E2 Lecture #1 - Skull
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
What do SSA fibers do?
special senses which relate the body to the external environment
Vision - CN II
Sound - CN VIII
Equilibrium - inner ear CN VIII
SVA fibers
senses associated with ingestion of food
smell and taste
smell - olfactory CN I
taste - CN VII, IX, X
SVE fibers
innervate skeletal muscle from the five pharyngeal arches
What do pharyngeal arches provide the foundations for?
The embryonic development of the head
CNs V, VII, IX, X
What cranial nerve innervates pharyngeal arch 1?
Trigeminal nerve (V)
mandible
What CN innervates pharyngeal arch 2?
Facial nerve (VII)
facial muscle
Stylopharyngeus AKA….
glossopharyngeal
third pharyngeal arch
What cranial nerve innervates pharyngeal arch 3?
Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
pharynx and larynx
What cranial nerve innervates pharyngeal arch 4?
Vagus nerve (X)
What cranial nerve innervates pharyngeal arch 6?
Vagus nerve (X)
Olfactory "Nerve" (CN I)
SVA fibers mediate smell from receptors in the olfactory mucosa of the nasal cavity
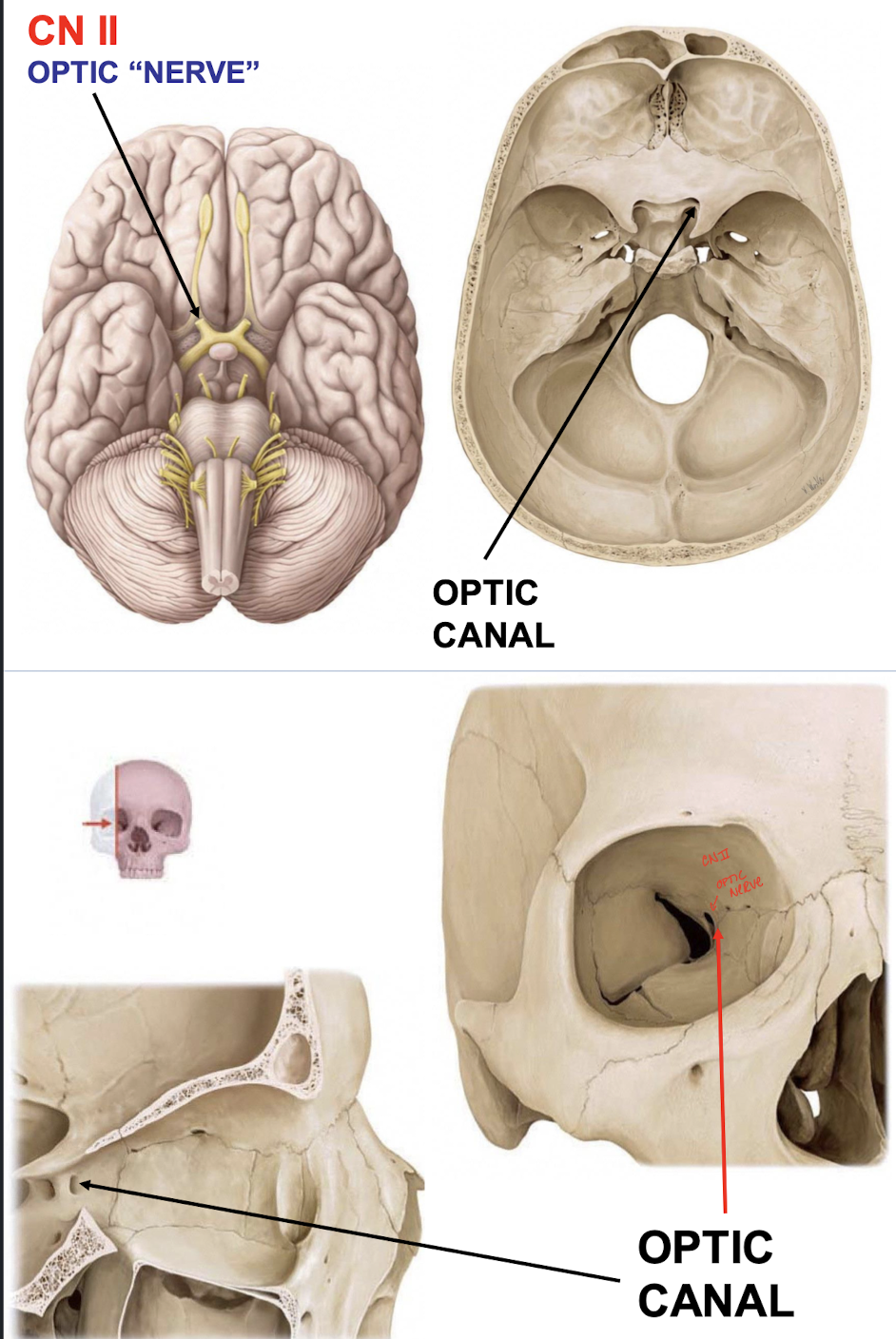
What kind of fibers are within the Optic "Nerve" (CN II)?
SSA fibers mediate vision from the ganglion cells of the retina
Oculomotor Nerve (CN III)
GSE fibers innervate most extraocular muscles in the orbit
GVE fibers to the ciliary ganglion
Trochlear Nerve (CN IV)
GSE fibers innervate the superior oblique muscle in the orbit
Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)
GSA fibers mediate general sensation from facial skin, oral and nasal mucosa, teeth, cornea, and conjunctiva, some meninges, the TMJ, and the anterior tongue
SVE fibers innervate 1st pharyngeal arch musculature (muscles of mastication)
Abducens Nerve (CN VI)
GSE fibers innervate the lateral rectus muscle in the orbit
Facial Nerve (CN VII)
SVE fibers innervate muscles derived from the 2nd pharyngeal arch (facial expression)
GVE fibers to the submandibular and pterygopalatine ganglia
Some afferents too
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (CN VIII)
SSA fibers convey inputs concering sound from the cochlea and equilibrium from the vestibular system
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX)
SVA and GSA fibers mediate sensation from posterior tongue, middle ear, and oropharynx
GVA fibers receive input from carotid visceral receptors
GVE fibers to the otic ganglion
SVE fibers innervate one 3rd arch muscle
Vagus Nerve (CN X)
SVE fibers innervate 4th and 6th arch muscles of larynx and pharynx
GVE fibers to larynx, pharynx, thorax, and abdomen
Some afferents too
Spinal Accessory Nerve (CN XI)
GSE fibers innervate trapezius and sternocleidomastoid
Hypoglossal Nerve (CN XII)
GSE fibers innervate all intrinsic and most extrinsic muscles of the tongue
What is the cranium divided into?
Neurocranium ("brain case") and viscerocranium (facial skeletal)
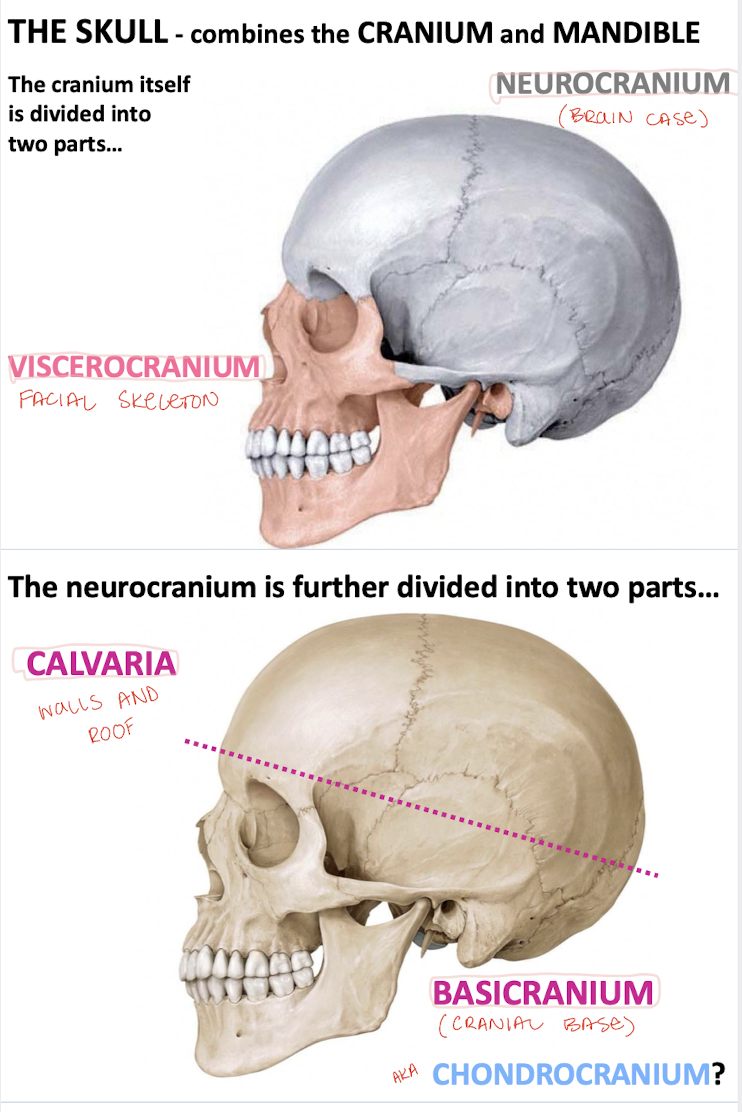
What is the neurocranium divided into?
Calvaria ("skull cap") and basicranium ("cranial base")
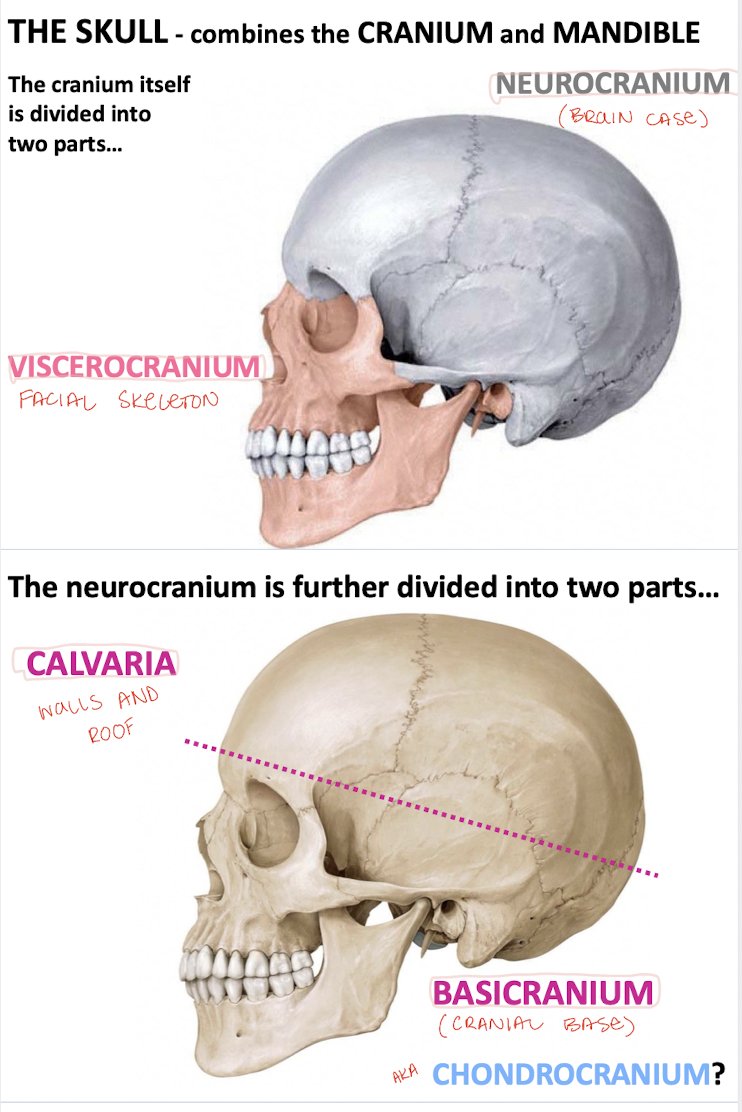
What do most of the bones of the cranial base form via?
Endochondral osteogenesis ossifying from cartilaginous precursors
What does the rest of the skull form via? (other than cartilaginous precursors)
Directly from mesenchyme via intramembranous osteogenesis
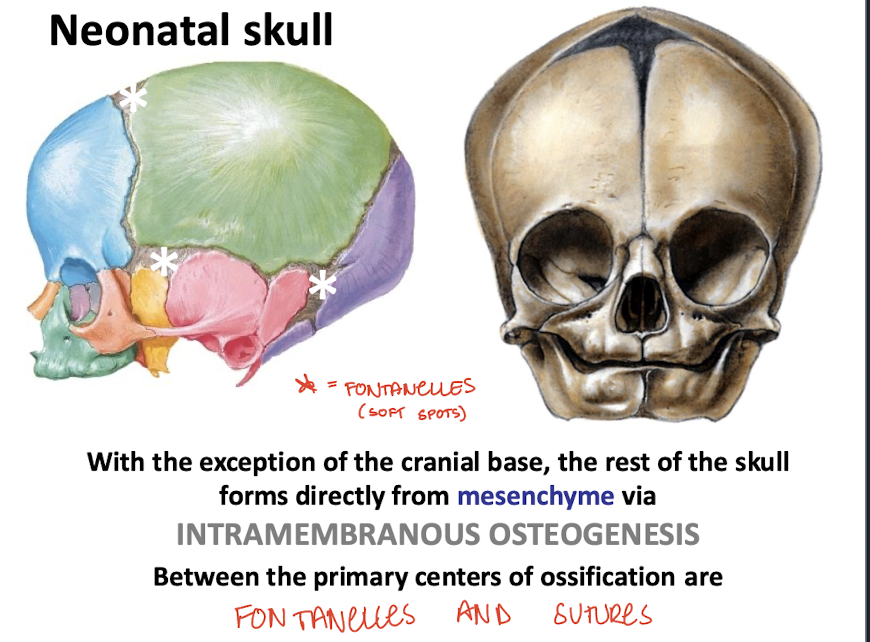
What are between the primary centers of ossification?
Fontanelles (soft spots) and sutures (emerging fibrous joints)
What kind of joints are the cranial sutures?
Fibrous joints or syndesmoses that are gradually obliterated as part of the normal process of skeletal maturation (fusing)
What is craniosynostosis?
Premature closure of the sutures that may lead to abnormal cranial morphology if untreated
-Increased intracranial pressure
-Seizures
-Developmental delay
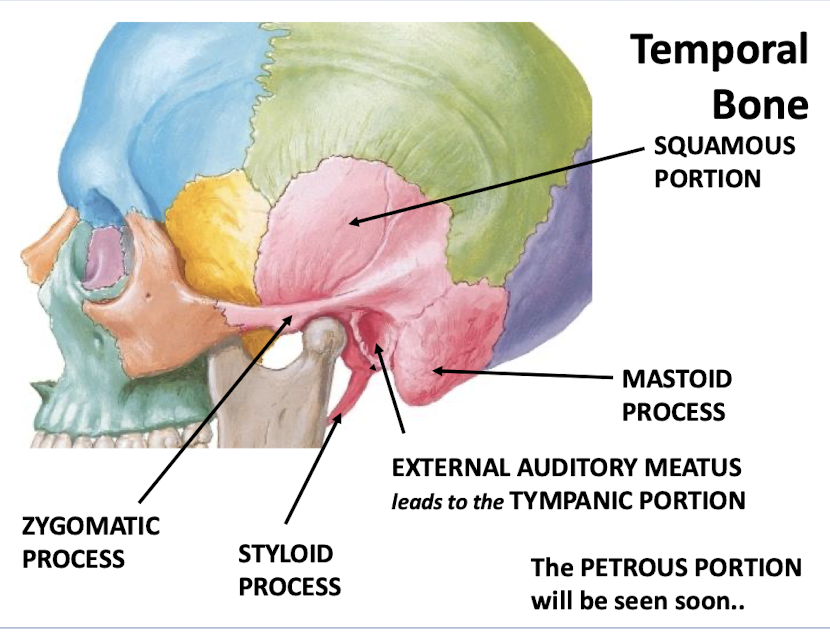
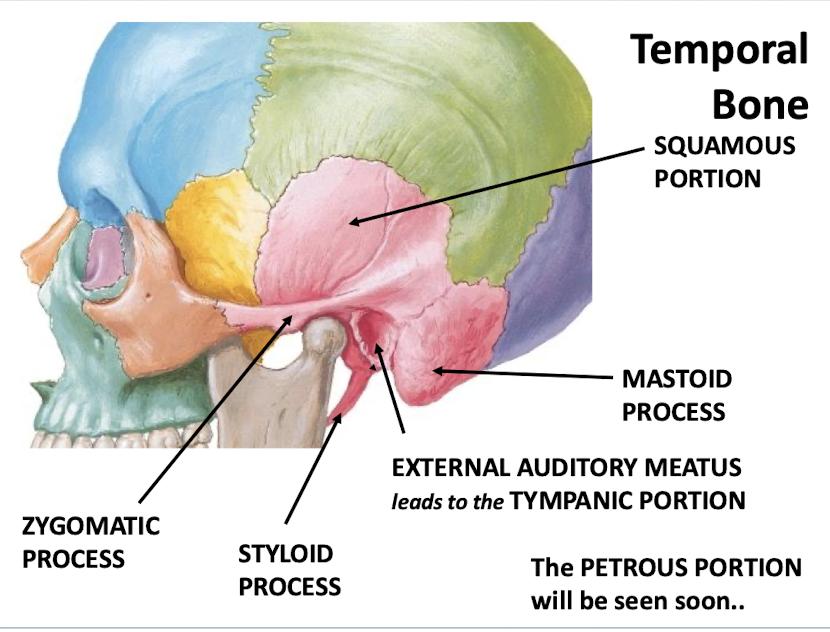
What are the major portions of the temporal bone?
-Mastoid process
-External auditory meatus leads to the tympanic portion
-Styloid process
-Zygomatic process
-Squamous portion
-Petrous portion
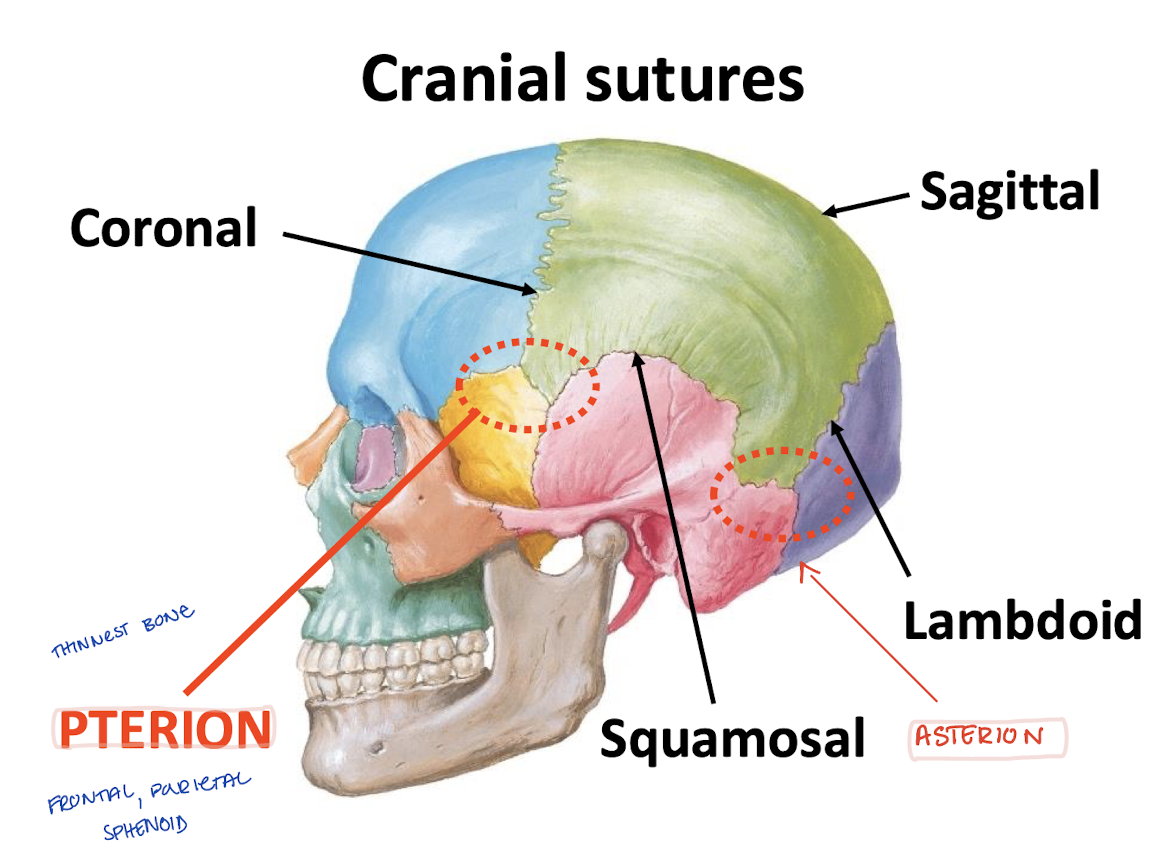
What are the cranial sutures?
-Coronal (frontal and parietal)
-Sagittal (parietals)
-Squamosal (squamous and parietal)
-Lambdoid (occipital and parietal)
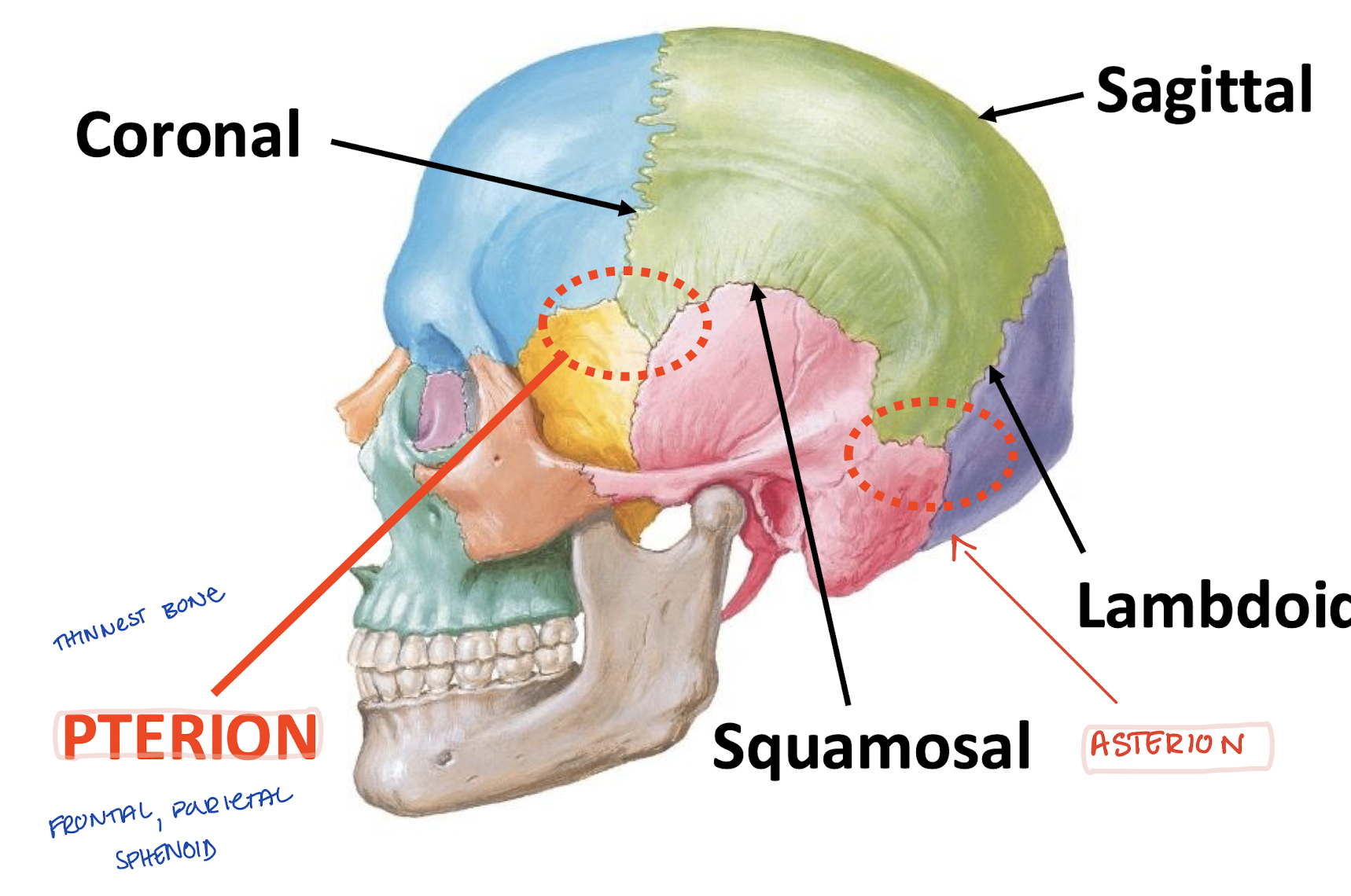
What is the asterion?
Where temporal, occipital, and parietal bones "unite"
What is the pterion?
Where frontal, parietal, temporal, and sphenoid "unite"
Region of thinnest cranial bone
What is the dura mater adhered to?
Firmly adhered to the inner table of cranial bone (deep surface)
Where do middle meningeal vessels lie?
deep grooves in the inner table of cranial bone
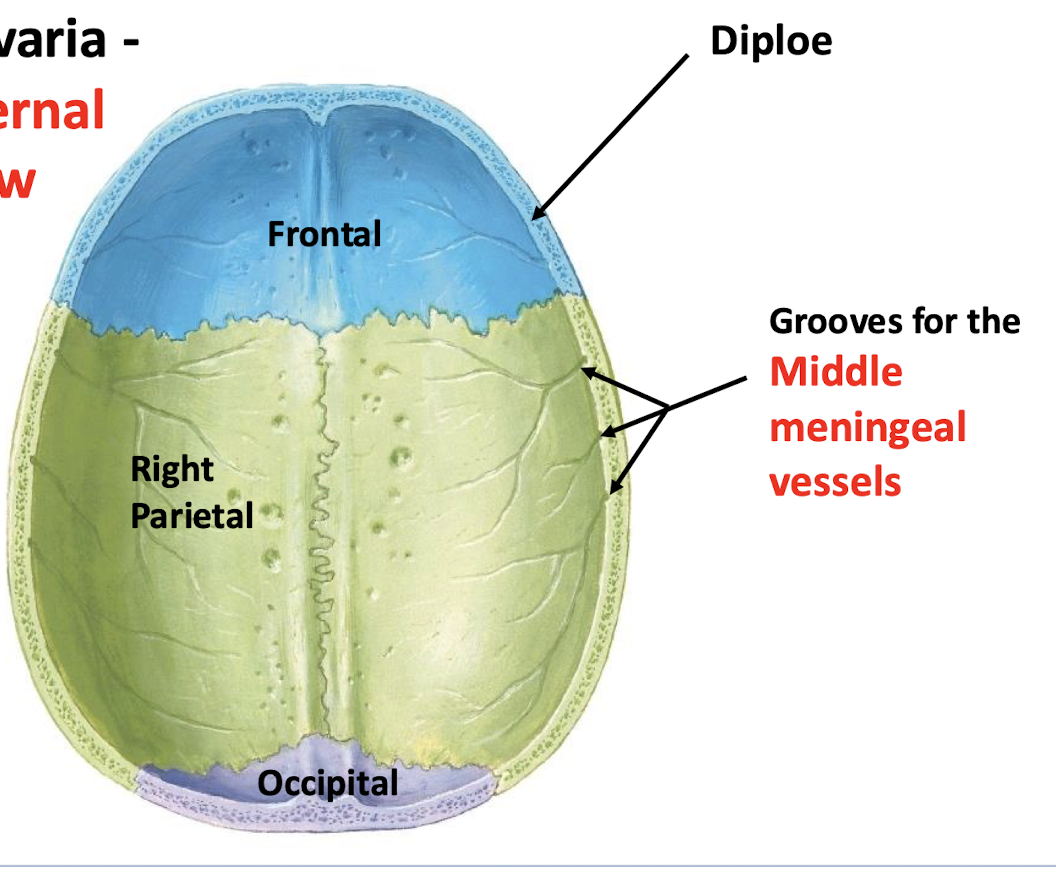
Where does the middle meningeal artery ramify?
at the pterion (thinnest bone at the temple)
What can a fracture of the pterion lead to?
Tearing of the middle meningeal artery → epidural hemorrhage → epidural hematoma
what is the spongy bone of the skull called?
diploe
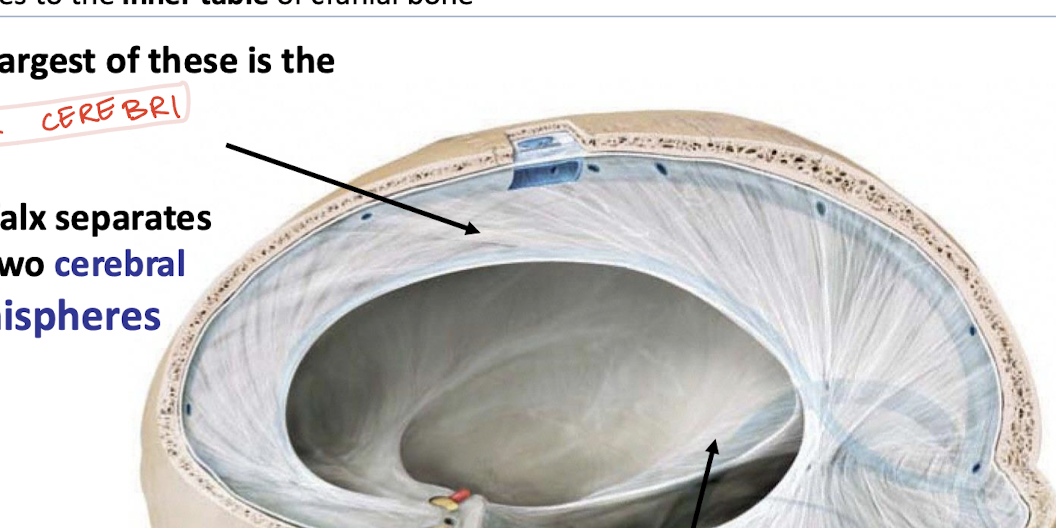
Dura mater septa function
limit brain movement
limit both rotary and translational forces from displacing cerebral and cerebellar hemispheres
What is the falx cerebri and what does it seperate?
The largest septa that separates the two cerebral hemispheres
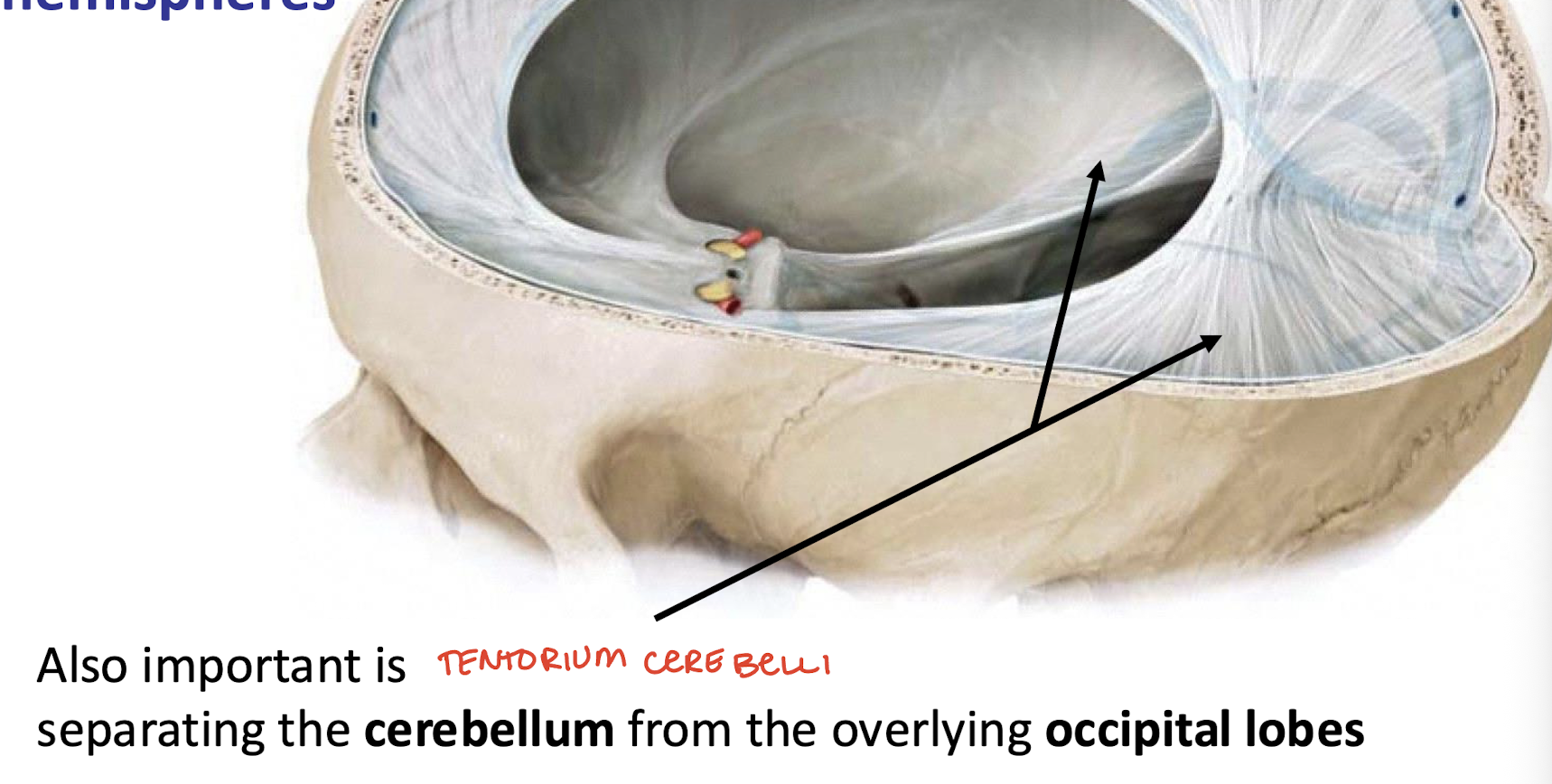
What does the tentorium cerebelli separate?
The cerebellum from occipital lobes below it
What is located the spaces between the periosteal and meningeal layers?
dural venous sinuses
What do dural venous sinuses drain? What structures do they anastomose with?
direct venous blood from the brain to the SVC
superficial veins of the diploe, scalp, and face
Name the structure that lies in the in this area
the superior sagittal sinus
The dural venous sinuses draining the head all drain and meet where?
Posteriorly towards the occipital region (confluence of sinuses)
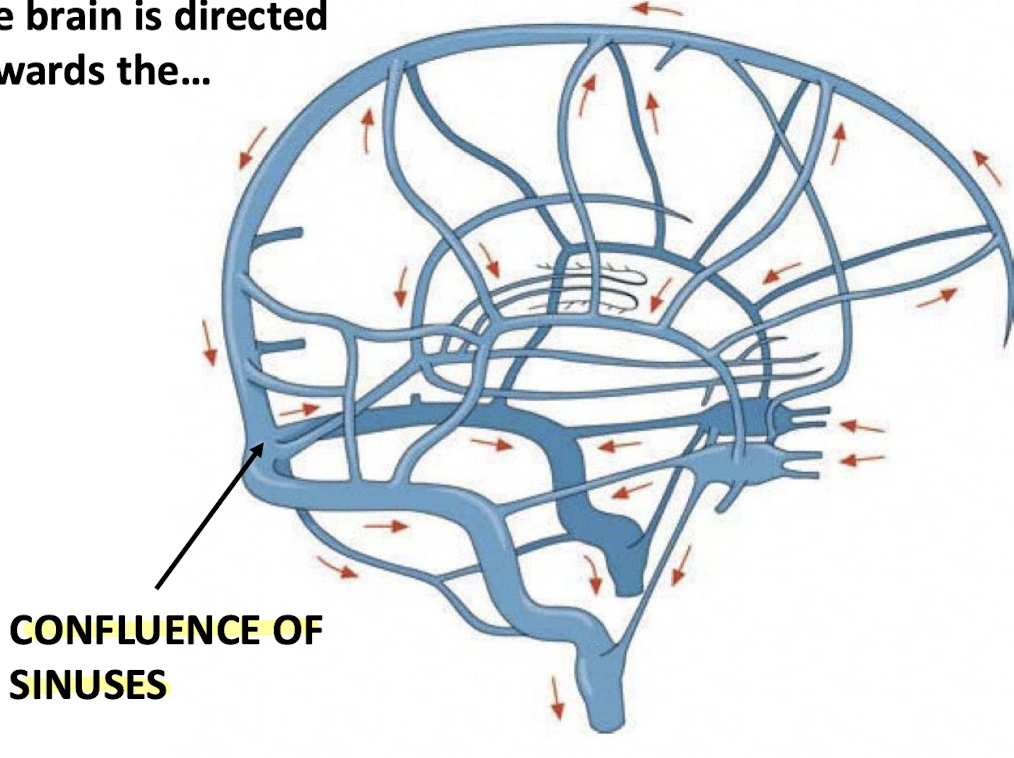
Where does the confluence of sinuses drain blood?
To either the internal jugular veins or the vertebral venous plexus
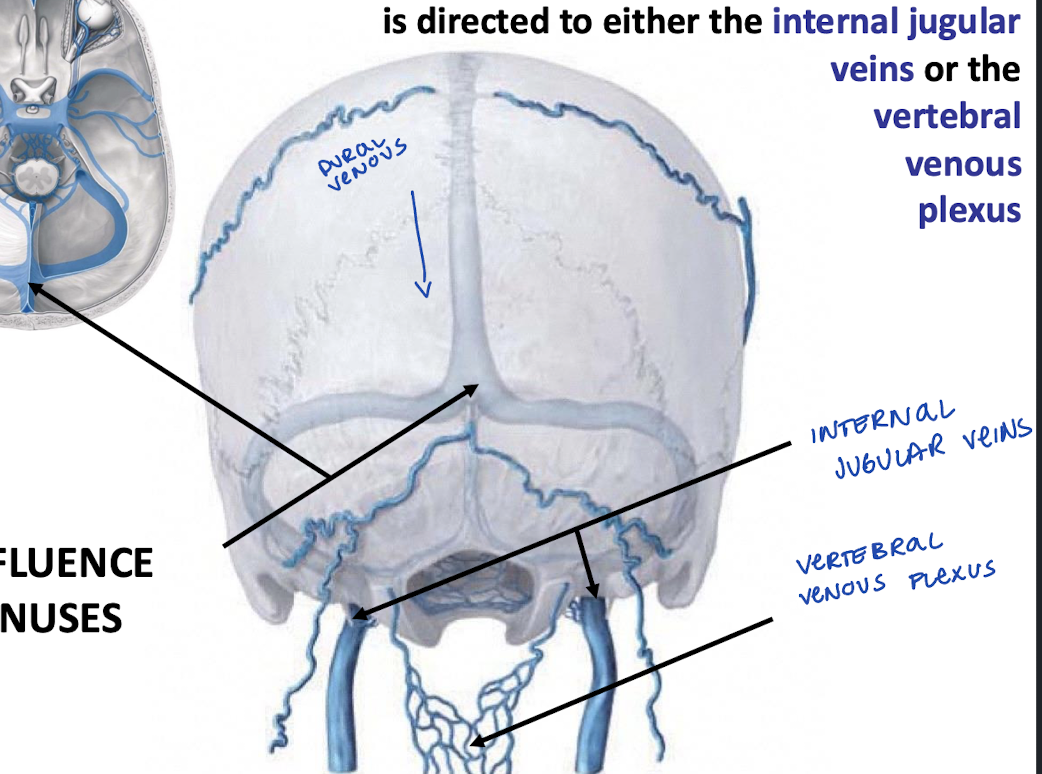
What are anastomoses between the basilar and vertebral venous plexus part of? (AKA, they make up the_____)
The cerebrospinal venous system (CSVS)
Clinical relevance of the vertebral venous plexus?
route for the spread of infection, emboli, and metastases
What are bridging veins?
They pierce both the arachnoid mater and the inner dura in order to drain into the dural venous sinuses
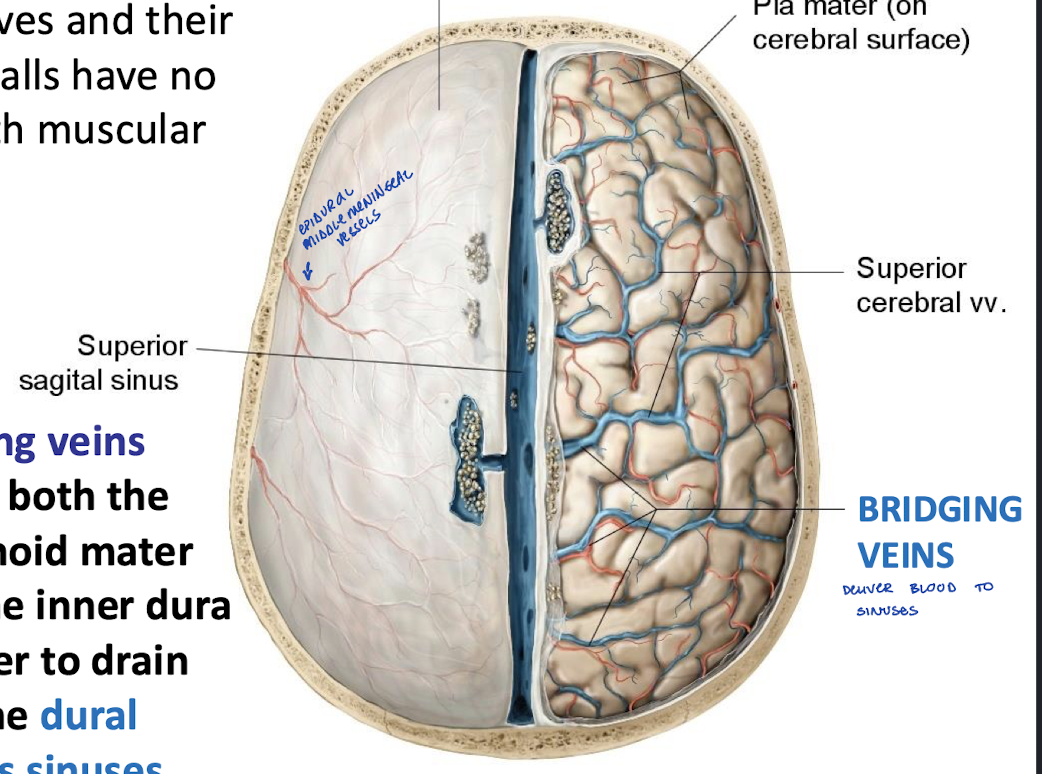
Tearing of a bridging vein as it enters a dural venous sinus produces what?
A subdural hematoma
More prone to this as you get older
What can a subdural hemorrhage cause?
An increase in intracranial pressure which can cause compression of and damage to delicate brain tissue
Clinical relevance of acute subdural hematomas? Prognosis? Emergent?
It has a high mortality rate and is a severe medical emergency
Less severe bleeds may be managed successfully
What can increased cranial pressure due to intracranial bleeds (epidural or subdural) produce?
Ischemia, crushing, and swelling of brain tissue
May cause portions of the brain to herniate against or through openings in the dura or even foramen magnum and cause symptoms distant from the site of the injury
The telencephalon gives rise to?
What does the telencephalon form into later during development?
the olfactory bulb
sulci and gyri of the brain
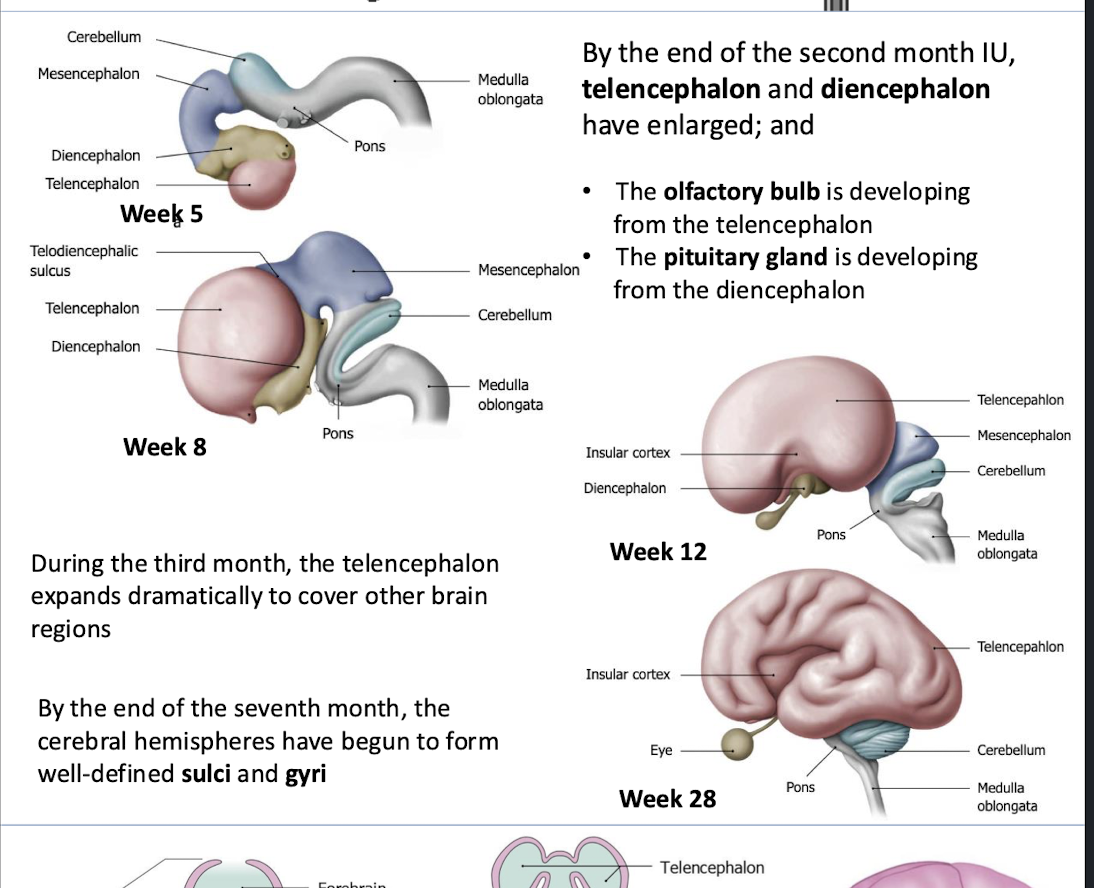
The diencephalon gives rise to?
pituitary gland
What is CSF secreted by?
Choroid plexus within the ventricular system of the brain
Where does the CSF circulate?
From the ventricles to the central canal of the spinal cord and the subarachnoid space as far caudally as the lumbar cistern
Where does CSF get reabsorbed?
Into the network of venous dural sinuses in the cranial cavity along with the metabolic waste discharged by the CNS
How is most of the CSF returned to the venous system?
By way of the arachnoid villi (granulations) that protrude from the subarachnoid space into the superior sagittal sinus
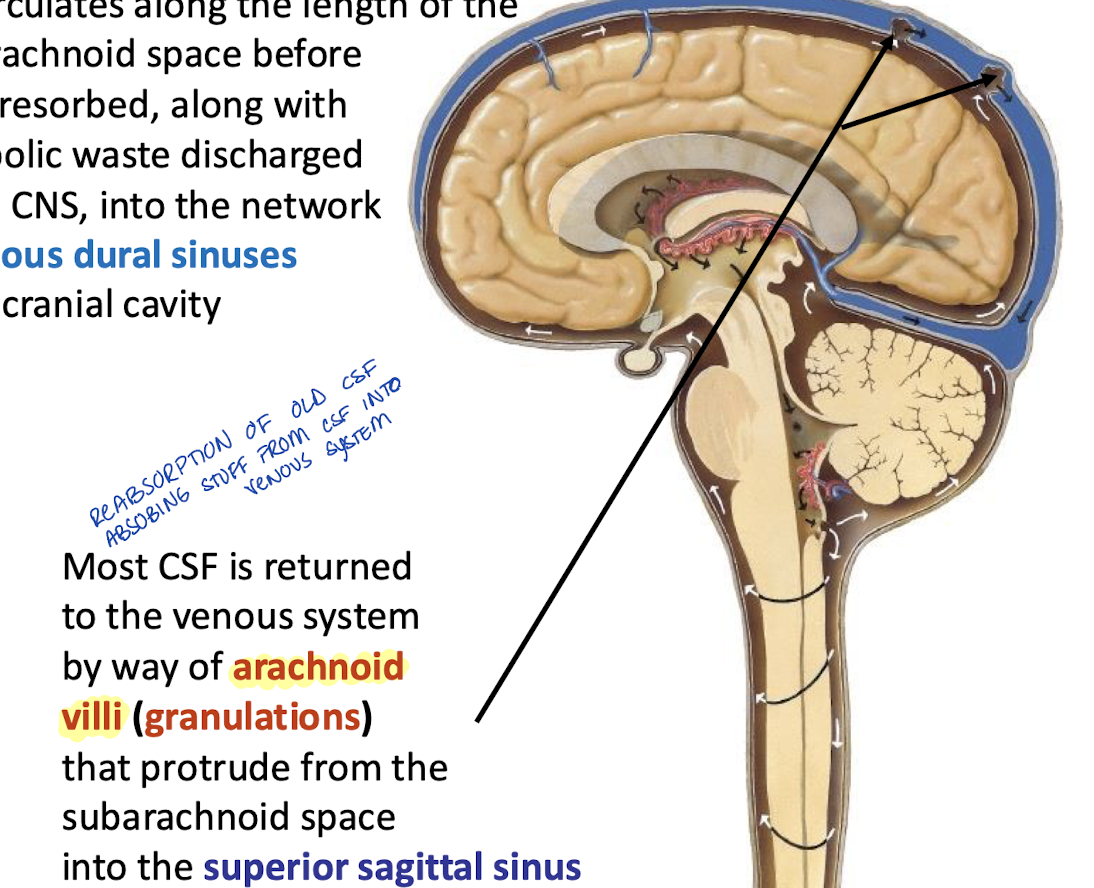
Where do arachnoid granulations (villi) reside?
In the arachnoid foveae impressed into the inner table of cranial bone within and adjacent to the superior sagittal sinus
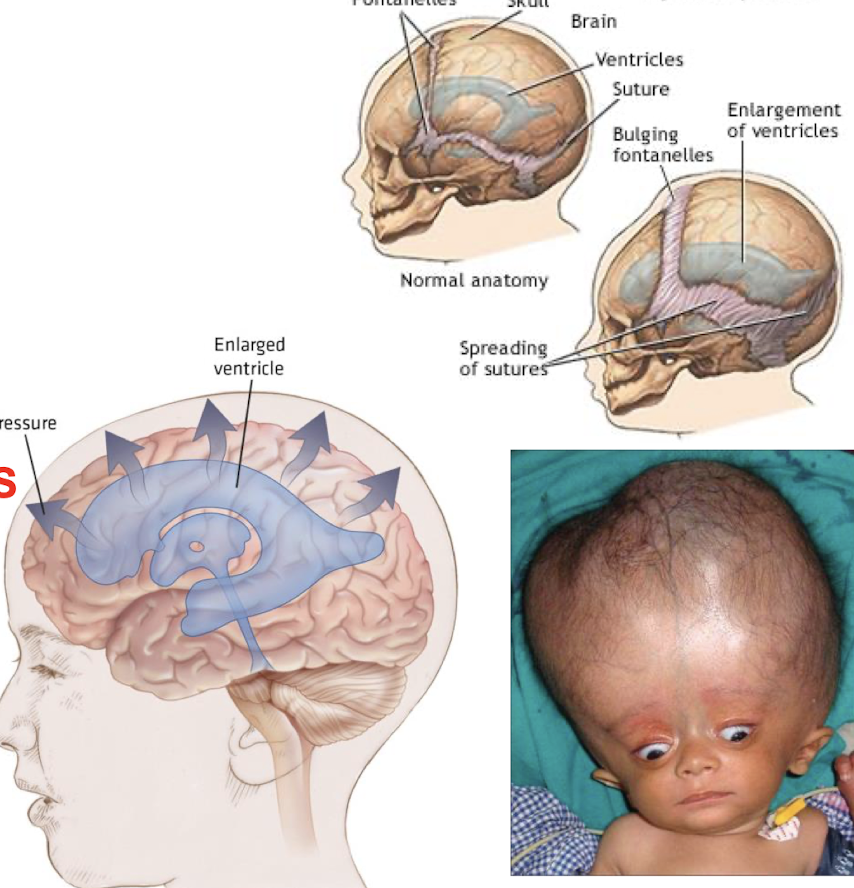
What is hydrocephalus caused by?
Obstruction of CSF circulation
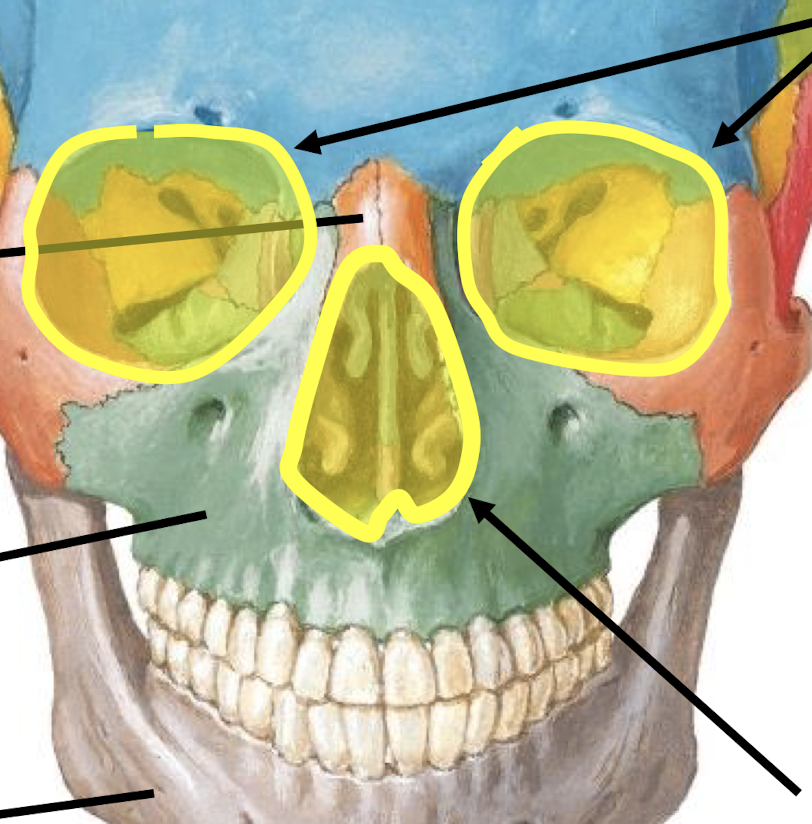
What are the openings in yellow called?
Orbits
Anterior nasal (piriform) aperture
What forms the roof of the orbital cavity?
Frontal bone
What forms the floor of the orbital cavity?
Maxilla bone
What forms the lateral wall of the orbital cavity?
Zygomatic bone
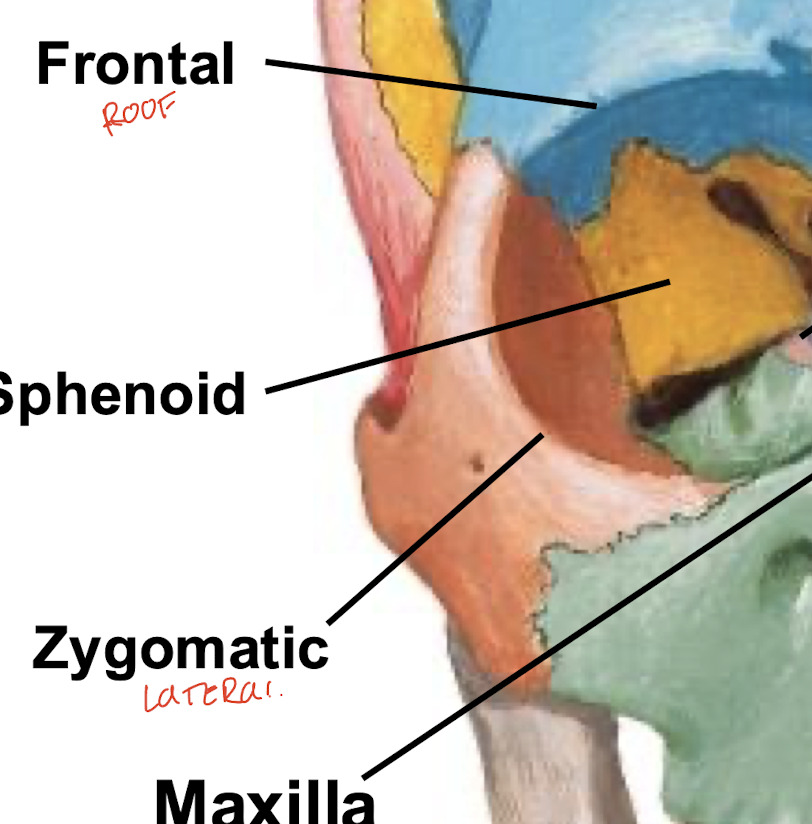
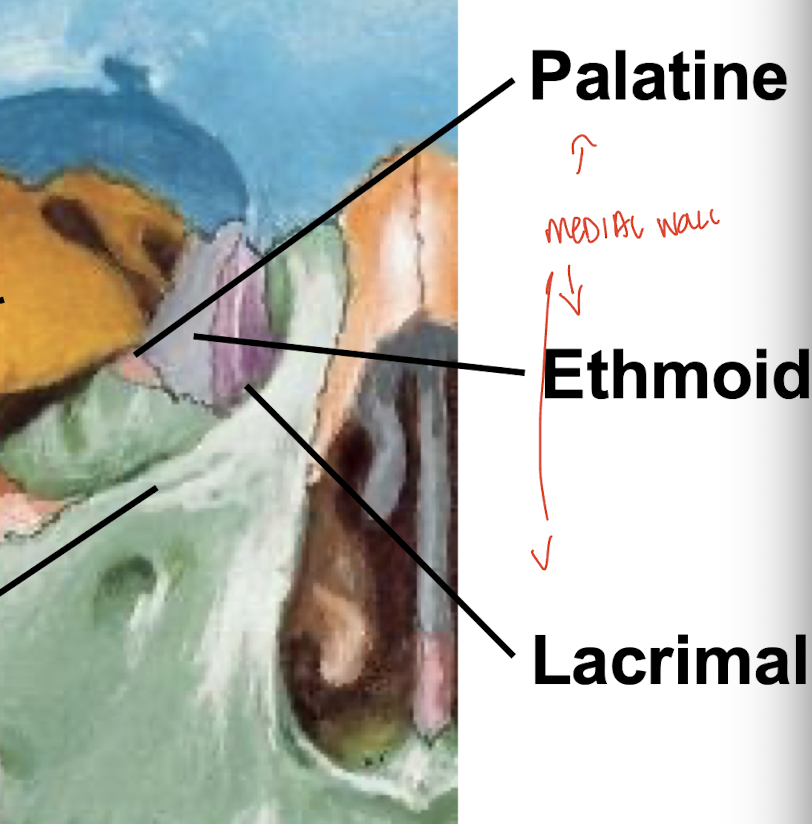
What forms the medial wall of the orbital cavity?
Lacrimal bone, ethmoid bone, and palatine bone
What are the inferior nasal conchae attached to?
The lateral walls of the nasal cavity
What is the importance of conchae (turbinates)?
They maximize surface area for the nasal mucosa lining the cavity
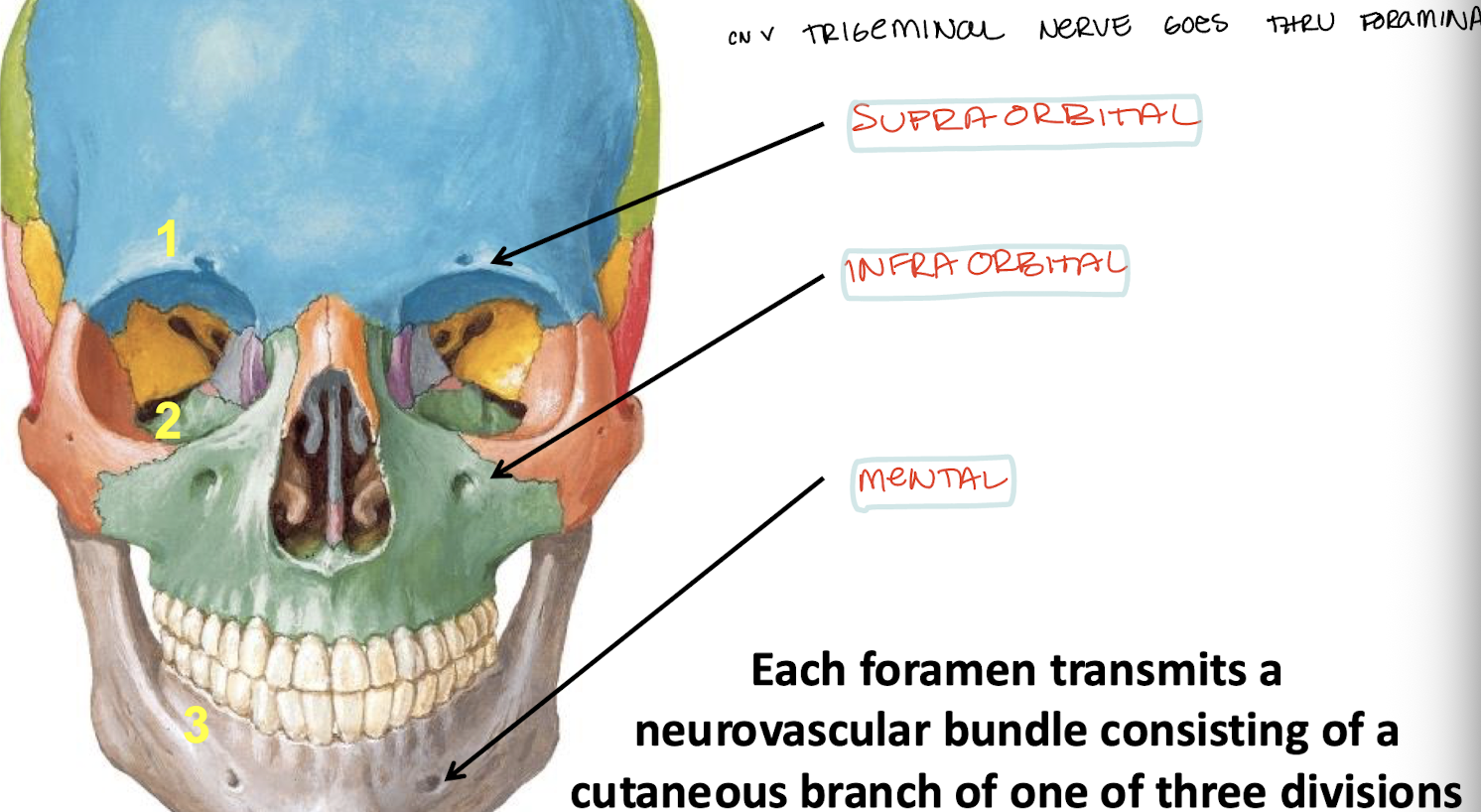
What are the 3 pairs of foramina in the anterior facial skeleton?
Supraorbital, infraorbital, and mental
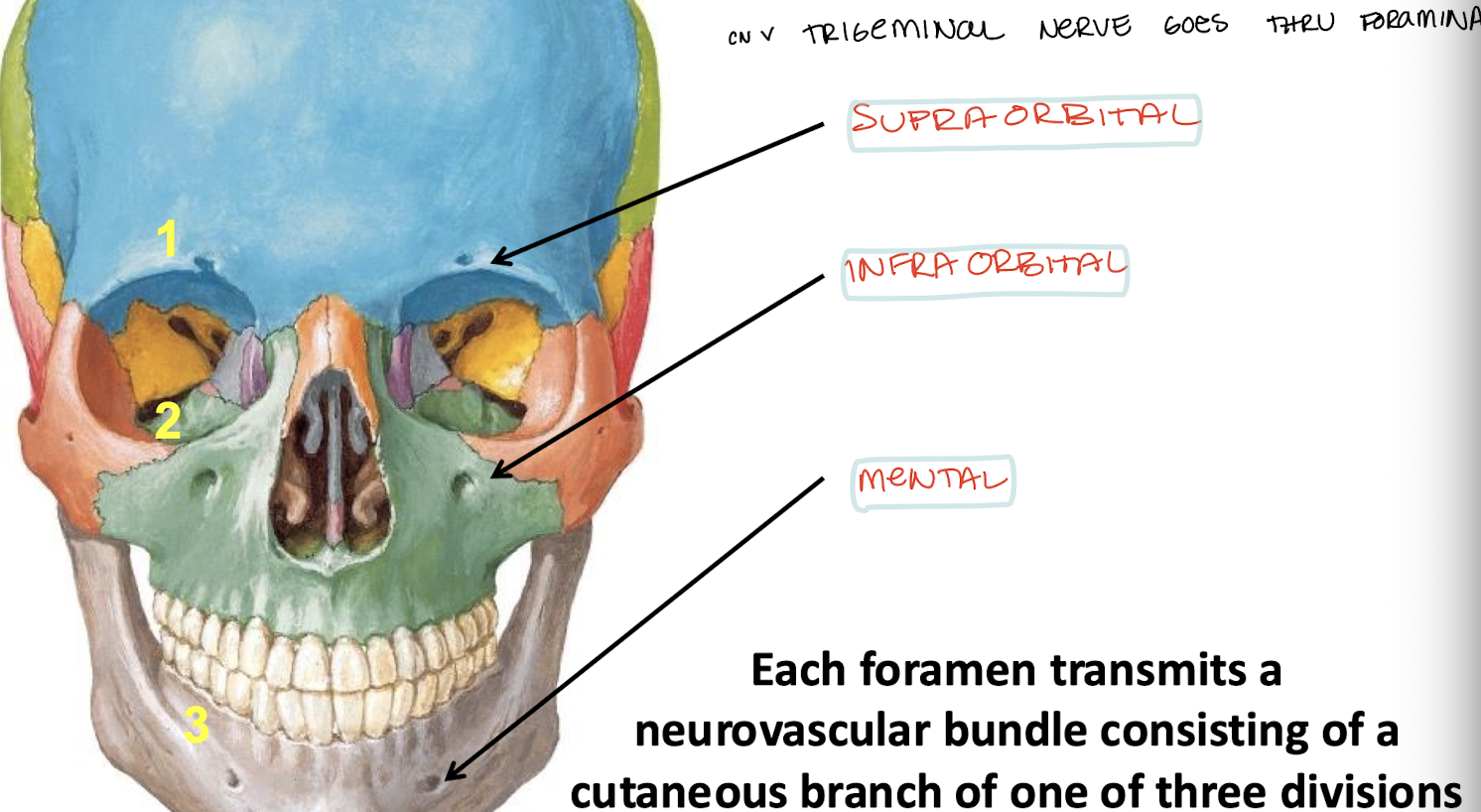
What does each foramen transmit on the anterior facial skeleton?
CN V vessels
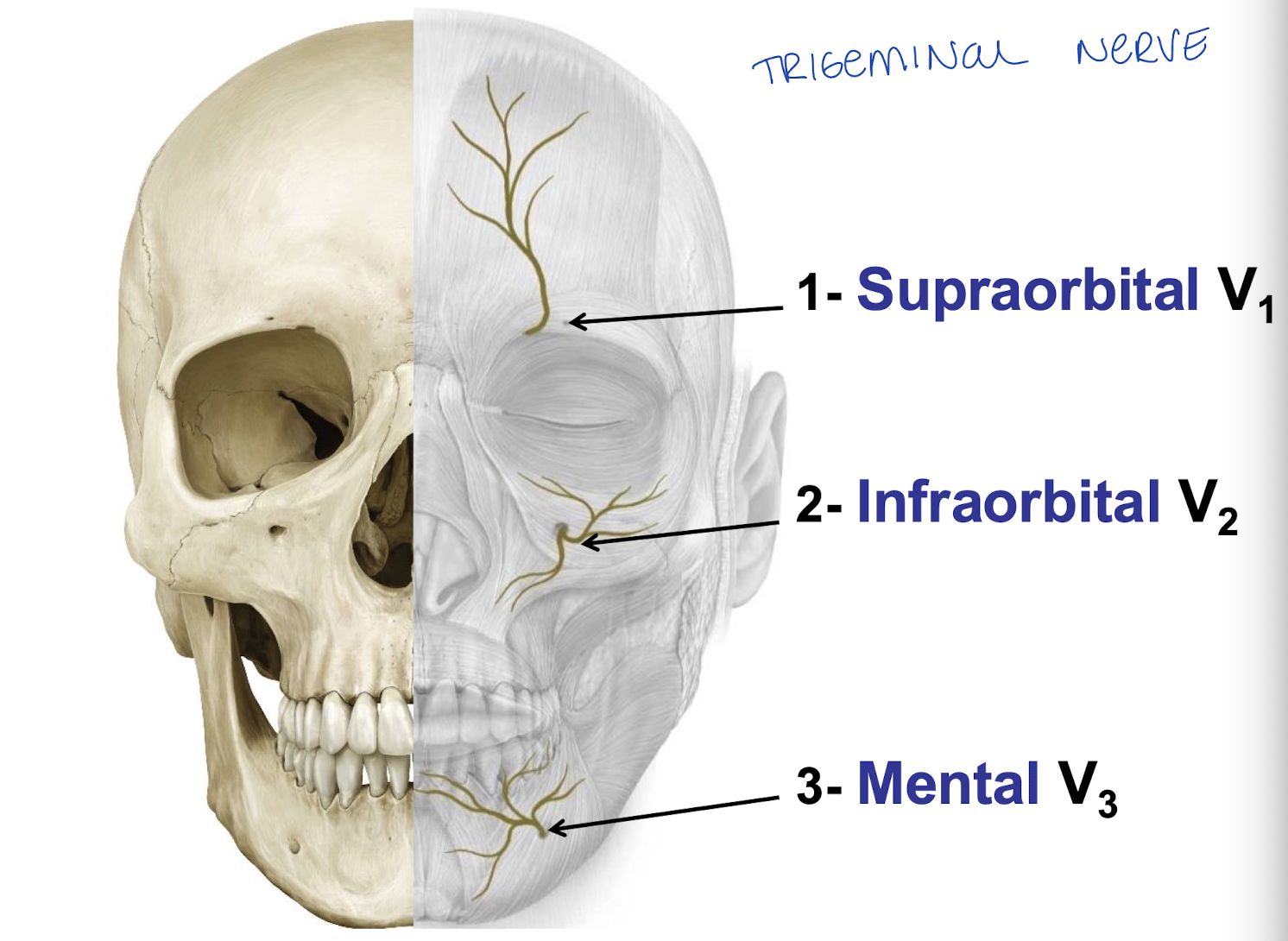
Branches of supraorbital, infraorbital, and mental CN V names.
supraorbital - V1
infraorbital - V2
Mental - V3
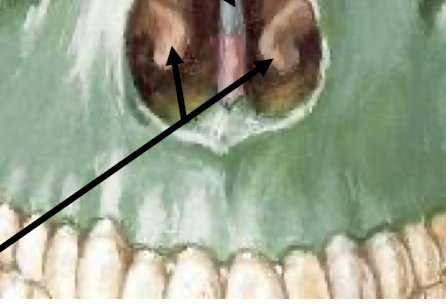
What are these?
inferior nasal conchae
What are the paranasal sinuses?
frontal
sphenoid
ethmoid
maxillary
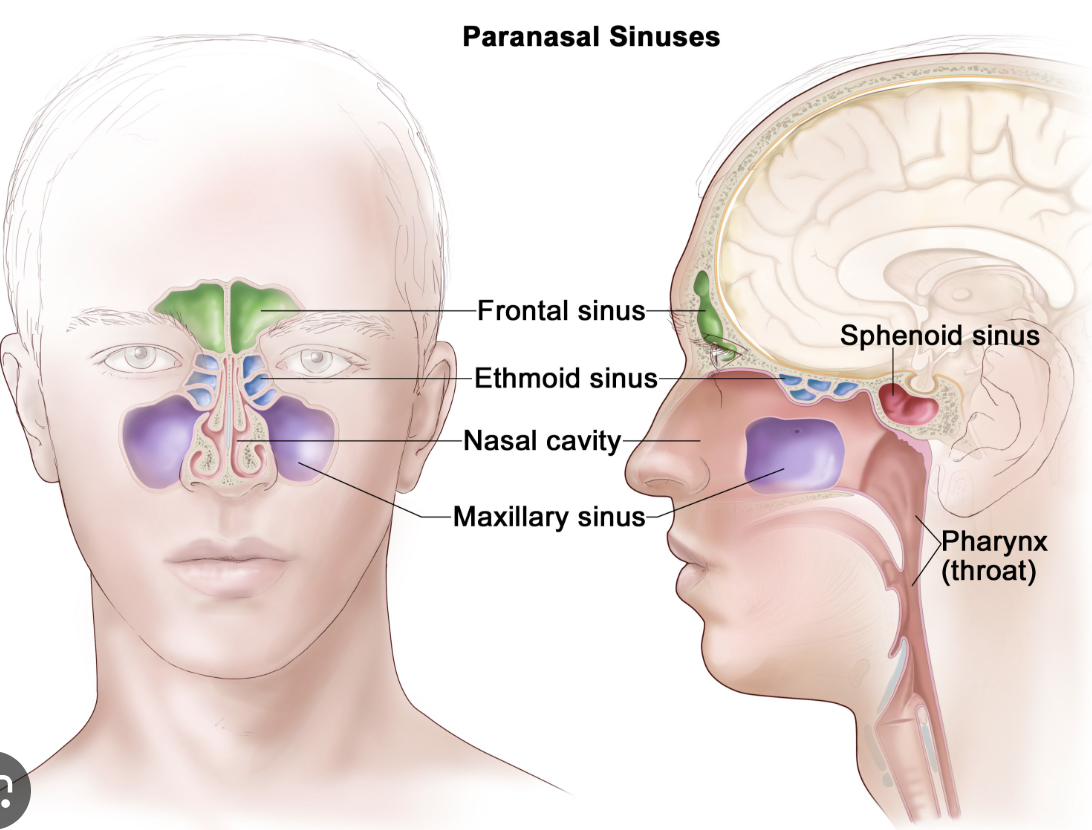
Infection and irritation of paranasal sinuses presents as a headache often. why?
the sinuses are closely located ear orbital, oral, and cranial cavities.
What is trigeminal neuralgia?
Pain frequently triggered by moving the mandible, smiling or yawning, or by cutaneous or mucosal stimulation
Symptoms include lancinating, paroxysmal pain, intermittent, unilateral, disabling
What is trigeminal neuralgia caused by?
Demylenation or compression of the sensory root endocranially (by the superior cerebellar artery)
Post-herpetic neuralgia, tongue piercing, ideopathic
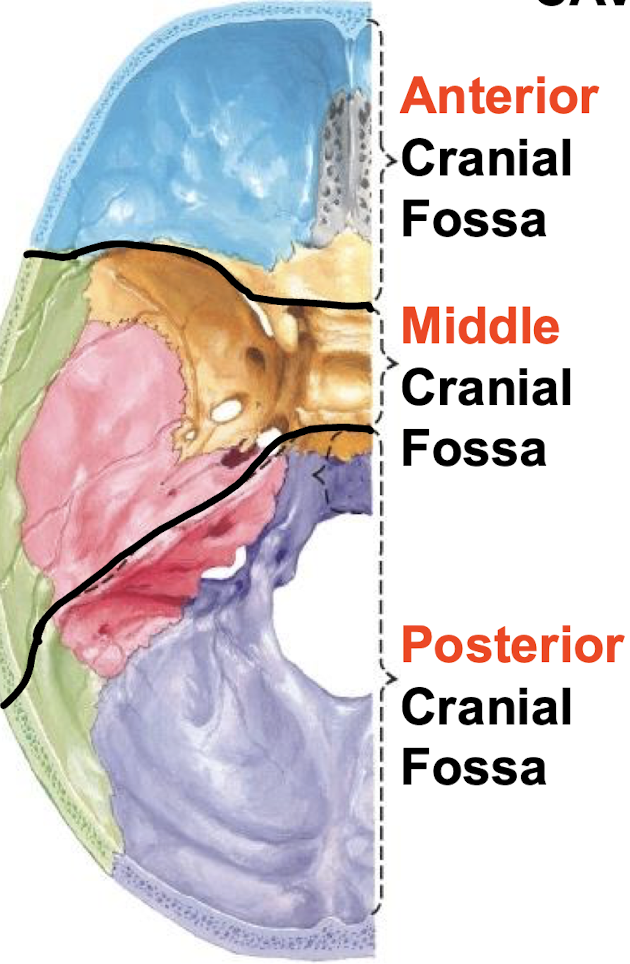
Name the floors of the cranial cavity
What is the treatment for trigeminal neuralgia?
Analgesics, anticonvulsants, surgical decompression, rhizotomy, gamma knife ablation
What are other CN V lesions?
Herpes zoster infx, neoplasm, dental/facial trauma, leprosy (hansen's disease)
What are some of the reasons suspected as to why we have sinsues?
-'Crumple zone'
-Lighten the head
-Warm and humidify inspired air
-Vocal resonance
What can infection and irritation of the paranasal sinuses (sinusitis) produce? Why?
Characteristic patterns of pain which may be confused with headache
because of how close to the brain they are….
Both the roof of the oral cavity and the floor of the nasal cavity are called?
The hard palate
What is the mandibular fossa?
The socket of the TMJ
What is the basilar suture?
A spheno-occipital synchondrosis
Cartilaginous joints that closes around 18yrs
What does the petrous temporal house?
The organs of hearing and balance
Dense, hard compact bone
What lies within the petrous temporal?
organs of hearing and balance
The cochlea and the vestibular apparatus
What rests at the anterior cranial fossa?
Frontal lobes and olfactory bulbs
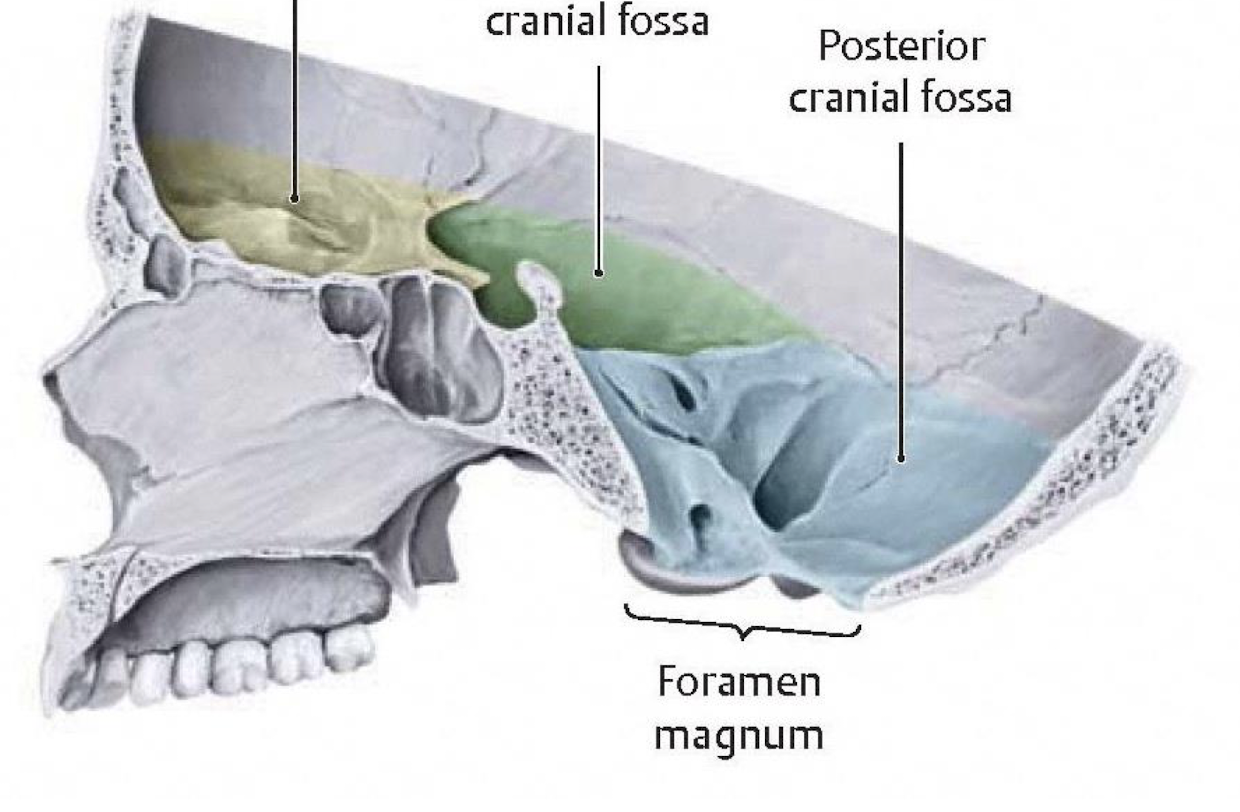
What rests at the middle cranial fossa?
Temporal lobes and pituitary gland
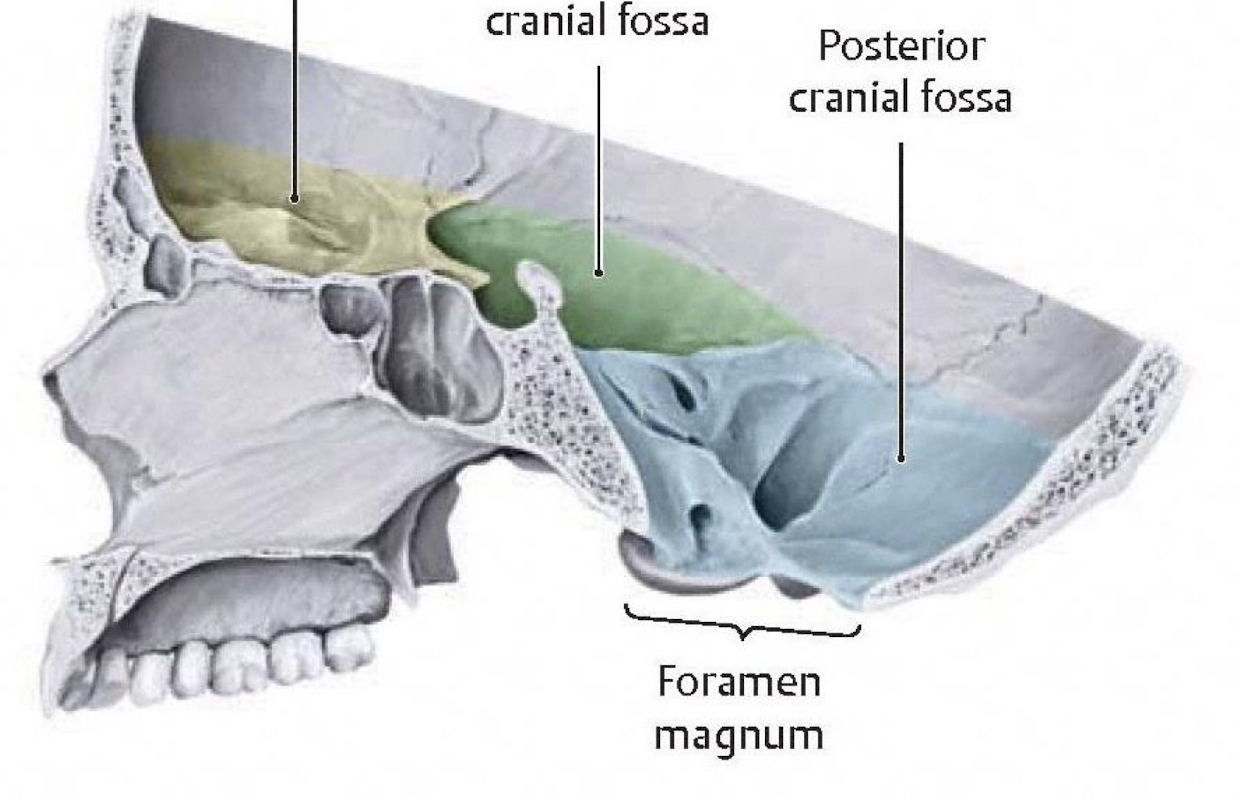
What rests at the posterior cranial fossa?
Cerebellum and brain stem
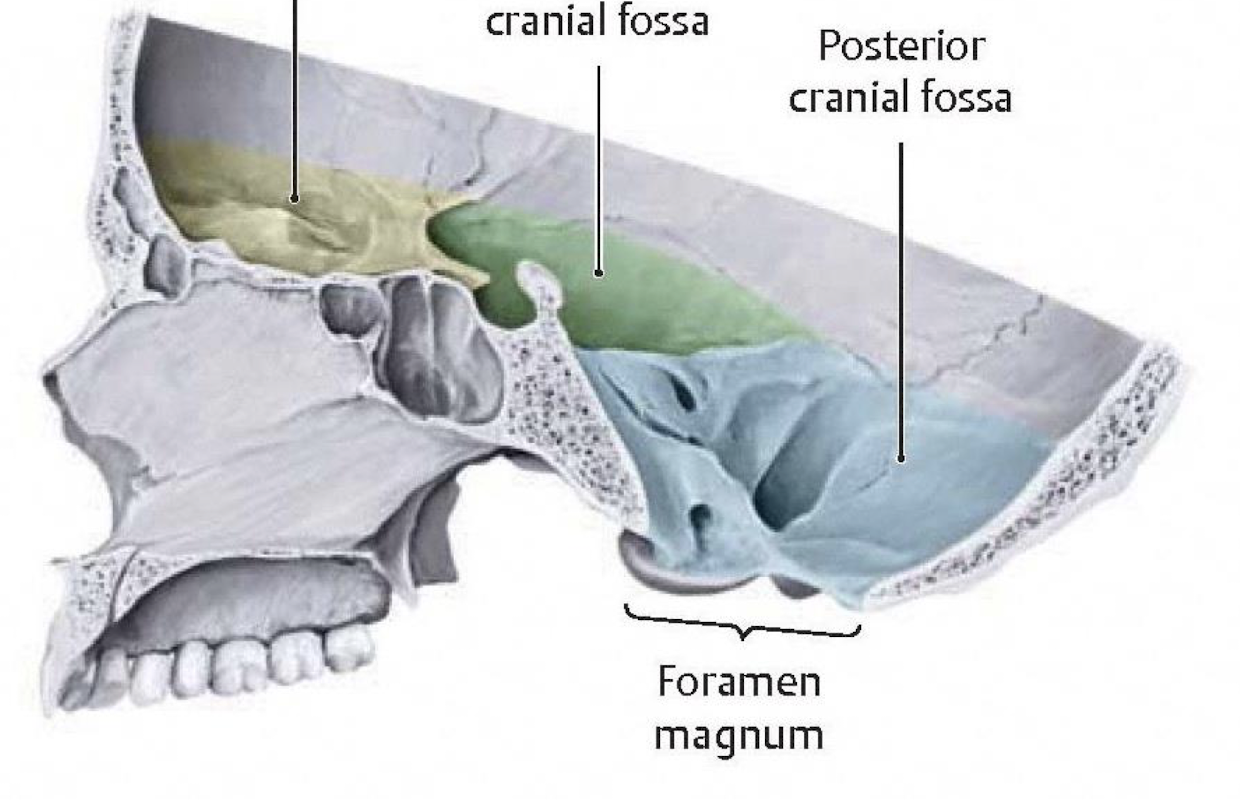
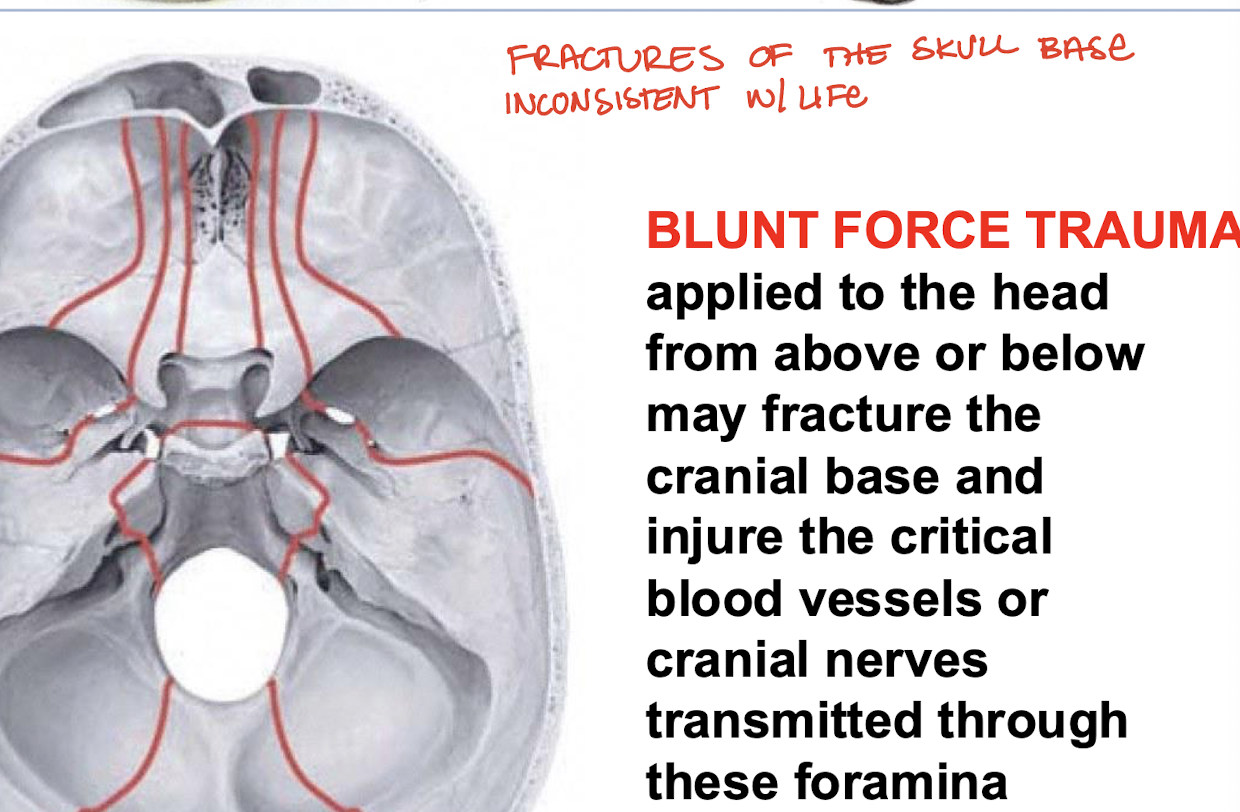
What would blunt force trauma applied to the head from above or below fracture?
The cranial base and injure the critical vessels or cranial nerves transmitted through the foramina
What bones form the anterior cranial fossa?
Frontal, ethmoid, and sphenoid bones
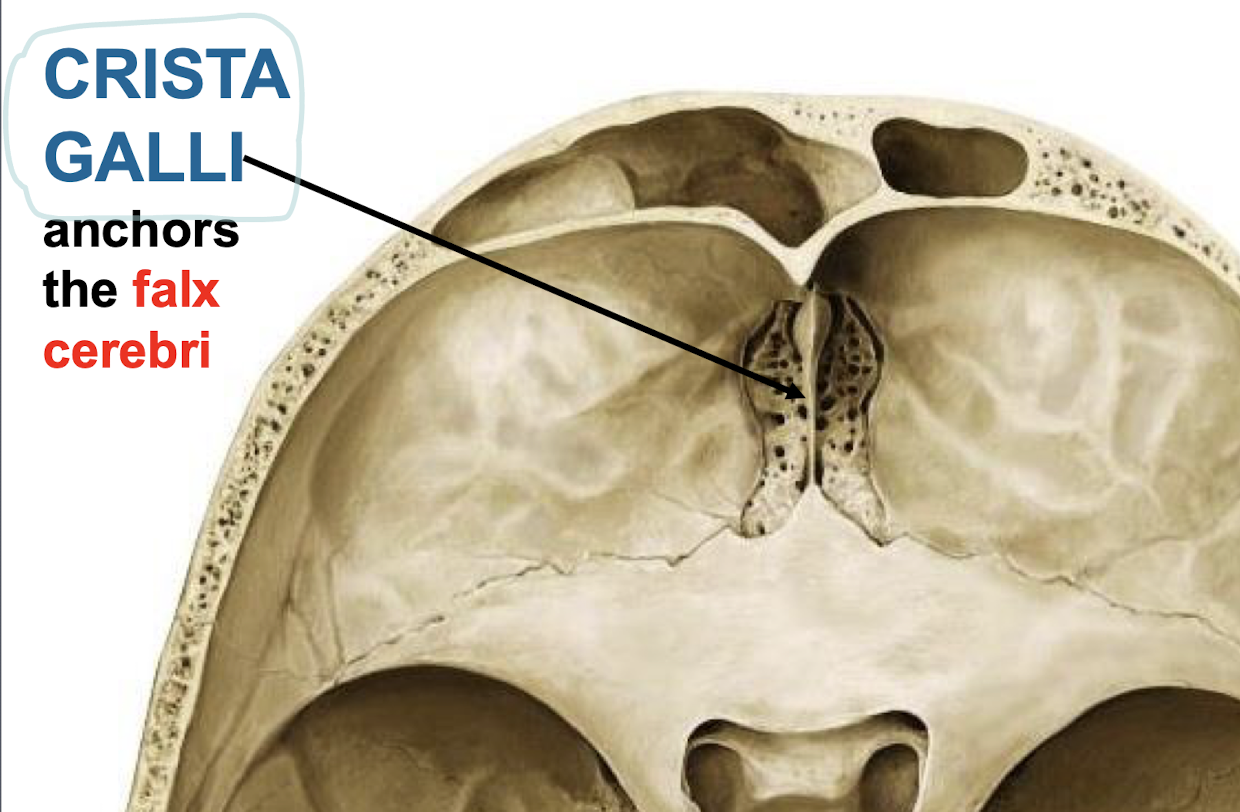
What anchors the falx cerebri?
Crista galli, an element of ethmoid
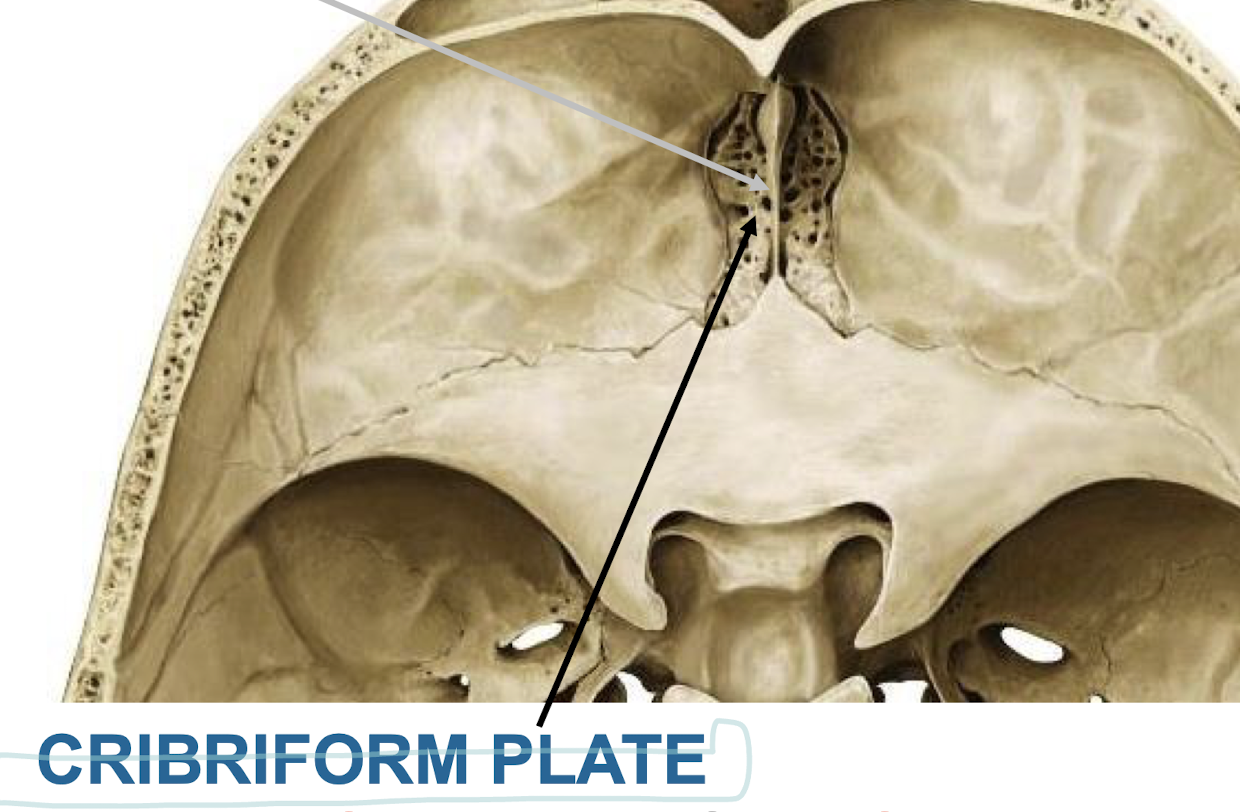
What does the cribriform plate transmit?
Olfactory nerves from olfactory mucosa of the nasal cavity to the olfactory bulbs (CN I)
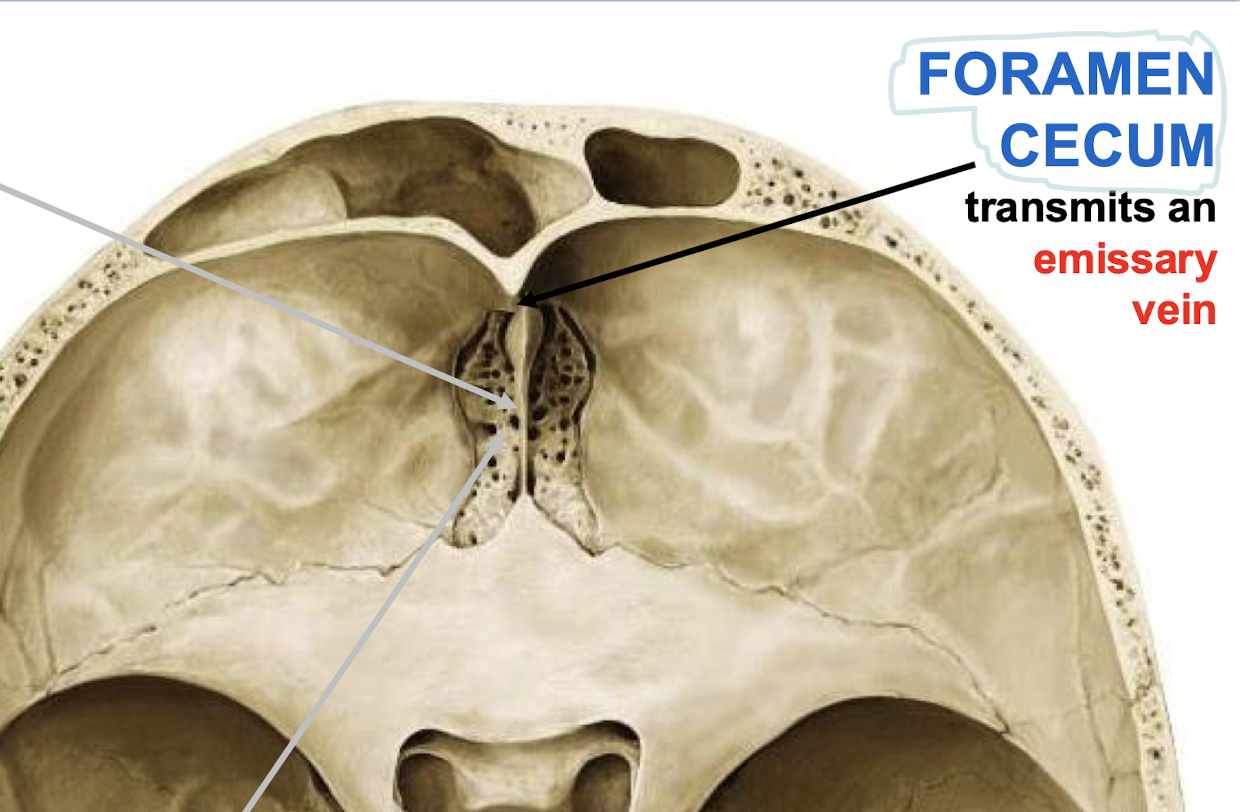
What does the foramen cecum transmit?
An emissary vein
What purpose do emissary veins serve?
bring blood from the face, scalp, and diploe to the venous dural sinuses
(they are valveless veins)
What is flow in emissary veins usually?
From intracranial to extracranial
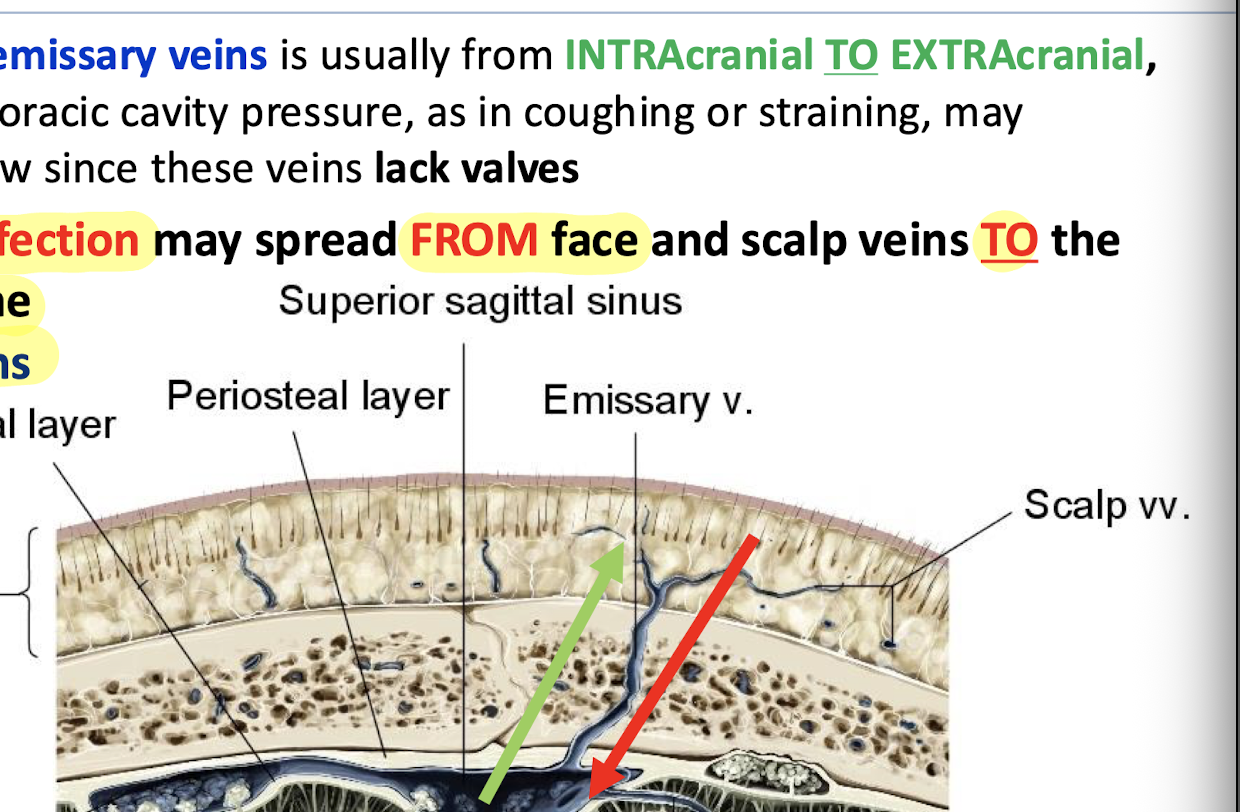
What can reverse the flow of emissary veins?
Increases in the thoracic cavity pressure, such as in coughing or straining
What bones make up the middle cranial fossa?
Sphenoid, temporal, and parietal bones
True or false: Infection may spread from face and scalp veins to the sinuses via emissary veins
True
What structures does the optic canal transmit?
CN II and the opthalmic artery to the orbit