Weak 4 - Collisions
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Name 3 collision detection
• Circle-Circle
• Circle-Line
• Box-Box
How does player movement and collision detection work together in a game?
update(); -> p.x + = p.speed *dt;What is collision detection in games?
the process of calculating and detecting geometric intersections between objects
Fundamental to games as it ensures realistic interactions between moving geometric shapes.
What are the three types of collision detection methods?
Pixel/Vertex Perfect
High precision but computationally expensive.
Requires exact point and normal vector (not covered in this course).
Bounding Volume
Approximates objects with simple shapes (e.g., circles, boxes) for simpler calculations.
Raycasts
Used for line-of-sight or point intersection checks.
How does bounding volume collision detection work?
Approximate the object with a simple shape (circle, box, etc.).
Transform the bounding volume as the object moves/rotates.
Compute the intersection of bounding volumes.
Avoid expensive operations like trigonometry and square roots where possible since it’s too slow
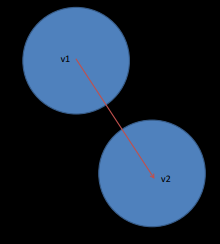
How do you check for circle-circle collisions?
if (dist2(v1, v2) > (r1 + r2)^2):
No collision
else:
Collision detected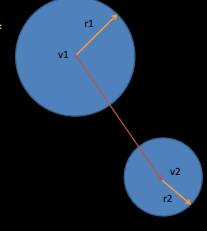
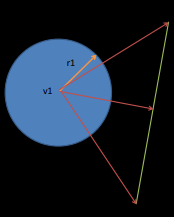
How do you check for circle-line collisions?What is it useful for?
Find the point on the line closest to the circle's center.
Compare the circle's radius to the distance to this point.
Similar to circle-circle detection but requires additional calculations for the closest point on the line.
Useful for detecting collisions between agents and walls.
What is the challenge of fitting a sphere?
Fitting a sphere around a set of points is harder than it sounds:
Easy approximate solutions by hand
•minimum solution for a set of points is difficult computationally expensive.
easy brute force solution
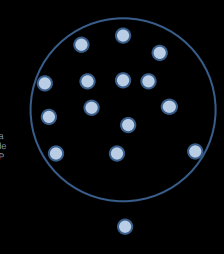
What happens when there’s a set of points?
draw a circle around them as tight as possible
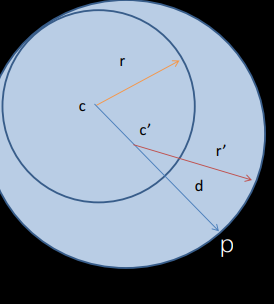
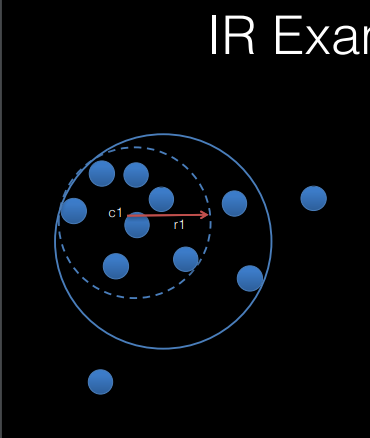
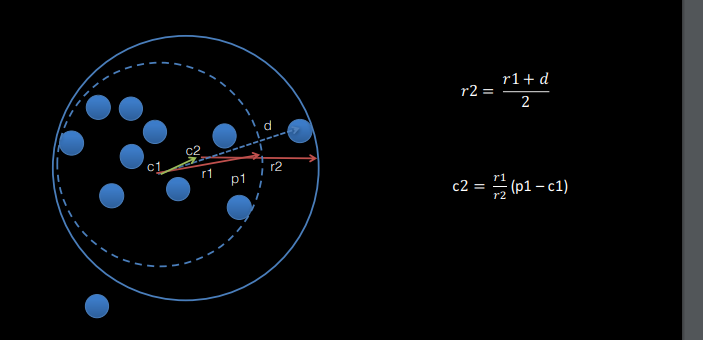
How can you bound an object in a circle?
Initialization:
Randomly select N points from the object (4 is preferred).
Pick the pair of points farthest apart; make their midpoint the center and their distance the radius.
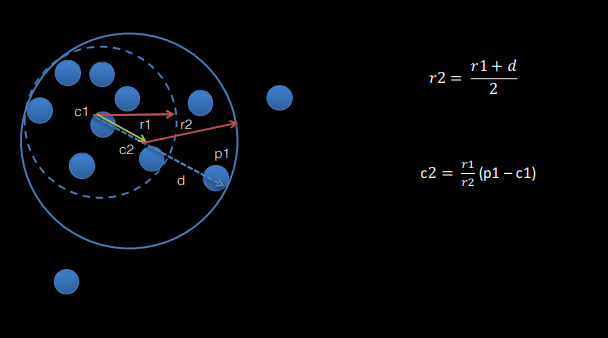
Iterative Refinement:
for all points in the cloud:
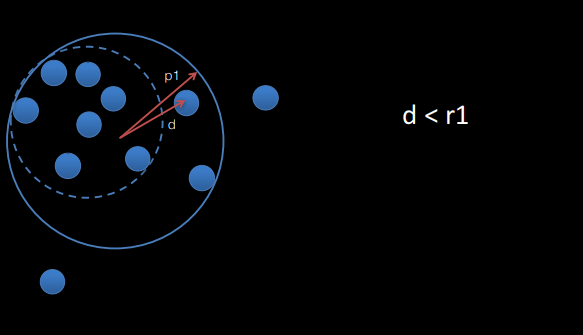
if the distance to the point from the centre is greater than r:
set the radius to the average of the old radius and new distance
move the centre along the vector connecting the centre and new point proportional to the change in radius
for all points in the cloud:
if the distance to the point from the centre is greater than r:
set the radius to the average of the old radius and new distance
move the centre along the vector connecting the centre and new point proportional to the change in radius
What is the iterative for the recursive solution? Is it good or bad? what’s a better solution?
O(n^5)
bad
Recursive (Welzl’s algorithm)
What’s the principle of Recursive (Welzl’s algorithm) ?
Given a set of points, P bounded by a minimum sphere S, then if Q is outside P, Q must be on the surface of S’ for P U Q
Write the Steps of the Recursive Solution:
• Remove a point from the cloud
• Recursively compute the smallest sphere for the remaining points
• if the given point is in the sphere
• return the sphere
• else
• recompute the sphere with the new point
Name the 4 sphere base cases.
0: dead end branch, return null
1: return point as sphere
2: return midpoint as center and dist and diameter
3: return trilateration
4: solve for sphere
Why does the rotation of a sphere not matter for collision detection?
rotationally invariant ; shape does not change regardless of rotation
very handy
translate the center along w the object
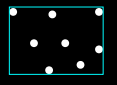
How would you calculate bounding in a box?
Calculate edges using min/ max points in the object
(simpler than bounding in a circle)
Name two types of box collision and define them
AABB - boxes translate with object but do not rotate
OBB - boxes translate and rotate similar to Unity but more complicated to calculate.
How will you calculate AABB? Also what does it stand for?
Axis-Aligned Bounding Box
if (!(A.maxx < B.minx || A.minx > B.maxx ||
A.maxy < B.miny || A.miny > A.maxy)):
Collision detected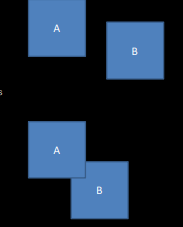
Give some characteristics of OBB and what does it stand for?
Orientated Bounding Box
they fit around an object (Race car)
easy to move
hard to find
hard to check

What is the collision detection sequence?
• Rule out as many collision detections as possible, as quickly as possible
• maintain some lists
• only check moving objects as sources
• Divide the world
• Divide the components
We have detected a collision between two objects, now what?
• take/inflict damage
• Stop moving
• Bounce apart
•Some done by collision system, some done in game logic (e.g., OnCollisionEnter2D())
Name the two types of collisions
particle (curling stones, no rotation, momentum conserved through translation)
rigid body(things that spin and topple, rotation, momentum can be transferred from translation to rotation)
Name some characteristics of perfect collisions.
pure conservation of momentum (usually square hits as well)
final speed of participants depend on the speeds and masses going in.
How do you resolve collisions?
Resolve impact(detect collision)
Capture special cases
Determine normals
Perform mass and velocity calculations
Transform results from collision coordinates
Calculate screen update
Name some special cases of collisions
E = 0, inelastic collision (objects stick together)
M= infinity, bouncing off a wall or the ground (mass),pure reflection
Why is Collisions with rotation significantly more complicated?
Can spin out as an animation,
spin if hit off axis
change spin rate and direction based on momentum, dont actually solve the rigid body equations.
How does Unity handle collisions?
Unity uses callback functions to handle collision events.
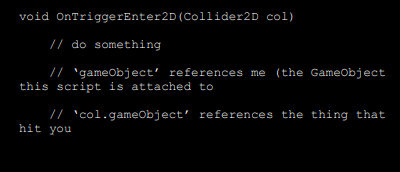
What is the difference between a trigger and a collision in Unity?
Trigger:
Detects overlaps without causing physical reactions.
Example: Sensors or proximity detections.
Collision:
Detects physical impacts and reacts (e.g., bouncing, stopping).