Ex phys exam 2 first part + heart topics
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
direct vs indirect calorimetry
Direct calorimetry measures heat production and indirect calorimetry measures gas exchange
direct MEASURES heat production and indirect ESTIMATES it
VO2 vs VCO2
VO2: volume of O2 (oxygen) consumed per minute
VCO2: volume of CO2 (carbon dioxide) produced per minute
Respitory Exchange Ratio (RER)
the ratio between the volume of CO2 produced and the amount of O2 consumed
RER=VCO2/VO2
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
amount of energy (cals) to maintain basic bodily functions at rest
Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR)
The rate at which the body expends energy (calories) at rest
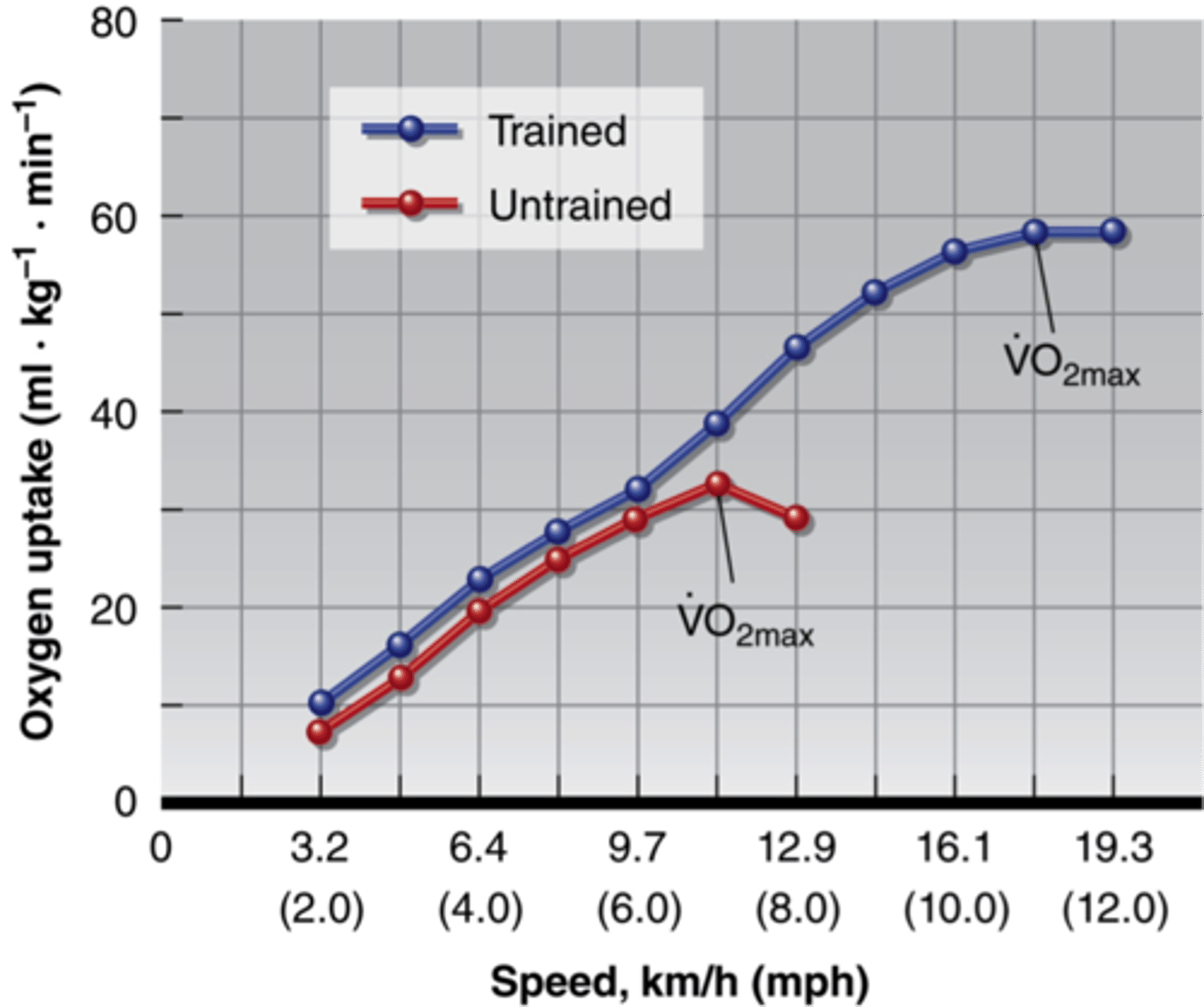
VO2 Max test
Highest amount of O2 an individual can take in &utilize during exercise
stoppage criteria for VO2 max test
1. participant tells you they have to stop
2. they fall off the treadmill
3. plateau in oxygen consumption
trained vs untrained
trained people will have a higher VO2 max then untrained. They can utilize more oxygen for a longer period of time.
Functions of the heart
Delivers O2 and nutrients•
Removes CO2 and other waste
• Transports hormones and other molecules
• Supports temperature balance and controlsfluid regulation•
Maintains acid-base balance•
Regulates immune function
Circulatory elements
1.Pump
2. Channels or Tubes
3. Fluid medium
Myocardium
cardiac muscle
What is the significance of intercalated discs?
They connect cardiac muscle fibres together.
Anatomy of Heart
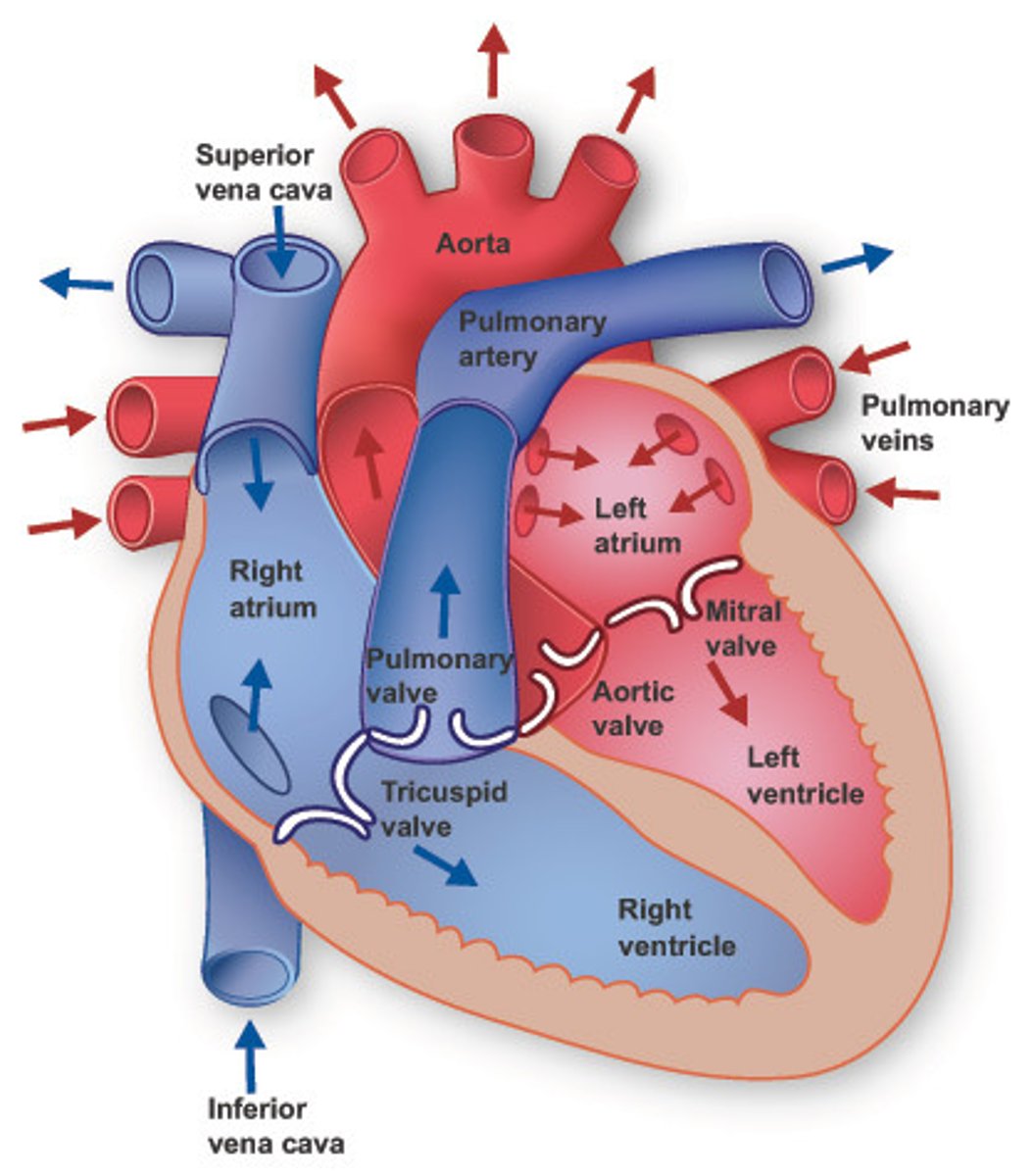
Blood flow through heart/lungs/body
deoxygenated blood from the body enters the heart, is pumped to the lungs for oxygenation, and then oxygenated blood returns to the heart to be pumped out to the body
where does blood go when it leaves the right ventricle?
pulmonary valve to pulmonary artery
oxygenated vs deoxygenated
oxygenated rich in oxygen brighter red color
deoxygenated low in oxygen darker red color
Process of electrical conduction
1. SA node initiates contraction signal
2. AV node delays, relays signal to ventricle
3. AV bundle relays signal to RV, LV
4. Purkinje fibers send signal into RV, LV
Polarization, depolarization , repolarization
polarization is heart muscle cells at rest
depolarization is an electrical process that initiates the contraction of the heart muscle
repolarization heart muscles return to resting state after contraction
pacemaker
the hearts pacemaker is known as the SA Node
ECG
recordings of heart's electrical activity
3 phases:
P wave- activation of atria
QRS complex- activation of ventricles
T Wave
Control of Heart Rate
-Parasympathetic activity slows heart rate; (vagus nerve)
sympathetic activity increases heart rate
(cardiac accelerator nerve)
Cardiac Cycle
All mechanical and electrical events occurring during one heartbeat
Stroke Volume
volume of blood pumped in one heart beat
End Diastolic Volume (EDV)
Volume of blood in the ventricles after diastole
End Systolic Volume (ESV)
Volume of blood in the ventricles after systole
Ejection Fraction (EF)
% of EDV pumped
normal % at rest is 60%
Q: at rest vs excercise
at rest q= 5 L/min
during exercise q=25 L/min
VC (vasoconsriction)
the narrowing of blood vessels
vasodialation
blood vessels widen
Systolic Pressure (SBP)
highest pressure in artery- top # when taking blood pressure
diastolic pressure (DBP)
lowest pressure in artery- bottom # when taking blood pressure
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)
Average pressure over entire cardiac cycle
Pressure differences in each type of blood vessel (veins vs arteries)
arteries= high BP
veins = low BP
what maintains/ controls BP?
barorecpeters and chemoreceptors
How blood flow changes based on need
The organs need more blood when exercising compared to when at rest
Functions of blood
1. trasnportation
2. temperature regulation
3. Acid- base (pH) balance
components of blood
55-65% plasma
40-45% forced elements
hematocrit=total percentage of volume composed of formed elements
What causes changes in Plasma?
dehydration and physical activity
What is the function of coronary arteries?
provide main blood supply to the heart