Barron's AP Biology - The Cell
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:20 AM on 11/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
1
New cards
Prokaryote
- Cells with no nuclear or internal membranes; i.e, lysosomes, vacuoles, and mitochondria
- Evolved 3.6 billion years ago
- Prokaryotes are classified in two domains: Archaea and Bacteria
- Contain small ribosomes
- Cells are small
- Contain naked, circular DNA
- Evolved 3.6 billion years ago
- Prokaryotes are classified in two domains: Archaea and Bacteria
- Contain small ribosomes
- Cells are small
- Contain naked, circular DNA
2
New cards
Eukaryotes
- Cells with internal membranes
- Evolved a billion years ago
- According to the theory of endosymbiosis, chloroplasts and mitochondria were formerly tiny prokaryotes that took up residence inside larger cells and formed permanent symbiotic relationship
- DNA is wrapped with histone proteins into chromosomes
- Metabolism is aerobic
- Cells are larger than prokaryotes
- Evolved a billion years ago
- According to the theory of endosymbiosis, chloroplasts and mitochondria were formerly tiny prokaryotes that took up residence inside larger cells and formed permanent symbiotic relationship
- DNA is wrapped with histone proteins into chromosomes
- Metabolism is aerobic
- Cells are larger than prokaryotes
3
New cards
Form and Function Go Together
- All cells do not look alike. Their function dictates their form and vice versa
4
New cards
Why Cells Are So Small
- The surface area of the plasma membrane, which controls what enters and leaves a cell, limits the overall size of the cell. This is because while the surface area of a sphere increases at one rate, the volume increases at a much faster rate
5
New cards
Cell Organelles
Typical animal cell:
A. Endocytotic vacuole
B. Nucleolus
C. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
D. Cell membrane
E. Cytoplasm (cytosol)
F. Rough endoplasmic reticulum
G. Ribosomes
H. Vacuole
I. Nuclear membrane
J. Mitochondria
A. Endocytotic vacuole
B. Nucleolus
C. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
D. Cell membrane
E. Cytoplasm (cytosol)
F. Rough endoplasmic reticulum
G. Ribosomes
H. Vacuole
I. Nuclear membrane
J. Mitochondria
6
New cards
Typical Plant Cell
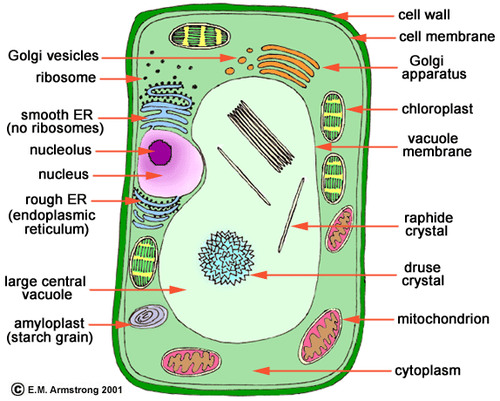
7
New cards
Nucleolus
- Prominent region seem in the nucleus during interphase
- Where ribosome components are synthesized and assembled
- Where ribosome components are synthesized and assembled
8
New cards
Nucleus
- Contains chromosomes (DNA) wrapped into a chromatin network
- Surrounded by selectively permeable membrane that contains nuclear pores for the passage of large molecules like mRNA
- Surrounded by selectively permeable membrane that contains nuclear pores for the passage of large molecules like mRNA
9
New cards
Ribosomes
- Site of protein synthesis
- Found free in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum
- Found free in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum
10
New cards
Golgi Apparatus
- Packages and secretes substances produced in the ER
- Lies near nucleus; consists of flattened membranous sacs
- Lies near nucleus; consists of flattened membranous sacs
11
New cards
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Membranous system of channels and flattened sacs that traverses the cytoplasm
- Rough ER
- Site of protein synthesis
- Smooth ER
- Site of protein synthesis
- Connects rough ER to Golgi apparatus
- Carries out various detoxification processes
- Rough ER
- Site of protein synthesis
- Smooth ER
- Site of protein synthesis
- Connects rough ER to Golgi apparatus
- Carries out various detoxification processes
12
New cards
Lysosomes
- Sacs of hydrolytic enzymes surrounded by a single membrane
- Principal site of intracellular digestion of macromolecules
- Carry out programmed destruction of cells, apoptosis, using their hydrolytic enzyme
- Found in large numbers in phagocytic white blood cells
- Absent from plant cells
- Principal site of intracellular digestion of macromolecules
- Carry out programmed destruction of cells, apoptosis, using their hydrolytic enzyme
- Found in large numbers in phagocytic white blood cells
- Absent from plant cells
13
New cards
Peroxisomes
- Contain enzyme that converts hydrogen peroxide to harmless water
- In liver cells, detoxify alcohol
- In liver cells, detoxify alcohol
14
New cards
Mitochondria
- Site of aerobic respiration, the process that generates ATP
- Internal membranes are called cristae membranes
- Enclosed in a double membrane because in ancient times these were tiny free-living cells that took up residence inside larger organisms. This is the theory of endosymbiosis
- Internal membranes are called cristae membranes
- Enclosed in a double membrane because in ancient times these were tiny free-living cells that took up residence inside larger organisms. This is the theory of endosymbiosis
15
New cards
Food Vacuoles
- Formed by phagocytosis
- Surrounded by a single membrane
- Surrounded by a single membrane
16
New cards
Central Vacuoles
- Found in mature plant cells enclosed in a specialized membrane called a tonoplast
17
New cards
Contractile Vacuoles
- Found in freshwater protista like amoeba and paramecia
- Pump out excess water that diffuses inward because organisms live in a hypotonic environment
- Pump out excess water that diffuses inward because organisms live in a hypotonic environment
18
New cards
Chloroplasts
- Present in all living plant cells
- Site of photosynthesis
- Contains the green photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll that absorbs light energy for photosynthesis
- According to the Theory of Endosymbiosis, chloroplasts were once free-living prokaryotes
- Site of photosynthesis
- Contains the green photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll that absorbs light energy for photosynthesis
- According to the Theory of Endosymbiosis, chloroplasts were once free-living prokaryotes
19
New cards
Cilia / Flagella
- Appendages that protrude from eukaryotic cells for locomotion
- Consist of special arrangement of microtubules: 9 pairs of microtubules + 2 singles (9 + 2)
- Cilia are short; flagella are long
- In paramecia, euglena, sperm, and human respiratory system
- Consist of special arrangement of microtubules: 9 pairs of microtubules + 2 singles (9 + 2)
- Cilia are short; flagella are long
- In paramecia, euglena, sperm, and human respiratory system
20
New cards
Cytoskeleton
- Complex network of protein filaments that extends through the cytoplasm and gives cell its shape and ability to move
- Ex: microtubules, microfilaments
- Ex: microtubules, microfilaments
21
New cards
Cell Wall
- Found in plant cells; not in animal cells
- In plants algae, it consists of cellulose
- In fungi, it consists of chitin
- Primary cell wall: immediately outside plasma membrane
- Secondary cell wall: where found, located outside primary wall
- In plants algae, it consists of cellulose
- In fungi, it consists of chitin
- Primary cell wall: immediately outside plasma membrane
- Secondary cell wall: where found, located outside primary wall
22
New cards
Plasma Membrane
- Selectively-permeable - fluid mosaic model
- Consists of a lipid bilayer with proteins dispersed throughout
- In vertebrates, cholesterol molecules are embedded in the interior of membrane for stability
- External surface has glycoproteins that functions in cell-to-cell communications
- Contains protein channels, pumps, and enzymes
- Consists of a lipid bilayer with proteins dispersed throughout
- In vertebrates, cholesterol molecules are embedded in the interior of membrane for stability
- External surface has glycoproteins that functions in cell-to-cell communications
- Contains protein channels, pumps, and enzymes
23
New cards
Transport
- Movement of a substance into or out of a cell
- Can be active or passive
- Passive: requires no expenditure of energy
- Active: requires energy
- Can be active or passive
- Passive: requires no expenditure of energy
- Active: requires energy
24
New cards
Passive Transport
- Movement of molecules down a gradient from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration; no energy (ATP) required
- Simple diffusion: no membrane required
- Facilitated diffusion: molecules diffuses through membrane channels
- Osmosis: type of diffusion where water diffuses across a membrane
- Countercurrent exchange: special case of simple diffusion - flow of adjacent fluids in opposite direction to maximize rate of diffusion
- Simple diffusion: no membrane required
- Facilitated diffusion: molecules diffuses through membrane channels
- Osmosis: type of diffusion where water diffuses across a membrane
- Countercurrent exchange: special case of simple diffusion - flow of adjacent fluids in opposite direction to maximize rate of diffusion
25
New cards
Water Potential
- Symbol is Greek letter psi = Ѱ
- Water moves across a membrane from a solution with higher water potential to a solution with lower water potential
- Water potential of pure water = 0
- Addition of solute to water lowers Ѱ
- Water flows from hypotonic solutions to hypertonic solutions
- Water moves across a membrane from a solution with higher water potential to a solution with lower water potential
- Water potential of pure water = 0
- Addition of solute to water lowers Ѱ
- Water flows from hypotonic solutions to hypertonic solutions
26
New cards
What Happens to a Cell in a Hypertonic Solution?
- Cell shrinks because water flows from higher water potential to lower water potential
- Hypertonic means higher concentration of solute
- Cell shrinking is called plasmolysis
- Hypertonic means higher concentration of solute
- Cell shrinking is called plasmolysis
27
New cards
What Happens to a Cell in a Hypotonic Solution?
- Animal cells swell or burst because water moves from higher water potential to lower water potential
- Hypotonic means lower concentration of solute
- Plant cells do not burst; they swell and become turgid
- Hypotonic means lower concentration of solute
- Plant cells do not burst; they swell and become turgid
28
New cards
What Happens to a Cell in an Isotonic Solution?
- Nothing happens to the cell because the concentrations of the solutions outside and inside the cell are equal
29
New cards
Aquaporins
- Special water channel proteins in certain cells that facilitate the rapid diffusion of massive amounts of water across a cell membrane
- They do not alter the water potential gradient; they only speed the rate of diffusion
- They do not alter the water potential gradient; they only speed the rate of diffusion
30
New cards
Active Transport
- Movement of molecules against a gradient from a region of low concentration to high concentration
- Requires energy (ATP)
- Requires energy (ATP)
31
New cards
Sodium-Potassium Pump
- Pumps Na+ and K+ ions across axon membranes against a gradient
- Returns the neuron to its resting state - polarized
- While the pump is working, no impulse can pass along the axon - an interval called the refractory period
- Returns the neuron to its resting state - polarized
- While the pump is working, no impulse can pass along the axon - an interval called the refractory period
32
New cards
Pinocytosis
- Cell drinking
- The uptake of large, dissolved particles
- The uptake of large, dissolved particles
33
New cards
Phagocytosis
- Engulfing of large particles or small cells by pseudopods
34
New cards
Ion-channel receptors
- Allosteric receptors that opens and shuts a gate in a membrane allowing an influx of ions
35
New cards
Cytoplasmic Receptors
- Reception: small, non-polar ligands diffuse directly through the plasma membrane and into the cytoplasm where they bind with an intracellular receptor
- Transduction: Once activated, the receptor converts a molecular signal to a cellular response
- Response: Can be a single step of a more complex signal transduction pathway
- Transduction: Once activated, the receptor converts a molecular signal to a cellular response
- Response: Can be a single step of a more complex signal transduction pathway
36
New cards
Signal Transduction Pathway
- A multistep process in which a small number of extracellular signaling molecules produce a major cellular response via a cascade effect
- The similarity in these pathways in bacteria, plants, and animals suggests that the pathways evolved hundreds of millions of years ago in a common ancestor
- Advantage of a multistep pathway: it provides many opportunities for coordination and regulation
- The similarity in these pathways in bacteria, plants, and animals suggests that the pathways evolved hundreds of millions of years ago in a common ancestor
- Advantage of a multistep pathway: it provides many opportunities for coordination and regulation
37
New cards
Gap Junctions
- Another example of cell-to-cell communication
- Provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent cells in animals
- Large molecules can pass from cell to cell
- In the heart, they enable cells to coordinate contractions of muscle tissue
- Plasmodesmata - channels between cells in plants
- Provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent cells in animals
- Large molecules can pass from cell to cell
- In the heart, they enable cells to coordinate contractions of muscle tissue
- Plasmodesmata - channels between cells in plants
38
New cards
Apoptosis
- Programmed cell death, brought about by signals that activate a series of suicide proteins
- Essential to the development of the nervous system in embryos and to normal operation of the immune system
- Different pathways involving about 15 different caspases carry out apoptosis
- Triggering signals can come from the nucleus of a cell when the DNA is irreparably damaged or from the endoplasmic reticulum when excessive protein misfolding occurs
- Signals can originate outside the cell and bind with all cell-surface receptor that triggers a signal transduction pathway to initiate apoptosis
- Mitochondria can initiate and apoptotic pathway by leaking relay protein into the cytoplasm
- An important example of cell communication
- Essential to the development of the nervous system in embryos and to normal operation of the immune system
- Different pathways involving about 15 different caspases carry out apoptosis
- Triggering signals can come from the nucleus of a cell when the DNA is irreparably damaged or from the endoplasmic reticulum when excessive protein misfolding occurs
- Signals can originate outside the cell and bind with all cell-surface receptor that triggers a signal transduction pathway to initiate apoptosis
- Mitochondria can initiate and apoptotic pathway by leaking relay protein into the cytoplasm
- An important example of cell communication