Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Muscle fiber
A skeletal muscle cell
Skeletal muscle tissue
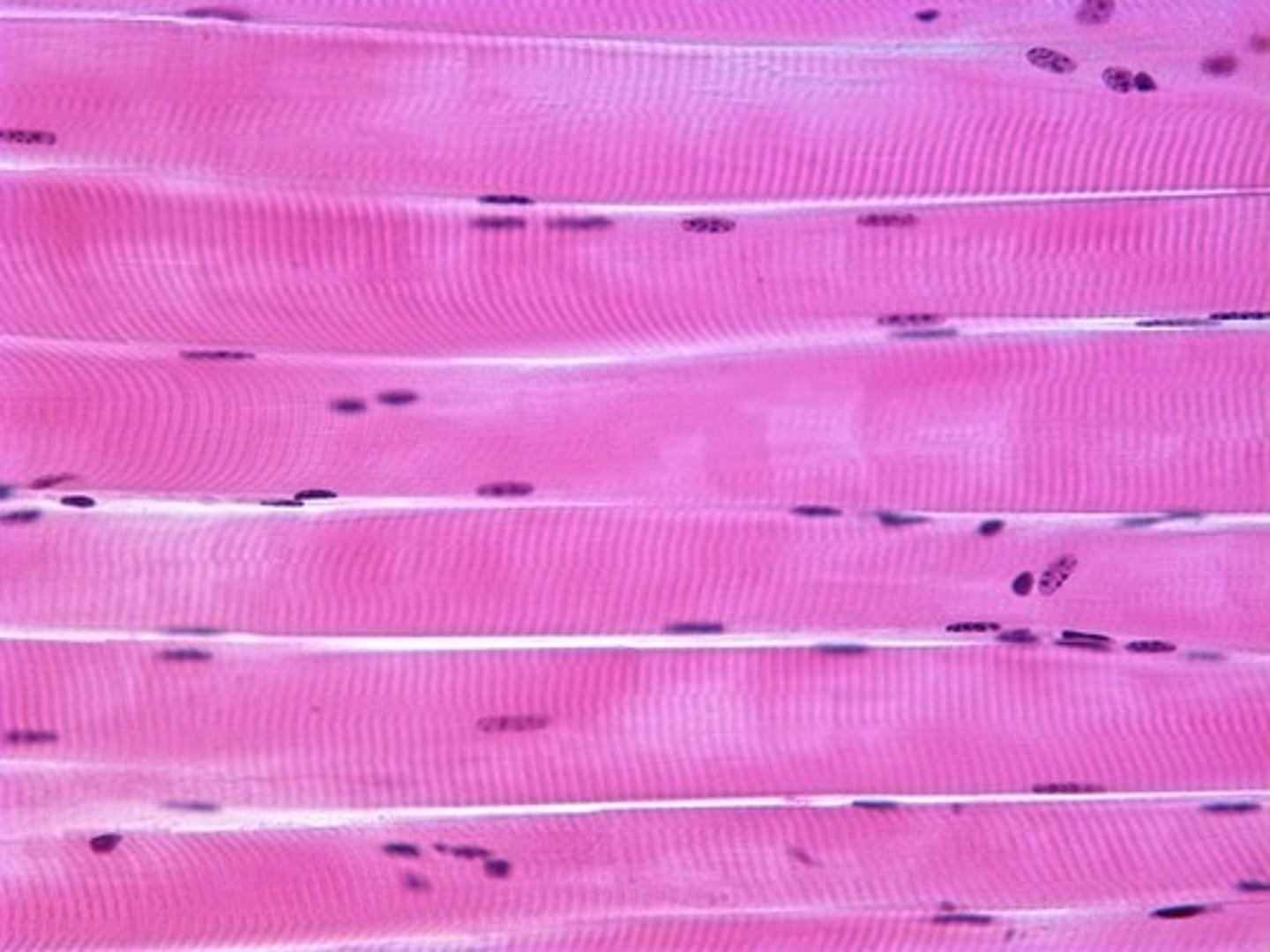
Long, cylindrical cells that are attached to bones of the skeleton. They have striations, are multinucleate, and under voluntary control.
Smooth muscle tissue
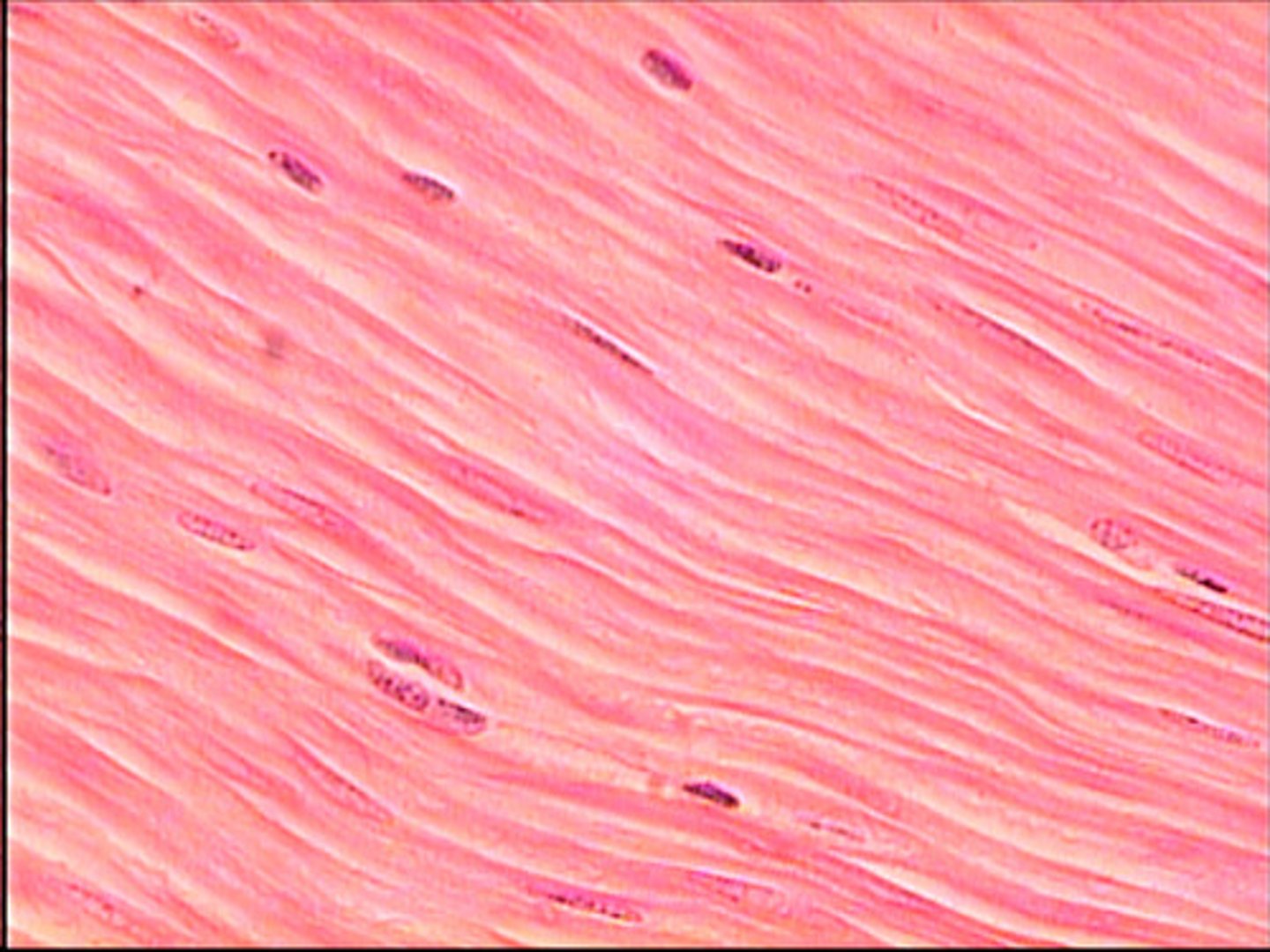
Spindle-shaped cells found in the walls of hollow organs. They are not striated, are uni-nucleate, and involuntary.
Cardiac muscle tissue
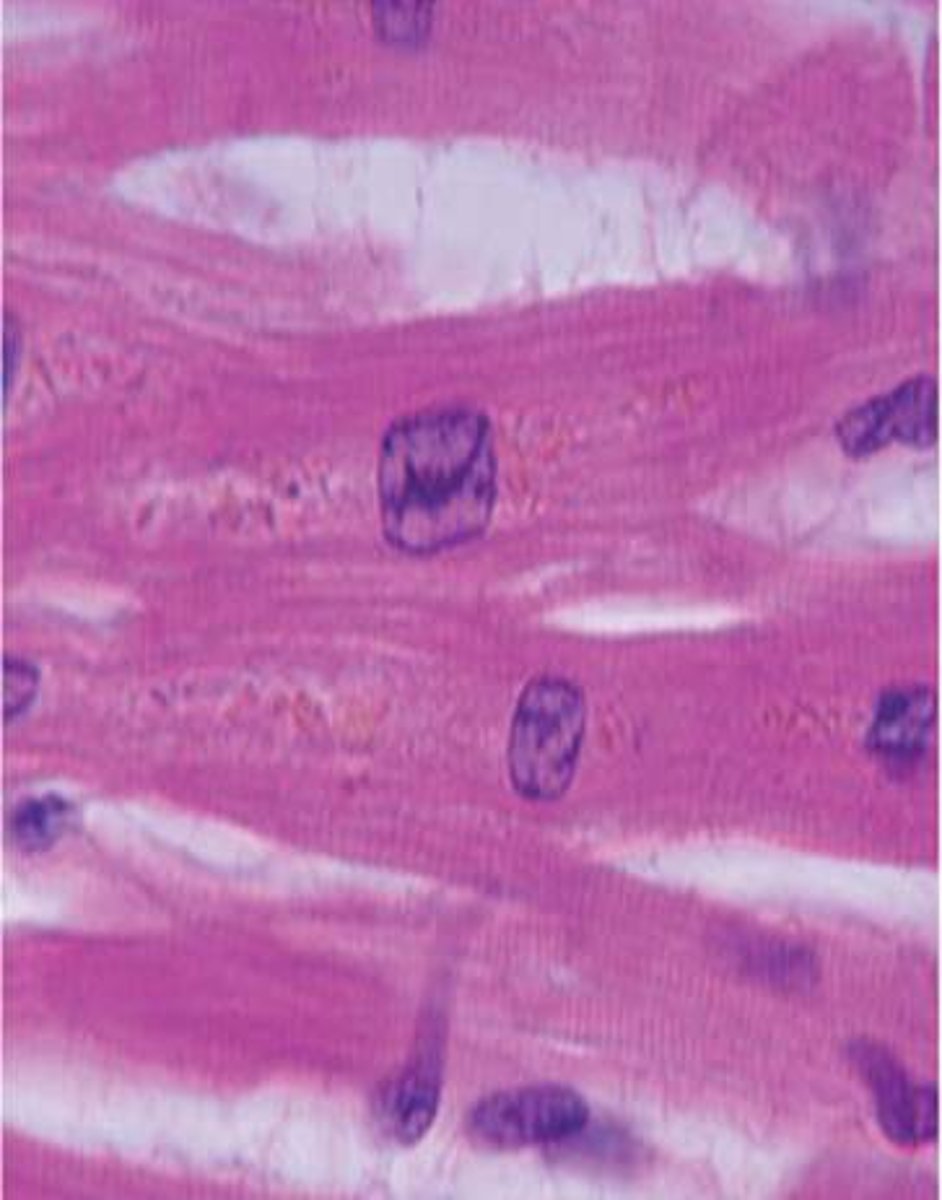
Branched cells found in the heart. They are striated, uni-nucleate, and involuntary.
Voluntary muscle
A muscle under conscious control.
Contractility
Ability to shorten forcibly when stimulated.
Excitability
Ability to receive and respond to stimuli
Extensibility
Ability to be stretched
Elasticity
The ability to recoil to resting length.
Epimysium
Dense irregular connective tissue surrounding entire muscle
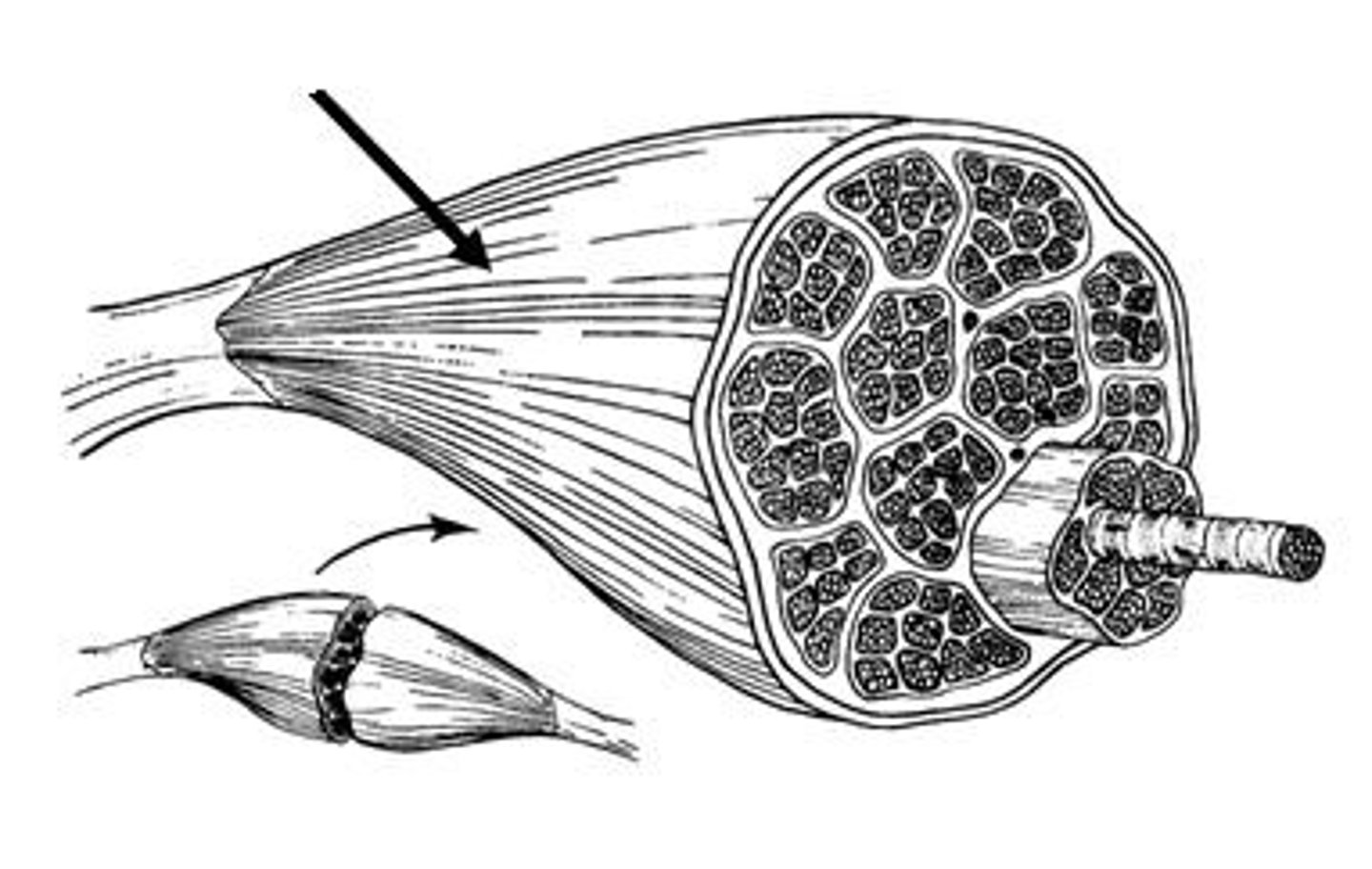
Perimysium
Fibrous connective tissue surrounding fascicles in a muscle.
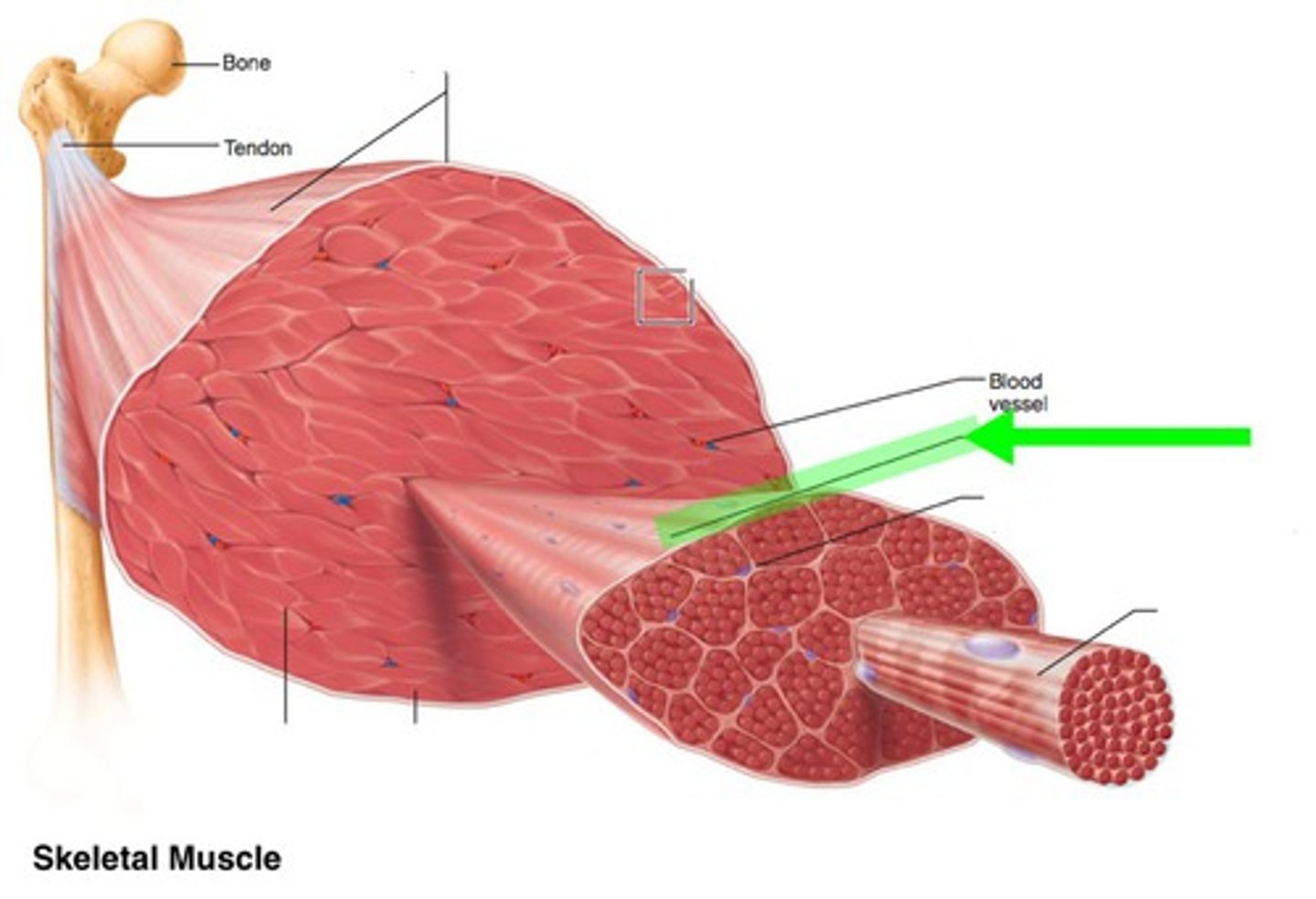
Fascicle
A bundle of muscle fibers.
Endomysium
Fine areolar connective tissue surrounding each muscle fiber.
Insertion
The attachment of a muscle tendon to a movable bone.
Origin
The attachment of a muscle tendon to a stationary bone.
Direct attachment
Epimysium of a muscle fused to periosteum of bone or perichondrium of cartilage.
Indirect attachment
Connective tissue wrappings of muscle extend beyond muscle as ropelike tendon.
Tendon
Connective tissue that connects muscle to bone.
Sarcolemma
Plasma membrane of a muscle fiber.
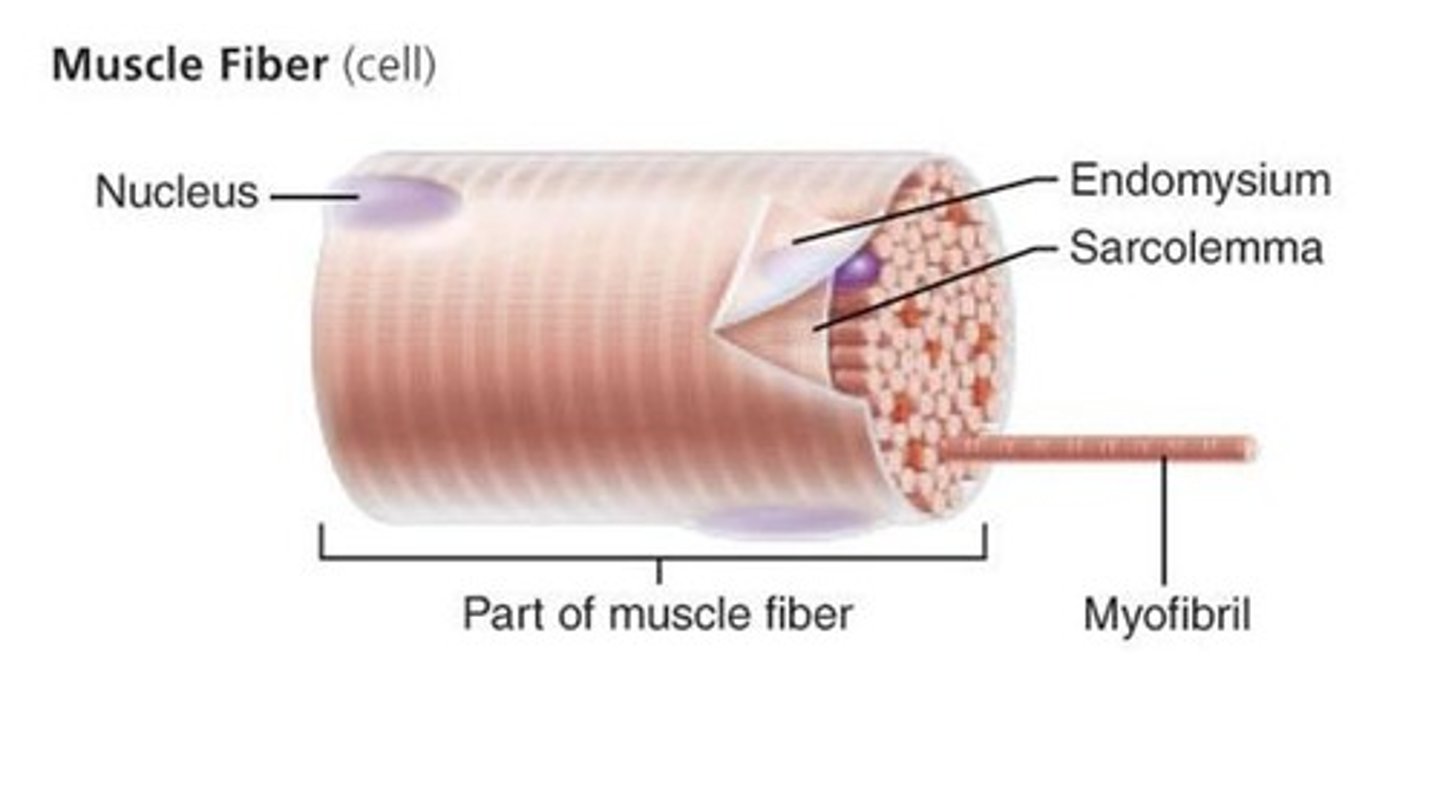
Sarcoplasm
Cytoplasm of a muscle fiber.
Glycosomes
Granules of stored glycogen.
Myoglobin
An oxygen-storing, pigmented protein in muscle cells.
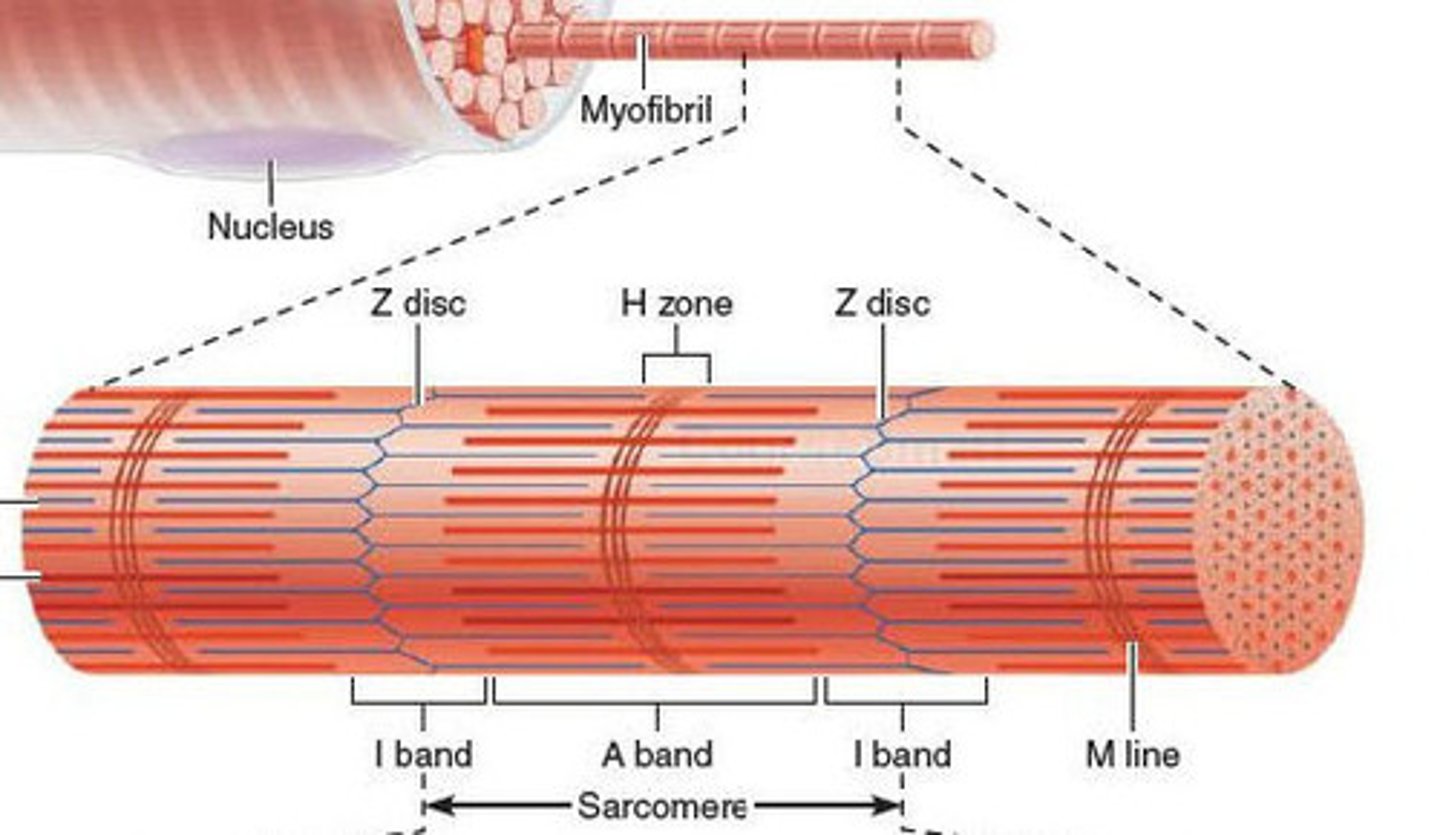
Myofibrils
Microscopic rods of protein filaments that make up muscle cells.
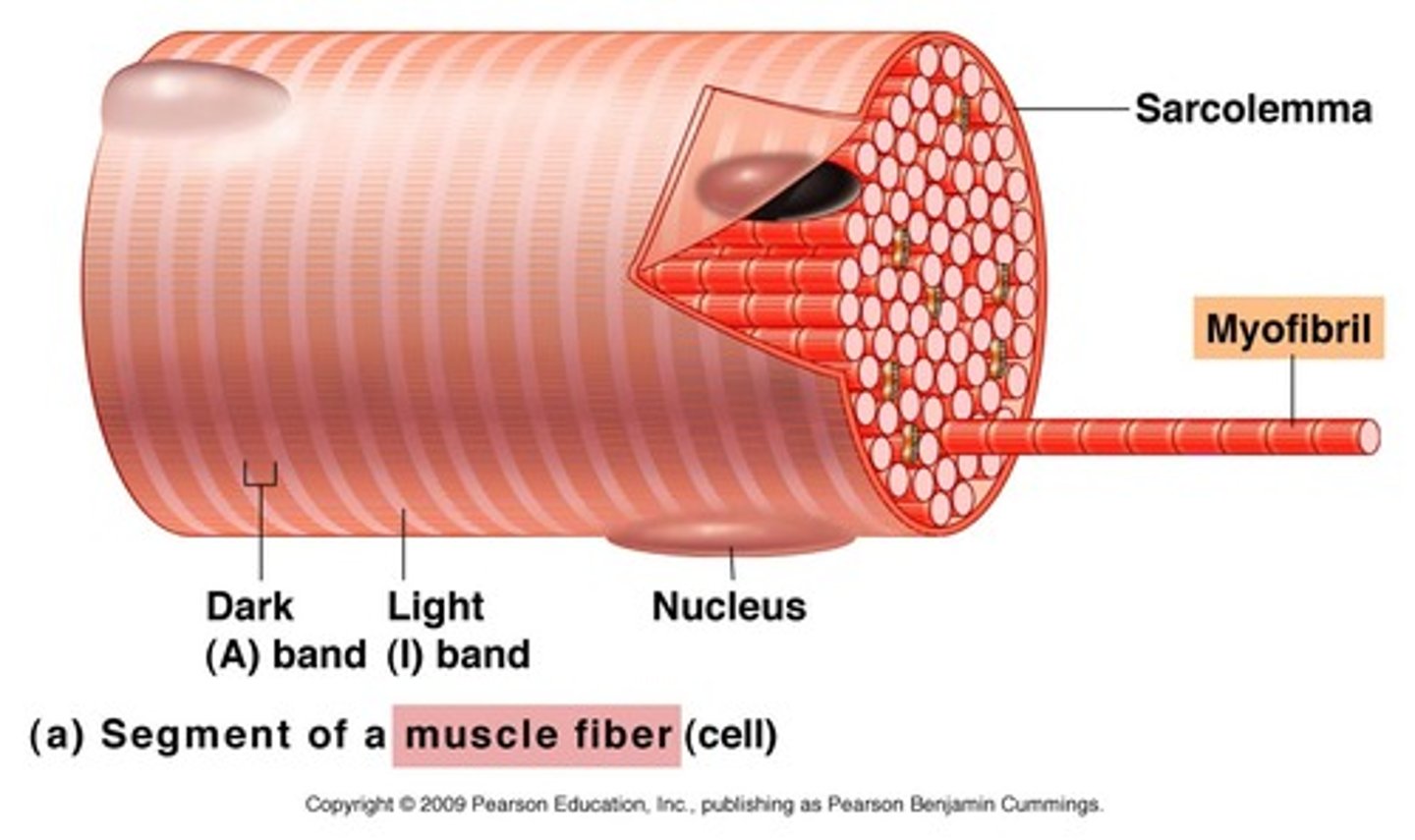
Striations
Alternate dark and light bands found on skeletal and cardiac muscle.
A band
Dark band striation on a muscle fiber.
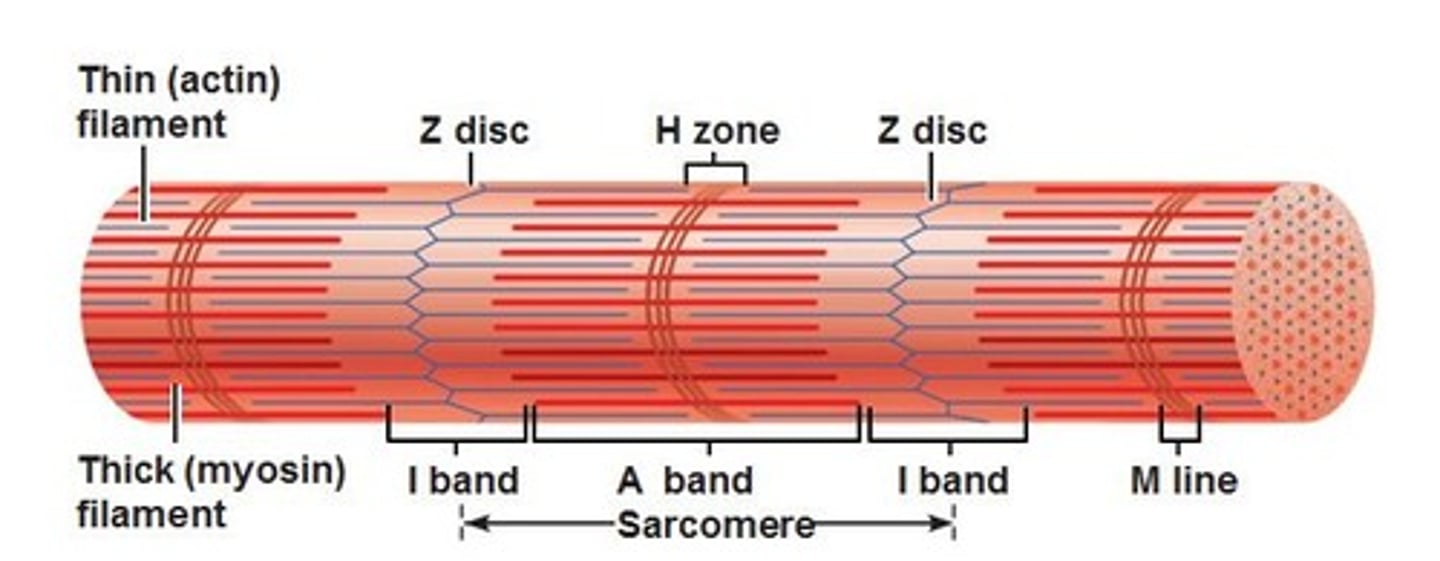
I band
Light band striation on a muscle fiber.
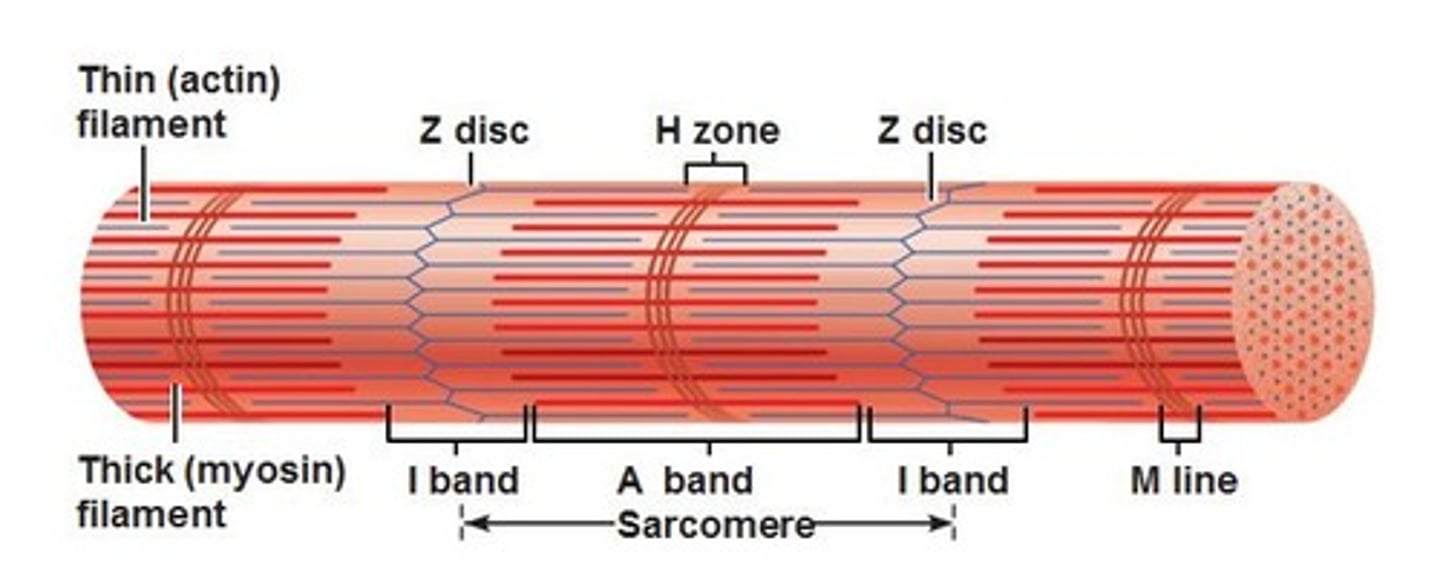
H zone
Lighter region in the middle of the dark A band
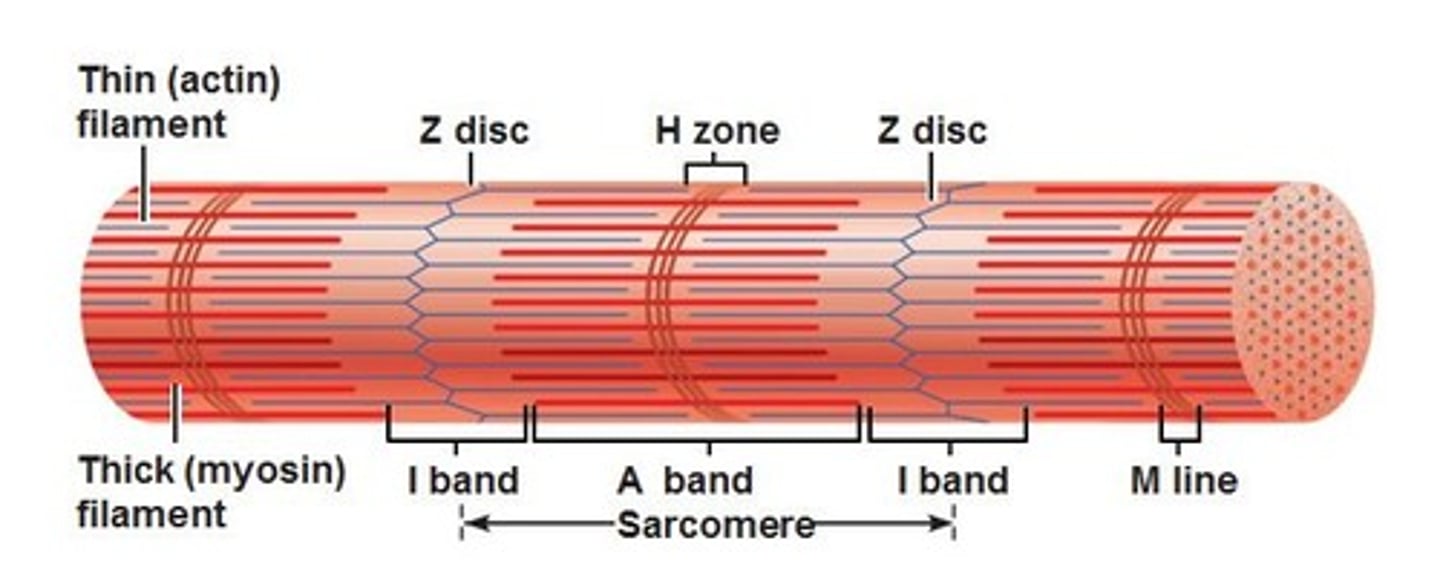
M line
Line of protein running along the middle of the H zone that anchors myosin into place.
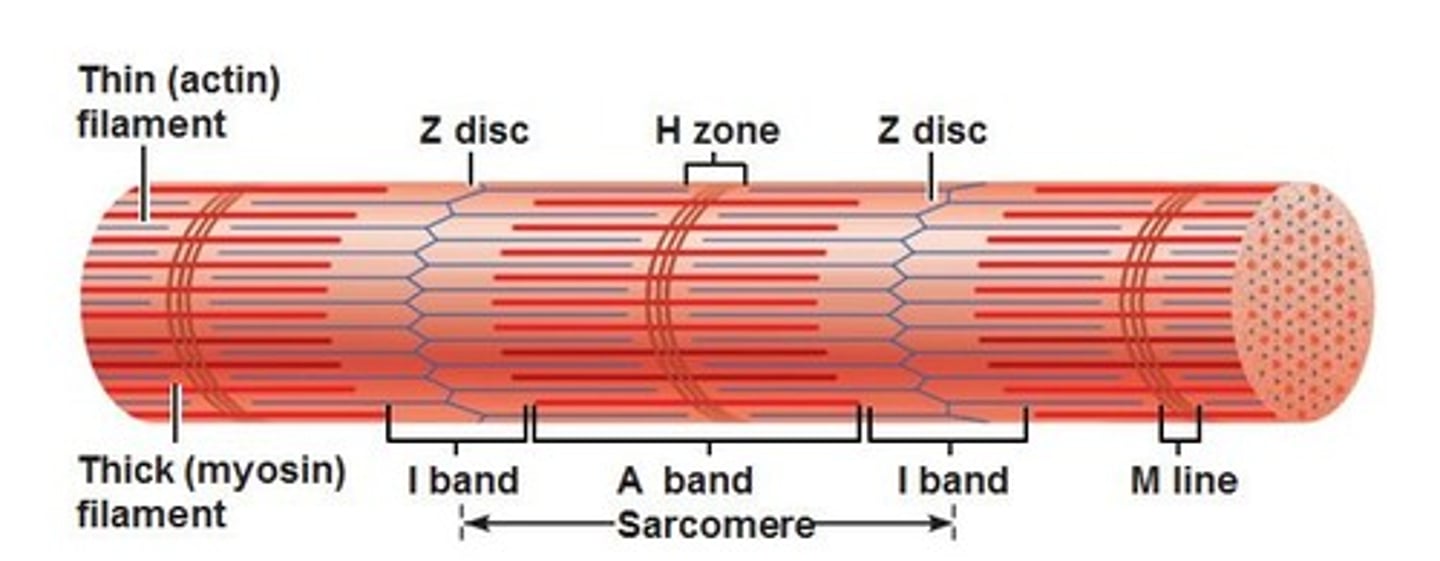
Z disc
Line of protein running along the middle of the L band that anchors actin into place.
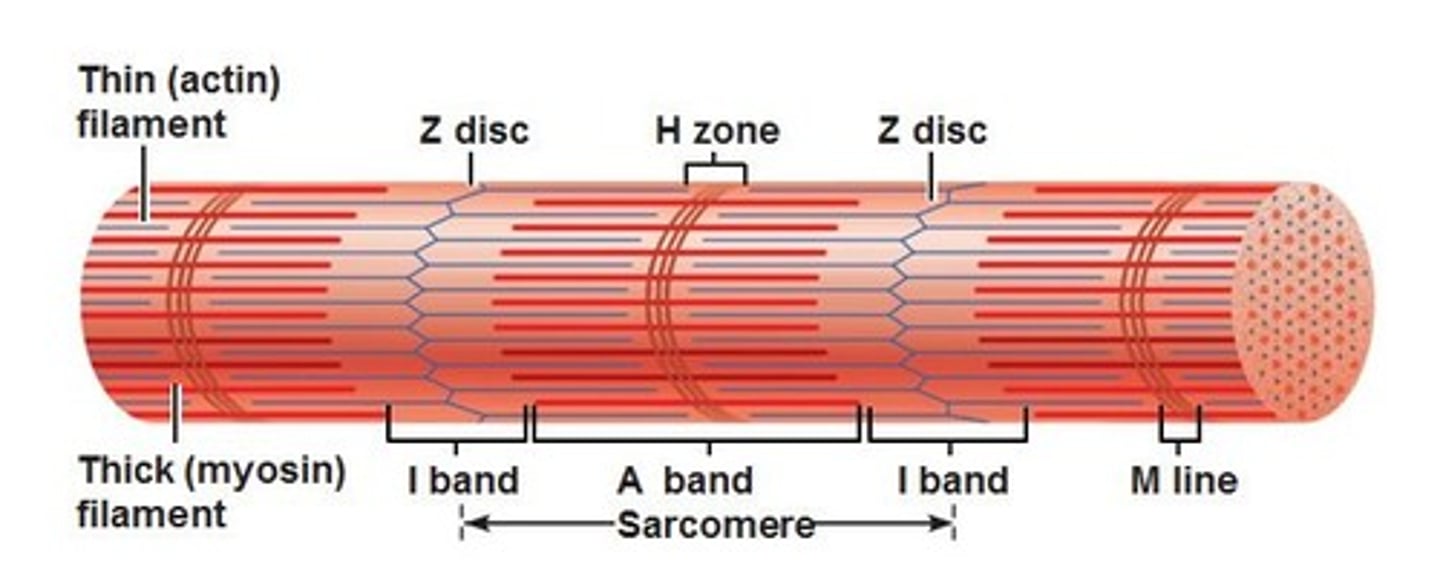
Sarcomere
Structural and functional unit of muscle contraction, running from Z disc to Z disc.
Myofilaments
The contractile proteins, actin and myosin, of muscle cells.
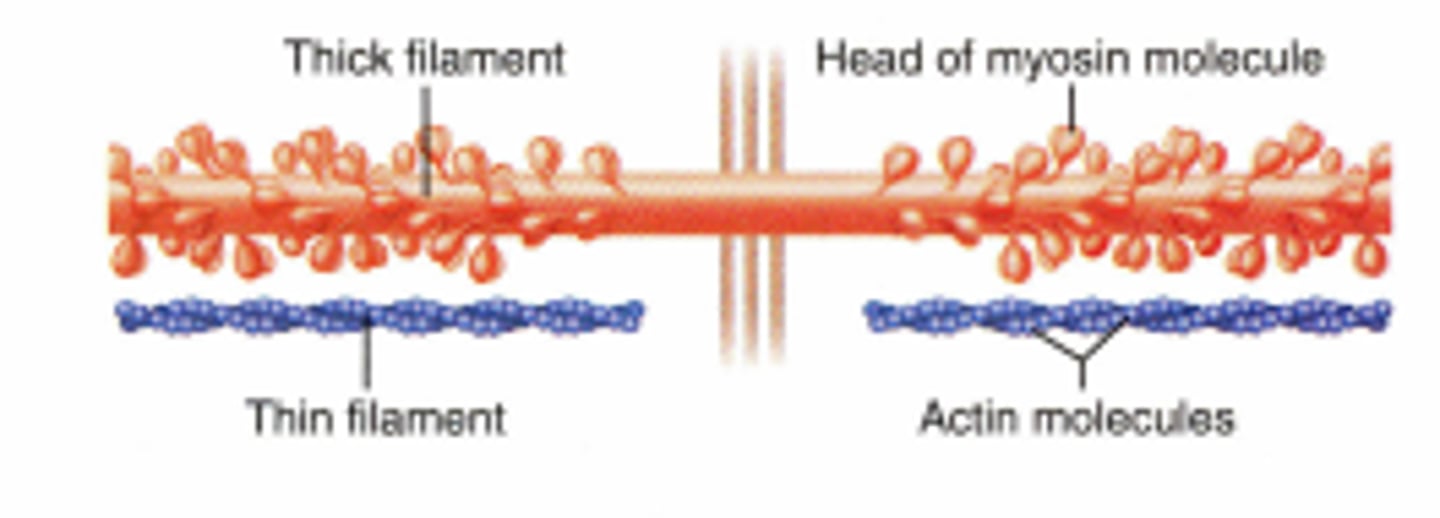
Myosin
The contractile protein that makes up the thick filaments of myofibrils.
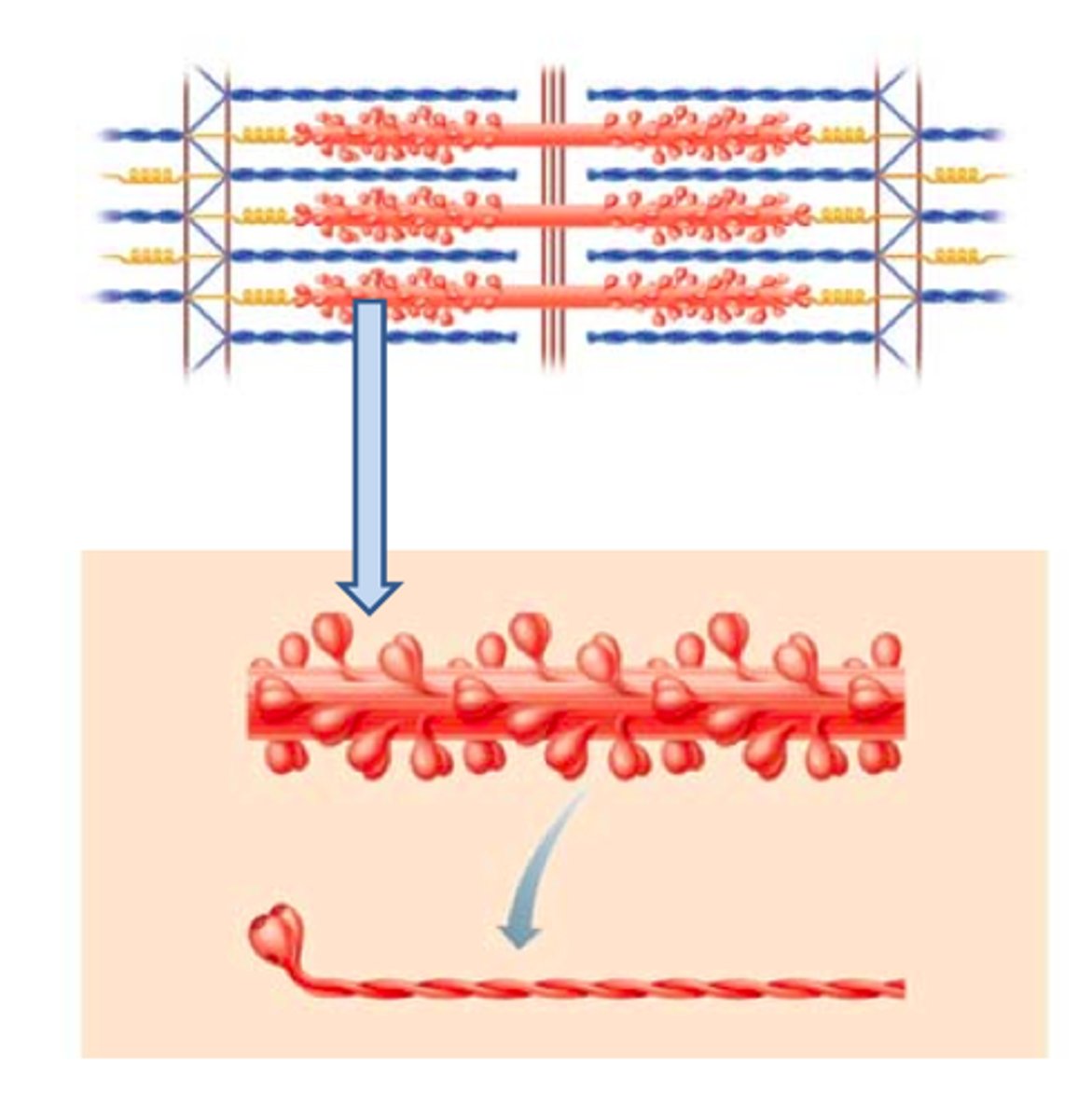
Actin
The contractile protein that makes up thin filaments of myofibrils.
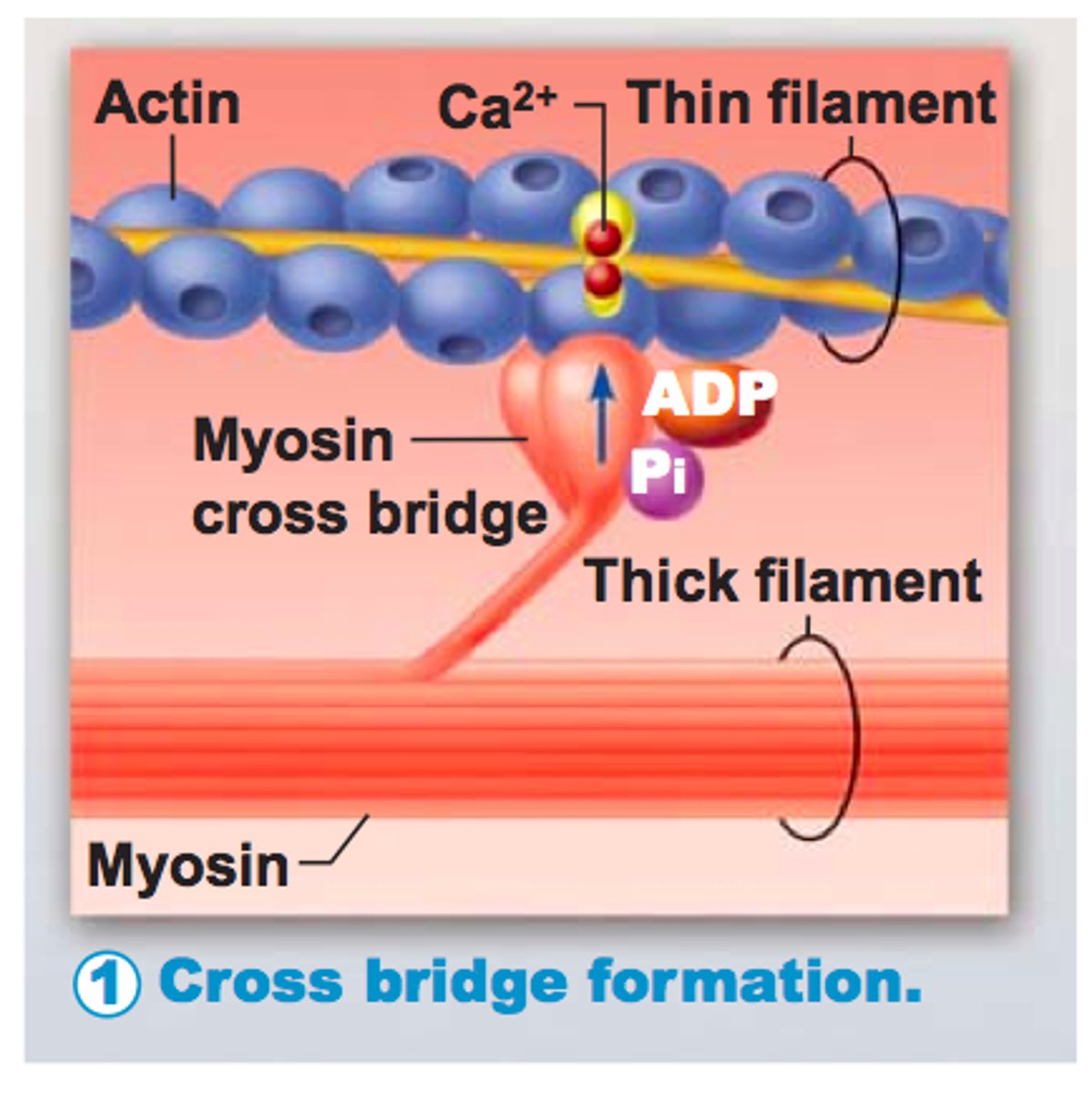
Cross bridges
Connections that form during muscle contraction between the heads of myosin filaments and receptor sites on the actin filaments.
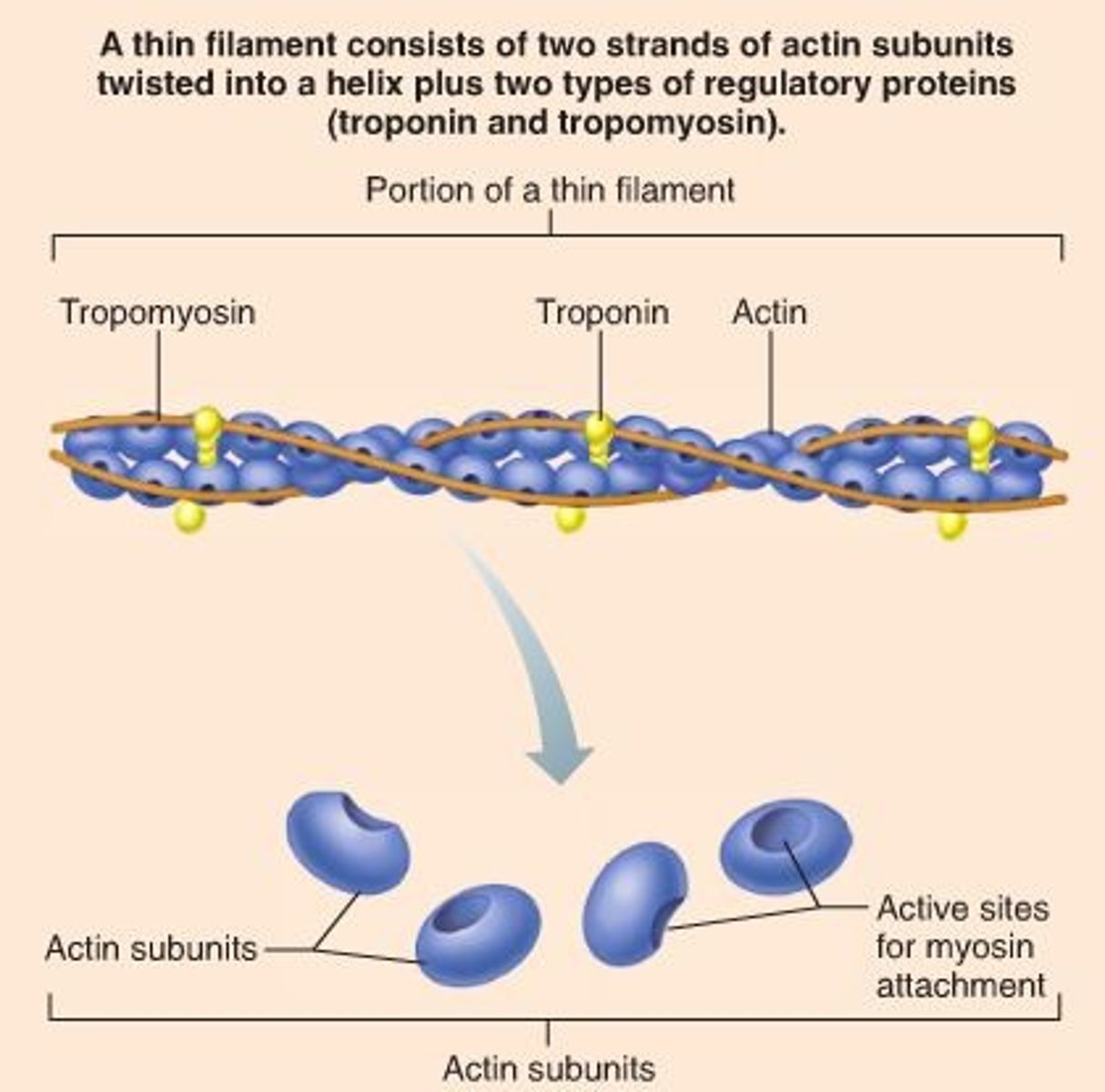
Tropomyosin
A protein that blocks the myosin binding sites on actin to prevent muscle contraction.
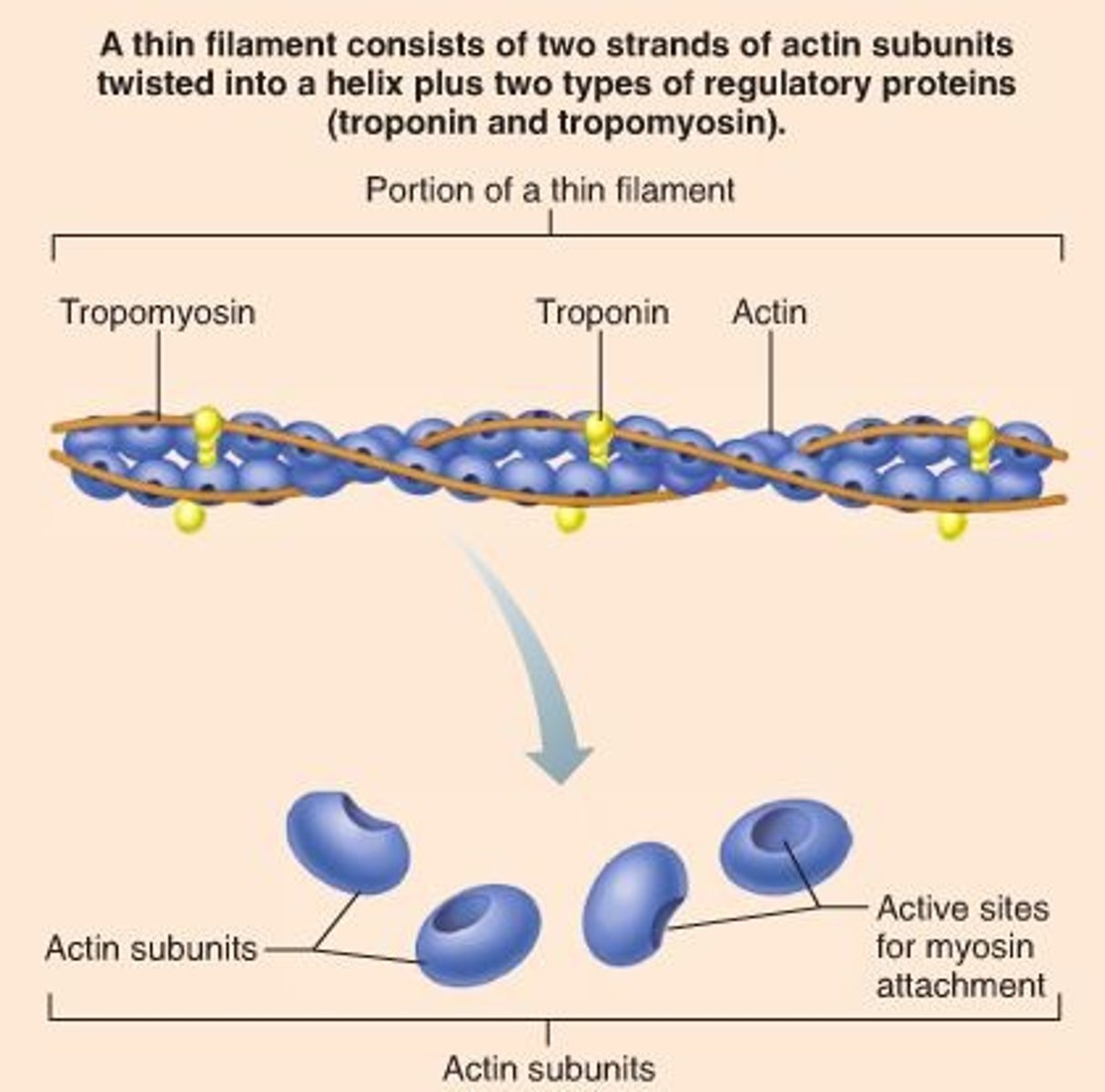
Troponin
A protein that anchors tropomyosin in place to block myosin binding sites, which shifts when it binds to Ca ions, pulling tropomyosin and exposing myosin binding sites.
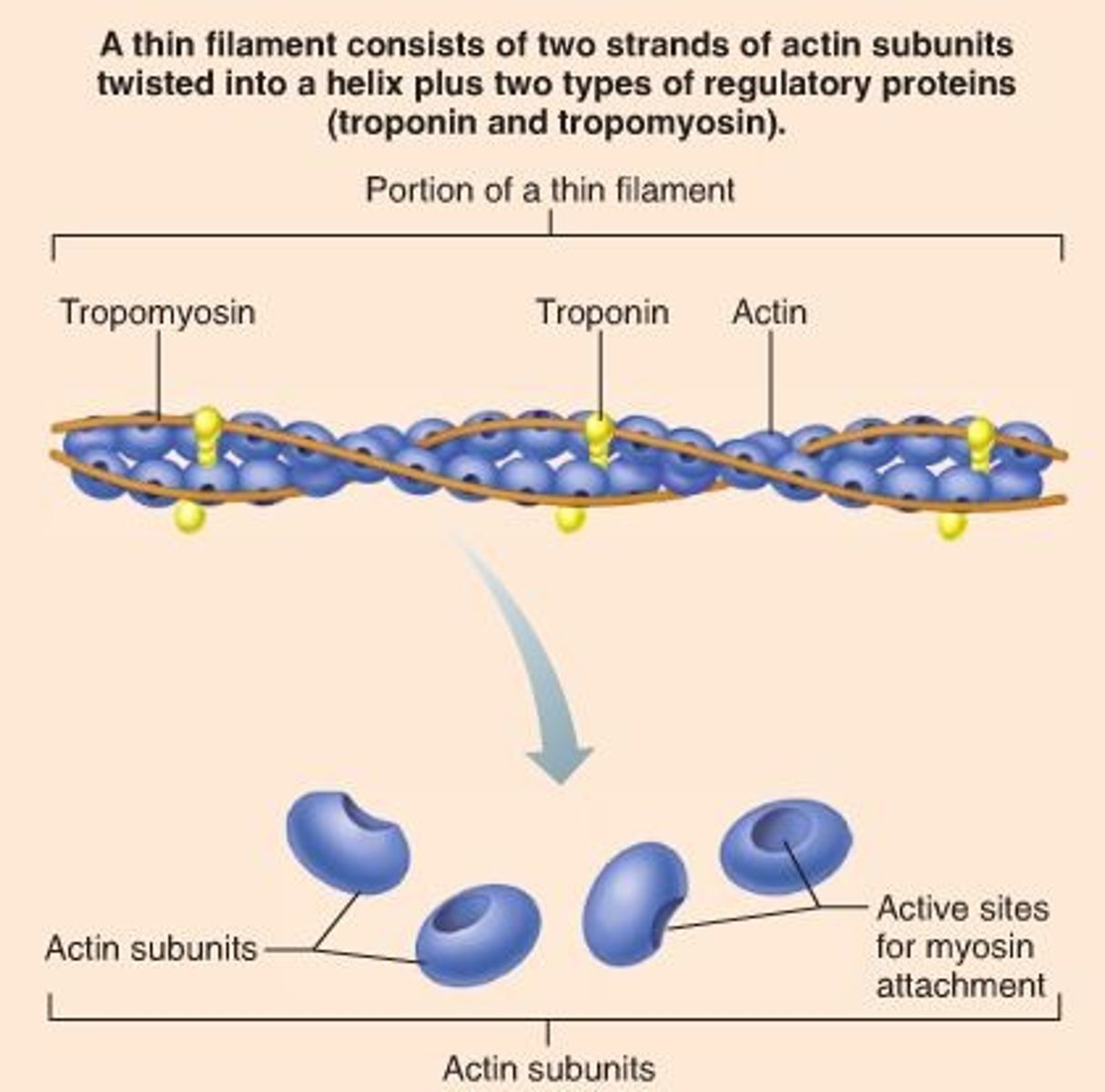
Titin
A protein that holds thick filaments in place; helps recoil after stretch; resists excessive stretching.
Dystrophin
A protein that links thin filaments to proteins of sarcolemma.
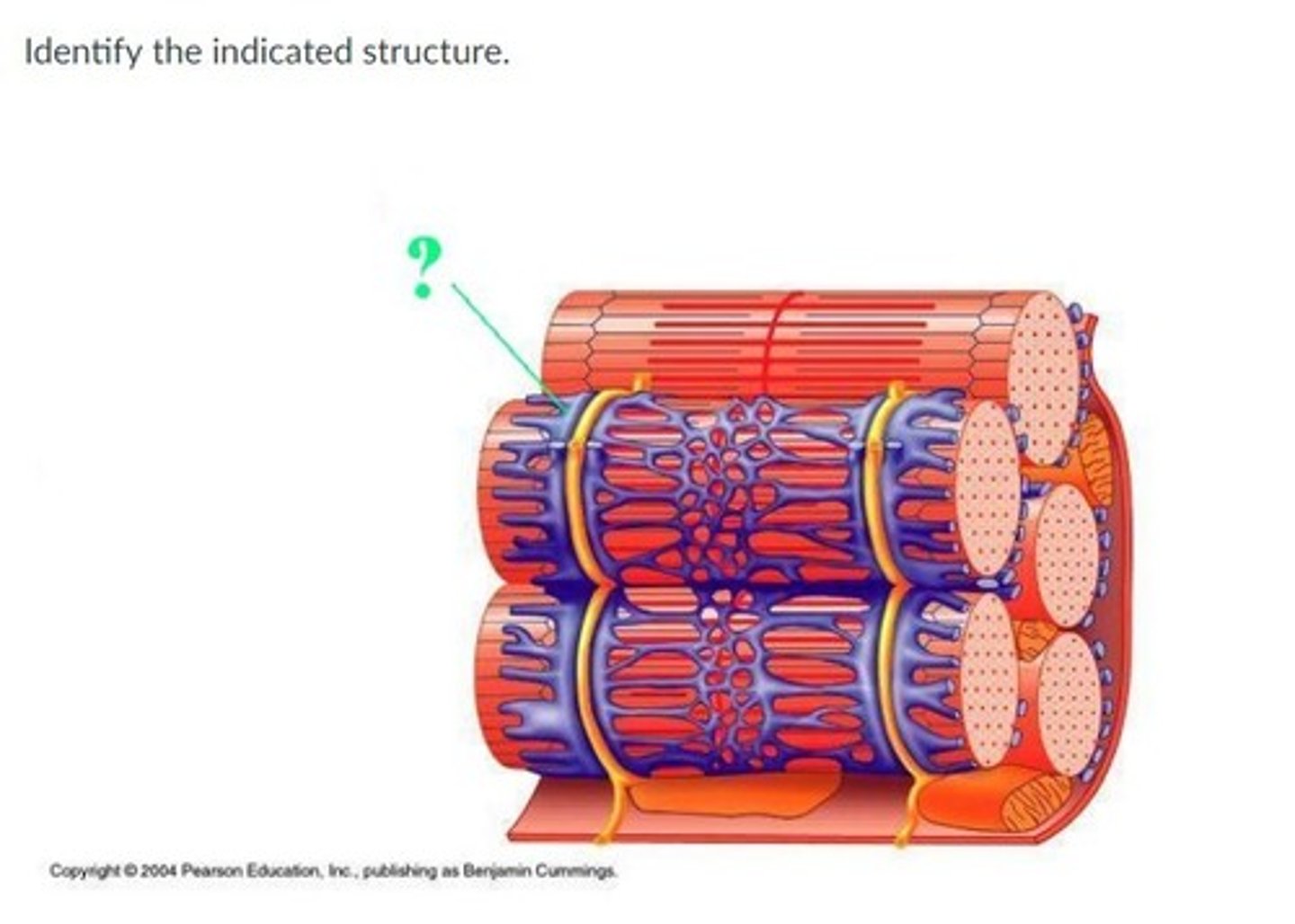
Terminal cistern
Enlarged end sacs of SR (sarcoplasmic reticulum) that surround a T-tubule on both sides.
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Modified endoplasmic reticulum in muscle fibers that store Ca ions.
T tubule
Projection of the sarcolemma into the interior of a muscle fiber.
Triad
The trio of a t tubule and the two terminal cisterns of the SR located on either side of the t tubule.
Contraction
Shortening of a muscle by the activation of cross bridges in sarcomeres to generate force.
Sliding filament model
States that during muscle contraction, thin filaments slide past thick filaments, causing actin and myosin to overlap more and shortening sarcomeres.
Action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon of a neuron to another neuron or an effector.
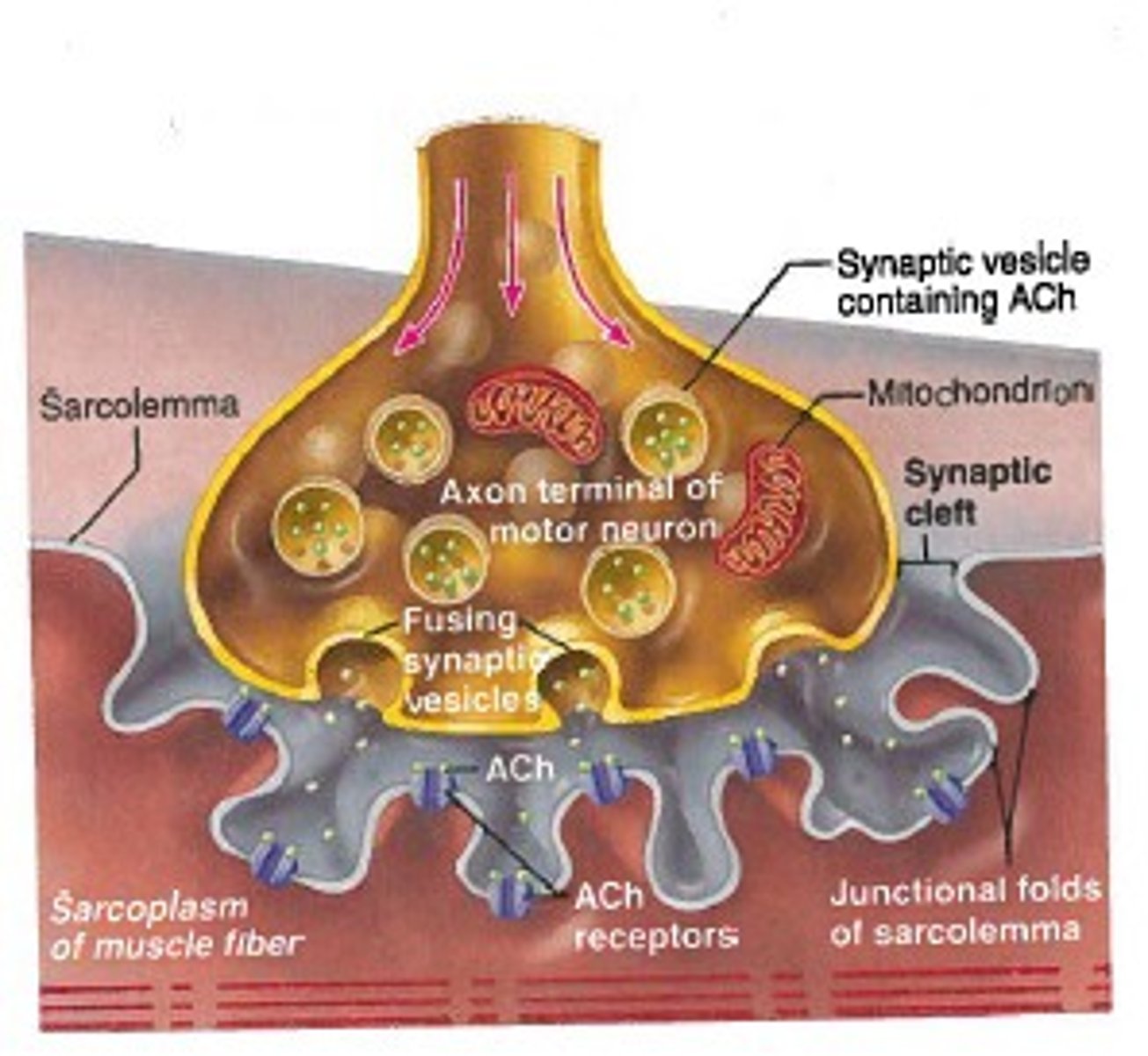
Neuromuscular junction
Region where a motor neuron comes into close contact with a skeletal muscle cell.
Synaptic cleft
The narrow gap that separates the presynaptic neuron from the postsynaptic cell.
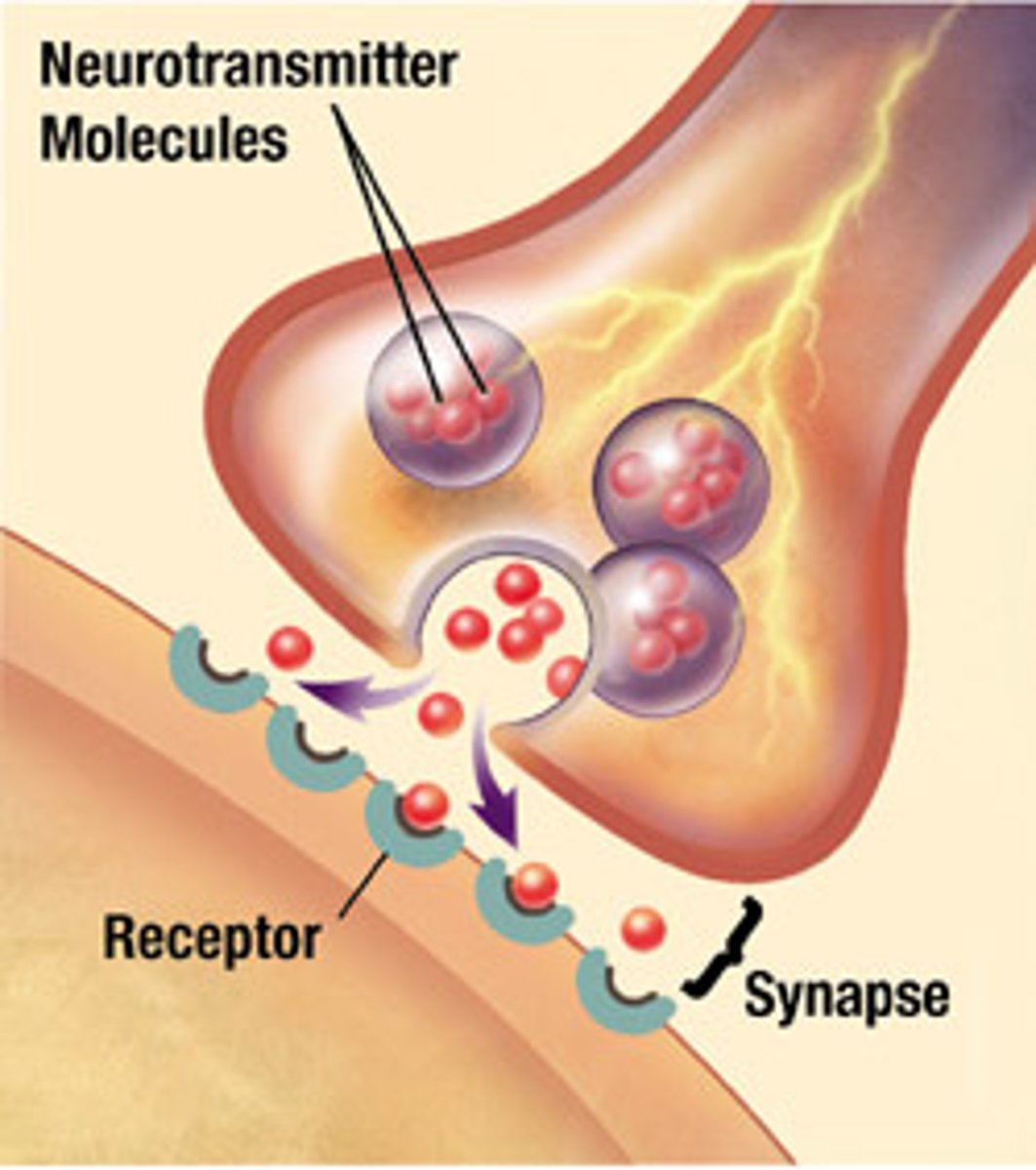
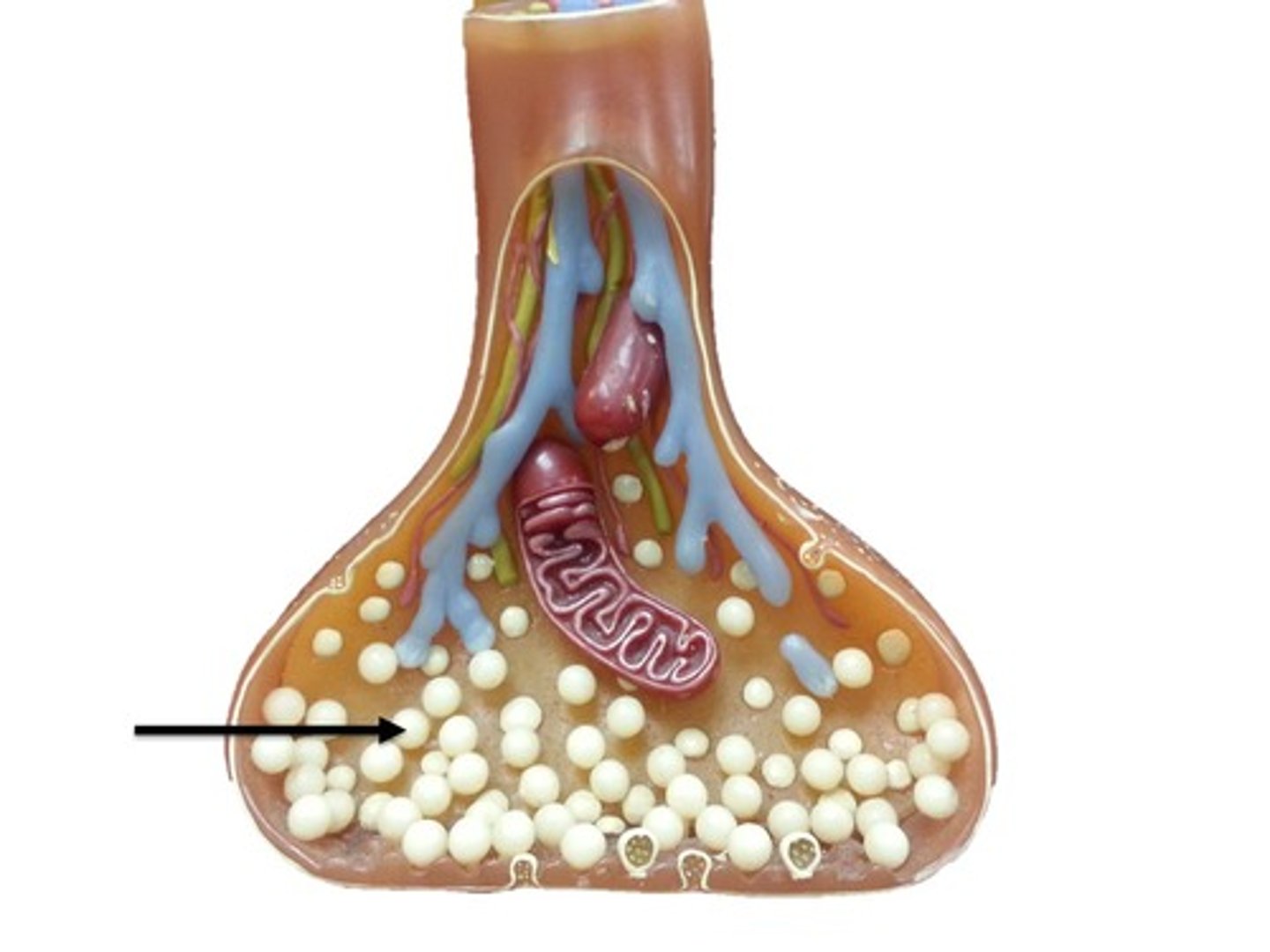
Synaptic vesicles
Membrane-bounded compartments in which synthesized neurotransmitters are kept in the axon terminal of neurons.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and is also involved in skeletal muscle contraction.
Junctional folds
Invaginations of the sarcolemma where ACh receptors are especially concentrated.
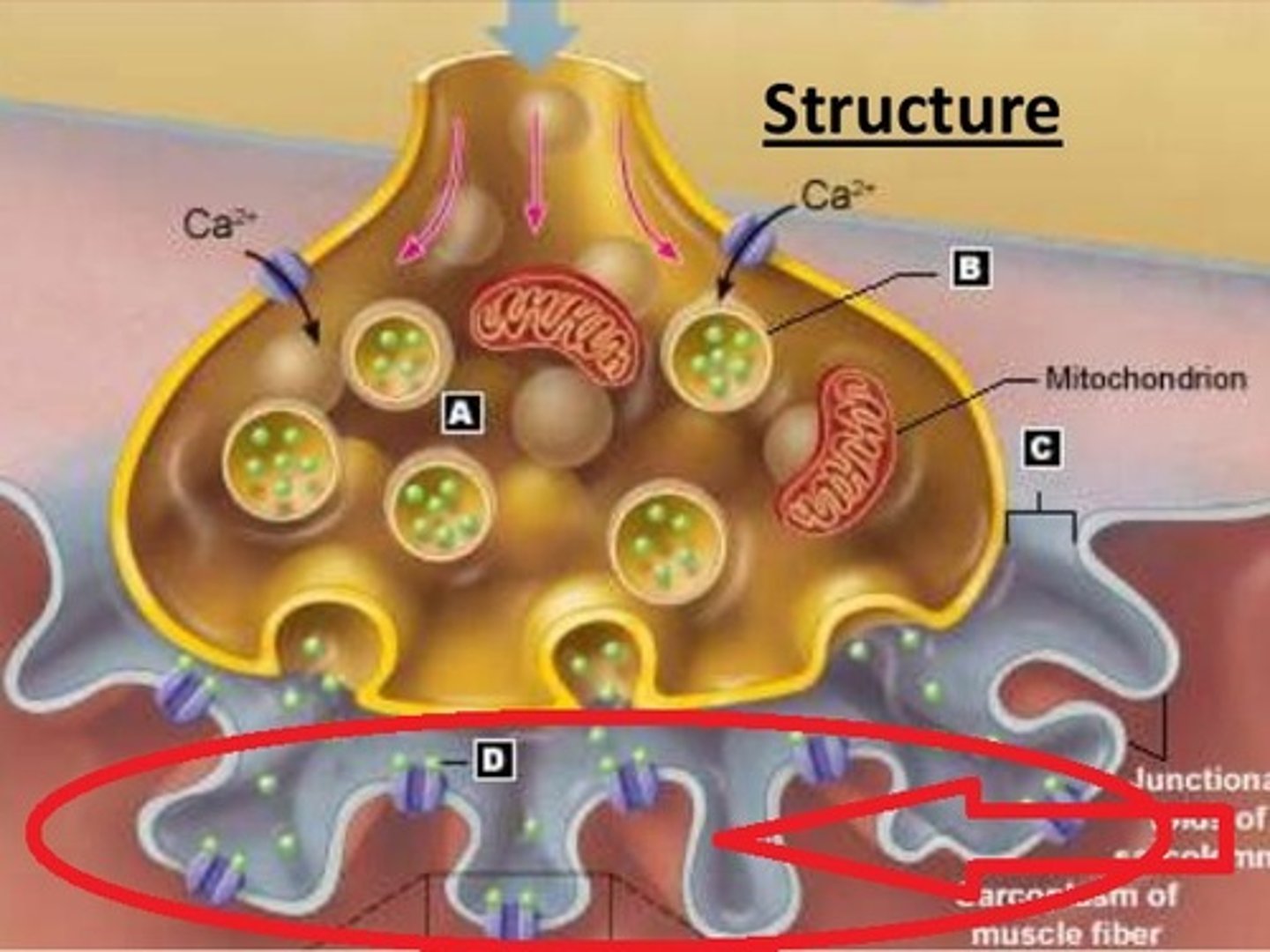
ACh receptors
Receptor proteins in the motor end plate of the sarcolemma that bind to ACh.
Acetylcholinesterase
The enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft.
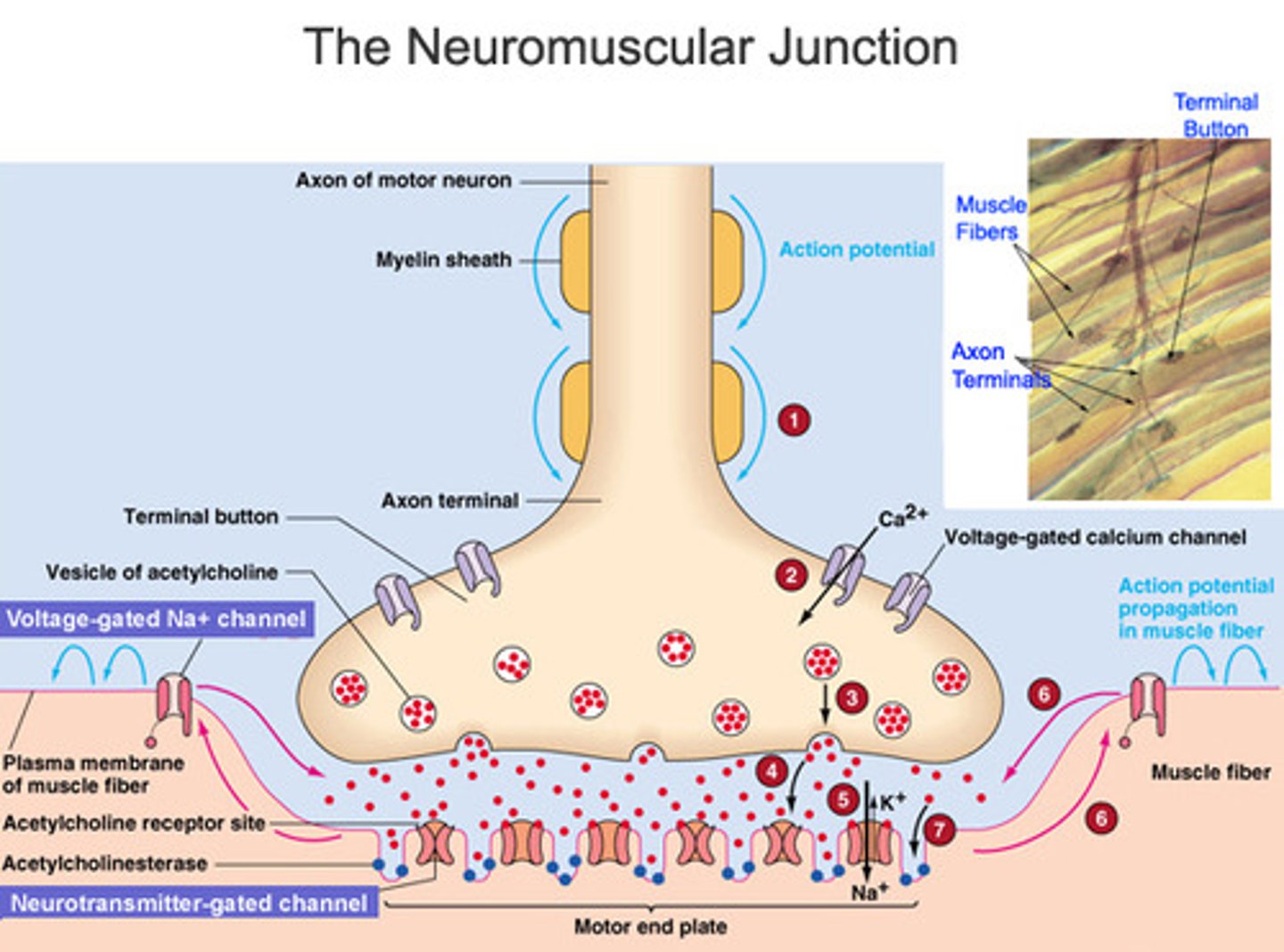
Polarized
A voltage (difference in charge) existing across the plasma membrane of a cell.
End plate potential
The depolarization of the motor end plate on a muscle cell.
Propagate
To multiply, spread out
Refractory period
The time during which a muscle fiber cannot be stimulated again for a specific amount of time after a stimulation, until repolarization is complete.
Excitation-contraction coupling
Events that transmit an action potential along sarcolemma (excitation) are coupled (linked) to sliding of myofilaments (contraction).
Depolarization
Generation and propagation of an action potential.
Repolarization
Return of a cell to its resting state.
Rigor mortis
The stiffening of the body after death.
Muscle tension
The force exerted by a contracting muscle on an object.
Load
The opposing force exerted on the muscle by the weight of the object to be moved.
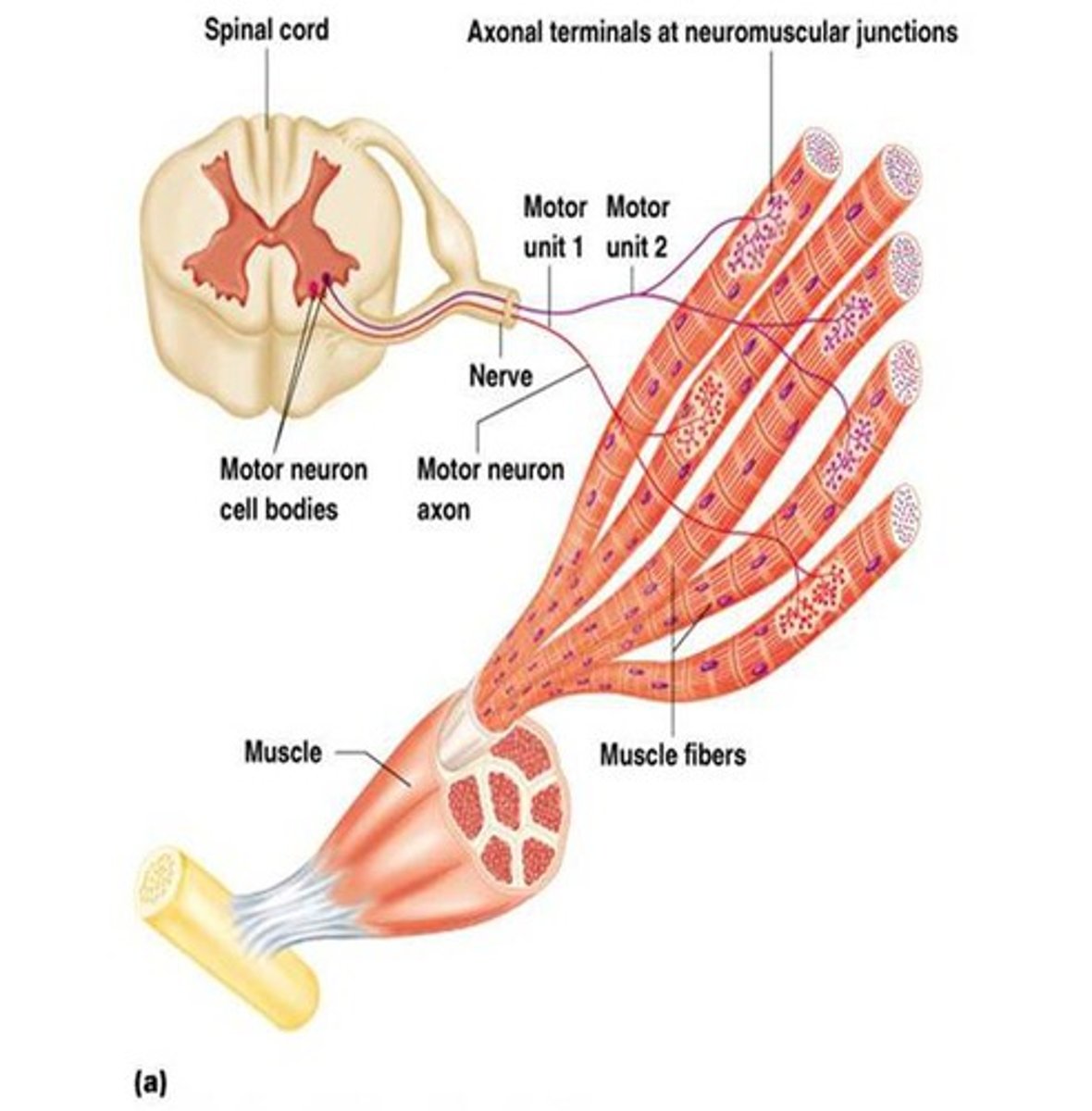
Motor unit
A motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates.
Myogram
Recording of a muscle contraction.
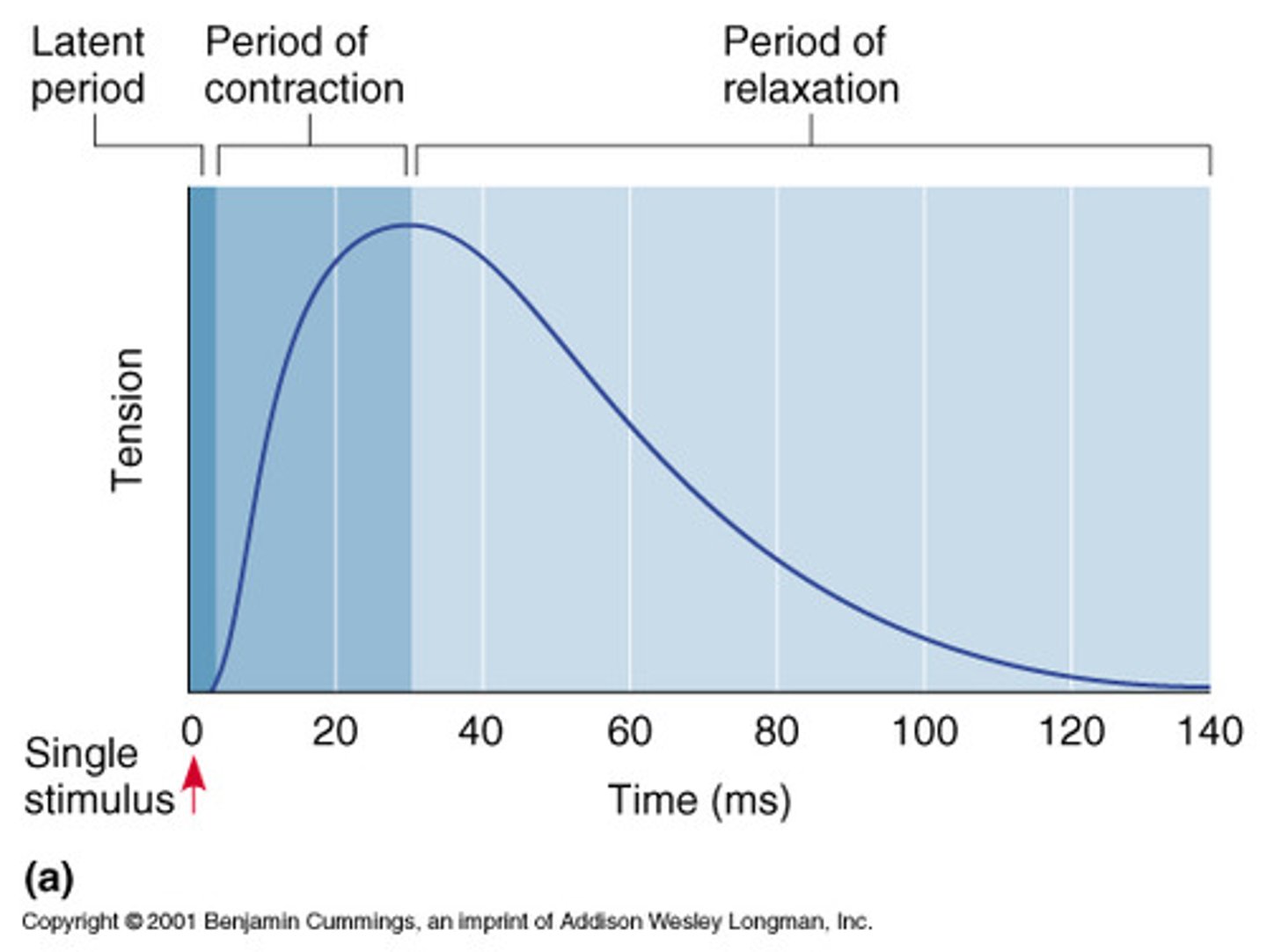
Muscle twitch
A motor unit's response to a single action potential of its motor neuron.
Latent period
The events of excitation-contraction coupling in which there is no muscle tension.
Unfused tetanus
Type of wave summation with partial relaxation observed between twitches, causing muscle to progress to sustained, quivering contraction.
Wave (temporal) stimulation
If two stimuli (action potentials) are received by a muscle in rapid succession, the effect is additive to the strength of the contraction.
Graded muscle response
variations in the degree of muscle contraction depending on demand.
Fused tetanus
Type of wave summation with no relaxation observed between twitches, causing maximum muscle tension in one smooth sustained contraction plateau.
Recruitment
(or multiple motor unit summation): stimulus is sent to more muscle fibers, leading to more precise control.
Subthreshold stimulus
A stimulus too small to cause muscle contraction.
Threshold stimulus
Stimulus is strong enough to cause first observable contraction of muscle.
Maximal stimulus
Strongest stimulus that increases maximum contractile force
Isotonic contraction
Muscle shortens because muscle tension exceeds load.
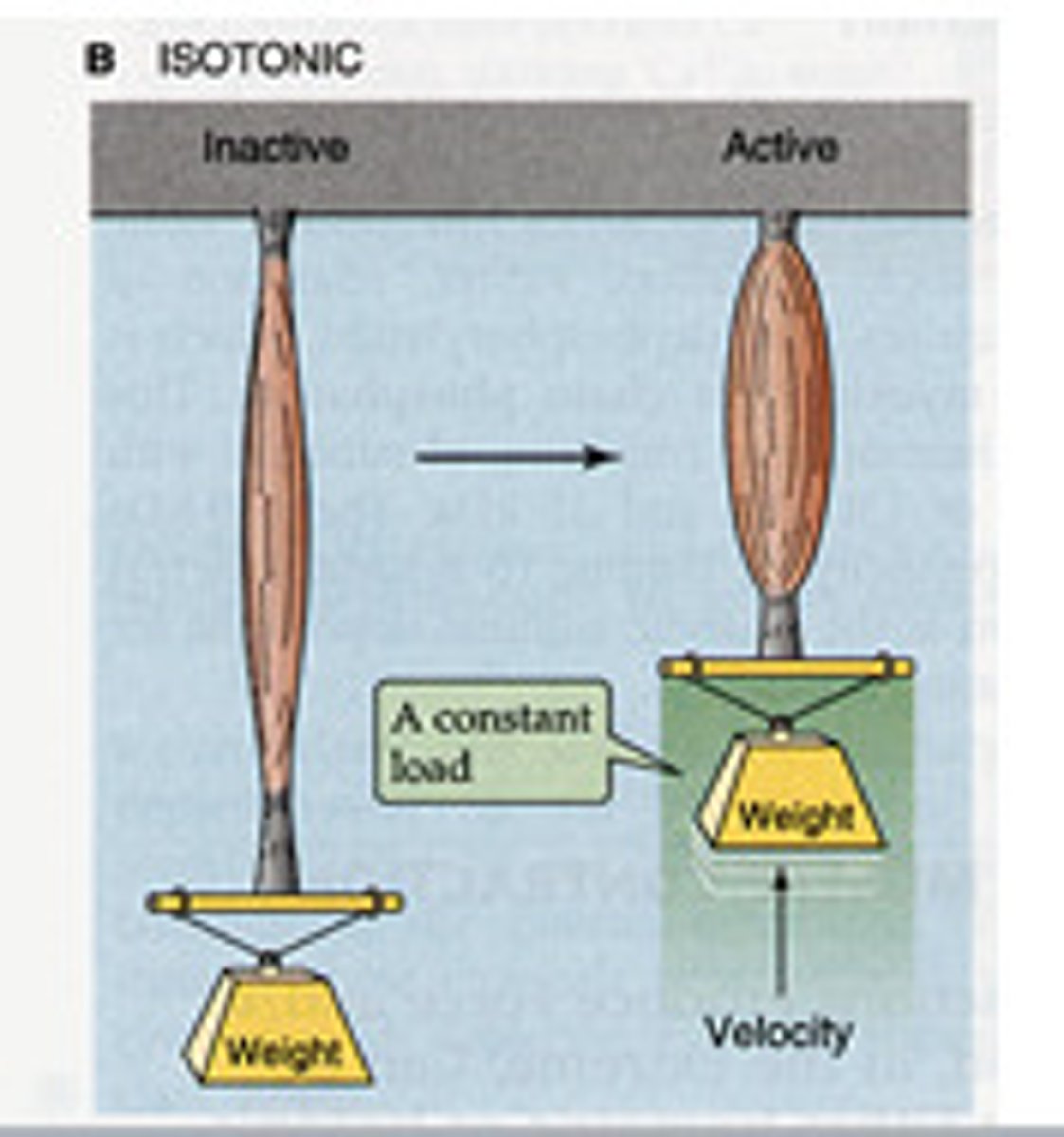
Concentric contraction
Muscle shortens and does work.
Eccentric contraction
Muscle lengthens to generate force.
Isometric contraction
Load exceeds maximum muscle tension so the muscle does not shorten.
Creatine phosphate
An energy storage molecule used by muscle tissue. The phosphate from creatine phosphate can be removed and attached to an ADP to generate ATP quickly.
Creatine kinase
An enzyme that carries out transfer of phosphate from creatine phosphate to ADP in muscle cells.
Glycolysis
The first step in releasing the energy of glucose, in which a molecule of glucose is broken into two molecules of pyruvic acid. This step does not require oxygen.
Lactic acid
Produced in muscle cells from the reduction of pyruvate (under anaerobic conditions) to regenerate NAD+ so that glycolysis can continue. A rise in lactic acid usually accompanies an increase in physical activity.
Aerobic respiration
The breakdown of glucose to generate ATP that requires oxygen.
EPOC
excess post-exercise oxygen consumption; another term for oxygen debt. The steps required for a muscle to return to its pre-exercise state.