CHEE3S - STUDY GUIDE
1/202
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Contributors: @remisabale on IG
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
203 Terms
What is Chemistry?
The science that deals with the composition of matter, properties of matter, how matter interacts with another kind of matter and how energy changes that result when matter is transformed
What is matter?
Anything that has mass and takes up space
What is composition?
The internal make up of matter; what kinds and numbers of particles in a substance
What is structure?
How particles are bonded together in a substance
What are properties?
Characteristics of matter used to identify the substance. Composition and structure are responsible the properties of a substance
How can you identify a physical property?
Characteristics of a substance that pertain to its appearance or physical state & is measurable
How can you identify a chemical property?
Characteristics that allow the substance to change to something new; it alters the internal makeup of the substance
How can you identify a quantitative property?
If it's measurable (often using tools)
How can you identify a qualitative property?
By using the five senses ( Taste, Smell, See, Touch, Hear)
How can you identify an intensive property?
Independent of the amount of substance; only depends on the type of
How can you identify an extensive property?
It is dependant on the amount of substance
What properties do these have?
Melting point of iron is 1535°C
Density
Malleability
Reactivity
Mass
Melting point of iron is 1535°C
~ physical, quantitative, intensive
Density
~physical, quantitative, intensive
Malleability
~physical, qualitative, intensive
Reactivity
~chemical, qualitative, intensive
Mass
~physical, quantitative, extensive
What is a physical change?
Only the state or the appearance of the substance is changed. The internal make up is the same
What is a chemical change?
Changes the internal makeup of the substance. Atoms are arranged differently in the final substance. (Also know as Chemical Reaction)
What is a nuclear change?
Produces entirely different atoms
Define energy
Whatever it takes to generate heat, produce electricity, or to move an object
What is Enthalpy?
Quantity of heat that has to do with a system that ABSORBS or RELEASES nrg during a chemical reaction.
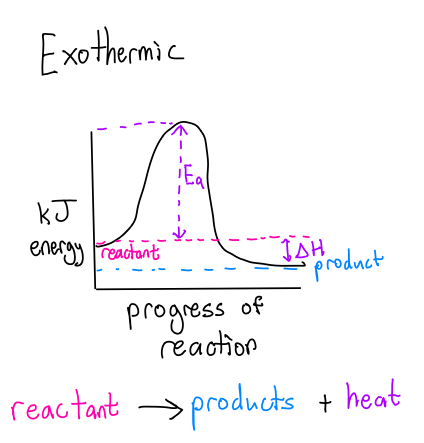
What is an Exothermic Rxn?
Nrg in the form of heat or light RELEASED to the surroundings after a rxn occurs (-)
Ea = Activation energy
ΔH = Enthalpy
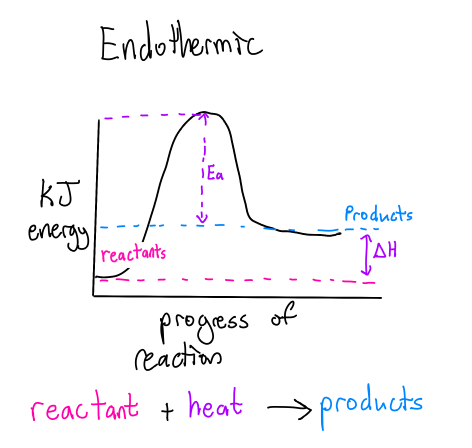
What is an Endothermic Rxn?
Nrg from surroundings and the systems is ABSORBED during the rxn (+)
Ea = Activation energy
ΔH = Enthalpy
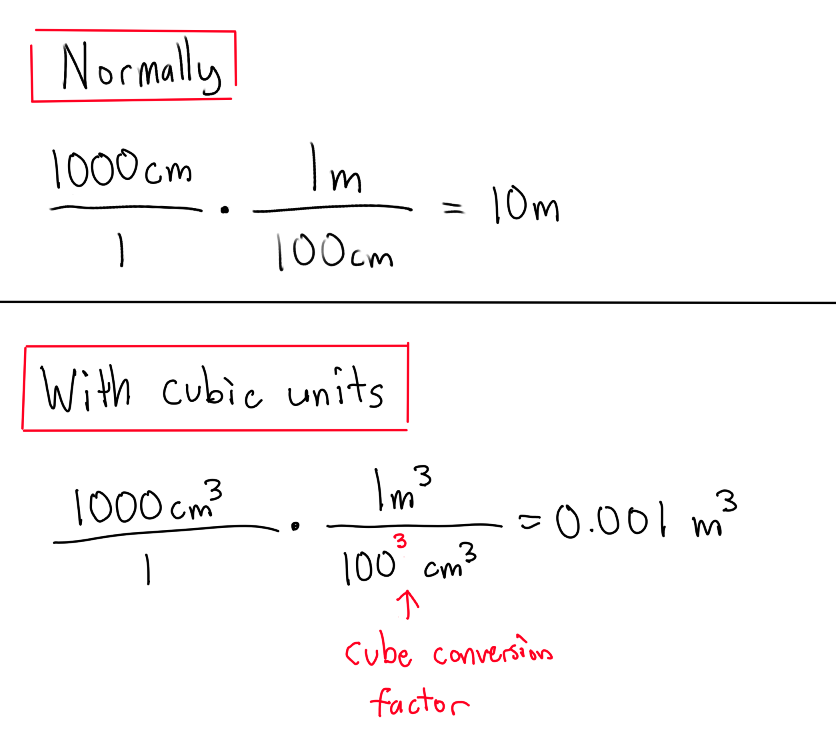
How is volume expressed?
As the amount of space or the amount of matter a container can hold.
Cubic units?
Expresses volume in 3d (don't forget to cube units and conversion factors while using dimensional analysis)
any length cubed
(eg) cm³, m³, etc
Capacity Units
Express volume of how much a container can hold
(eg) L, mL, qt, gal, fl.oz, etc
1 gal = ? liters
3.785 L
1 gal = ? qt
4 qts
1 qt = ? liters
0.946 L
1 fl.oz = ? mL
29.6 mL
What is a derived unit?
When a measurement is the result of a certain relationship between variables
°C to °F FORMULA
(°C x 1.8) + 32
°F to °C FORMULA
(°F -32) / 1.8
°C to K FORMULA
°C + 273
What is Farenheit?
Temp scale used in the US
What is Celsius?
Temp scale used in Canada
What is Kelvin
Temp scale that uses the same degree measure at Celsius but has its zero set to absolute zero (no negative)
What is absolute zero?
the lowest possible temperature (0 Kelvin)
All molecular motion stops = Death
What is density?
The mass of a substance per unit volume.
d=m/v
Accuracy and Precision
Accuracy: How close you get to a target value
Precision: How close your trial results are to each other
What is specific gravity?
Density of a substance divided by the density of another substance at standard. (density of H2O = 1g/mL at 4°C)
Sp.gr = Density of subs at 20°C/Density of water at 4°C
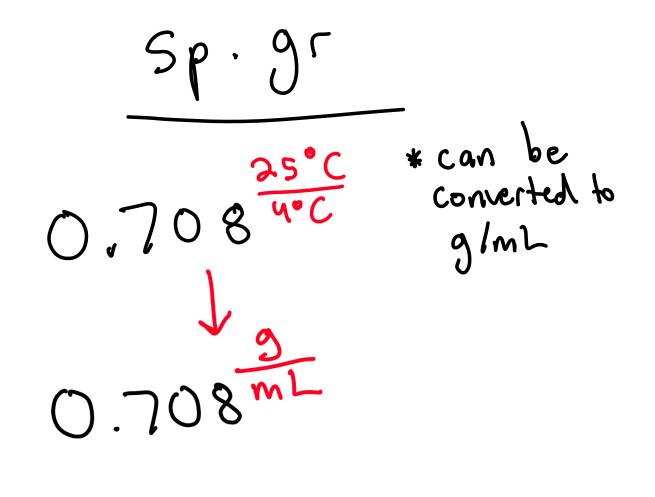
What is specific heat?
Amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1g of substance by 1 degree celcius
Formula of specific heat and calculations
Q = energy lost or absorbed (J or cal)
m = mass (g or kg)
c = specific heat constant (J/g°C or cal/g°C)
ΔT = change in temperature (°C)
remember to include units in calculations
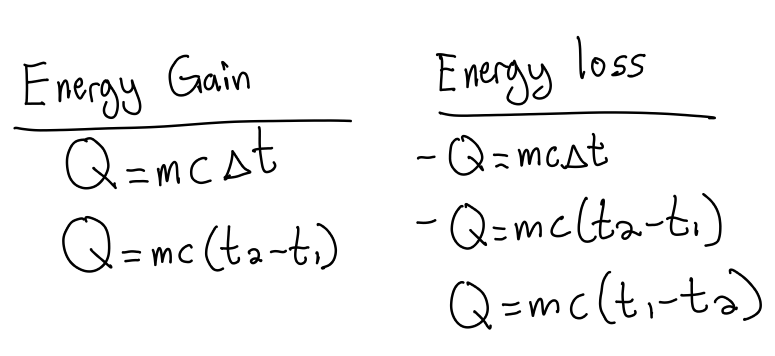
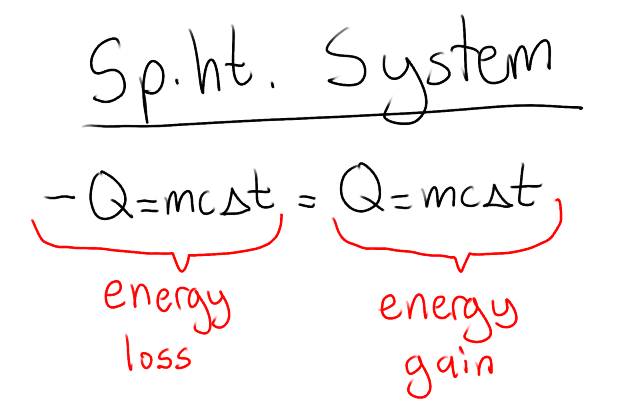
Specific heat systems calculation guide
energy lost = energy gained
heat from hotter substance goes to cooler substance !!
cold - gains heat
hot - loses heat
Q = energy lost or absorbed (J or cal)
m = mass (g or kg)
c = specific heat constant (J/g°C or cal/g°C)
ΔT = change in temperature (°C)
*both systems have the same final temperature
*make sure units from both substances are the same
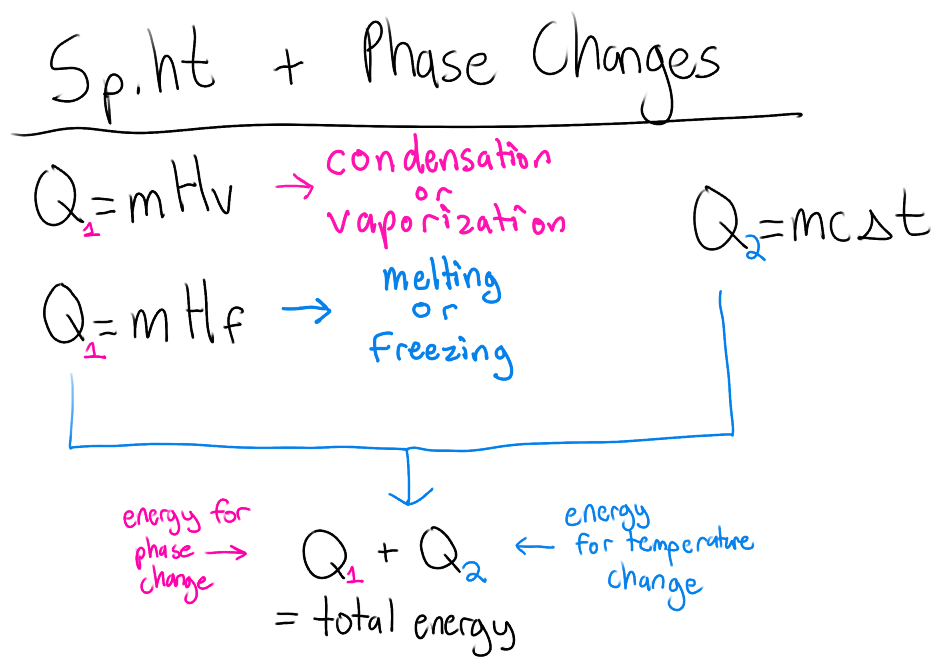
Specific heat calculations with state changes guide
use heat of fusion/heat of vaporization
remember temperature doesn’t change during a state change
Q = energy lost or absorbed (J or cal)
m = mass (g or kg)
c = specific heat constant (J/g°C or cal/g°C)
ΔT = change in temperature (°C)
Hf = heat of fusion (J/g)
Hv = heat of vaporization (J/g)
What is "The Mole/Mol"
Special unit in chemistry that is used to clump together a particular number of particles.
6.022 × 10²³ particles in a mol.
Define particle examples
An atom of Na
A molecule of H2O (covalent, non-metal)
An ion of a Na+SO4^2- (Charge)
A formula unit of NaCl (ionic, metal and non-metal)
A photon of light from particles
1 cal = ? Joules
4.184 J
1 lb = ? g
454 g
1 mi = ? km
1.61 km
What is molar mass?
Total grams in 1 mole of a substance
How to find: Add up all the molar masses of all the atoms in a formula
1 cm³ = ? mL
1 mL
What are ionic compounds/bonds?
metals transfer electrons to non-metals
combining capacity is the number of bonds an element can form
(eg) Na³⁺ gain 3 e⁻ from 3 bonds
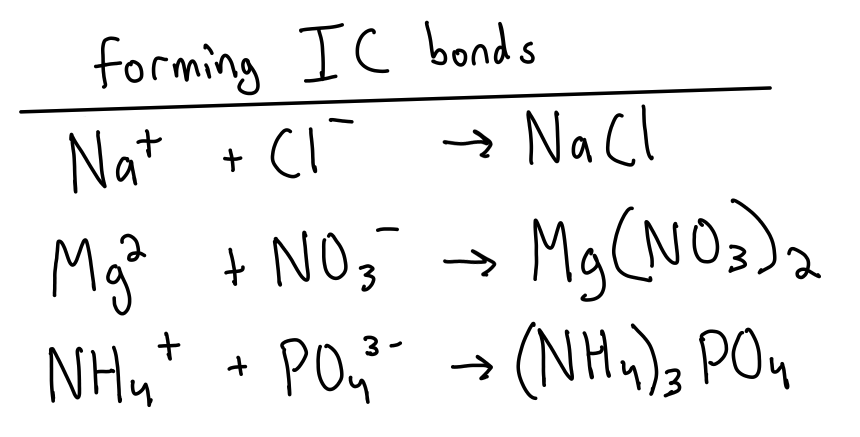
How do you write/form an ionic compound formula?
metals/positive ions go first
bracket the entire polyatomic ion if it’s used in the formula
“criss-cross” method
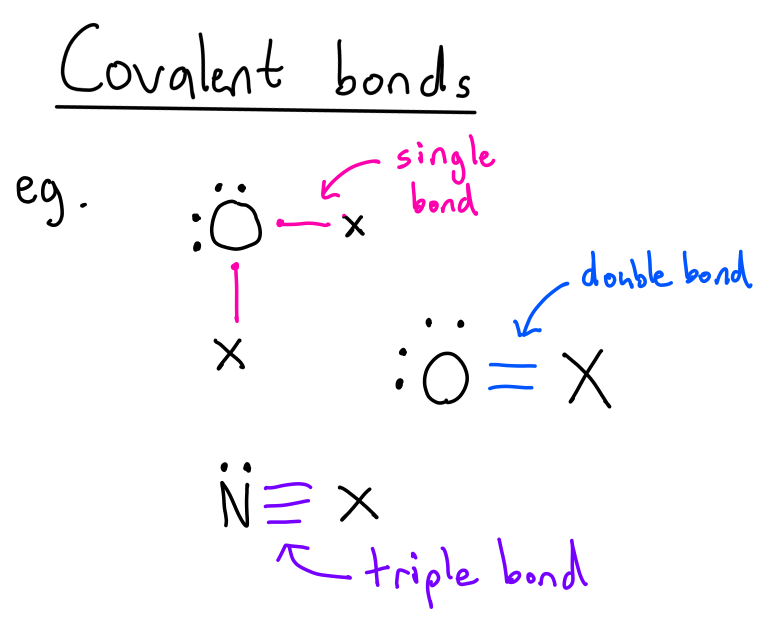
What are molecular/covalent compounds/bonds?
e⁻ are shared by atoms in order to complete their valence shell
there are single bonds, double bonds, triple bonds, etc.
How do you name ionic compounds?
Use the actual name of the first element
Add an “ide'“ at the end of the second element
(eg)
NaCl = Sodium Chloride
How do you name molecular compounds?
add prefixes to the beginning of each non-metal
add an “ide” to the end of the second non-metal
if the first element is mono, don’t use mono
1 - mono
2 - di
3 - tri
4 - tetra
5 - penta
6 - hexa
7 - hepta
8 - octa
9 - nona
10 - deca
(eg)
NI₃ = nitrogen triiodide
How to calculate molar mass of a compound?
add up the molar masses of each element in the compound including how much there are
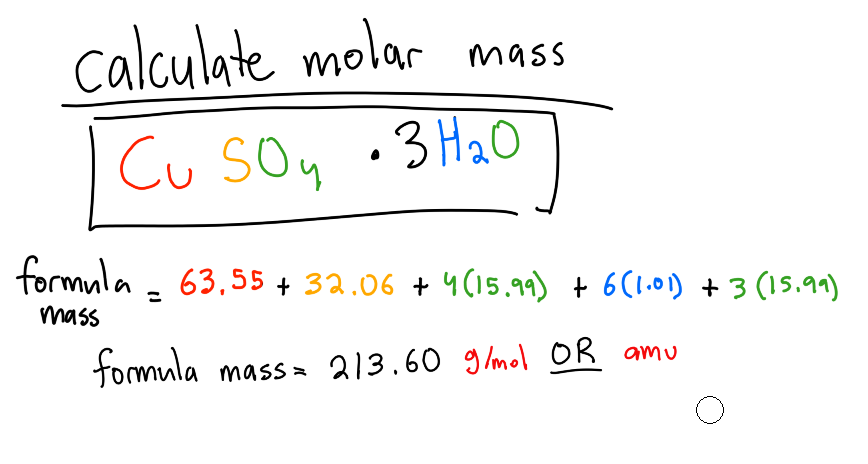
BONUS QUESTION
How much atoms of nitrogen are in 46.0g N₂?
remember to change the mols of a diatomic element into mols of the single element
1 mol N₂ = 2 mol N

What is the density of water?
1.00g/mL
1g H₂O = 1mL H₂O
What is the specific heat of water?
H₂O
c = 4.184 (J/g°C)
What does the state of matter depend on?
How close particles are to each other
What does the ability to have shape and definite volume depend on?
How tightly packed the particles are and how strong the attractive force is between them
Describe the particles, shape and volume of solids
definite shape, definite volume because the particles are very close and have strong attractive forces between them.
Describe the particles, shape and volume of liquids
shape is not definite (takes shape of container), definite volume. Particles are farther apart, allowing the particles to slide over each other. Has less attractive forces compared to solids
Describe the particles, shape and volume of gases
shape and volume are not definite because of the lack of an attractive force. The particles are very far apart and moving randomly with high kinetic energy.
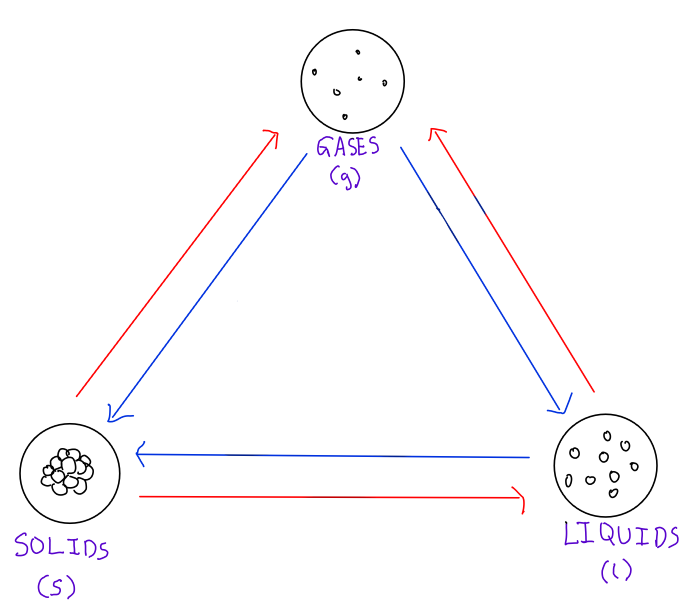
What are all the state changes?
State changes will always involve an absorption or release of energy
Closer particles → Farther particles = Energy gain
Farther particles → Closer particles = Energy loss
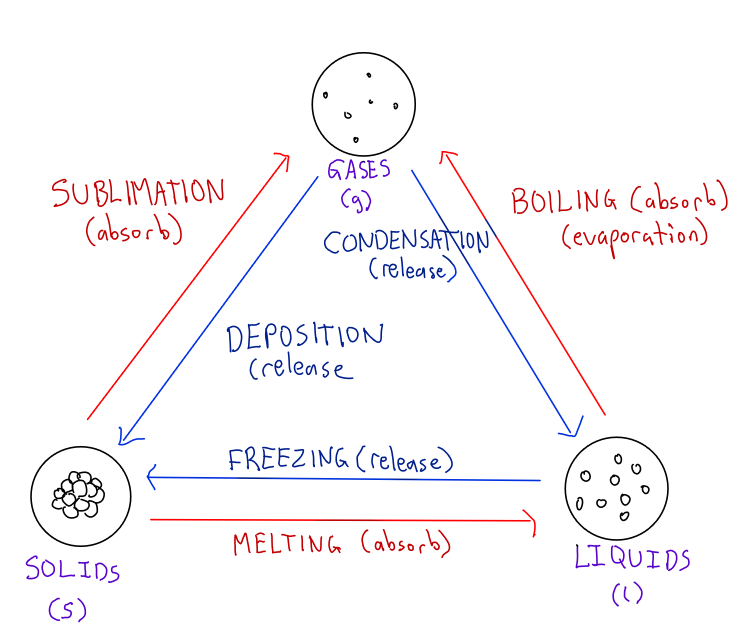
What is melting point?
Temp at which a solid turns into a liquid
Also temp at which a liquid turns into a solid
Melting point = Freezing point
What is boiling point?
Temp at which a liquid turns into a gas
vigorous bubbling that occurs within the body of the liquid as it vaporizes internally.
defined as the substances’ highest temp in the liquid state.
molecules reach max speed
What is a volatile substance?
a substance that easily evaporates, has a low boiling point, high vapour pressures.
what is the difference between molar mass, molecular mass and formula mass?
molar mass:
used to show the mass of one mole of substance in grams
uses grams per mole ( g/mol )
usually used for conversions using mass/moles
molecular mass:
FOR MOLECULAR/COVALENT COMPOUNDS
used to show the mass of one mole of substance in amu
uses atomic mass units ( amu )
usually used for calculations with percent composition, etc
formula mass:
FOR IONIC COMPOUNDS (aka salts)
used to show the mass of one mole of substance in amu
uses atomic mass units ( amu )
usually used for calculations with percent composition, etc
What is heat of fusion?
The amount of heat required to melt a specific amount of substance at it’s melting point.
used for melting and freezing
symbol: Hf
unit: J/g
What is heat of vaporization?
The amount of heat required to evaporate a specific amount of substance at it’s boiling point.
used for evaporation (not condensation)
symbol: Hf
unit: J/g
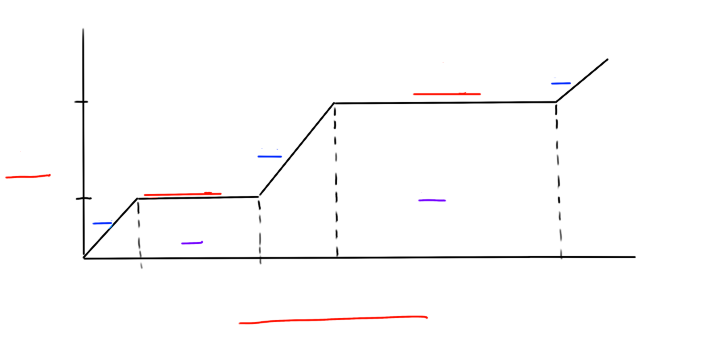
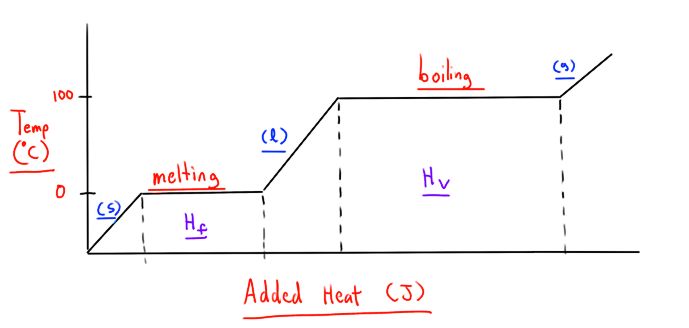
What is the heating curve of H20?
fill in the blanks.
What are the chemical properties?
Reacitivity:
how a substance changes when interacting with other substances
Heat of Formation:
Amount of heat released when a substance is formed (J/g)
Heat of Combustion:
Amount of heat released when a substance reacts with oxygen in a combustion reaction (KJ/g)
(could also be just J/g i think)
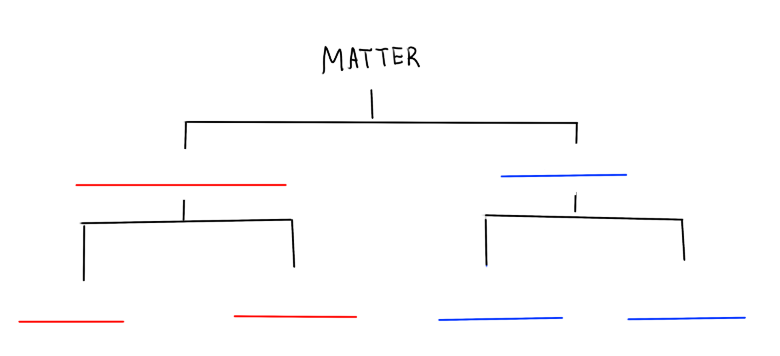
What is the Classification of Matter diagram?
fill in the blanks
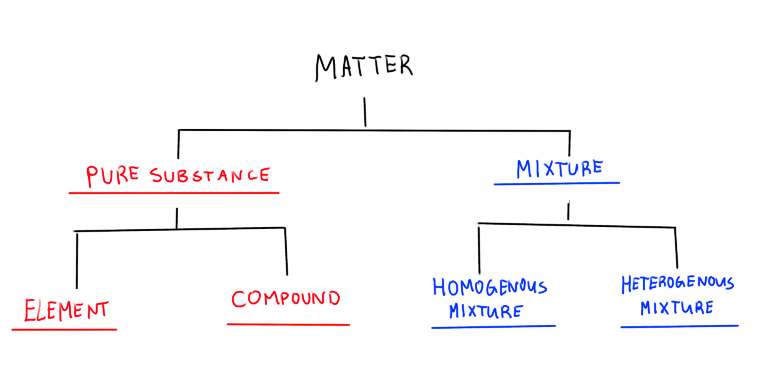
What is a pure substance?
Homogenous matter that has fixed and definite composition
What is an element?
A pure substance with only one kind of atom
What is a compound?
A pure substance that is composed of two or more kinds of atoms in a fixed proportion
What is a mixture?
A kind of matter with a variable composition and proportion
What is a homogenous mixture?
A mixture of two or more substances appearing as only one phase
What is a heterogenous mixture
A mixture of two or more substances appearing as two or more phases
Classify each substance
air
polluted air
hydrogen gas
ozone
water
tap water
steel
blood sample
Classify each substance
air (homogenous)
polluted air (heterogenous)
hydrogen gas (element)
ozone (element)
water (compound)
tap water (homogenous)
steel (homogenous)
blood sample (heterogenous)
What is an atom? What are the charges and masses of each subatomic particle?
The smallest unit structure of an element
Three subatomic particles
Protons, positive (p⁺) mass: 1.673e-24 g
Neutrons, neutral (n°) mass: 1.675e-24 g
Electrons, negative (e⁻) mass: 9.110e-28 g
BONUS INFO ABOUT ATOMIC STRUCTURE
p⁺ and n° are located in the nucleus and make up the mass of the atom
e⁻ are found constantly moving in the shells (orbits) around the nucleus
The mass of protons and neutrons are 1.00 amu
The mass of an electron is approximately 1/1837 amu and is considered negligible
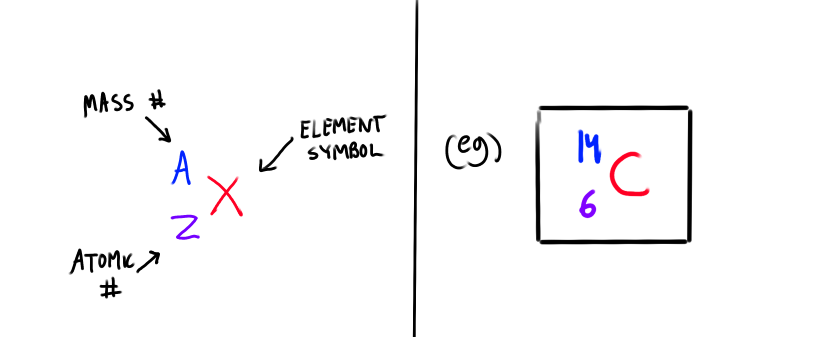
What is Atomic number, Atomic mass and Mass number?
Atomic Number (Z
Number of protons in an atom; cannot change
Atomic Mass
Average relative mass of the isotopes of an element
Mass Number (A)
number of protons and neutrons in an atom. Changes depending on the isotope (different # of neutrons)
What is Hyphen notation for isotopes?
Element - Mass number
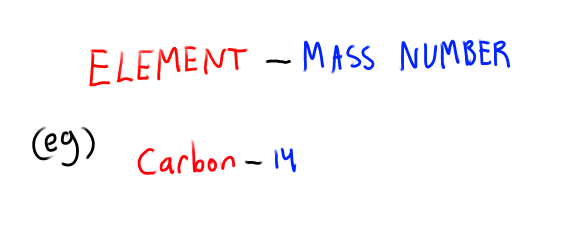
What is the A-Z notation for isotopes?
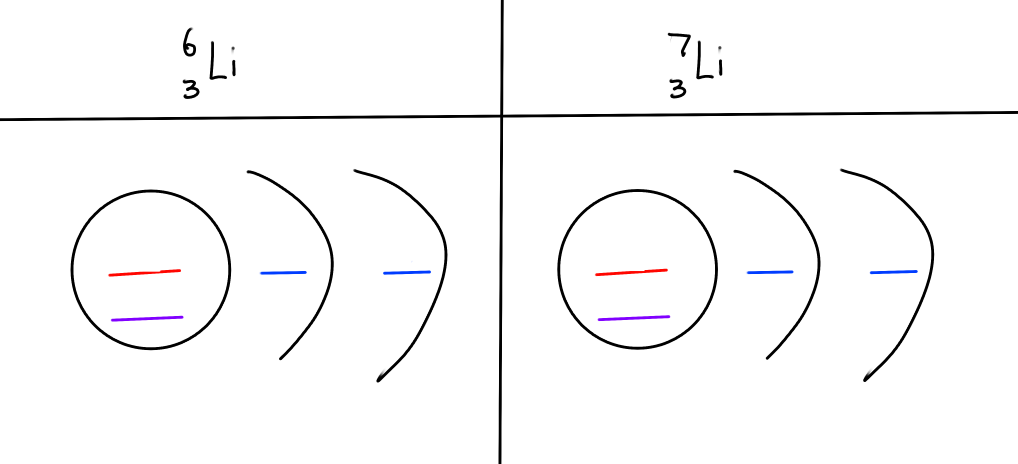
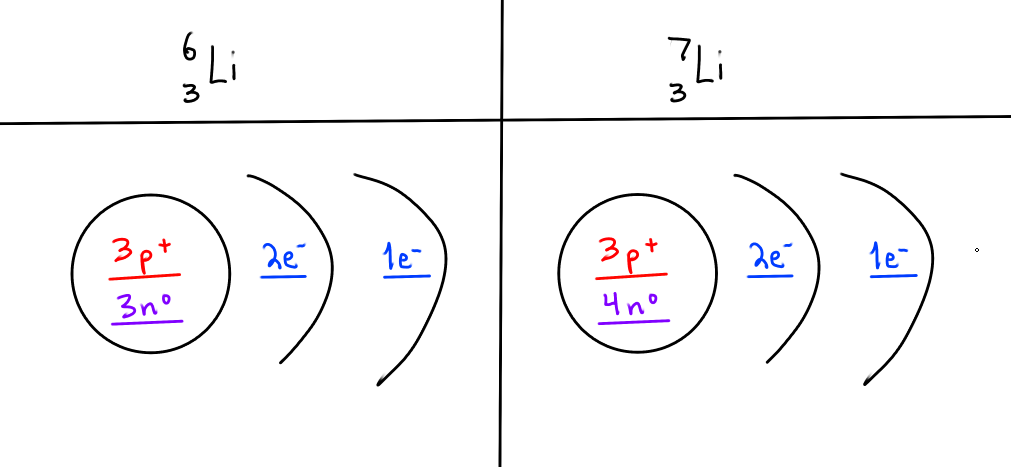
BONUS: drawing isotopes with Bohr diagrams
L-6 and L-7
fill in the blanks
Only neutron number changes
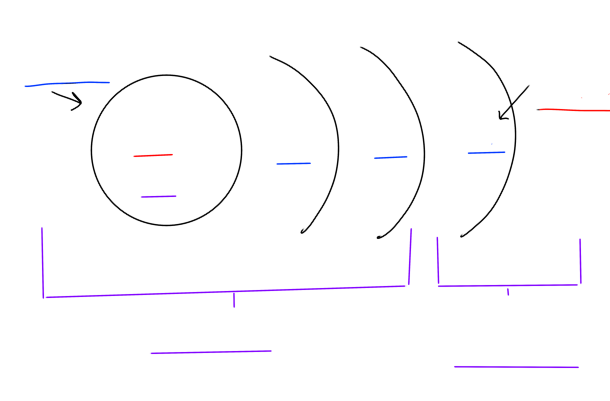
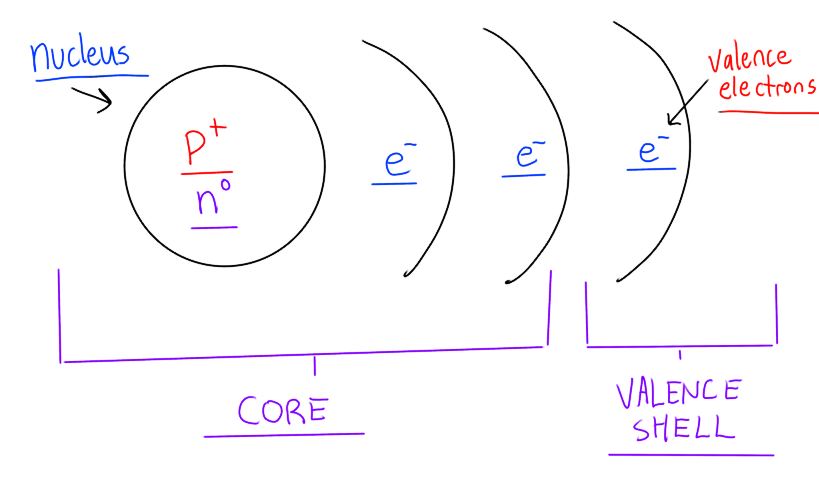
Fill in the blanks of the atomic structure
Atoms have a nucleus with protons and neutrons, shells with electrons
The core of the atom includes the nucleus and inner electrons
The last shell occupied by electrons is the valence shell
Electrons both spin on their own axis and orbit around the nucleus randomly and continuously
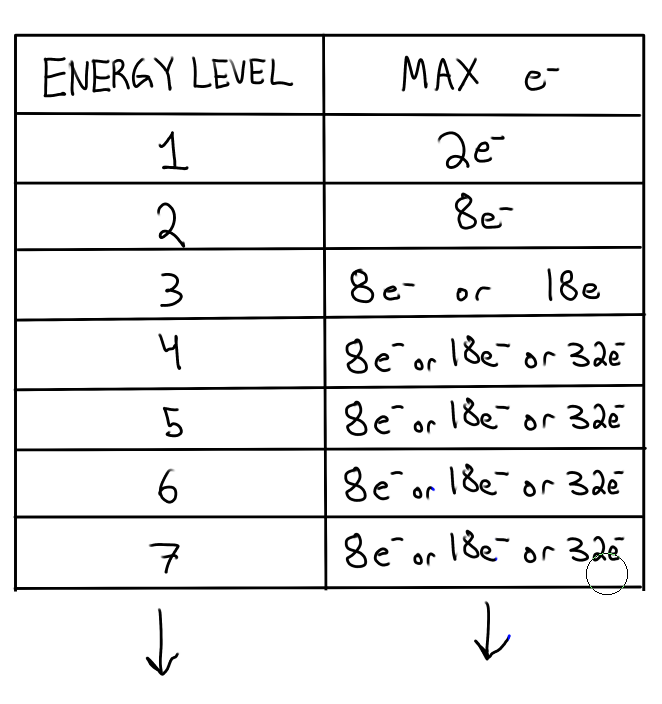
How much electrons can fit in each energy level? (not orbitals)
After element #20: Calcium, the number of max e- that can occupy the energy levels 3 or higher changes.
What do the period number and family number tell us?
Period Number
number of energy levels/shells
Family Number
number of valence electrons for main group elements/representative elements (A)
DOESN’T WORK ON TRANSITION METALS, LANTHANIDES AND ACTINIDES
How do you write electron arrangements?
(eg)
Aluminum-27
2 - 8 - 3
hyphens separate the energy levels
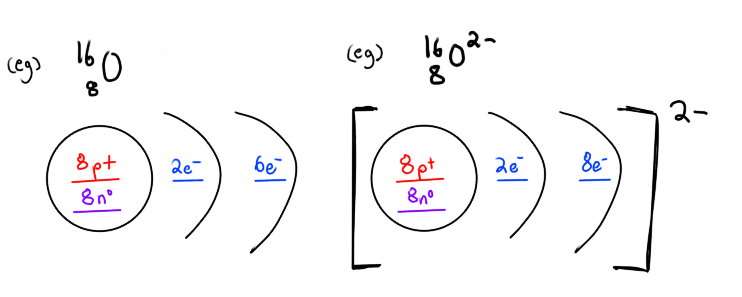
BONUS: Atomic structures of ions
need brackets and the charge on the top right
How do you calculate the average atomic mass?
depends on percent abundance of the isotopes of the element and their specific masses in amu
ALWAYS ROUND TO 2 DECIMAL PLACES

Avg Atomic Mass calculation example:
remember intermediate answer is 4 sig figs

How do you calculate the abundance of isotopes?
set the percents to be the unknown
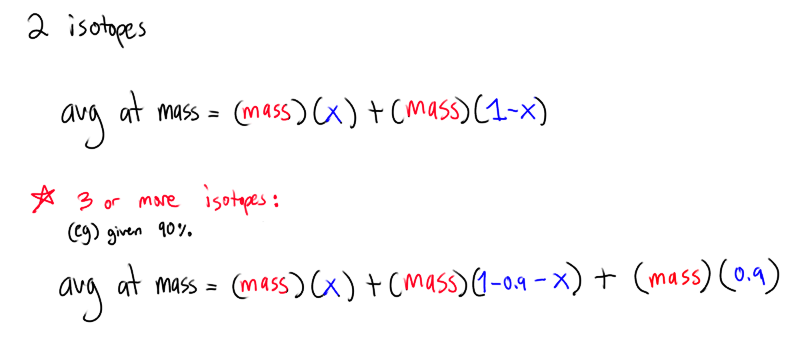
Percent abundance calculation example:

What is a hydrate?
a hydrate is an ionic compound with water molecules loosely bonded to its crystal lattice
Formula has an ionic salt and water
the water can be separated by heating the substance
the ionic salt that is left is called an anhydrous salt (without water)
How are hydrate formulas written?
salt ᐧ nH₂0
(eg)
Mg(NO₃)₂ ᐧ 3H₂0
How are hydrates named?
Start with the name of the ionic compound
add the molecular compound prefixes before hydrate based on number of water molecules
eg)
Mg(NO₃)₂
magnesium nitrate trihydrate
What is a dissociation equation for hydrates?
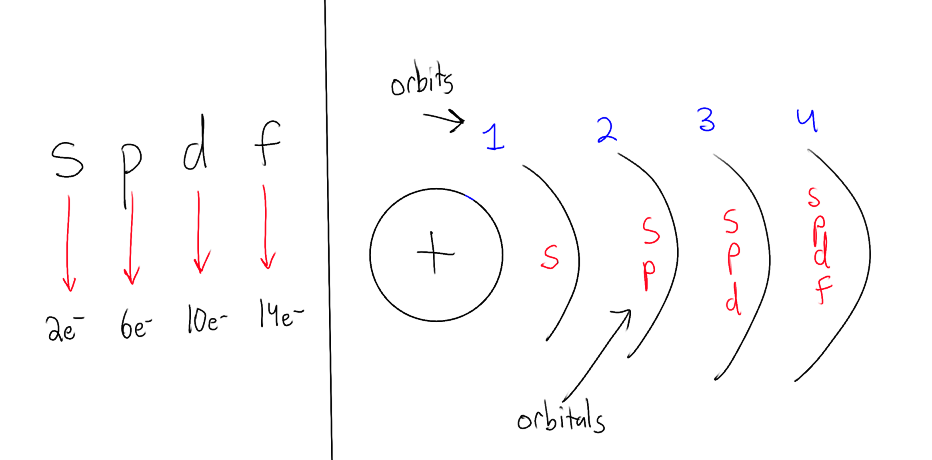
What are principal energy levels/quantum levels?
The orbits/shells around the nucleus
each energy level has a specific amount of quantized energy that increase as you go farther away from the nucleus
(eg) n = 1, 2, 3…
higher “n” value requires more energy
What are orbitals/subshells?
within the shells/orbits are subshells/orbitals that can hold 2, 6, 10 or 14 electrons.