Chapter 21: Medical Assistant Skills
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is measuring or recording height and weight used to do?
Determine if a patient is overweight or underweight.
What is microcephaly and what is it caused by?
The condition of a small head. It can be caused by a congenital defect, infections, or drug/alcohol abuse during pregnancy.
In what unit is weight recorded by?
Kilograms. 1 kilogram is equivalent to 2.2 pounds.
When measuring or recording height, what should you have the patient do?
Remove their shoes.
True/False: If a patient is an infant, they can leave their diaper on.
True.
If a patient is going through ____, they must have their weight closely monitored.
Chemo
True/False: You must always cover the patient as much as you can during any examination or procedure.
True.
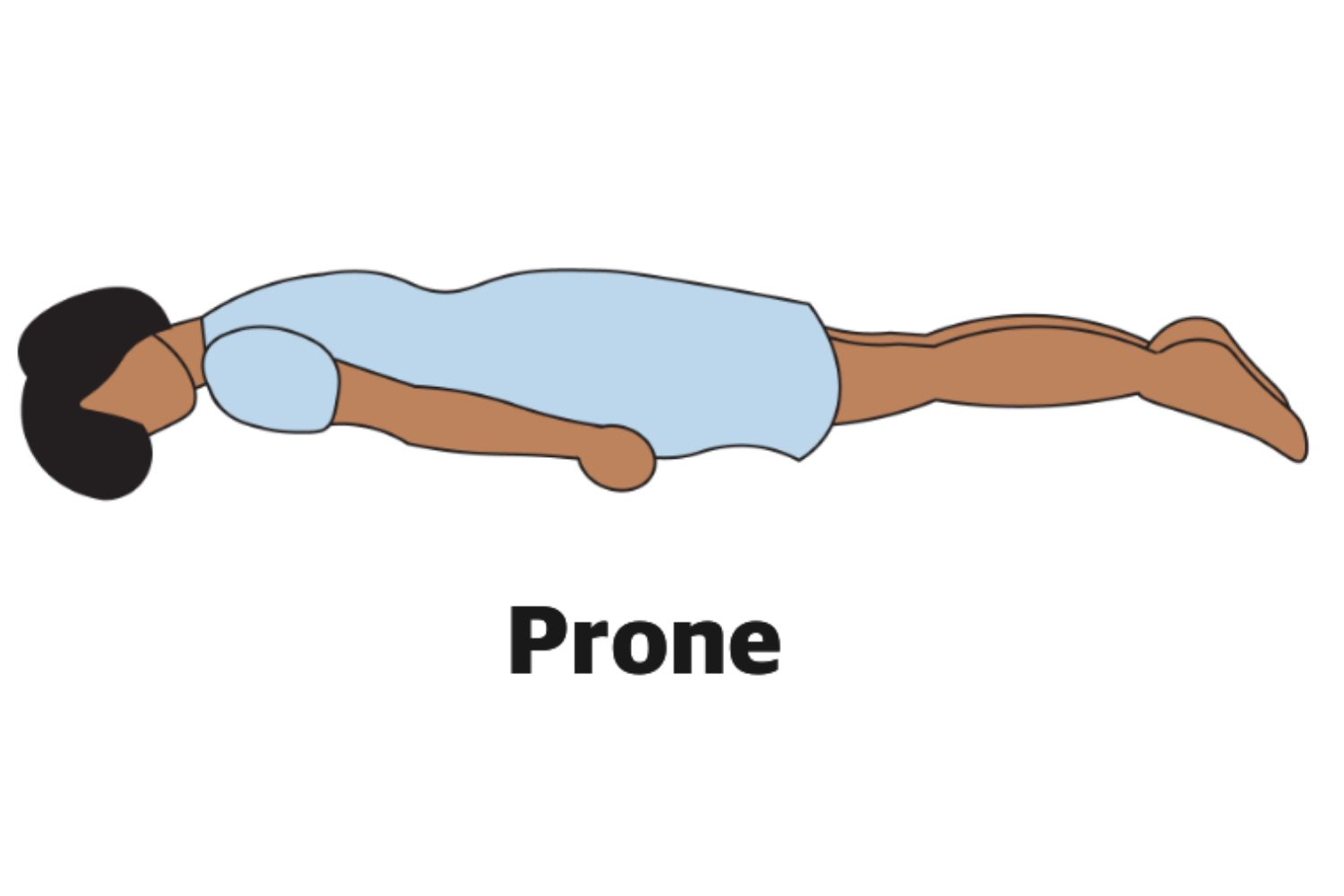
What is the prone position and why is it used?
The patient is lying on their abdomen with their legs together and the face to the side. The position allows the physician to examine the spine.
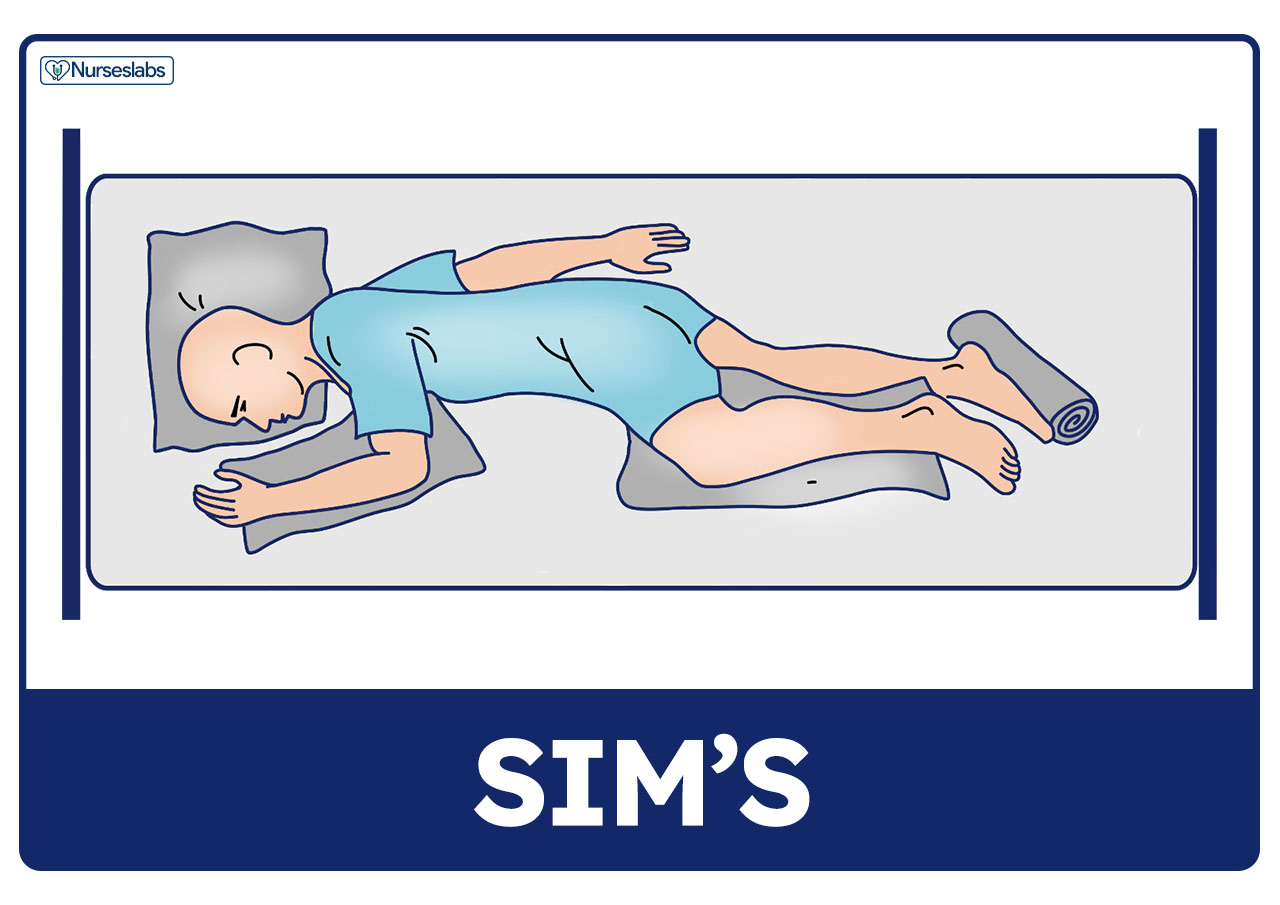
What is the Sims’ position and when is it used?
The patient lies on their left side with the right leg bent up near the abdomen. It is used for enemas and rectal examinations.
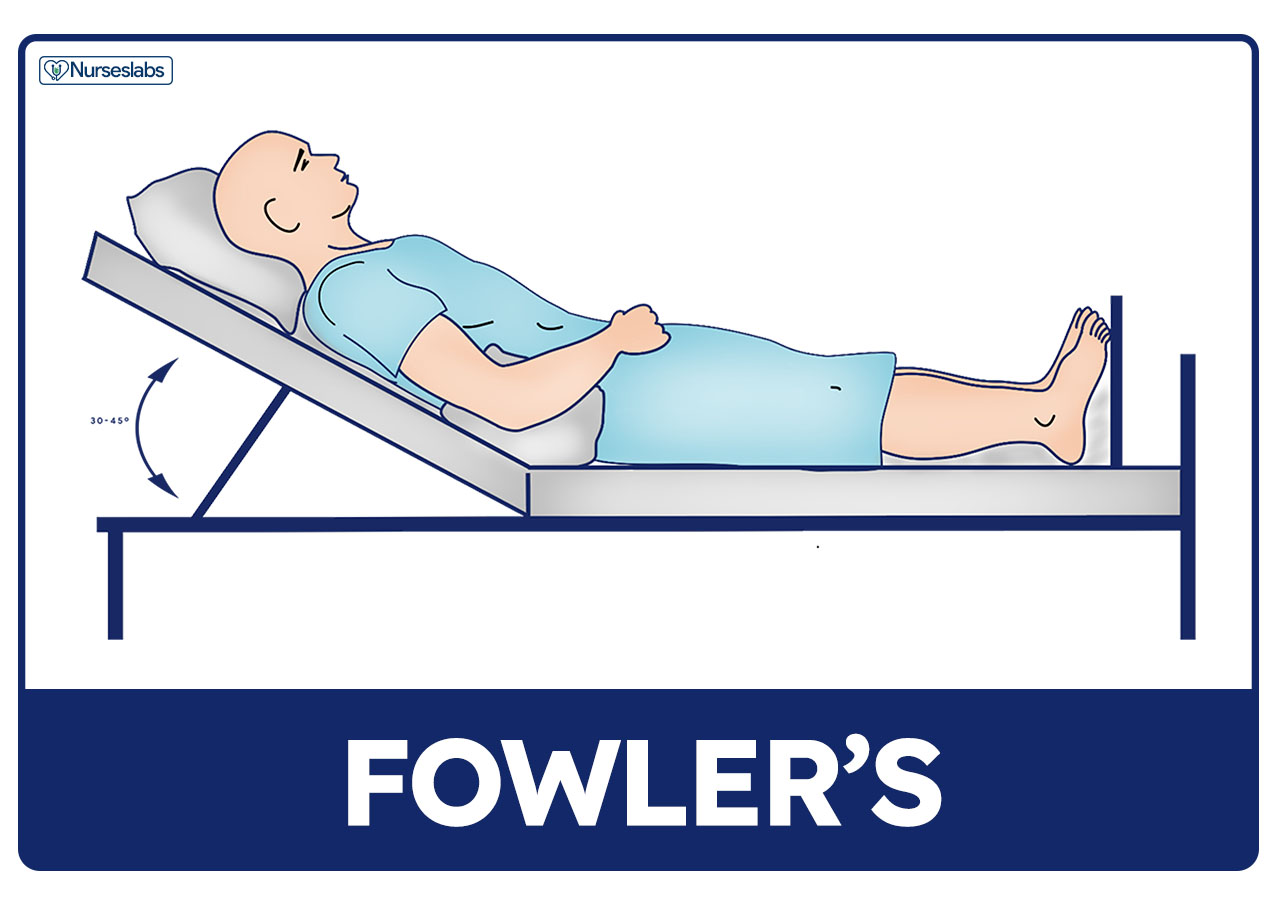
What is the Fowler’s position and when is it best used?
The patient lies on their back with their head elevated at one of the several different angles. It is best used when the patient is experiencing trouble breathing.
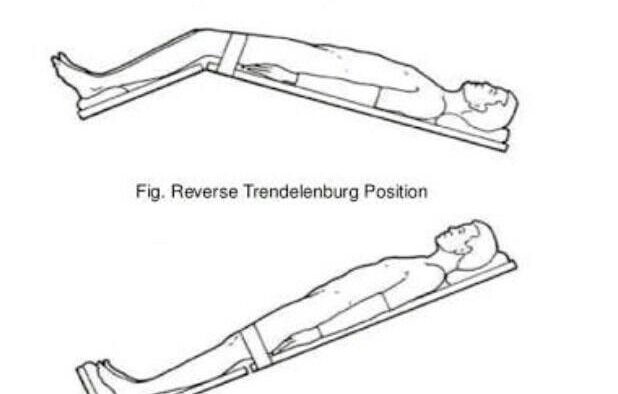
What is the Trendelenburg position and when is it used?
The patient lies on their back with the head lower than the feet or with both head and feet inclined downward. It is used to improve surgical access to the pelvic area and increase venous return to the heart and facilitate venous catheter placement.
What are Snellen charts?
Special charts that use letters or symbols in calibrated heights to check visual acuity. It is important that the patient does not squint when viewing.
What is considered to be normal visual acuity?
20/20 vision, meaning that a person can see at 20 feet what the average person can see at the same distance.
What is the abbreviation for the right eye?
OD or oculus dexter
What is the abbreviation for the left eye?
OS or oculus sinister
What is the abbreviation for both eyes?
OU or oculus uterque
What is another term for papanicolaou?
A pap smear.
What is the act of percussion?
The process of tapping various body parts during an examination.
What is auscultation?
Process of listening for sounds in the body.
What is an opthalmoscope?
A lighted instrument used to examine the eye.
What is an otoscope?
A lighted instrument used to examine the ear.
True/False: Instruments do not have to be warm before the physician uses them.
False. Instruments should be warmed before usage.
What is a stethoscope?
An instrument used to listen to internal body sounds.
What is a tuning fork?
An instrument that has two prongs and is used to test hearing acuity.
True/False: Explaining all procedures to patients during prep helps the patient when they are nervous.
True.
What are hemostats?
Instruments used to compress or clamp blood vessels to stop bleeding.
What are suture removal sets?
Sets of instruments that include suture scissors and thumb forceps.
True/False: When assisting with minor surgery and suture removal, all standard precautions must be followed at all times.
True. Treat every patient as if they are infectious.
What is an electrocardiogram?
Machine that graphically traces the electrical activity of the heart.
True/False: When recording activity with an electrocardiogram, it is important to remind the patient that the machine will NOT electrocute them.
True.
Chest electrodes are passed at ___ specific locations on the chest and various parts of the body.
Six
What is the abbreviation used for both arms, both legs, and the chest?
RA for right arm
LA for left arm
RL for right leg
LL for left leg
C / V for chest
One millivolt electrical input causes the stylus (recording needle) to move ____ millimeters on the graph.
Ten. It is equivalent to ten small squares or two large squares.
What is the troche or lozenge?
It is a large, flat disk that is dissolved in the mouth.
What is an enteric coated medication?
It is a medication with a special coating that doesn’t dissolve until it makes contact with the small intestine.
What are suppository medication?
They are cone-shaped objects that have the base material of cocoa butter or glycerin. It is mixed with the medication and inserted into the rectum or vagina to stimulate peristalsis and provide aid.
What are the various ways medication can be administered?
Oral
Rectal (Ointments, suppositories)
Injections
Topical or Local (Transdermal patches)
Sublingual (Given under tongue)
What are the six rights to observe when administering medication?
Right medication
Right dose or amount
Right patient
Right time
Right method of route or administration
Right documentation
True/False: If a prepared medication is not administered, it does not need to be discarded.
False.
Where are expired medications destroyed?
They are destroyed in approved receptacles.