(2) larynx, trachea
1/12
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
larynx is where?
connects pars nasalis pharyngis and tranchea, containing organ of phonation.
eq+ru: located in caudal part of intermandibular space
su+car: more caudally
walls of larynx are supported by means of the cartilagines laryngis.
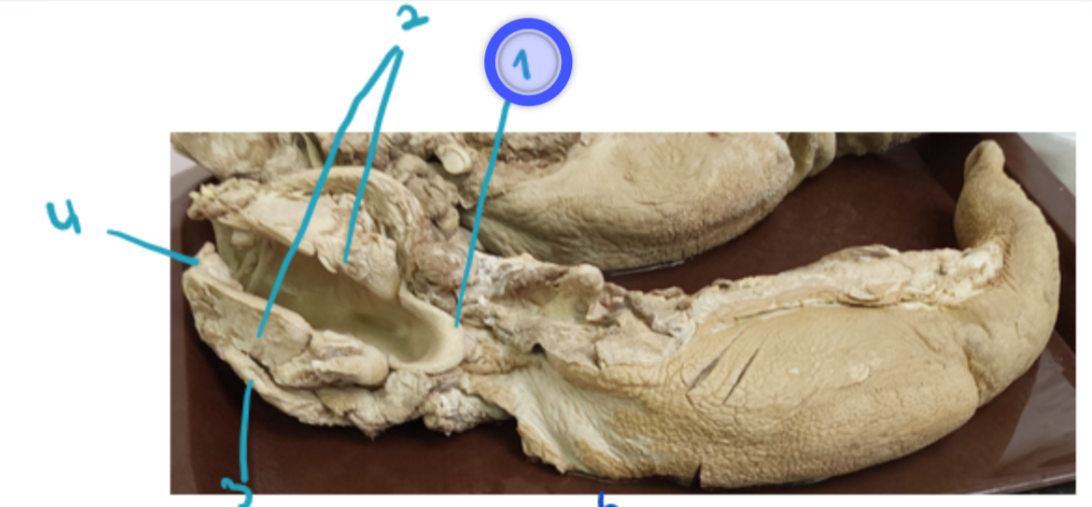
identify these structures. (general)
epiglottis (unpaired, most rostrally)
cartilago arytenoidea (paired, dorsally)
cartilago thyroidea (unpaired)
cartilago cricoidea (unpaired, ring-shape, most caudally)
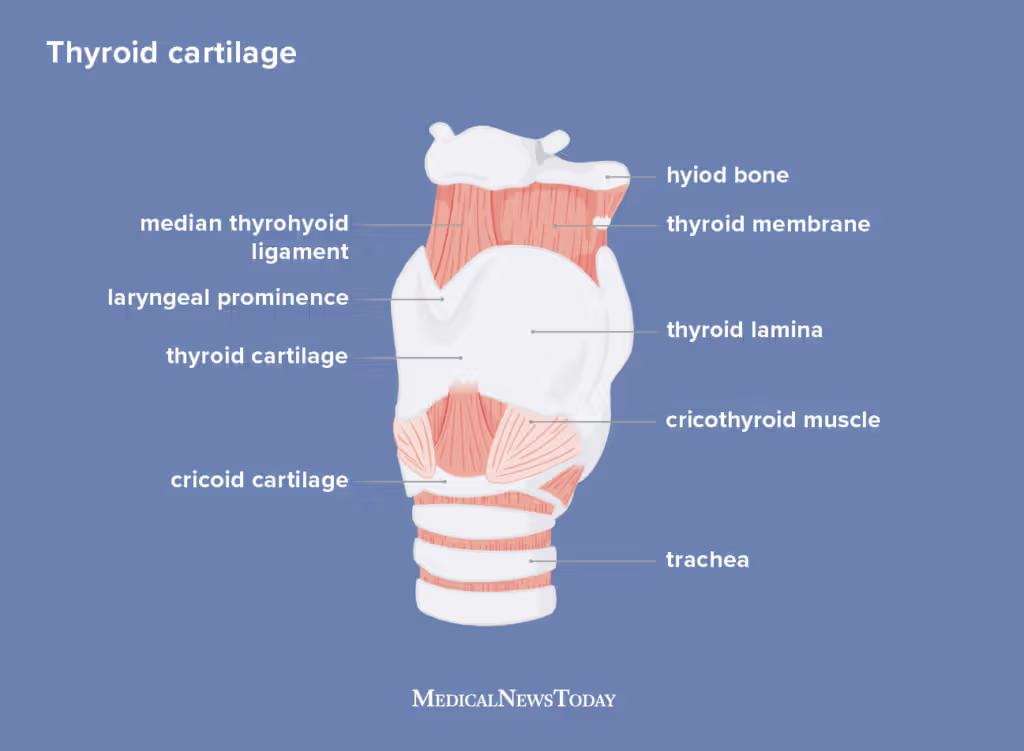
Describe structures of cartilago thyroidea (new - video on it)
lamina dextra et sinistra (forms the cartilage, ventrally fused)
prominentia laryngea (adams apple - more in man)
cornu rostrale et caudale (dorsal ends of rostral + caudal border of lamina, rostral horns serves for articulation with thyrohyoideum and caudal horn with the lamina cartilaginis cricoiceae)
fissura thyroidea (separates on both sides cornu rostrale from rostral border of lamina)
incisura thyroidea caudalis (on caudal border of laminae)
incisura thyroidea cranialis (on caudal border of laminae fusion, deep in eq, serves for access of the cavity)
linea obliqua (serving for muscular attachment, on lateral surface of laminae)
cornu rostrale, fissura thyroidea + incisura thyroidea = absent in su.
Describe the structures of the cartilago arytenoidea (new)
facies dorsalis formns apex cartilaginis arytenoideae
basis cartiliganinis arytenoideae - points caudally
from facies lateralis - arises the processus muscularis
facies medialis - smooth
processus vocalis
processus corniculatus - starting from apex in dorsomedial direction.
process cuneiformis - continuing rostrally from processus corniculatus
facies articularis - on dorsal margin for articulation with the cricoid cartilage.
cartilago interarytenoidea - in su and car, bw. both arytenoid cartilages.
cartilago sesamoidea - on dorsal surface of cartilago arytenoidea.
What are the structures of epiglottis ? (new)
basis
apex - pointed in ca, eq + small ru and roudned in bo+su.
facies lingualis - in contact with tongue
faices laryngea - directed into laryngeal cavity
margines laterales - both surfaces meet here.
petiolus epiglottidis - stalk, continuing caudally from base, in contact with thyroid cartilage.
processus cuneiformis - in eq, with dorsocaudal direction, from each side of base.
What are the structures of cartilago cricoidea? (new)
lamina cartilaginis cricoideae - broad, dorsally
arcus cartilaginis cricoideae - ventrally, narrower
facies articularis arytenoidea - located on both sides of rostral border of lamina, for articulation with arytenoid cartilage.
facies articularis thyroidea - caudally to previous, articualting with caudal horn of thyroid cartilage.
crista mediana - dorsally directed, for muscular insertion on lamina.
joints of the larynx, include:
articulatio cricothyroidea
lig. cricothyroideum - connects
art. cricoarytenoidea
lig. cricoarytenoideum
art. thyrohyoidea
lig. thyroepiglotticum → lig. hyoepiglotticum
lig. cricotracheale
lig. arytenoideum transversum
lig. vestibulare (absent in fe)
lig. vocale
The cartilages of larynx are connected to each other, to the hyoid apparatus and to the trachea by articulations, ligaments and muscles.
Muscles of larynx include?
m. cricothyroideus
m. cricoarytenoideus lateralis
m. cricoarytenoideus dorsalis
m. arytenoideus transversus
m. thyroarytenoideus → m. ventricularis + m. vocalis (not divided in ru, su + fe)
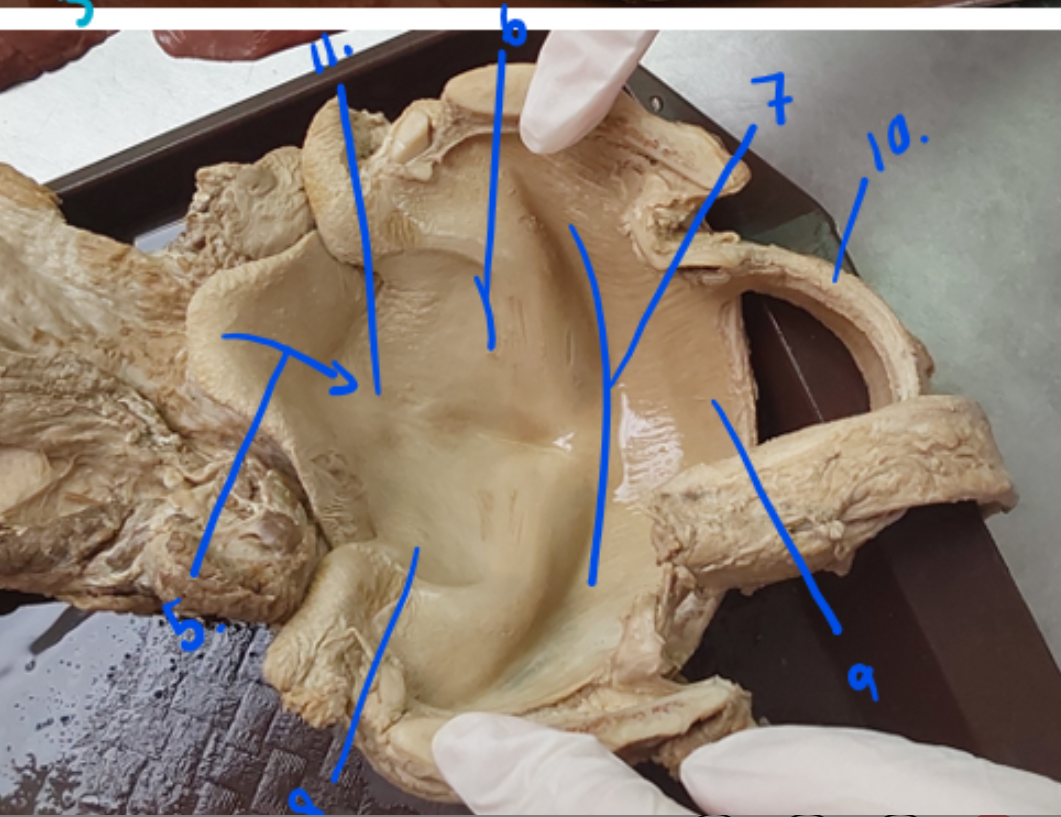
identify these structures of cavum laryngis.
auditus laryngis
plica vocalis (caudally located fold to rima)
lig. vocale and m. vocalis
rima glottidis (narrow, vertical slit, forming organ of phonation, has 2 paired folds - plica volcalis et vestibularis)
divides into: pars intercartilaginea (dorsally) and pars intermembranacea (ventrally)
plica vestibularis (rostral fold to rima)
formed by m. ventricularis and lig. vestibulare
cavum infraglotticum (from glottidis to trachea)
rings of trachea
vestibulum laryngis (most rostrally, from auditus laryngis → glottidis)
Voice is produced when glottis is narrowed and widened by the action of laryngeal muscles → causing vibration of the respiratory air → voice.
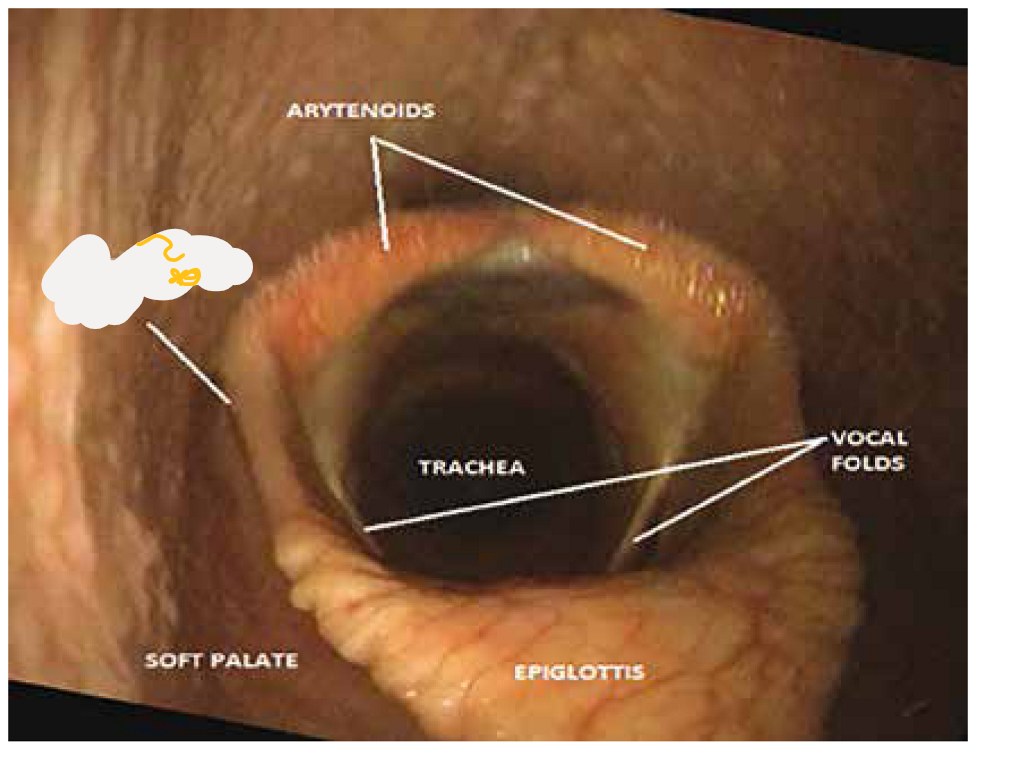
this structure of cavum laryngis is?
Plicae aryepiglotticae (aryepiglottic folds) - laryngeal inlet is ventrally bounded by epiglottis, on both sides by means of these folds, extending laterally from the lateral parts of the epiglottis to the arytenoid cartilage)
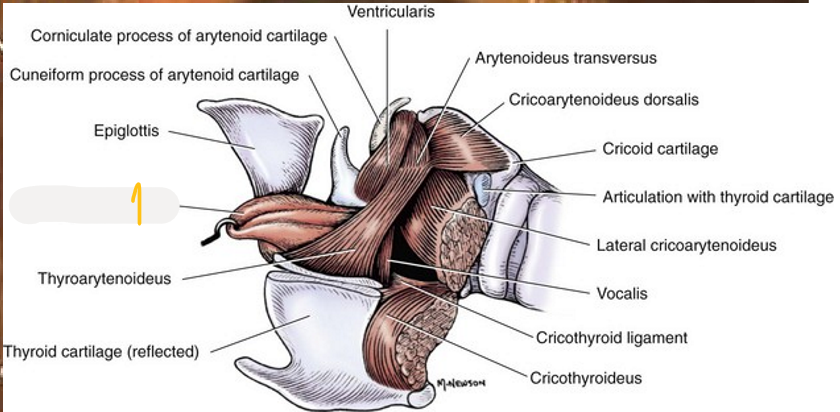
In ew, su and ca, ——-, is formed laterally on both sides.
ventriculus laryngis is formed (of cavum laryngis)
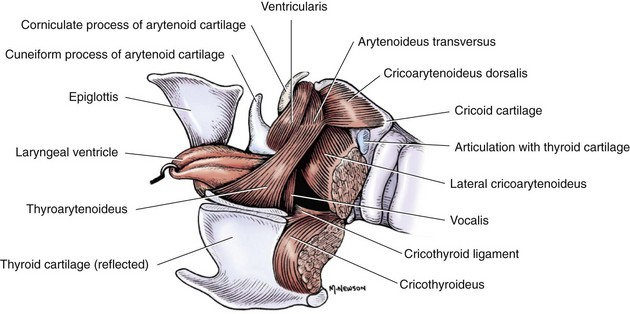
Which structure lies in the midline of ventral surface of vestibulum laryngis in eq + su?
Recessus laryngis (median laryngeal recess)
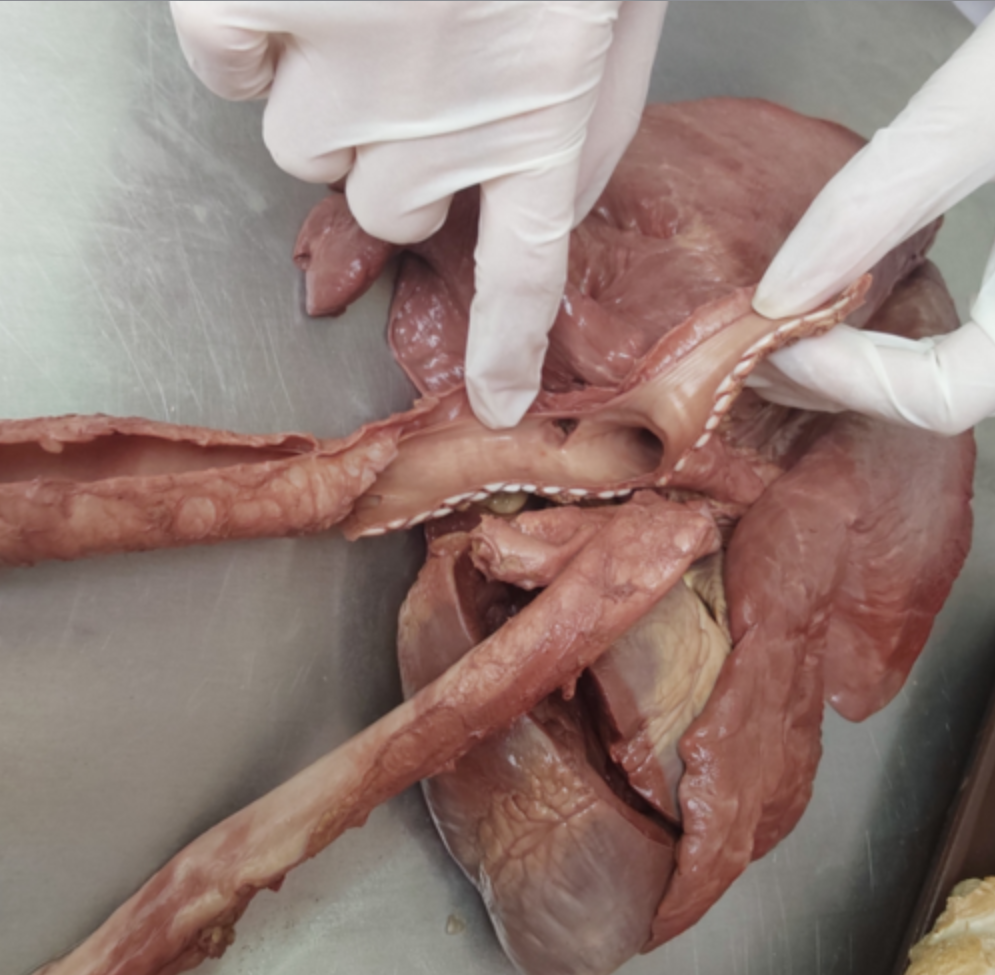
what structures can you see here? (4)
Main character: Trachea.
pars cervicalis: ventrally to esophagus and musculus longus colli on neck.
pars thoracica: goes caudally into mediastinum inside thoracic cavity. It divides dorsally to the base of heart, into left and right main bronchus (bifurcatio trachea)
RU + SU: bronchus trachealis, arising cranially to bifurcatio trachea, and to the right.
walls of trachea are supported by cartilagines tracheales (number and shape differs among species)