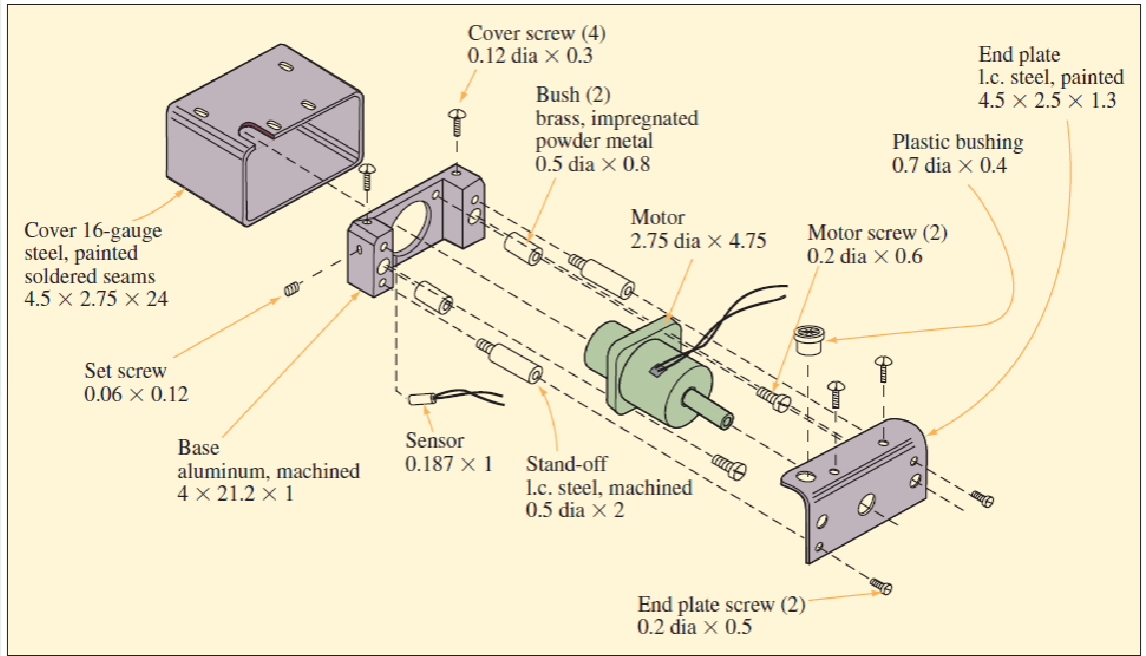
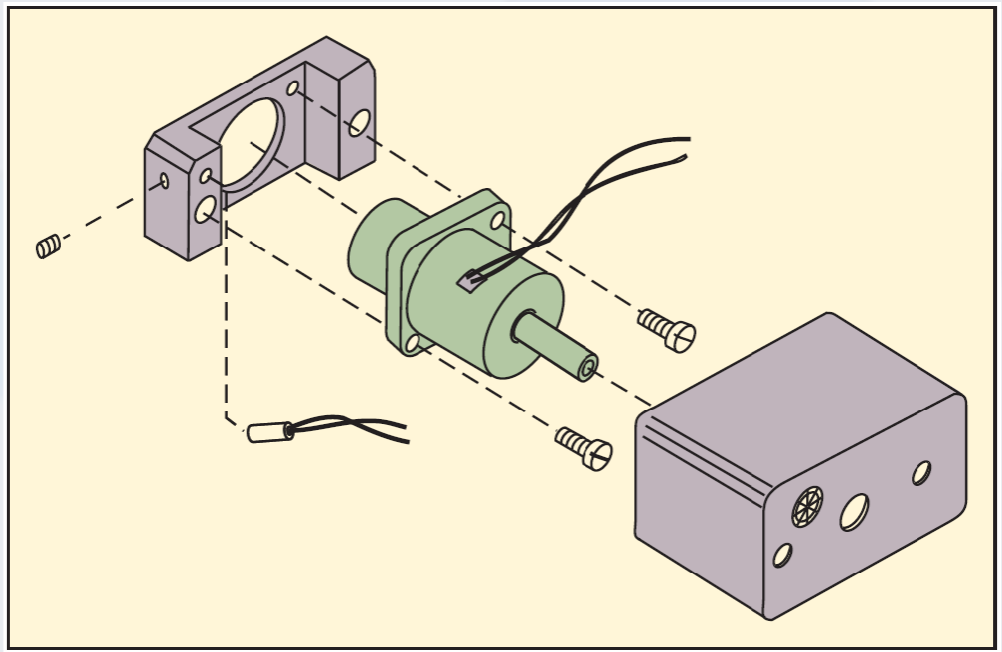
Designing Products for Manufacture and Assembly
Traditional approach
“We design it, you build it” or “over-the-wall”
Concurrent engineering
“Let’s work together simultaneously”
3 Criteria Against which each part must be examined
1. During the operation of the product, does the part move relative to all other parts already assembled?
2. Must the part be of a different material than, or be isolated from,
other parts already assembled?
3. Must the part be separate from all other parts to allow the
disassembly of the product for adjustment or maintenance?
Ecodesign
Ecodesign: the incorporation of environmental considerations in the design and development of products or services
The whole life cycle is considered
The product is considered as a system
A multi-criteria approach is used
An extension of other important requirements such as quality, costs,manufacturability, functionality, and so on
Application of ecodesign can benefit business
Services
Why ? Because services are unique each time as they depend on customer interaction.
What ? Co production.
How ? By understanding what makes a good customer journey.
Designing Service Products
Service products are very different
Direct customer involvement introduces significant variability in the
processQuestions to address:
How will this variability be addressed?
What are the implications for operational cost and the customer service
experience?
Similarity to current services
New service should fit into the current service experience for the customer
Similarity to current process
Even the greatest service ideas require operational support to execute
The more similar they are to the current process, the more of that support is already in place
Financial justification
New services are costly and should be financially justified
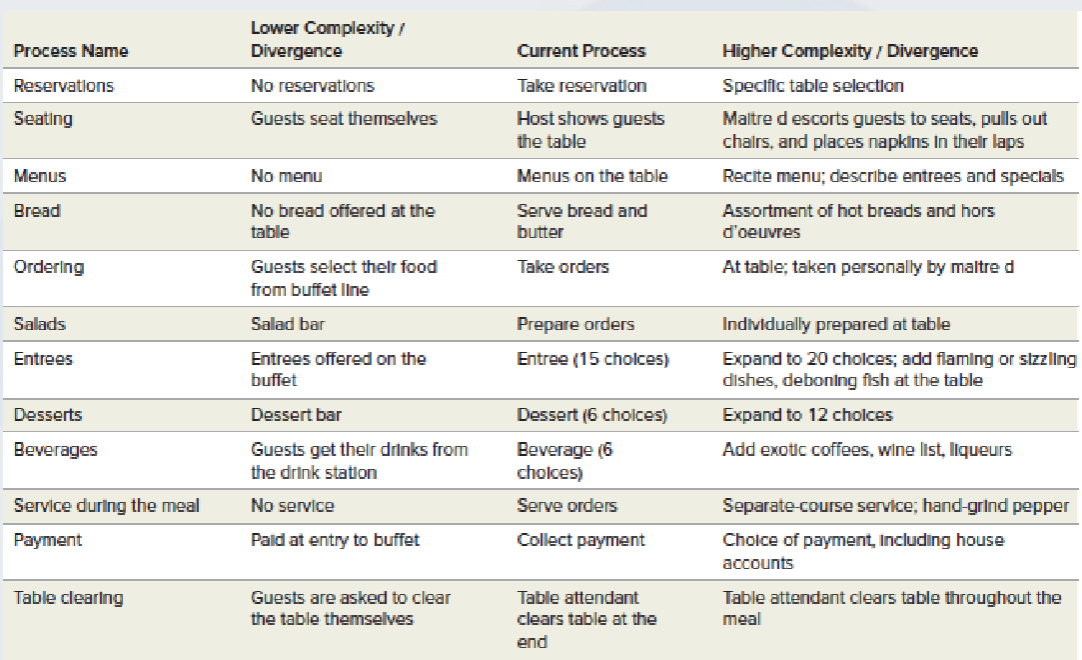
Complexity
the number of steps involved in a service and the possible actions that can taken at each step
Divergence
the number of ways a customer/ service provider interaction
The result may be a combination of higher complexity/divergence on some steps and lower complexity/divergence on others
Can be used to determine ≠ resource requirements such as worker skills, layout, and process controls.
Process Alternatives for a Family Restaurant
Economic Analysis of Project Development Costs
Economic analysis is useful in at least two different circumstances
1. Go/no-go milestones
2. Operational design and development decisionsBuilding a base-case financial model
Compute net present value
Good estimates of cash flows
Sensitivity analysis for “what if” questions
Calculates change in NPV corresponding to a change in the factors included in the model
Can be used to model different scenarios
Possible Sensitivity Analysis Scenarios
Longer product development time
Higher/lower sales volume
Higher/lower sales price
Higher/lower development costs
Measuring product development performance
• A steady stream of new products is important to competitiveness
• Firms must respond to changing customer needs and competitor
moves
• Ability to identify opportunities and bring new products to market is
critical and Must also be efficient
Time to market
There are two aspects to this, the frequency of new product
introductions and the time from initial concept to market introduction
Productivity
Such measures as the number of engineering hours, the cost
of materials, and tooling costs are used in these measures
Quality
Measures that relate to the reliability of the product in use,
the product's performance features compared to customer
expectations, and the ability of a factory or service process
to produce the product
Summary
Product development is a major challenge that directly impacts the
long-range success of a firmMany companies today outsource product design to companies that specialize in different industries
Product development is a multistep process that is unique to each organization
Different sets of criteria drive the design of a product
Criteria that relate to customer wants are fundamental
Criteria related to cost, manufacturability, and impact on the environment are also important
Service products are different because direct customer involvement in the process introduces variability
Summary continued
Financial justification of service features ensure that customers can be retained while the company is making a profit
Economic analysis that consists of estimating the timing and magnitude of future cash flows is used to understand the financial implications of a product development project
Sensitivity analysis can be used to answer “what if” questions that relate to project timing and costs
Generating a steady stream of new products to market is important to the competitiveness of the firm
Measures that relate to time to market, costs, and quality be used to evaluate product development success