ACS Final Exam Flashcard Set
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 1-16 of the Preparing for Your Examination in General Chemistry 2nd Edition
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Isotope
Has the same amount of protons but differing neutrons
Atom
where # protons is equal to # electrons
Ions
where # protons is greater than # electrons
Main group elements
The lightest group elements. “Representative elements” They are at the top of the group.
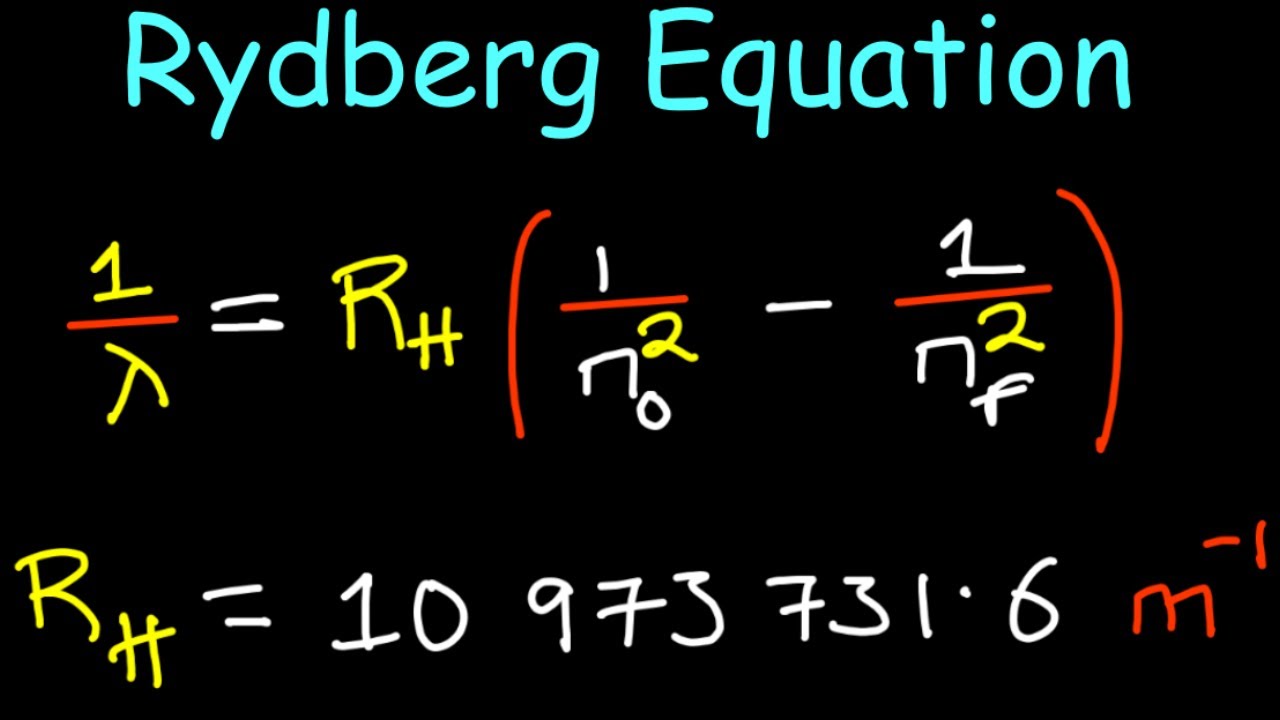
Rydberg formula
1/ wavelength can also be the Transition energy
Energy being absorbed
transition where the election is being promoted to a a higher energy level. On a diagram this is represented by an arrow pointing upwards, the farther the energy levels, the longer the arrows.
How are photon energy and wavelength related?
They are inversely related. So the shortest wavelength had the highest energy and the longest wavelength has the lowest energy.
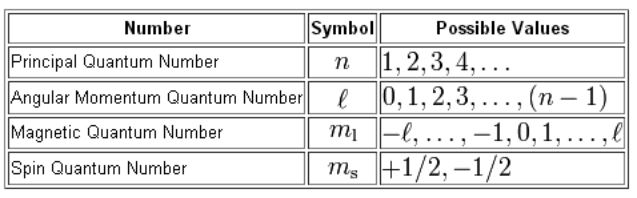
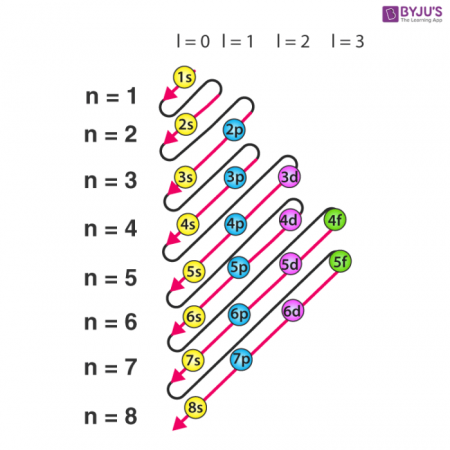
Rules for Quantum Numbers
Allowed values for n: 1 to infinity. Allowed values for l: 0 to n-1. Allowed values for ml: -l to 0 to +l. Allowed values of ms: -1/2 or +1/2.
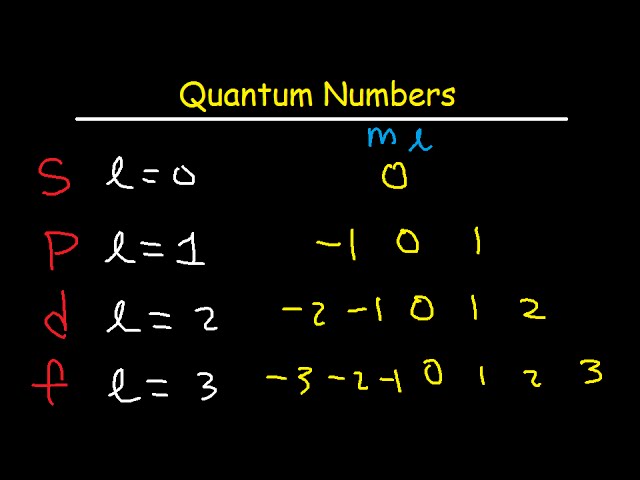
Relationship of quantum number and energy level
l=0, s orbital. l=1, is p orbital. l=2, is d orbital. l=3, is f orbital.
Valence configuration
the electron arrangement of an atom’s outermost electrons which are the elctrons in the highest energy level that help in bonding.
Ground state electron configuration
the lowest energy state
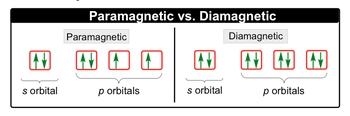
Paramagnetic
It must have unpaired electrons
Zeff
The effective nuclear charge the valence electrons experience. As you move across a period, the shielding ability of the inner electrons does not change. The nuclear charge is increasing as you move left to right. The Zeff increases as you move from left to right across a period.
Atomic Radius
As you go down a column (group) the atoms get larger b/c ,pre energy levels are needed to house tje electrons. From left to right across a row (period) the size of an atom decreases b/c th Zeff increases, holding the valence electrons tighter.
Atomic radius of ions
-X>X>+X.
Ionization Energy
The energy needed to remove an electron from a gaseous atom or ion. It is “harder” to remove an electron from a small atom, the smaller the atom the larger the ionization energy needed to remove an electron.