CNS Depressants - Quiz 1
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Hu Lectures
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
The ideal Inhalation Anesthetic
nonflammable
good chemical and metabolic stability
low incidence of myocardial effects
low incidence of hepatic and renal damage
rapid induction and emergence from anesthesia
adequate skeletal muscle relaxation
wide margin of safety
Lipid Hypothesis of 1899
+original, modification
Protein Hypothesis
Name this molecule
+class, formulation
Nitrous Oxide (N2O)
aka laughing gas
gaseous general anesthetics
formulation: inhalation

Name this molecule
+class, formulation
Cyclopropane
gaseous general anesthetics
formulation: inhalation
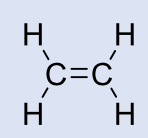
Name this molecule
+class, formulation
Ethylene
gaseous general anesthetics
formulation: inhalation
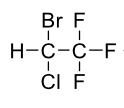
Name this molecule
+brand, class, formulation
Halothane (Fluothane)
Volatile Liquid General Anesthetics
formulation: inhalation
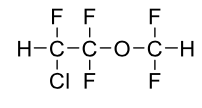
Name this molecule
+brand, class, formulation
Enflurane (Ethrane)
Volatile Liquid General Anesthetics
formulation: inhalation
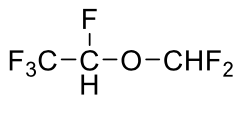
Name this molecule
+brand, class, formulation
Desflurane (Suprane)
Volatile Liquid General Anesthetics
formulation: inhalation
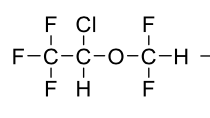
Name this molecule
+brand, class, formulation
Isoflurane (Forane)
Volatile Liquid General Anesthetics
formulation: inhalation
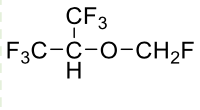
Name this molecule
+brand, class, formulation
Sevoflurane (Ultane)
Volatile Liquid General Anesthetics
formulation: inhalation
General Side Effects of Volatile Liquid General Anesthetics
+cause, ADEs/: bromide, chloride, fluoride, storage conditions
Side effects are due to halide metabolites
Bromide and Chloride effects
sensitizes the heart to NE and EPI causing ventricular fibrillation (heart beats faster, gets out of sync, and then stops beating)
arrhythmia (abnormal heart beat)
Fluoride
kidney and liver damage due to bioaccumulation
Storage = 15-30°C
Packaging of Fluranes
Color-coded
sevoflurane = yellow
isoflurane = purple
enflurane = orange
desflurane = blue
Advantages of injectable anesthetics
no special equipment needed to administer
many have faster onset than inhaled agents
rapid recovery; suitable for outpatients
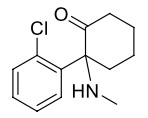
Name this molecule
+brand, aka, formulation
Ketamine HCl (Ketalar)
aka “Special K”
formulation: IV anesthetic
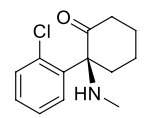
Name this molecule
+brand, formulation
Esketamine (Spravato)
formulation: IV anesthetic
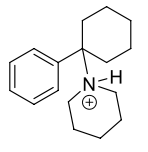
Name this molecule
+aka, formulation
Phencyclidine
aka: “Angle Dust, PCP”
formulation: IV anesthetic
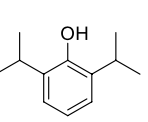
Name this molecule
+brand, formulation
Propofol (Diprivan)
formulation: IV anesthetic
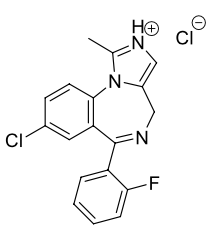
Name this molecule
+brand, formulation
Midazolam HCl (Versed)
formulation: IV anesthetic
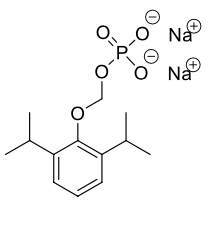
Name this molecule
+brand, formulation
Fospropofol (Lusedra)
formulation: IV anesthetic
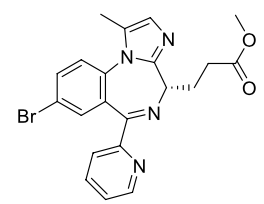
Name this molecule
+brand, formulation
Remimazolam (Byfavo)
formulation: IV anesthetic
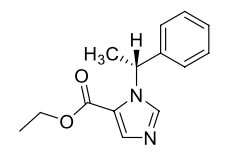
Name this molecule
+brand, formulation
Etomidate (Amidate)
formulation: IV anesthetic
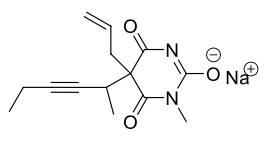
Name this molecule
+brand, formulation
Methohexital Sodium (Brevital Sodium)
formulation: IV anesthetic
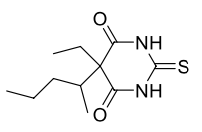
Name this molecule
+brand, formulation
Thiopental Sodium (Sodium Pentothal)
formulation: IV anesthetic
Sedative def.
a drug that exerts a calming effect with little to no effect on motor or mental functions
Hypnotic def.
a drug that produces drowsiness and encourages the onset and maintenance of sleep
resembling as close as possible natural sleep
Anxiolytic def.
a drug that specifically relieves excessive anxiety, a sense of apprehensive expectation that is either appropriate to the situation or excessive
panic attacks, phobias, etc.
Sedative and hypnotics
+moa, receptors