Biology 2 - Genes and Health
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
define osmosis
the net movement of water from an area of lower concentration to higher concentration through a partially permeable membrane, which doesn’t use energy from respiration
define diffusion
the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to and area of lower concentration
define active transport
the movement of particles from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration against the concentration gradient while using energy from respiration
what proteins are involved in facilitated diffusion?
carrier and channel
what molecules pass across a membrane via facilitated diffusion?
charged molecules (channel proteins) and large molecules (carrier proteins)
what is endocytosis?
a substance is taken across a membrane by being engulfed by the membrane and pinched off into the cell creating a vesicle
what is exocytosis?
a substance is released from a cell when the vesicle fuses with the membrane and releases the substance out of the cell
what is a membrane made of?
phospholipid bilayer, glycolipids/proteins, cholesterol
what is Fick’s law?
rate of diffusion = (surface area x concentration difference)/thickness of membrane
how are lungs adapted for rapid gas exchange?
massive surface area (alveoli), short diffusion pathway, moist surfaces
what is ATP used for?
the cell can’t get all its energy from glucose so the energy released from glucose is used to make ATP which stores and releases energy
what is ATP often known as?
universal energy currency
where is ATP formed?
mitochondria via aerobic respiration
what is the role of cholesterol in a membrane?
provides structure and support
what is the role of protein in a membrane?
selective transport of molecules, and communication
what is the role of glycoproteins in a membrane?
act as receptors, bind to signalling molecules
what is the role of glycolipids in a membrane?
cell recognition and stability
what is the role of phospholipids in a membrane?
controls the cell’s internal environment
what is the aqueous environment inside the cell?
cytoplasm
what is the aqueous environment outside the cell?
tissue fluid
what are the two 3D structures that a protein could have?
globular or fibrous
what are the characteristics of globular structure?
round, compact, multiple polypeptide chains, coiled, hydrophilic inside, hydrophobic outside, soluble
what are the characteristics of fibrous structure?
long insoluble polypeptide chains, tightly coiled around each other, lots of bonds makes it strong, often found in supportive tissue
what is the order of polypeptides structure?
primary (sequence of amino acids), secondary (alpha helixs, beta pleated sheets), tertiary (3D specific shape), quaternary (2+ polypeptides forming a protein)
what is the function of DNA?
to store genetic information
what is the function on RNA?
to transfer genetic information
how do ribosomes work with RNA?
they read RNA to make polypeptides (translation)
what are DNA and RNA types of?
nucleic acids
what is a gene?
a length of nucleotide bases that provides a code to sequence amino acids to form a polypeptide
what are exons?
coding regions of DNA (genes)
what are introns?
non-coding regions of DNA
what is DNA made up of?
two polynucleotide strands (made up of mononucleotides)
what is RNA made of?
a single stranded polynucleotide
what are two examples of RNA?
messenger and transfer
when is RNA made?
it’s copied from DNA for protein synthesis
what is transcription?
the process of DNA being copied into mRNA to transfer genetic information to the ribosomes
what is a gene?
a length of nucleotides that provides a code for a sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide
what is the role of DNA polymerase?
it forms hydrogen bonds between the nucleotide bases during DNA replication to join the strands-
what is the name of Meselson’s and Stahl’s experiment?
semi-conservative replication
how are proteins formed?
amino acids linked by peptide bonds to make a polypeptide
what are the differences between DNA and RNA?
DNA double helix - RNA single stranded, DNA’s sugar is deoxyribose - RNA’s sugar is ribose, DNA has thymine - RNA had uracil
what are the 4 DNA nucleotide bases?
adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine
what 3 things are mononucleotides made of?
sugar (deoxy/ribose), phosphate, nucleotide base
how are bases bonded in the DNA double helix?
hydrogen bonds
what practical investigates the effect of alcohol on cell membranes?
beetroot test
what model is often used to show the structure of cell membranes?
fluid mosaic model
what are the properties of gas exchange surfaces in living organisms?
large surface area to volume ratio, thickness of surface, difference in concentration
what is an enzyme?
a biological catalyst that reduces activation energy
what is the difference between intra/extracellular enzymes?
intra - catalyses reactions inside cells
extra - catalyses reactions outside of cells
what are mutations caused by?
a change in the nucleotide base sequence in DNA (substitution, deletion, insertion, duplication, inversion)
how does cystic fibrosis occur?
by a mutation in a gene that codes for CFTR protein (Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane conductance Regulator)
what is an allele?
a version of a gene
what is a genotype?
the alleles a person has
what is a phenotype?
the observable characteristics in an organism
what is incomplete dominance / codominance?
both alleles present are expressed in phenotype
what is the diagram often used to display inheritance?
pedigree diagram
what does cystic fibrosis do to gas exchange?
thick mucus is unable to move up cilia so airways can become blocked by mucus and gas exchange can’t take place in the area below the blockage
what does cystic fibrosis do to the digestive system?
the tube connecting the pancreas to the small intestine can become blocked by mucus, which prevents digestive enzymes from pancreas reaching the small intestine so the person won’t digest food well and won’t get as many nutrients
what does cystic fibrosis do to the reproductive system?
men - the tubes to the testicles can be absent or become blocked by mucus so sperm cannot reach the penis
women - mucus can prevent the sperm reaching the egg
what is the strand of DNA that mRNA copies bases from?
template strand
what is a stop codon?
the stop codon is the last 3 nucleotide bases of a gene that mark the end of the polypeptide chain
what are anticodons?
an anticodon is the 3 bases on a tRNA that are complementary to the codon
what is the nature of the genetic code?
triplets, non-overlapping, degenerate
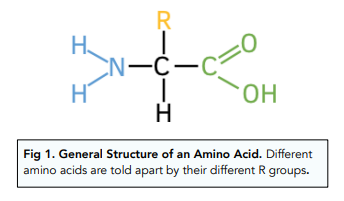
what is the structure of an amino acid?
amino group, variable r group, carboxyl group
what does the primary structure of a protein determine?
the amino acid sequence
what does the secondary structure of a protein determine?
folding patterns (alpha helixs, beta pleated sheets)
what does the tertiary structure of a protein determine?
the 3D shape of the polypeptide chain
what does the quaternary structure of a protein determine?
joining with other polypeptide chains to make a protein
what model is used to show the active site and substrate?
induced fit model (replaced lock and key model)
3 reasons why genetic screening is used?
identification of carriers, preimplantation genetic diagnosis, prenatal testing
what are two types of prenatal testing?
amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling
explain amniocentesis
a sample of amniotic fluid is obtained, DNA from fetal cells is analysed, 1% chance of miscarriage, usual results take 2-3 weeks but rapid test is 3-4 days (but rapid test only looks for a few common disorders)
explain chorionic villus sampling
cell sample taken from chorionic villi and DNA analysed, 1-2% chance of miscarriage, main results in a few days but in depth results in a few weeks