BIO 325H Transgenic Animals - Exam 4
1/64
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Model Systems
organisms that can be easily studied experimentally to answer specific biological questions. The answers obtained may be a general application to other organisms because of the evolutionary relationship between all organisms, we all share a common ancestry and biochemical pathways.
Common ones:
Bacteria - E. Coli
Yeast
Nematode
Zebrafish
Mice
Humans are not good types of these because they are not manipulatable and their lifespans are too long. The ethical implications of testing on humans is also bad.
Forward Genetic Analysis
An analysis for a gene that involves mutagenizing a gene first and then screening for new phenotypes, you are identifying mutated gene sequences. This aims to identify the sequence change (mutation) that causes a specific mutant phenotype. The starting point is a mutant cell/organism and then the mutant gene is identified.
Make a library of mutants. A collection of many individuals harboring random mutations in their genome.
Screen or select for phenotype of interest. Find individuals that have an altered trait (if it doesn’t work repeat or redo experimental design)
Determine # of complementation groups. Do individuals have mutations in same gene or different genes. This is done with crosses.
Find mutant genes
Further study the function of each identified gene.
Reverse Genetic Analysis
Genetic Analysis in which you begin with gene sequencing to make specific mutations, then you find the associated phenotype or what happens when a certain gene becomes mutated. This relies upon gene sequence information already available and tries to gain insight into the underlying function of that gene by generating mutations in the gene to cause phenotype.
Wild type mouse that has knockout done on it
tissue specific knockout mouse
inducible knockout mouse (like a temperature sensitive mutation)
Can use this to determine the time of action of a specific gene or allele.
Random Mutagenesis
Mutagenesis that occurs with Forward Genetic Analysis, organism is just mutagenized. Most mutations are silent and only some will have an impact. Sometimes 1 mutation can impact 2 genes so to figure out what gene is actually affecting phenotype we must construct 2 transgenes in plasmid and determine which gene restores wild type phenotype.
Saturation Mutagenesis (saturate genome with as many mutations as possible, through chemical or radiation or whatever) :
Null Mutants
Hypomorphic and hypermorphic mutants
conditional mutants
dominant negative
suppressor
Targeted Mutagenesis
Mutagenesis that occurs with reverse genetic analysis, organism is mutagenized at a specific gene. A specific gene is mutagenized in vitro, mutant DNA is put into the cells, and rare homologous recombination replaces normal gene with mutant gene. This is reverse genetics with gene targeting and CRISPR is an alternate method to this.
Selection
The process for finding mutants in forward genetic analysis by growing individuals in a mutant population under selective conditions and studying the survivors.
Screen
The process for finding mutants in forward genetic analysis by sorting among individuals in a mutant population for those that have an interesting phenotype.
Plasmid
little extra chromosomal pieces of DNA that are put into E Coli or other bacteria so they can replicate autonomously from the chromosome. This happens via transformation
Transformation
the process by which a cell or organism takes up foreign DNA. This happens when plasmids with certain foreign DNA are injected into bacteria or other organisms.
Complementation testing
Testing that reveals whether 2 mutations are in a single gene or in different genes. A complementation group is synonymous with a gene. (+) indicates wild type progeny or complementation and (-) indicates mutant progeny or no complementation. Complementation is more likely to happen with genes or mutations farther apart.
Positional Cloning
Mutant Gene identification technique that works by 2 methods (meiotic mapping with markers or deletion mapping).
Meiotic mapping is when you would put markers close to candidate genes and see if the markers would separate or not from the genes during Meiosis to see if a mutation was present there (just like SNP markers in past units).
Deletion mapping deletes the genes and sees which ones are impactful.
Both ways help to identify candidate genes and then you can go ahead and sequence exons of those candidate genes in mutant strains to look for the mutation. Finally you find the likely gene where the mutation is present.
Genome sequencing
Mutant gene identification technique that works by sequencing the genome of mutant strains and comparing genome sequences of different strains with mutations in a single complementation group to find the likely gene where mutation is present.
We don’t have any perfect genome to compare another genome too
We can’t compare because there will be many silent mutations so we have to compare these to organisms who have undergone the same mutagenesis so silent mutations are ruled out.
knockout mouse
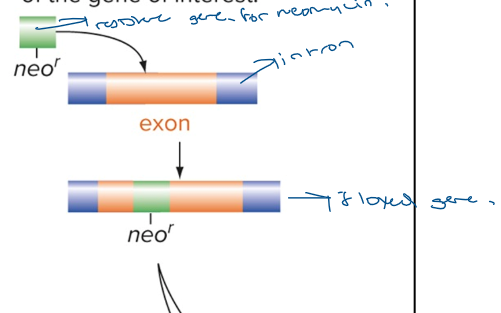
mouse made when the functional allele of a specific gene is replaced with an amorphic or nonfunctional allele. The amorphic allele is constructed by inserting drug resistance gene (neomycin resistance gene). The mutant DNA construct is taken up by embryonic stem cells made from agouti mouse. This technique uses recombinant DNA techniques, a gene specifying resistance to the drug neomycin is inserted into an exon of the gene of interest (leads to a floxed gene).
used when we want to understand what a particular type of gene does in an organism.
DNA injected into each blastocyst cells
Most cells will just discard this piece of random mutated DNA but some will take that piece and find the actual gene associated with it, leading to rare homologous recombination.
hoping that this DNA is accepted and that embryo is not further genetically modified or mutated.
hoping that knockout ES cells are found in germ line cells, this can be tested with a cross with another completely black mouse.
This happens only in 1 of the chromosomes, not both, leading to a heterozygous mutation
leads to a resistance against neomycin drug.
Resulting mice are chimeras with agouti (brown) and black spots.
Embryonic Stem cells
undifferentiated cells from the inner cell mass of embryos that can grow and divide in culture. They are totipotent which means that they can become any type of cell, including germ cells. They are used in the formation of knockout mice. The blastocyst is a stage of development in zygote formation.
Chimera Mice
knockout mice that contain cells from 2 different sources. The genotype of the black cells is homozygous recessive as they are not neomycin resistant, they are homozygous for both coat color and neomycin resistance. The tan brown/agouti cells are heterozygous for gene X and neomycin resistance and they are homozygous for their coat color.
If chimera gonads are made of knockout cells, an agouti or just black mouse will be possible from each cross, no chimera again because this time the embryo will be uniform.
If chimera gonads are not made of knockout cells, only uniform black mouse will be possible.
Analysis of knockout mouse
This is a loss of function mutant
Function of the knockout gene can be investigated by crossing out heterozygous brothers and sisters to make homozygous knockouts.
if a gene is essential, homozygotes may not be viable.
Knockout mice are heterozygous for the gene and are usually phenotypically normal, we want to obtain mice that are homozygous recessive for a mutation so we would do a heterozygous cross between similar siblings that are heterozygous for knockout to obtain ¾ mice progeny that are homozygous recessive.
You can end up with either a black mouse, an agouti mouse with knockout gene, or an agouti mouse with no knockout gene so how do we distinguish?
Take part of 2 agouti mice and then do PCR on them, amplify them, and see which one has neo resistance gene and which one doesnt and discard one that doesn’t.
Conditional Knockout Mice
Mice that have an allele that is functional but can be inactivated by changing the experimental conditions. This is done with the Cre/loxP recombination system. This is done for essential genes.
temperature sensitive mutations: protein functions at one temperature but stops working at a higher or lower temperature
cell specific knockout: knockout of a gene in a subset of cells in the developing organism.
Generate ES cells with a floxed exon by putting loxP all around exon and around the nemocyin resistance gene.
a. this happens in the heterozygous state, the loxP around the neo resistance gene also tells us to do homologous recombination and those 2 sites are used to loop out the neo resistance gene. A floxed mouse is wild type, no deletion has occurred in any cell yet.
Generate Mice with the floxed gene and cre transgene. The gene will be knocked out only in cells that express Cre. The homozygous floxed mice are crossed with the transgene mice expressing Cre recombinase only in the tissue of interest. The Cre recombinase deletes the floxed gene only in those cells that express Cre. The rest of the body still has the intact floxed gene.
Cre recombinase is added to specific tissues or cells and that exon will be looped out and become nonfunctional in that tissue or cell specifically. Floxed genes are still functional with LoxP around all sites
Promoter
major cis-acting regulatory element that is just a DNA sequence that is usually directly adjacent to the gene. It binds to RNA polymerase and often has a TATA box that allows a basal level of transcription.
Enhancer
Major cis-acting regulatory element that is just a DNA sequence that can be far away from gene. It can augment or repress the basal level of transcription. May be located either 5’ or 3’ to the transcription start site. It can still function when moved to different positions relative to the promoter.
Transcription factors
Proteins act in trans to control transcription initiation. These are sequence specific DNA binding proteins that bind to promoters and enhancers. They recruit other proteins to influence transcription. There are 3 types: basal factors activators, and repressors.
Ectopic Expression
gene expression in a tissue in which it is normally not expressed. Tissue specific enhancers are used to drive this expression of desired proteins. This is done with 2 things: a promoter and an enhancer specifically for that gene or cell type.
Reporter genes
genes that identify enhancers in eukaryotes. We can identify enhancers by:
constructing a recombinant DNA molecule that has a putative enhancer sequence fused to a reporter gene such as the Green fluorescent protein (GFP)
put GFP into basic promoter, put enhancer specific eye cells.
generating a transgenic organism that has the recombinant DNA in its genome.
Cre/loxP Recombination system
The bacteriophage Cre protein causes crossing over between 2 loxP DNA sequences. Cre Recombinase is used to excise a specific gene using unique cDNA sequences. This causes the recombination at a specific cleavage point from the bacteriophage area. This causes the recombination between 2 DNA sequences that have loxP site. You put the loxP site into the gene you want to knockout. This is used to make a conditional knockout mouse.
Anatomy of eye in flies
Flies have compound eyes with many independent ommatidia. Each ommatidium has 8 photoreceptor neurons with 1-6 extending the entire length around 7 and 8. 7 is on top of 8.
Flies missing number 7 (aka sevenless gene and mutation) were identified through manual screening experiment in 2000.
Formation of the eye
Mutant screens identified genes needed for the formation of the different photoreceptors in the ommatidium. Precursor cells (white) receive signals to differentiate into photoreceptors in a particular sequence. The last photoreceptor to differentiate is R7.
If these precursor cells do not differentiate into photoreceptors they will become lens cells.
8 first, then 2 and 5, then 3 and 4, then 6 and 1, and then 8.
Mutations that caused loss of photoreceptor R7, resolved into only 2 complementation groups or genes. Why just two??
sevenless and BOSS or Bride of Sevenless were the only two mutations to cause the loss of the R7 cell.
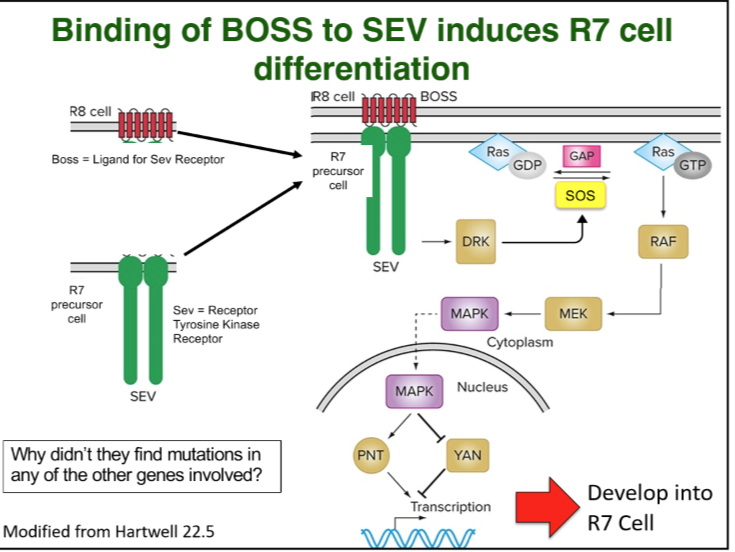
Wild type Boss gene in R8 cell leads to a signal transduction cascade in R7 becoming initiated and R7 forming.
Binding of BOSS to SEV induces R7 cells differentiation
BOSS is a ligand/receptor in R8 cell that binds to R7 precursor cell that contains Sev receptor tyrosine kinase.
This interaction produces a signal transduction pathway with many other important proteins like SOS, Ras, and GAP that work to fully help the precursor cell develop into an R7 cell through transcription of some other proteins or factors.
Ras is a protein made from oncogene made for cancer regulation in other cells of our bodies too.
Components of Genetic pathways missed in primary genetic screens
Pleiotropy: genes may be involved in several developmental pathways, including viability, thus they are missed when mutated
can be overcome by a modifier screen which is a very powerful genetic approach.
Redundancy: Two or more genes may perform the same function so a mutation in one will not result in a mutant phenotype.
Modifier Screen
Screen that may identify pleiotropic genes. Basically testing what other genes interact with the 1st one discovered, putting them in the same biological pathway.
Organism used for mutagenesis has a hypomorphic mutation that results in a sensitized background = put the system on the brink of failing.
looking for mutations that help or hinder a gene that is mutated and are just on the brink of failure.
Heterozygous mutations in a pleiotropic gene may modify the phenotype caused by the hypomorphic mutation = push the system over the brink.
Sevenless is a null mutation which is not a good starting point for this type of modifier screen. We want a subtle mutation that gives us a partial low function. This hypomorphic mutations will produce a weak signal that induces differentiation of R7 cells only 50% of the time in case of seveless.
Enhancer mutation
Mutations that worsen the phenotype of the hypomorphic sensitized strain. In the case of sevenless, now 100% of the ommatidia will fail to form the R7 cell. This would be a heterozygous mutation. This enhances the mutant phenotype and stimulates the R7 pathway so when it is mutated, the other bad gene works more to repress the pathway, leading to failure of R7 cell production.
Suppressor Mutation
Mutations that improve the phenotype of the hypomorphic sensitized strain. In the case of sevenless, now 100% of ommatidia form the R7 cell. This would be a heterozygous mutation. This represses the mutant phenotype and represses the pathway, so when it is mutated, the other good gene works more to stimulate the pathway, leading to success of R7 cell production.
Why can we get a mutation in RAS or this sevenless gene in eye cells of flies?
Ras is very important for all cells of flies and coupling the reduced amount of Gene A with a hypomorphic sevenless mutation would be a big problem in the eye but not in the liver or anywhere else in fly. These genes and mutations are sensitized due to them being hypomorphic mutations and they are only affected particularly by gene A or B in the eye with sevenless. Other cells don’t have hypomorphic sevenless mutation that will affect them with mutation of RAS.
RAS protein
a member of the small GTPase protein family that works as an ON/OFF molecular switch. These switches are used for signal transduction pathways.
In the ON state when it has a GTP bound to it and this happens due to the SOS (son of sevenless) protein
In the OFF state when it has a GDP bound to it and this happens due to the GAP protein
Scenarios
If you decrease GAP by 50% in normal fly, R7 cell will still form all the time
If you decrease SOS by 50% in normal fly, R7 cell will still form half of time, like a hypomorphic mutation now
If you decrease GAP by 50% in hypomorphic fly, R7 cell will form all time now like as a suppressor mutation
If you decrease SOS by 50% in hypomorphic fly, R7 cell will not form much now like as an enhancer mutation.
Sevenless and GFP expression
Use the sev enhancer to drive the expression of GFP in wild type eyes. 5 precursor cells express the sevenless protein and only one becomes R7 cell because only one can touch the R8 cell and become R7. BOSS is only expressed in the R8 cell.
What happens if we activate RAS in a sevenless null mutant?
In sevenless null mutants that don’t have an active sevenless at all, we can activate RAS by mutating it to RAS G12V which permanently activates Ras protein. We can only express this activated Ras in eye cells by using a regulatory gene enhancer and promoter in only the eye cells before the Ras G12V DNA sequence.
Will cause Ras G12V to only be expressed in the eye cells, will cause cells to override laws of sevenless in mutant flies and nothing different will happen in wild type flies.
Sev - Ras G12V is epistatic to sev-
constitutive active Ras no longer needs to be activated by sevenless, the sev enhancer drives transcription of 5 R7 precursor cells and causes 5 R7 cells to form,
Epistasis
a gene interaction in which the effects of alleles at one gene hide the effects of alleles at another gene.
Genetic interactions that can be defined by analysis of double mutants
Conditions:
Phenotypes of single mutants must be different
Mutant alleles must be null or constitutive
Epistasis:
Start with mutations in gene A and gene B
phenotype of double mutant resembles one of the single mutants.
Analysis of Developmental Pathways
Characterize the action of each gene in a pathway
Location and timing of gene expression
during development, where and when is the mRNA found?
Location of the protein product
during development, where and when is the protein found?
Developmental Phenotypes
what cells or tissues are affected by loss-of-function?
Pattern Formation
Coordination of events leading to the formation of a body with a particular morphology.
Positional Information
Each cell in the body must become the right cell type based on its relative position. At appropriate time, each cell receives this information that tells it where to go and what to become. Translate this information into expression of specific transcription factors. Cells may respond by division, migration, differentiation, or death.
Syncytial Blastoderm
stage of drosophila development that occurs by 13 rapid mitotic divisions without any cell division, just one large cell with 13 nuclei floating in cytoplasm
Cellular Blastoderm
stage of drosophila development formed by cellularization that begins during interphase of 14th division. Drosophila have a bilateral body plan with an anterior and posterior side.
Maternal Effect Genes
Genes that produce proteins that control transcription and translation during early segmentation. In successive levels of the hierarchy, genes are expressed in narrower bands.
Females have already put these transcription factors/genes in the egg and this will lead to a chain reaction that leads to the formation of the correct fruit fly body plan.
These cytoplasmic maternal effect genes lead to products that establish morphogenic gradients in the egg
Morphogen
A substance that defines different fates in a concentration dependent manner (protein or small molecule). Changes the way in which the cell/nucleus is gonna transcribe genes.
Gap genes
Genes/transcription factors that are expressed only in certain broad regions of the embryo, activate pair rule genes in a series of seven stripes. These are the first zygotic genes that are expressed in the embryo and their products control division of the body axis into rough, generalized regions.
Binding sites in promoter regions of these genes have different affinities for bicoid, hunchback, caudal, and nanos proteins
They encode transcription factors that control the expression of pair rule genes.
Pair rule genes
Genes/transcription factors that begin to segment the fly body into different chunks. Levels of these genes restrict expression of segment polarity genes to a series of 14 stripes, one per segment.
Segment Polarity genes
Genes/transcription factors that work to divide the fly into 14 segment sized units finally
Hox genes
Genes that are important for determining the different body parts in the corresponding areas of the fly.
Bicoid
a maternal effect gene whose protein acts as a morphogen, is a transcription factor and also a translational inhibitor for the caudal mRNA. It is concentrated or helps to segment the fly and development in the anterior part of the fly. Hunchback is another transcription factor concentrated in the anterior region.
Produced by the mother but will have an effect in how the embryo develops.
Phenotype of the embryo is determined by the genotype of the mother, not by the genotype of the embryo itself.
Nanos and Caudal
Proteins that act as morphogens to segment the fly body and help its development in the posterior region, they are mostly concentrated there.
Determining the Cis elements and transcription factors that control expression of a particular gene
We do this by doing EC transgenic experiments where we:
take the DNA that surrounds the coding region and try to find the enhancers that are responsible for the control of that gene.
substitute actual gene or coding region with a reporter gene like GFP to give color or visual report.
look at specific piece of DNA where enhancer is and see what transcription factors bind to it and see whether it has a unique binding site.
Example: Even skipped gene is controlled by multiple enhancers and a combination of transcription factors allows for even skipped to be encoded in different parts of the Drosophila body.
What is the difference between X- linked inheritance, mitochondrial inheritance, and maternal effect genes?
X-linked inheritance is when a gene or mutation on the X chromosome affects progeny if they inherit that X chromosome.
Mitochondrial inheritance is when progeny inherit their mitochondrial DNA and genes from their mothers only
Maternal effect genes is when the mother’s genotype affects the progeny for specific genes or pathways, only mother’s genotype determines progeny’s phenotype.
Creation of Knockout Mouse
The gene of interest is mutagenized by the insertion of a drug resistance marker
The DNA constructs are added to the culture medium of embryonic stem cells
Cells that have incorporated the DNA construct into their genome are selected with drugs
PCR is used to identify cell lines whose chromosomes acquired the DNA construct through homologous recombination
Cells are injected into blastocysts, which are implanted in surrogate mothers which give birth to chimeric mice
Chimeric mice are mated with normal mice and progeny with the altered chromosome are identified and used in further matings to produce mice with two copies of the inactivated gene.
Creation of conditional knockout mouse
Create a gene targeting construct containing 2 introns and an exon of the gene to be conditionally knocked out
Generate ES cells in which sequences in the targeting construct replace the corresponding DNA sequences in the wild-type gene in the mouse genome.
Remove the drug resistance gene with Cre
Inject ES cells that are heterozygous for the floxed gene into host blastocysts and generate heterozygous mice.
Perform crosses to generate a moues that is homozygous for the floxed allele, and also carries a transgene for Cre.
Knockin mouse
mice in which a gene has been altered by targeted mutagenesis. The alteration can be a point mutation or a large insertion of DNA. These are important for studying hypomorphic diseases.
Create construct with a point mutation
Use loxP sites only flanking the neo resistance gene
ES cells with neo resistance gene are selected, WT exon is replaced with mutated exon
Cre expression cuts out neo resistance
ES cells are moved to foster mother and embryo
same as others, mice are chimeric, must do additional tests and crosses to see agouti and transgene come out.
Transgene
gene that Contains additional or altered DNA through gene targeting
pronuclear injection
a method of DNA transfer used for many vertebrates
Floxed gene
gene that is useful for making conditional knockouts
T-DNA
A vector of bacterial origin used for making transgenic plants
AAV vector
genetically engineered viral genome that transfers a therapy gene.
Packaging Cells
These cells generate viral particles for gene therapy
Cas9
an Endonuclease used for genome editing along with sgRNA
Genetically modified organism
Any plant or animal that carries a transgene.
Why do we need to add neomycin resistance to genes that we are trying to create
knockouts or knockins on?
This selects for only the cells that have the target gene incorporated into the genome. Otherwise you would have to observe the phenotype that you want and only cross those individuals. Would be much harder and time consuming when analyzing hypomorphic gene mutations.
What might be the advantage of a knockin strategy over a transgene strategy?
The knockin strategy has the advantage that the gene X regulatory sequences do not need to be characterized because they are already present in gene X on the mouse chromosome. Suppose that you employed instead a transgene that would express a Protein X–GFP fusion protein. To ensure that the fusion protein is made in those cells in which gene X is normally expressed, the transgene would have to contain a DNA fragment with the gene X regulatory sequences. You would have to conduct several experiments to identify such a DNA fragment.