chap 6 from pp - neuroplasticity
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chap 6 from pp - neuroplasticity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What is Malleability
often called neuroplasticity, is the brain's ability to change and adapt throughout life.
What does Malleability involve?
Forming new neural connections
strengthening or weakening existing ones
reorganizing networks in response to experiences, learning, injury, or environmental changes.
Malleability allows the brain to
Recover from damage, learn new skills, & adapt to new situations.
When is Malleability the most pronounced?
It’s most pronounced in early development but continues into adulthood
Synaptic Plasticity
The ability of the nervous system to change is called neuronal plasticity
Synaptic Plasticity is involved in
Strongly involved in embryological development
Also involved in all memory and learning processes.
Three types of synaptic plasticity:
Long-term synaptic plasticity
Short-term synaptic plasticity
Homeostatic plasticity
Learning
Is the process by which organisms modify their behavior to adapt to the changing conditions of the environment around them.
Long-term synaptic plasticity basis of
learning
memory
Homeostatic plasticity allows
neuronal circuits to maintain appropriate levels of excitability & connectivity
Malleability
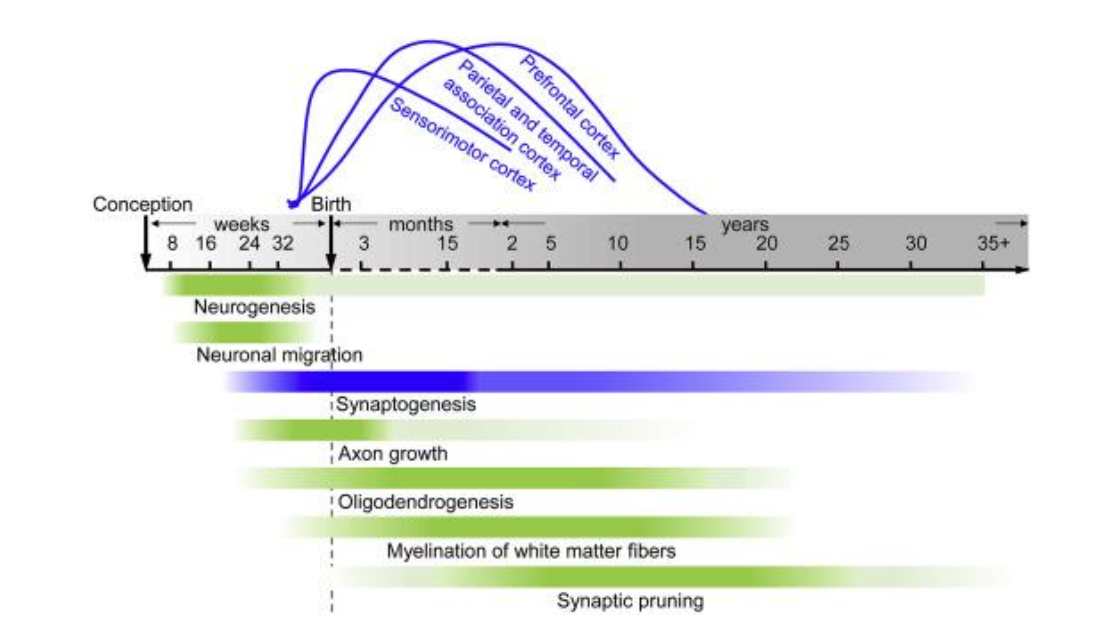
most critical period from week 32 - 5 years
Malleability in Adulthood
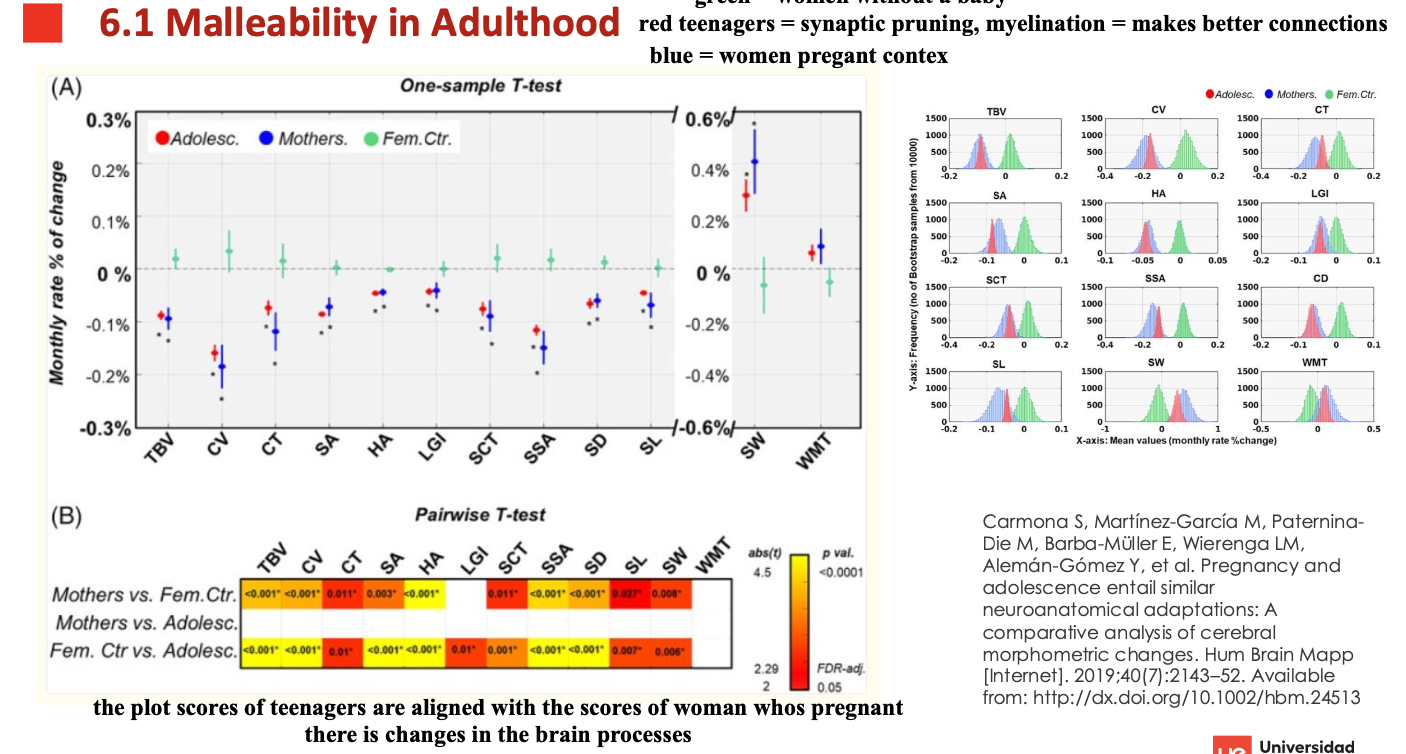
the plot illustrates that the pregnant women & a teenager goes throw the same brain plasticity
Illustration that the pregnant women brain plasticity
The illustration of the stimuli to creation of action potential
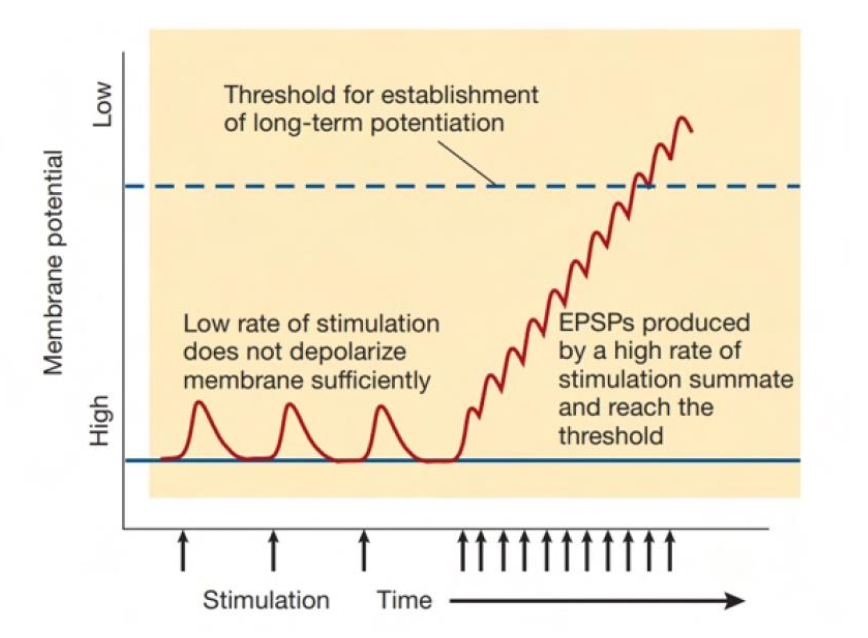
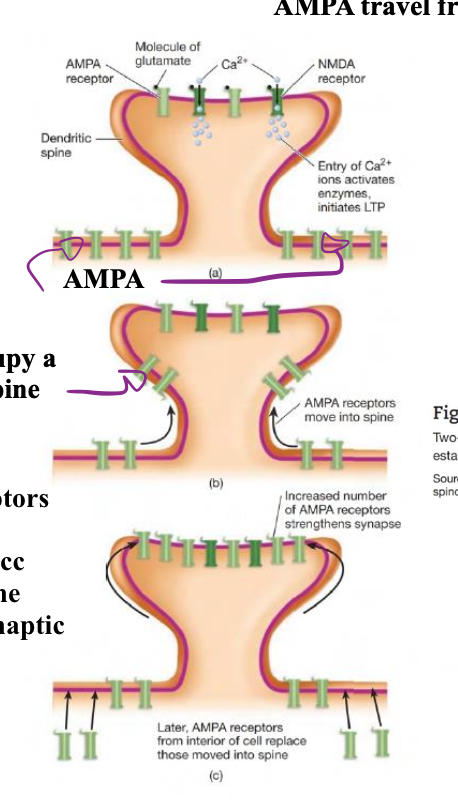
LTP (Long Term Potentiation) process:
Stimuli leads to an action potential if the threshold value becomes -55mV
This signal can lead to induction of long-term potentiation.
The excitatory glutamate contains two receptors: NMDA & AMPA
as action potential reaches the terminal button Glutamate is released.
When molecule of glutamate binds the NMDA receptor, the calcium channel cannot open because the magnesium ion blocks the channel.
The depolarization of the membrane evicts magnesium ions to leave the membrane, while calcium ions flows inside the membrane.
The calcium bind provokes and activates the receptor AMPA to move from the buttom along the spine to the top of the synapsis.
When AMPA finally enters its destination (top of post-synapsis) they improve and strengthen the connection & changes of synapsis.
CREB (transcription factor)
Transcription factor capable of binding DNA and regulating gene expression, dopaminergic neurons
Role of NMDA receptor
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor
glutamate receptor & predominantly Ca2+ ion channel
Role of AMPA receptors
Glutamate-gated ion channels
Synaptic changes.
Illustartion of AMPA
WHAT IS LEARNING
It is the process by which we acquire knowledge about the world.
WHAT IS MEMORY
It is the process by which knowledge is encoded, stored, consolidated, and subsequently retrieved.
Process of learning & memory
Encoding (Learning)
Consolidation (Memory)
Storage (Memory)
Retrieval (Memory)
TYPES OF LEARNING
IMPLICIT LEARNING (It is unconscious) AND EXPLICIT LEARNING (It is conscious)
ASSOCIATIVE AND NON ASSOCIATIVE LEARNING (i.e., conditionin, Change in our response i.e., habituation and sensitization).
MEANINGFUL LEARNING (It integrates and relates the new information with the one we already had).
COOPERATIVE LEARNING
COLLABORATIVE LEARNING
EMOTIONAL LEARNING
OBSERVATIONAL LEARNING
EXPERIENTIAL LEARNING
DISCOVERY LEARNING
MEMORISTIC LEARNING
RECEPTIVE LEARNING