1.5 joints
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
1
New cards
what cell type makes up cartilage?
chondrocytes
2
New cards
what materials make up cartilage?
chondrocytes, collagen (& other organic matrix components) & water
3
New cards
most common joint
synovial joint
4
New cards
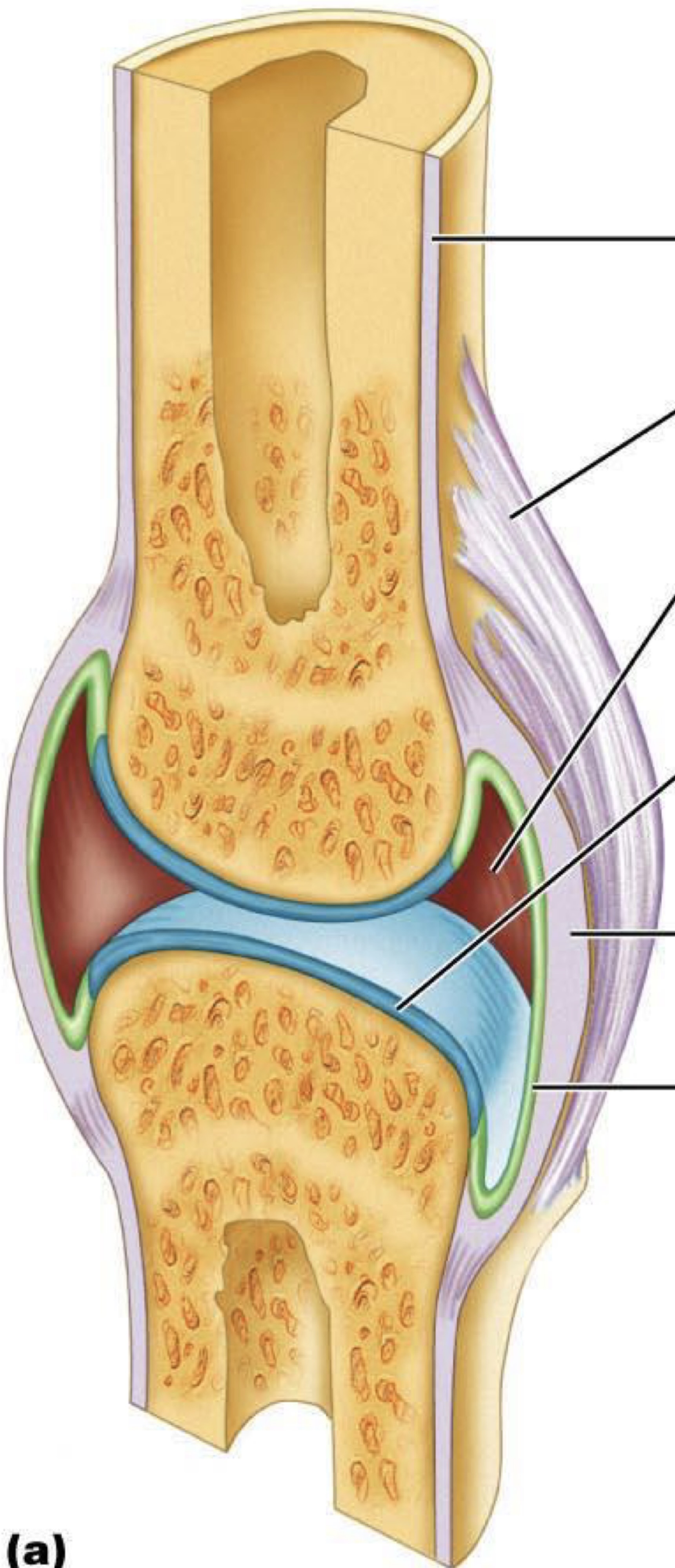
label this
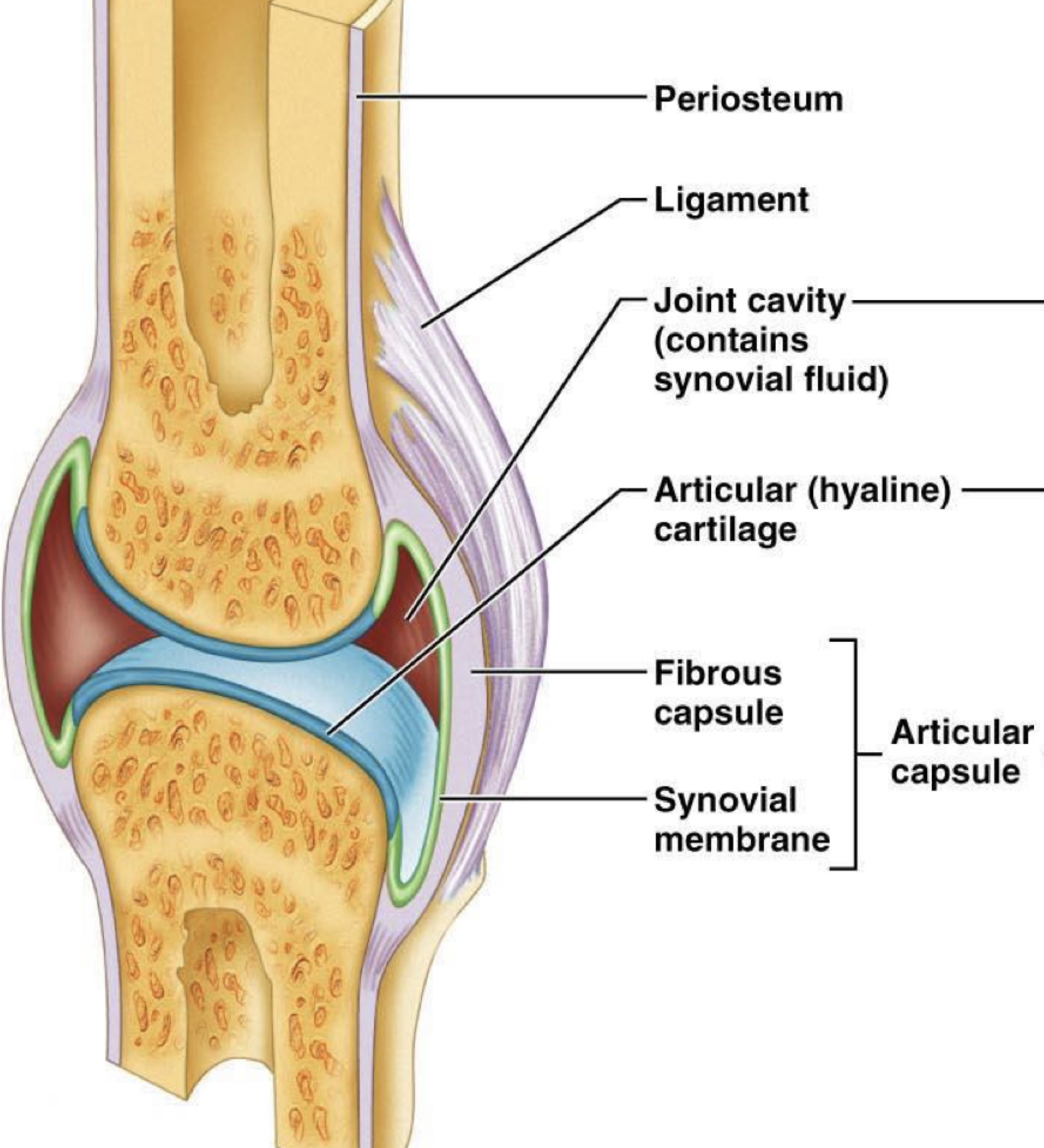
5
New cards
synovial membrane
surrounds joint space of synovial joint
secretes synovial fluid
secretes synovial fluid
6
New cards
fibrous joint capsule
strengthens synovial joint
7
New cards
a healthy shoulder in arthroscopy should be:
smooth & white
8
New cards
what can a diseased shoulder joint look like in an arthroscopy?
rough & bumpy with detached tissue, synovial fluid becoming discoloured
9
New cards
what is the function of articular (hyaline) cartilage?
providing smooth gliding surface (lubrication)
shock absorption (stiff to compression)
distributes load & protects underlying bone
shock absorption (stiff to compression)
distributes load & protects underlying bone
10
New cards
articular cartilage:
what is the vasculature like?
what does this mean for healing properties?
what is the vasculature like?
what does this mean for healing properties?
no vasculature/nerve supply
limited capacity for healing/repair
limited capacity for healing/repair
11
New cards
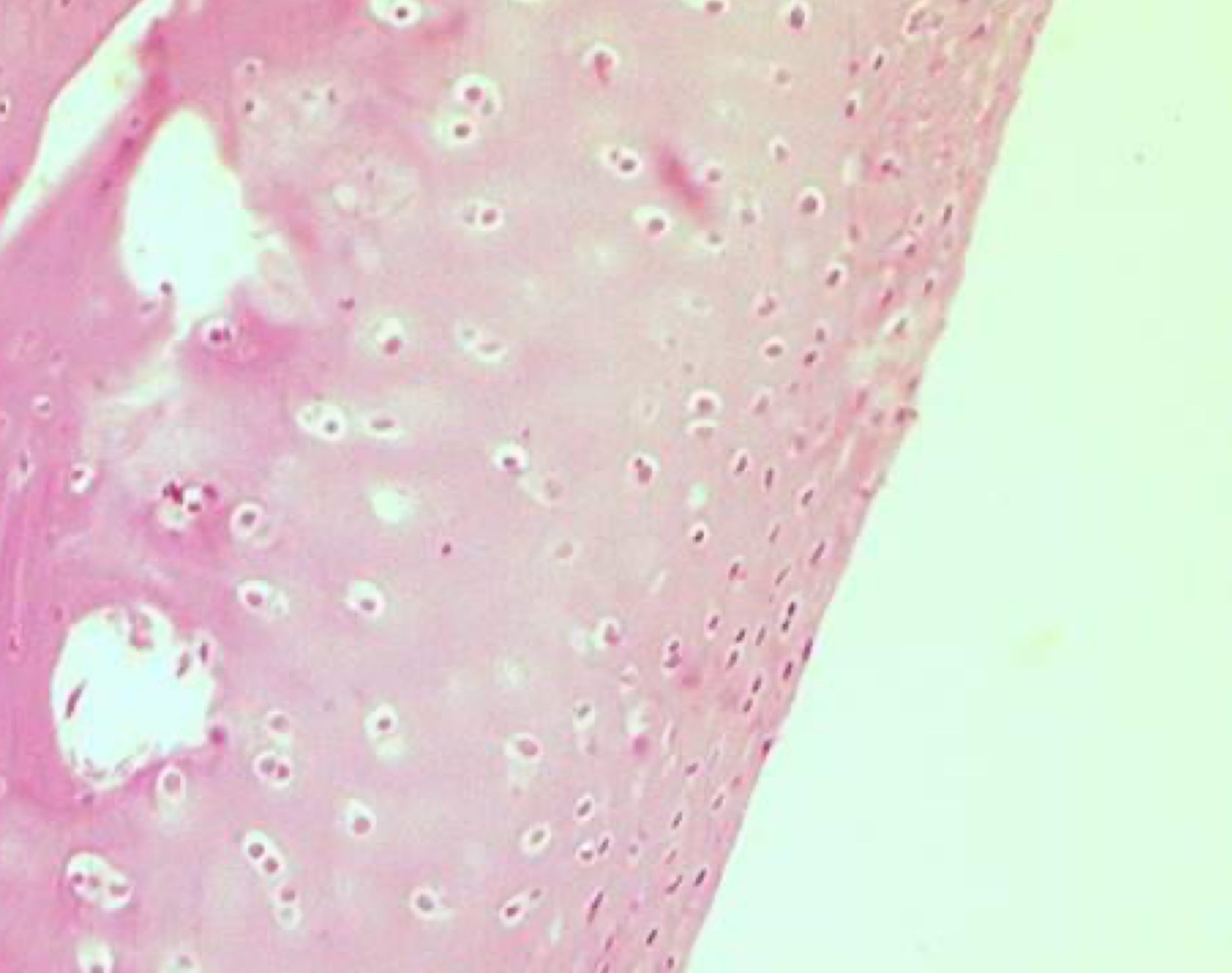
spot the chondrocytes
dark pink dots within white spaces = chondrocytes
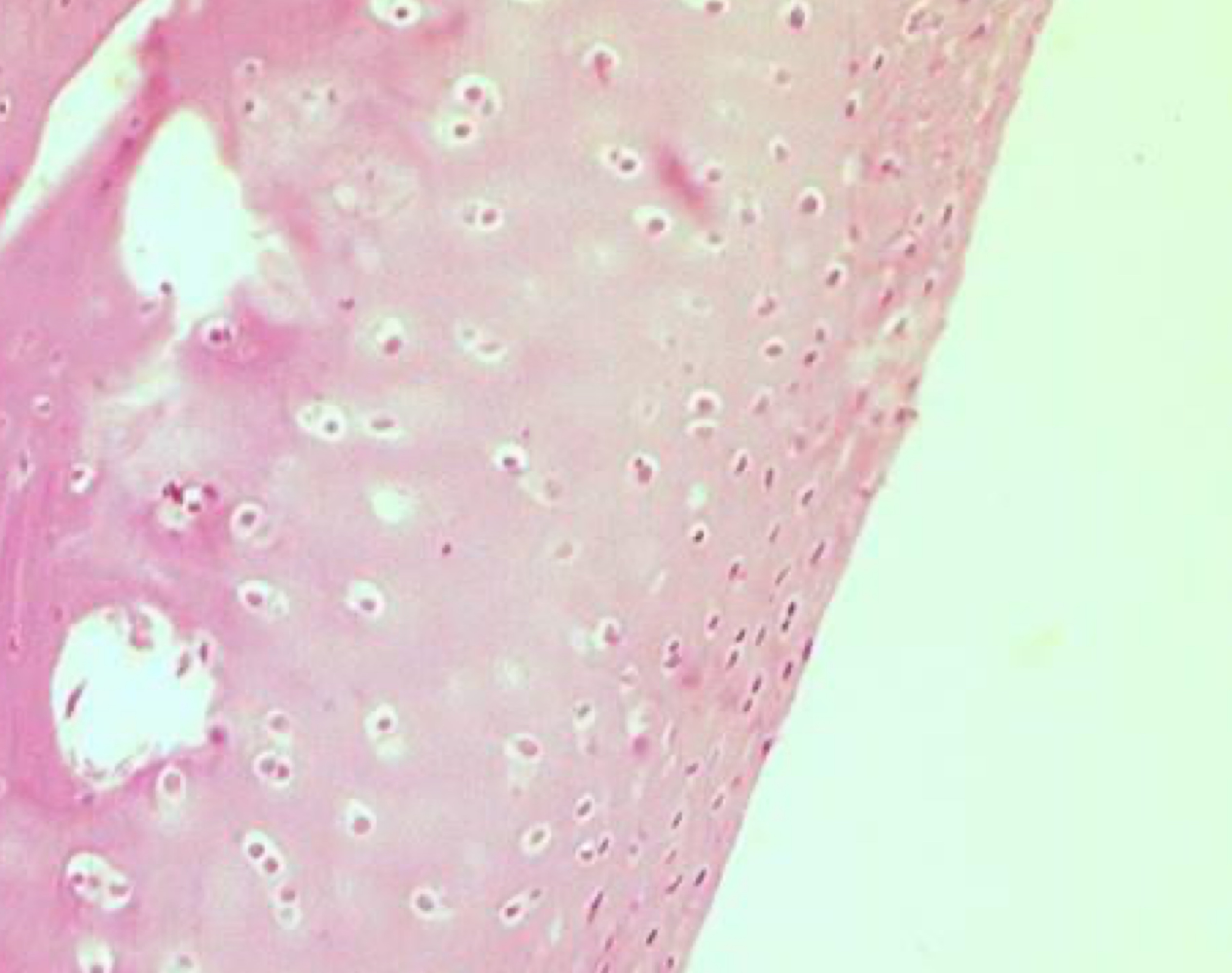
12
New cards
synovial fluid
clear/straw coloured
contains hyaluronic acid
provides lubrication, shock absorption & nutrient/waste transport
contains hyaluronic acid
provides lubrication, shock absorption & nutrient/waste transport
13
New cards
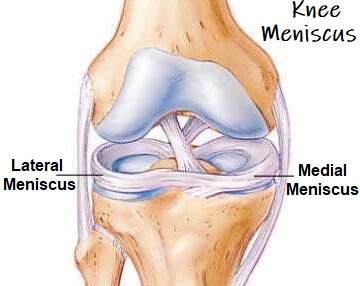
menisci
accessory joint structure for shock absorption (not every joint has this)
c-shaped piece of tough, rubbery cartilage
c-shaped piece of tough, rubbery cartilage
14
New cards
bursae
fluid filled sack, cushioning tendon as it pushes against sesamoid bone
15
New cards
tendon sheath
like bursae but wrap around tendon where they pass over joints
16
New cards
synsarcosis joint
only muscular attachment (e.g. scapula onto ribcage)
17
New cards
fibrous joint
least mobile joint, connecting neighbouring bones w little to no movement (e.g. flat bones within skull)
18
New cards
cartilaginous joints
some motion, but not too much (e.g. pelvis allowing child to pass through canal, intervertebral disks)
19
New cards
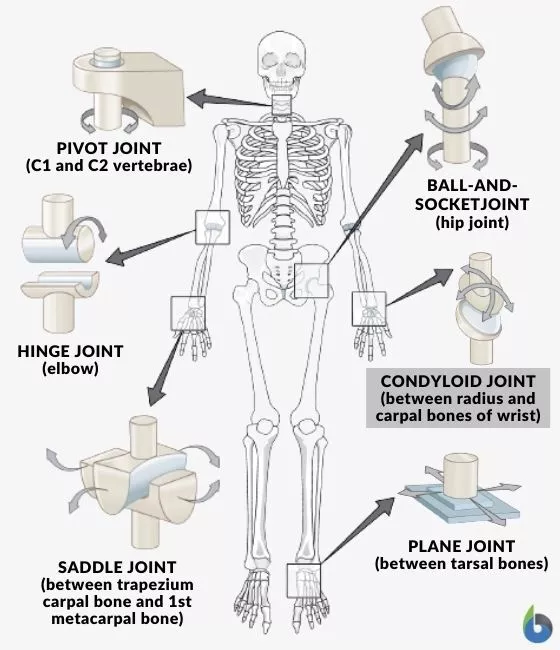
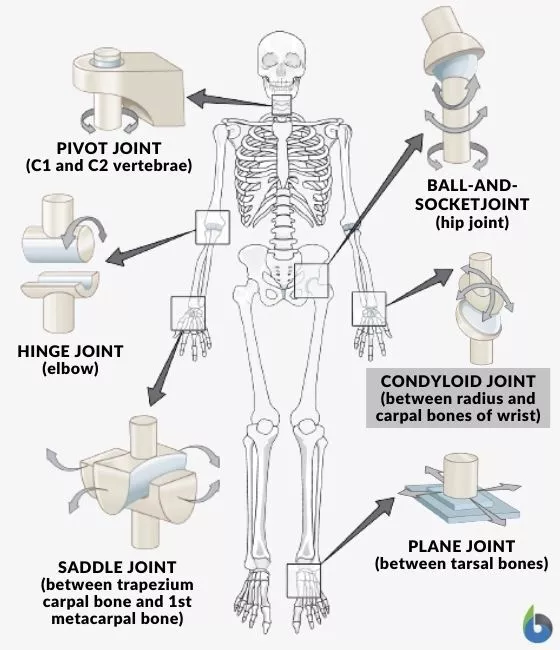
multi-axial joint example
ball & socket
20
New cards
bi-axial joint example
condyloid
saddle
saddle
21
New cards
uni-axial joint example
pivot
hinge
hinge
22
New cards
gliding joint example
planar
23
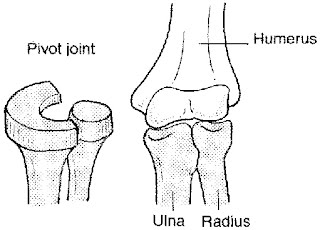
New cards
pivot joint
peg fitted within ring, peg rotates around ring (or vice versa)
24
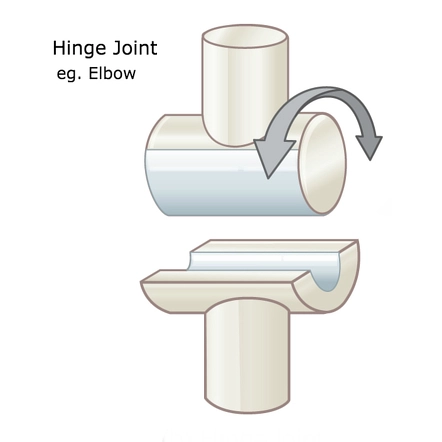
New cards
hinge joint
one articular surface convex, other is concave, usually a 'notch' is present to limit motion
25
New cards
condylar joint
convex surface w corresponding concave cavity
26
New cards
saddle joint
two surfaces - convex in one direction, concave in the other at right angles
27
New cards
joint motion
when two or more bones meet to allow movement
28
New cards
what does a greater range of movement increase? why?
greater the range of movement = higher the risk of injury
strength of the joint is reduced
strength of the joint is reduced
29
New cards
moment arm
length between joint axis and the line of force acting on the joint