characteristics of living organisms (rote learn)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
what are the 5 kingdoms
- plants
- animals
- fungi
- protoctists
- bacteria
which kingdoms are eukaryotic
plants, animals, fungi, protoctists
eukaryote
a type of cell that has a nucleus
prokaryote
a simple cell that does not have a nucleus - the DNA is free in the cytoplasm
are plants uni or multicellular
multicellular
what are plant's cell walls made from
cellulose
what do plants store carbohydrates as
sucrose or starch
examples of flowering plants
- cereals e.g maize
- herbaceous legumes e.g peas and beans
are animals multi or unicellular
multicellular
what do most animals have some type of and what does this mean
- nervous coordination
- means they can respond rapidly to changes in their environment
what can animals usually do
move around from one place to another
what do animals often store carbohydrate as
glycogen
examples of animals
- mammals e.g. humans
- insects e.g. houseflies and mosquitoes
are fungi usually multi or single celled
some are single-celled
what is the body of a multi-cellular fungi called and what is it made up of
- body called mycelium
- made up of hyphae (thread-like structures)
what does the hyphae contain
lots of nuclei
can fungi photosynthesise
no they do not have chloroplasts or chlorophyll
what are the cell walls of fungi made of
chitin
how do fungi feed
saprotrophic nutrition
saprotrophic nutrition
- secretion of extracellular enzymes
- into the area outside their body
- to dissolve their food
- so they can the absorb the nutrients
what do fungi store carbohydrate as
glycogen
example of single-celled fungi
yeast
example of multicellular fungi that has a mycelium and hyphae
mucor
are protoctists single or multicellular
single-celled
size of protoctists
microscopic
what 2 things can protoctists be like
- can have chloroplasts and be similar to plant cells
- others are more like animal cells
plant-cell like protoctist exmaple
chlorella
animal-cell like protoctist example and where does it live
amoeba (lives in pond water)
pathogenic example of a protocist and what does it cause
- plasmodium
- responsible for causing malaria
protoctist diagram
diagram added
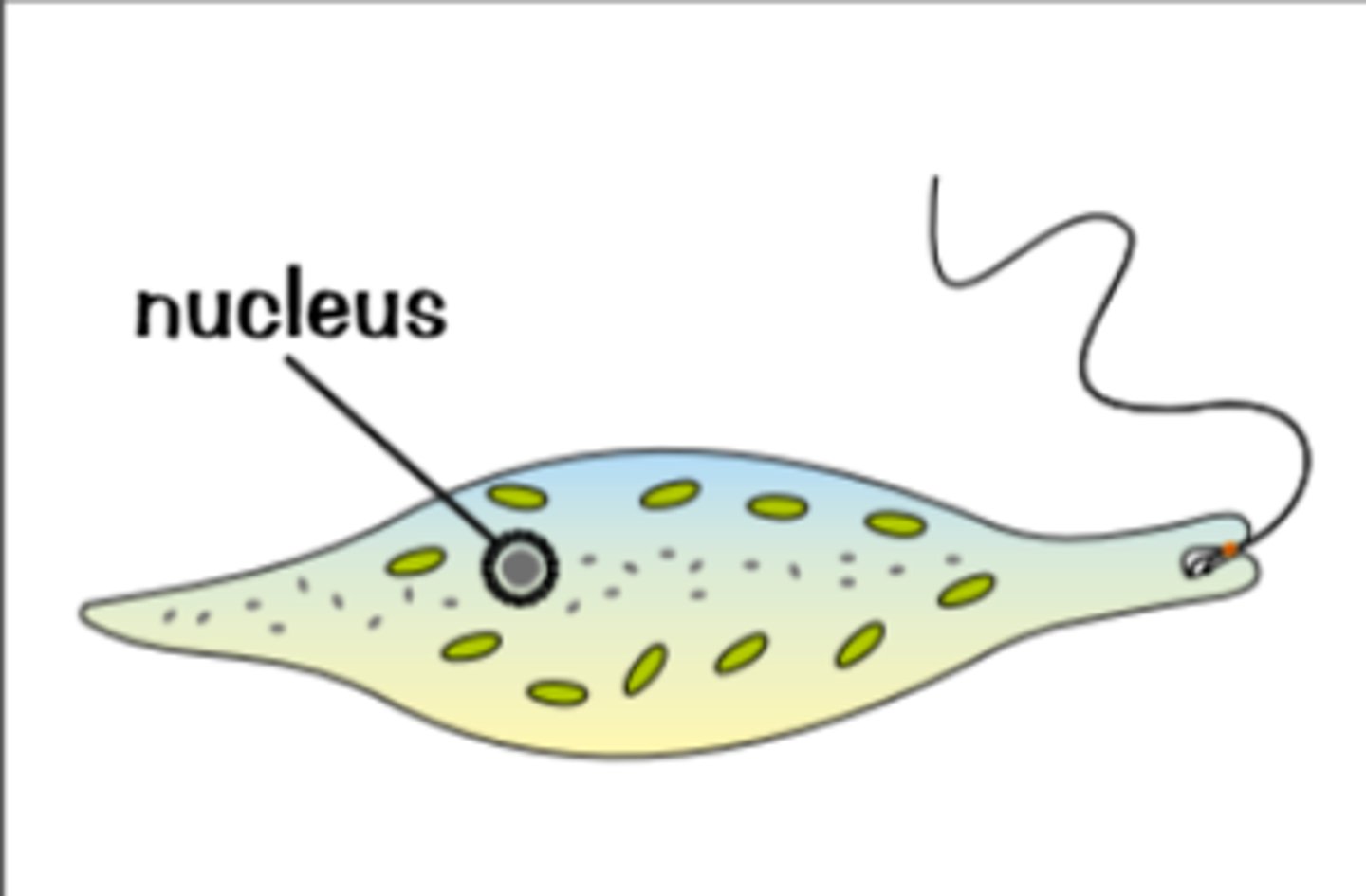
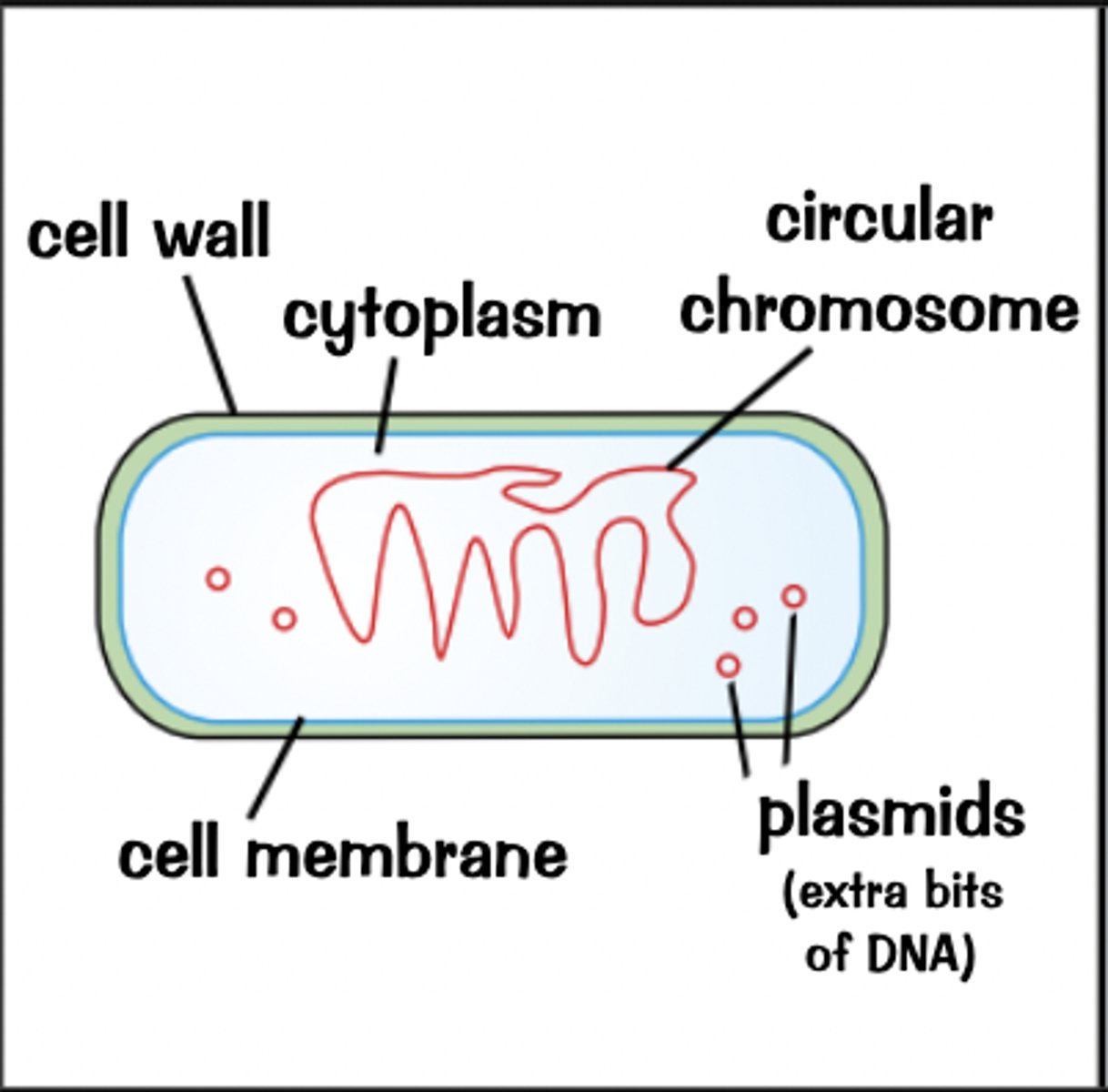
are bacteria multi or single celled
single celled
size of bacteria
microscopic
do bacteria have a nucleus and if not what do they have instead
- no
- they have a circular chromosome of DNA
extra bits of DNA in cytoplasm called plasmids also
what can some bacterium do
photosynthesise
how do most bacteria feed
off other organisms (both living and dead)
do bacteria contain plasmids and what are they
- yes
- extra bits of DNA
example of rod shaped bacteria and what is it used to do
- lactobacillus bulgaricus
- can be used to make milk go sour and turn into yoghurt
example of spherical bacteria and what does it cause
- pneumococcus
- acts as pathogen causing pneumonia
bacteria diagram
diagram added
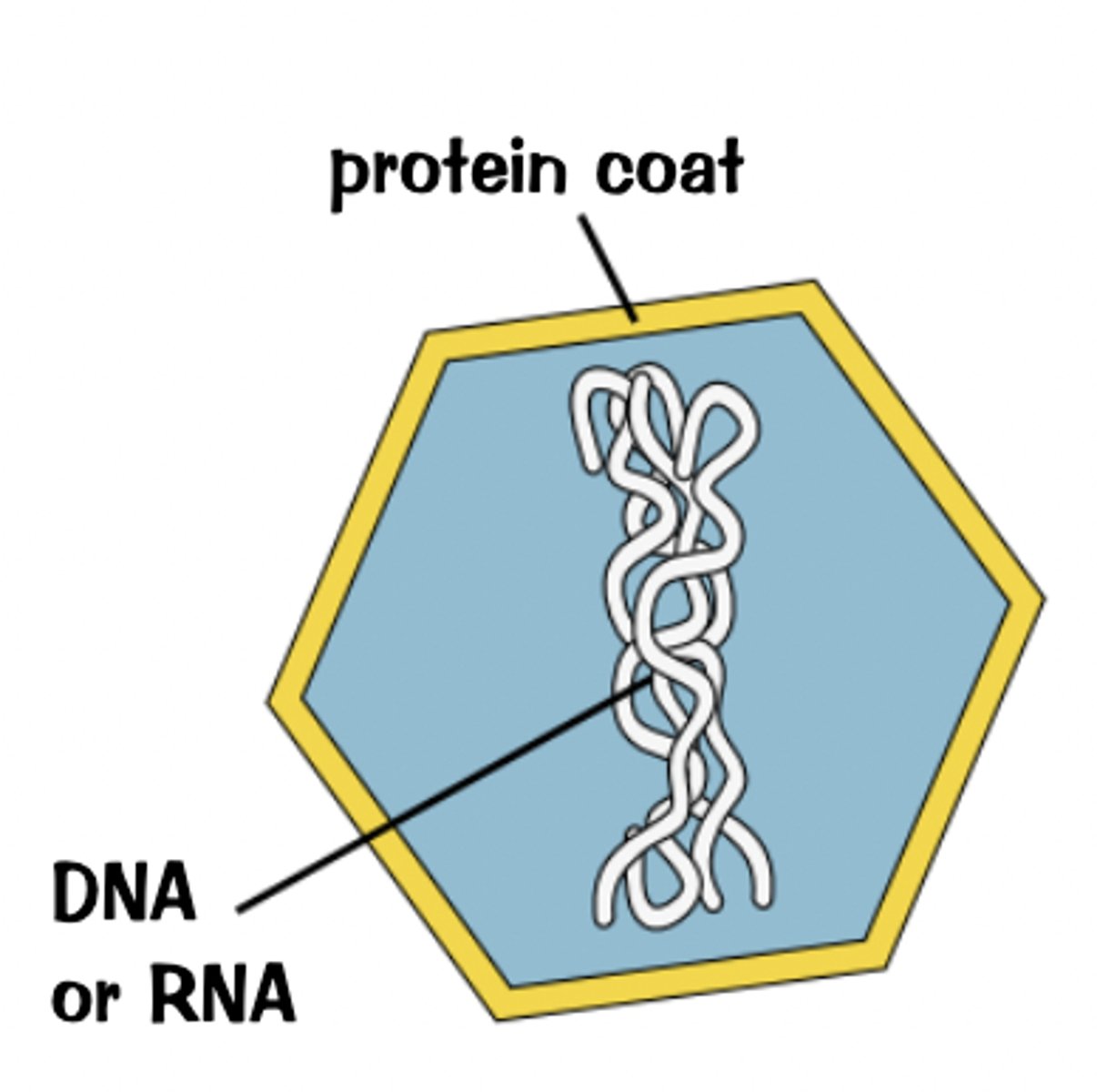
what are viruses and are they bigger or smaller than bacteria
- particles rather than cells
- smaller than bacteria
how can viruses reproduce
only reproduce inside living cells
how is a virus an example of a parasite
it depends on another organism to grow and reproduce
what do viruses come in
loads of diff shapes and sizes
what do viruses infect
all types of living organisms
what do viruses have instead of a cellular structure
protein coat around some genetic material (either DNA or RNA
3 examples of viruses
- influenza virus (causes flu)
- tobacco mosaic virus
- HIV (causes AIDS)
what does tobacco mosaic virus do
make the leaves of tobacco plants discoloured by stopping them from producing chlorolats
virus diagram
diagram added
pathogen
organisms that cause disease
what do pathogens include
some fungi, protoctists, bacteria and viruses