Year 9 Biology
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Ecology
The scientific study of interactions between organisms and their environments, focusing on energy transfer. Therefore it is a science of relationships.
Biosphere
Life supporting portions of Earth composed of air, land, fresh water, and salt water
Ecosystem
Living organisms interacting with their physical environment, functioning as a unit
Community
All the living organisms (different species of plants and animals) in an ecosystem at a particular time)
Population
The number of organisms of one species living in an ecosystem at any given time. Eg: Number of clownfish in the reef
Organism
Any unicellular or multicellular form exhibiting all of the characteristics of life, an individual
Biodiversity
Number of different species, variety within species, vital for healthy sustainable ecosystem
Habitat
The place where an organism lives. Eg: A snail in the pond scum of a little pond
Competition
Competition occurs between organisms for food, shelter, mates and survival
Predator
An organisms that hunts, kills and consumes another organism (a prey) for energy
Prey
An organism that is hunted, killed and consumed by another organism (a preydator) for energy
Mutualism
A symbiotic relationship that benefits both species. Eg: Shrimp remove parasites form larger fish
Parasitism
A symbiotic relationship where one species benefits (parasite) and the other is harmed (host). Eg: Ticks
Commensalism
A symbiotic relationship where one species benefits and the other is neither harmed nor helped. Eg: Orchids growing on a tree
Bio Hierarchy
1. Biosphere
2. Ecosystem
3. Community
4. Population
5. Organism
Biotic
Definition: All living or once-living organisms in an ecosystem.
Examples: Plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and even dead organic matter like fallen leaves.
Role: They directly and indirectly influence other organisms through interactions like predation, competition, and decomposition.
Abiotic
Definition: All the non-living physical and chemical elements in an ecosystem.
Examples: Sunlight, water, temperature, air, soil, and minerals.
Role: They are crucial for the survival of living things and can limit the growth and diversity of populations.
Symbiosis
The relationship between two organisms or different species that benefits one or both organisms
The three types of symbiosis
1. Mutualism
2. Commensalism
3. Parasitism
Photosynthesis
Plants making their own food using the energy from sunlight
Producers (autotrophs)
Organisms that make their own food
Consumers (heterotrophs)
Organisms that rely on other organisms for energy and nutrients
Decomposers
Organisms that break down the dead remains of other organisms (dead or decaying) such as plants or animals into simpler molecules that can be absorbed
Feeding relationships
1. Producer - Consumer
2. Predator - Prey
3. Parasite - Host
Food Chain
A simple model that shows how matter and energy move through the different trophic levels of an ecosystem
Food Web
Show all of the possible feeding relationships in a community at each trophic level. It represents a network of interconnected food chains.
Trophic Levels
Each link in a food chain is known as a trophic level. Trophic levels represent a feeding step in the transfer of energy and matter in an ecosystem.
Energy
The amount of fuel that an organism represents to its predators or consumer measured in joules.
- As you move up a food chain the available energy decrease
- Energy is transferred upwards but is diminished with each transfer due to the energy used by the organism in the process of living
-Energy enters ecosystems as light energy from the sun. It passes along the food chain as chemical energy
- About 10% of energy available at one level is transferred to the next level
- For example, if producers have 100% energy, primary consumers will have 10% and secondary 1%
Pyramids of energy
- Some energy is also wasted because consumers cannot digest all the food that they eat
- Because energy is lost in a food chain, energy is converted to biomass (the mass of plant and animal tissue) declines as each level, limiting the length of food chains
Pyramids of Biomass
Biomass is the amount of organic matter comprising a group of organisms in a habitat measured in kilograms.
•As you move up a food chain available biomass decreases.
•To sustain a kilogram of top predator requires many kilograms of prey.
•To sustain many kilograms of herbivores requires a very large mass of producer (grasses).
Productivity
Productivity is the rate at which living tissue can be produced by the ecosystem.
•The productivity of a field of grass can be described as adding kilograms per day.
•The productivity of beef cattle can also be described in terms of how many kilograms per day are being added.
Pyramids of Number
Number is the amount of organisms in a habitat.
•As you move up a food chain generally the number decreases.
•However, one large producer may be capable of supporting many consumers.
Above the second trophic level the pyramid of number usually decreases
Bushfires
A bushfire is an unplanned vegetation fire. It is a generic term that includes grass fires, forest fires and scrub fires.
Causes of bushfires
Bushfires are caused by both natural ignition sources like lightning and human activities, including accidental and deliberate acts. Key factors like dry vegetation, high temperatures, and strong winds create conditions that allow fires to start and spread rapidly.
Plant regeneration after Bushfires
Plant regeneration after a bushfire occurs through several mechanisms, including resprouting from protected buds and germinating from seeds stored in the soil or released by the fire. Common examples include eucalypts using epicormic shoots, grasstrees resprouting from a protected apical bud, and banksias whose cones open to release seeds after a fire.
Droughts
Long periods of unusually low precipitation
What do plants need to grow and survive
- healthy soil that provides water and minerals
- CO2 and water, with sunlight to photosynthesise and produce
glucose and O2 - oxygen.
- Root hairs increase the surface area of the roots for efficient
absorption of water (by osmosis) and minerals from the soil
Plants in hot arid habitats
- Reflect extreme sunlight
- Store and conserve water
- Defend against increased predation
Plants in cold low precipitation habitats
-Avoid or tolerate freezing
- Shallow root systems
- Potent flowers to attract pollinators
Osmosis/Diffusion
Diffusion is the general movement of any substance from a high to a low concentration area, while osmosis is a specific type of diffusion where only water molecules move across a semipermeable membrane from a high to a low water concentration
Active Transport
- Carrier molecules pump soil minerals into plants
- Process requires energy
Loss of Biodiversity
- Clearing of native vegetation
- Introduced plants and diseases
- Poaching and illegal trade in wildlife
- Pollution of species or habitats
Nervous System
The network of nerve cells and fibres that transmits nerve impulses between parts of the body.
Motor Neuron
The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland
Sensory Neuron
The nerve cell that carries impulses from a sense receptor to the brain or spinal cord
Relay Neuron
The nerve cell that connects sensory and motor neurons
Labelled Neuron
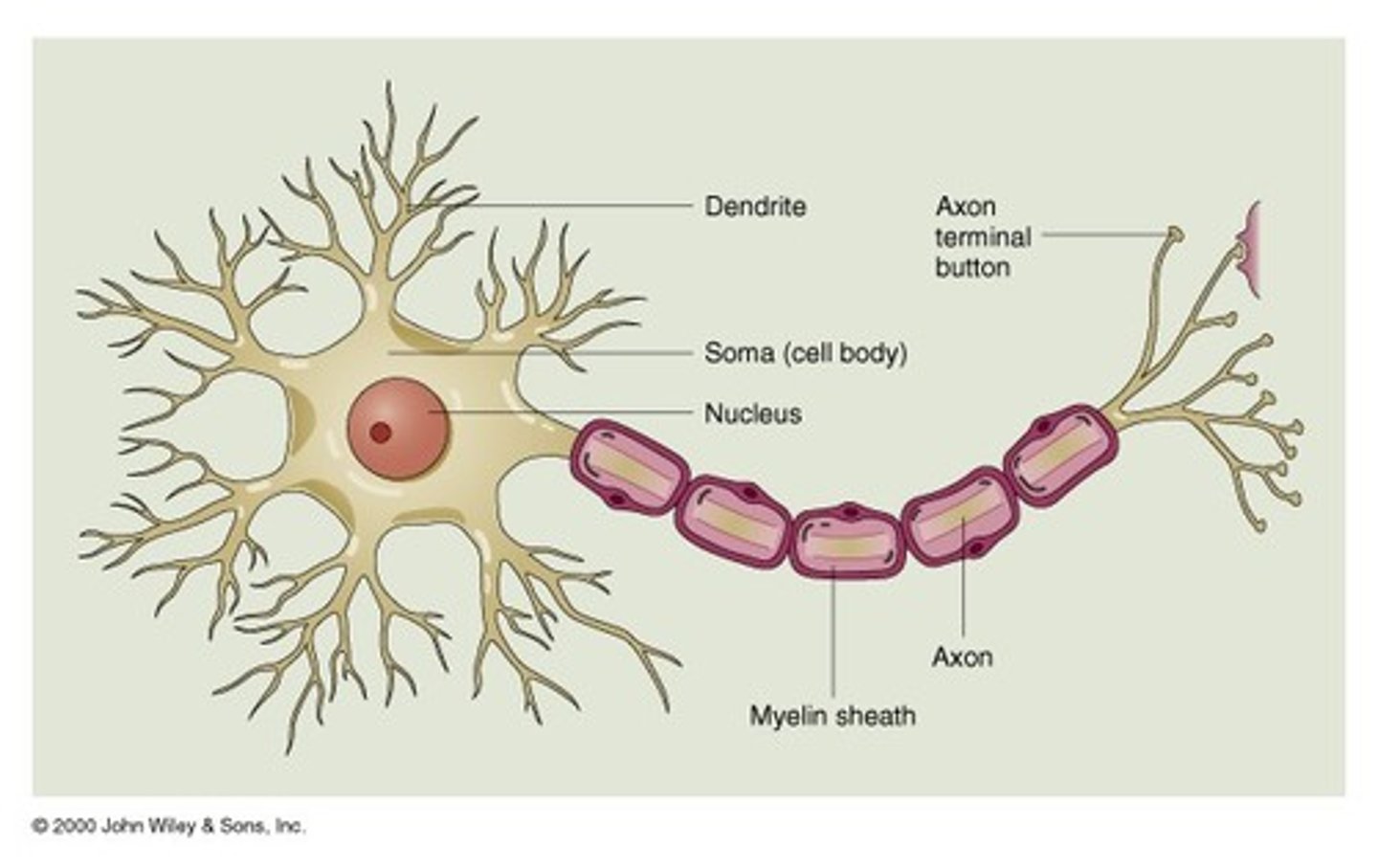
Nucleus
Contains DNA of the cell and is generally in the centre
Cell body
In charge of the neuron's activities
Axon
Sends messages from the cell body to the dendrites of other neurons
Axon Terminal
Sends messages to other neurons (across the synapse)
Dendrites
Receives messages from other neurons
Myelin Sheath
Covers the axon to protect it and help messages travel faster and easier
Schwann cell
A Schwann cell is a type of glial cell in the peripheral nervous system that forms the myelin sheath, an insulating layer that speeds up nerve impulses. These cells also provide support and nutrients to axons and are crucial for nerve development and repair.
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath to which voltage-gated sodium channels are confined.
Muscle Fibres
Cells that contract to produce movement.
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals released in the synapse
Synapse
A junction where information is transmitted from one neuron to the next.
Spinal Reflexes
Simple pathways in the nervous system that rapidly generate muscle contractions
Spinal Reflex Example
- Heat stimulus from iron
- Pain receptor in fingers senses high temperature
- Sensory neuron carries impulse to spinal cord
- Relay neuron connects sensory neuron to motor neuron in spinal cord
- Motor neuron carries impulse to to muscle
- Muscle contracts
- Hand moves away from heat
The Pupil Reflex
Reflex contraction of the muscles of the iris in response to a bright light causing the pupil to become smaller.
Goitre
An abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland located at the base of the neck
What gland and hormone is involved with Goitres
The thyroid gland, which enlarges due to various reasons and its function can be affected by thyroid hormones and thyroid stimulating hormones from the pituitary gland.
Causes of a goitre
- Grave's disease (hyperthyroidism)
- Toxic multinodular goitre (hyperthyroidism)
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis (hypothyroidism)
- Iodine deficiency
Factors increasing the risk of a goitre
- Being female
- Over 40
- Family history of a thyriod diseases
- Radiation exposure to the neck or chest
Symptoms of a goitre
-enlarged thyroid
-due to underactive thyroid or lack of iodine in diet
-appears as a lump or "bubble" on the neck
Diagnose and treatment for a goitre
Diagnose:
- Physical exam
- Blood tests
Treatment:
- Surgery
Chemical equation for Cellular Respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
How does oxygen get to the cells
You breathe in oxygen, then it travels through the bronchial tubes and alveoli in your lungs. Then it gets pumped to your heart, where it gets pumped all around your body.
How does glucose get to the cells
Absorbed in small intestine into bloodstream, blood delivers glucose to cells
How is carbon dioxide removed from the body
It is removed through the lungs when we breathe out
Cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen
Homeostasis
•The maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment despite fluctuations in the external environment.
•A stable environment allows the body to function efficiently.
•To maintain homeostasis the body must be able to sense changes in the internal and external environment and compensate for these changes
•A feedback system is a way in which the body responds to a change (or stimulus) with the response altering the original stimulus
Stimulus Response model
Homeostasis uses the stimulus response model to keep the internal environment stable (within defined limits).
The stimulus response model has 5 components
Stimulus
The change in the environment
Receptor
Detects the change in the environment. A nerve then sends a nerve impulse to the modulator/control centre
Modulator
The part of the body that decides on the response.(control centre) This part sends messages (neural & hormonal) to the effectors
Effector
The part of the body that carries out the repsonse
Response
The desired action
Negative feedback
When the response is opposite to the stimulus
Ectotherms
An animals that warms itself mainly by absorbing heat from its surroundings and so do not need to eat often/much. However, they are only active when they are warm / summer.
Endotherms
Humans are endotherms. We produce most of our heat using cellular respiration and so we need to eat a lot/often. However, we can be active at any time of the day/season.
Thyroid
Controlled by the brain to make thyroxine
Thyroxine
Controls the rate of cellular respiration in cells (metabolism) and therefore heat production.
How heat is gained
•Heat lost in respiration from all cells in the body.
•Heat released from respiration in muscle cells during exercise.
•Absorbing heat from the sun and environment on a hot day.
•Eating hot food and drinking hot drinks.
How heat is lost
•Radiating heat from the warm blood flowing in capillaries just beneath our skin.
•Evaporation of sweat from the skin cools the skin beneath.
•Heat lost in the warm breath we breathe out.
•Heat lost from warm urine and faeces expelled from the body.
Effects of Exercise
- Generate heat
- Brain detect a higher blood pressure
- Brain sends nerve impulses to the sweat glands
- The sweat glands are activated to reduce the temperature
Carbohydrates are...
Fully digested to glucose which is absorbed in the small intestine (by the villi)
Glucose
Blood contains glucose which is an important source of energy for the body (Cellular Respiration).
The glucose in blood must be kept within a normal range for the body to work properly.
If it rises or falls significantly, the body can usually bring it back to normal. This process maintains homeostasis.
Regulation of glucose by hormones
Hormones are chemical messengers produced in one part of the body and carried in the blood to cause some action in another part of the body. Different hormones have different actions.
The level of glucose is regulated by the hormones, insulin and glucagon, both released by the pancreas.
The pancreas ...
Detects the changes in blood glucose concentration and releases the appropriate hormone
Pancreatic cells
Alpha cells produce glucagon.
Beta cells produce insulin.
Insulin
A protein hormone synthesized in the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into tissues
Excretory system
The system that removes waste from your body and controls water balance
Kidney
Organ that removes urea, excess water, and other waste products from the blood and passes them to the ureter
Bladder
Elastic, hollow, muscular organ that provides temporary storage for urine.
Cortex
Outer layer of the kidney
Medulla
To concentrate urine and regulate water and salt balance in the body
Pelvis (renal pelvis)
Large, funnel-shaped area within each kidney. It collects urine from the major calices and then narrows to become the ureter.
Ureter(s)
The tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.